Organizational Structure for Effective Management
Get the best assignment sample on Organizational Structure for Effective Management.
Introduction
Organizational structure comprises of a system which states the way certain activities are comprehended within an organization so as to achieve their goals and objectives. Specsavers is a UK based organization which is a multinational optical retail chain founded in 1984 by Doug and Mary Parkins and operates mainly in United Kingdom, Ireland, Australia, South Africa and Nordic Countries.
The main objective of Specsavers is providing their customers with a range of optician services for eyesight testing. They have been in this business for more than 30 years and have been working with their store partners for providing best value optometry, audiology as well as other healthcare services to their customers.
Company background
Specsavers believe in manufacturing lenses and frames in accordance with international standards and believe it to be of highest quality. They provide their customers with 100% satisfaction by providing them with best quality products and ensure lifelong service guarantee of their products for maximizing customer satisfaction.
They believe in creating products which are manufactured in an eco-friendly manner and make people believe that using their products would enable them to become the best version of themselves. They firmly believe that beauty cannot be bounded by any specific standards and make their customers believe it too.
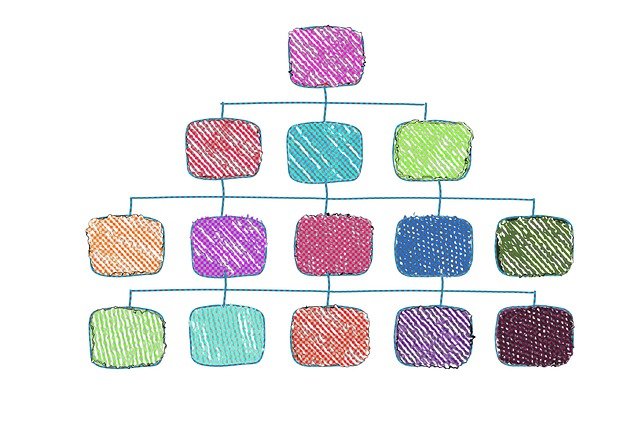
Organizational structure of Specsavers
Organizational structure can be classified into four types based on their procedures. Mechanistic structure can be classified as the official procedures and practices done by Specsavers which have a very organized structure such as packaging and marketing of the products manufactured by them (Mullins, 2016). This is comparatively easy to organize but becomes difficult to adjust in accordance with the changing environment.
They also have a compact structure which means that their decision making authority is held by the top management heading Specsavers. They believe in a line hierarchy where managers are solely responsible for working of the different departments within Specsavers and believe in a flat management level.
Theme 1: Historical and Theatrical basis of organizational structure
Importance of organizational structure
Organizational structure helps in providing guidance for all the employees taking help of a layout of the official governing regulation ships that would help in governing the workflow of The Specsavers (Cole, 2015). Organizational Theory is important as it helps in identifying the patterns and structures and it is used for solving problems, maximizing efficiency and productivity as well as meeting expectations of stakeholders.
Henry Fayol Theory
Henri Fayol has computed a management theory on the interaction of management with employees. The concepts covered are addressed broadly so that Spacesavers can use it.
The theory includes the 14 principles of management and includes the five basic ways in which management should interact with personnel for controlling and planning the production process. This includes the following 5 steps
- Planning- According to Henry Fayol’s theory, management of an organization must plan and schedule every part of the industrial process as it constitutes the initial and most important part for an organization (Miles et al.2020).
- Organizing- Henry Fayol had argued that alongside planning, it is essential that the management must also make use of all the necessary resources such as raw materials, personnel and ensure that all these come together at the appropriate time of production.
- Commanding- the management theory formulated by Henry Fayol states that the management of an organization must encourage and direct activities to be performed by employees.
- Coordinating- Management Theory formulated by Henry Fayol states that the management operating within an organization must make sure that all the employees are working together in a cooperative manner for getting the work done
- Controlling- Manager should evaluate and develop strategies so that employees working within an organization follow the commands made by management and work together.
Synergy Theory
Synergy is a concept through which value and performance is combined for summing greater than separate individual parts. In case two companies merge for efficiency or sale, the results are denoted with a synergy merge. Synergy demonstrates potential benefits for being achieved by companies.
Specialization Theory
The specialization theory states that division of large jobs into smaller jobs is assigned to workers. Such division of knowledge generates specialized knowledge for task and saves time as well as increase productivity. The total output is enhanced as workers specialize in a similar kind of activity that trades along with other kind of specialized workers. As total output is enhanced one worker specializes in another type of activity and trades along with other kind of specialized workers.
American and European Approaches’ to organizational structure
The European companies engage with assuming a role within formal as well as informal institutions for meeting societal interests. It is customary that initiatives and collaborative interests exist while researching for proper organizational structure. The classical view of an organizational structure grew during great depression of 1930 (Braithwaite et al. 2017). It resulted in a temporary shift through which organizations survived and emerged in bureaucratic structures as public attention shifted. At beginning of 20th century, business sector in US has been thriving. Max Weber concluded that as societies embrace capitalism such work has little influence on management practices until midst of 20th century.
Formal organizational structures
Organizational structure can be classified into four types based on the structures that each of them constitute.
Mechanistic versus organic
Organizations which have mechanistic structure are the ones which have formalized their procedures and practices and constitute of a very high hierarchical structure. Organizations following this structure find it easy to organize things but it becomes difficult for them to adjust in case of a rapidly changing environment (Bhattacharyya, 2009). Specsavers follow this structure as it becomes easier on their part to organize things. Organistic structures on the other hand have fewer job specializations; fewer layers in management process and limited amount of direct supervision. They are hardware to manage but better at adapting to changing environment.
Centralized versus decentralized
In case of centralized organizational structure, decision making and authoritative power is held by the top management of an organization. On the other hand, in case of decentralized structure, power and authority is further handed down on organizational structure.
Line, Line and Staff, Matrix, Team
Line hierarchies can be considered as structures in which departments are given responsibilities for generating revenue and managers responsible for main functions (Buchanan, 2019). Staff hierarchy structures are those in which departments are considered to be revenue partners such as accounting departments and they are responsible for supporting line functions.
Flat versus Tall
Tall structures have more management levels and it helps organizations better understand different parts. Specsavers have tall structures. Fast structures on the other hand have fewer management levels.
Informal organizational structures
Informal organizational structure consists of unofficial relations, which includes interactions within people of an organization which are created outside the periphery of official culture. For creating a better work culture, informal organizations encourage employees to interact and develop a bonding among each other for better productivity. It is considered to be a social relationship that arises spontaneously as people start associating with each other within an organization based on their level of participation (Buchanan et al. 2013). It consists of three types of groups such as horizontal, vertical and mixed and people can associate differently with these three types of informal groups. People from such informal groups follow this so that they can benefit from each other in some way or the other.
Difference between formal and informal structure
| Criteria | Formal | Informal |
| Authority | Formal organizations have clear ranking in accordance to administration and it is clearly documented. Jurisdiction is appointed from higher and usually the management is responsible for taking major decisions relating to employees (Handy, 1993). | Informal organizations do not follow ranking for influencing employees. Less emphasis is given on jurisdiction and it is equally distributed among all the members within an organization |
| Structure | They are very analytical in a manner in order to reach their goals and objectives and enables members to work together and reach a desired set of objectives | They are not at all analytical and there is absence of extensive requirements as their goals might be temporarily or entirely social |
| Influence | Members of formal organizations look forward to the higher authority for drawing motivation and getting the essential influence | Members of informal organizations are not pressured by the higher authority or seniors for completing work and each member have an equal influence on each other (De Menezes et al.2017) |
| Members | There is a specified process which is used for hiring, firing and replacing members within an organization. Expectation in accordance to every member are documented and executed in a proper way | They provide an emotional benefit for their members. Relationships among members of the office are more personal and therefore no expectations are done on behalf of employees. |
Table 1: Difference between formal and informal structure
(Source: created by author)
Benefits of informal organisational structure
Provide social control
Members constituting within an informal organization share common thoughts and cultural beliefs than those in formal organizations. Interests and ideas of members are promoted within the organization which helps in addition to its strength and helps in developing a commitment that would help the organization in accomplishing its set of goals and objectives.
Provide satisfaction
Social interaction among team members help in establishing cooperation and coordination among different team members (Syssner and Meijer, 2017). It helps top management in better coming up with strategies that would motivate members to perform better. It becomes easier for members to achieve their formal goals as well as inspire other team members to work.
Promote communication
In case of informal organizations, members better understand each other and thereby help each other in better performing their work thereby enabling promotion of effective communication. This in turn helps organizations in better setting up their goals and objectives and motivating employees to perform better.
Promotes creativity
In an informal organization, people get a chance to explore their creativity and work according to a way that would initiate a faster process for completing it (Lumineau and Schilke, 2018). They can come up with new ideas and utilize them for completing their work without fear of being judged or getting rejected.
Drawbacks of informal organisational structure
Lack of control over information
In an informal organization, there are high chances of a rumours getting spread and misleading the employees. It happens in many cases, there are high chances of a work getting delayed due to spread of rumours
Role conflicts
There is absence of a systemic working structure leading to greater delay in work. Absence of smooth functioning results in greater delay of work and lack of motivation among team members to get the work done (Liu et al. 2017). No expectations are outlined or documented for team members leading to less interest among team members to upgrade their existing working skills.
Resistance to change
In case of informal organizations, there are high chances of employees opposing the chances and policies of management. Therefore it becomes quite difficult on the organization’s part to implement policies and strategies opposed by employees.
More emphasis is given on personal interest of employees
In case of informal organization, more emphasis is given to individual satisfaction rather than to the goals and objectives within an organization (Galbraith, 2014). This results in delay for achieving goals and objectives framed by organizations.
Organizational effectiveness
Achievement of goals and objectives
Organizational effectiveness helps in better achieving goals and objectives that are framed for increasing productivity and effectiveness within organizations (Johnson et al. 2018). It helps in better decision making capability of employees, improves their leadership capability thus guiding them better and creating better work culture.
Organizational efficiency
Organizational effectiveness is the efficiency with which an organization is able to meet its objectives. It therefore helps in improving organizational capability and at the same time motivating employees for performing better and upgrading their skills. This would also help in generating more profit for organizations.
Growth
Organizations also help in achievement of long term objectives such as profitability and market growth enabling sharing of long term objectives for technological competitiveness. By means of this, organization sets procedures on effectiveness of process and how effectively it is able to meet its goals.
Sustainability
Sustainability helps to promote a better management of business and enhances capacity, quality as well as profitability for business. In this manner, management capacity is improved through quality and profitability.
Competitive advantage
Organizational effectiveness helps in generating competitive advantage for organizations by helping them build by strategies and formulating goals that would help them in creating a better position in the market (Kansal and Singhal, 2018). Competitive advantage would help them in fetching better clients and increase their customer base.
External benchmarking
Organizational effectiveness can help an organization in benchmarking their performance and set up an example for other organizations to achieve their goals and objectives. This would not only help an organization for expanding in the market but also set a global perspective for other organizations.
Theme 2: Analysis of the relationship between organizational structure and business strategy
An organizational structure is a system that helps in bounding ways in which certain activities are directed in order to achieve goals and objectives framed by an organization. Organizational structure determines the way information flows between different levels within an organization including activities such as rules, roles and responsibilities. A business strategy is considered to be a long term plan that is framed for an organization in order to reach out for completing the desired set of goals and objectives framed by an organization (González-Rodríguez et al. 2018). The strategy that is encompassed contains the company’s goals and objectives as well as the type of products and services that the company visions to build up. In other words, an organizational strategy is affected by an action plan to reach at specific goals so that organization is able to fit well with logical strategies. Therefore, this strategy helps to sum up simplicity at different levels through interactions with different levels of business. The relationship between organizational structure and strategy helps organizations in creating a strong base that would help them for creating better prospects and expanding in the market. The way an organization would strategize its policies would help them better communicating it to their team members so that it becomes easier on the employees part to formulate ways for achieving goals and objectives set for them. Organizational structure supports business strategy. If an organisation thinks of changing its business strategy, it must change its structure in order to support the new strategy. This is essential so that organizations can cope up with the changes happening and formulate ideas that would help them in better adjusting and incorporating new ideas for setting up and achieving a new set of goals and objectives which are designed. It will also help in generating optimal results.
Conclusion
Organizational structure is essential for an organization in order to achieve desired goals and objectives framed by them. Specsavers is an organization which has been in the industry for more than 30 years and believes in providing quality products for their customers. The glasses produced by them are of superior quality and they even promise to provide superior services to their customers. They have a great organizational structure but still it can be improvised so that they can better build up their strategies and create a better position in the market. Certain policies can be developed so that they can have better competitive advantage in the market.
References
Bhattacharyya, D.K., (2009). Organisational systems, design, structure and management. Himalaya Publishing House.
Braithwaite, J., Herkes, J., Ludlow, K., Testa, L. and Lamprell, G., (2017). Association between organisational and workplace cultures, and patient outcomes: systematic review. BMJ open, 7(11).
Buchanan, D. A. & Huczynski, A.A. (2013). Organisational Behaviour: An Introductory Text (8th ed), Prentice Hall, Hemel Hempstead.
Buchanan, D.A. and Huczynski, A.A., (2019). HucBuc: Organizational Behaviour. Pearson.
Cole, GA (2015), Management Theory and Practice, Cengage Textbooks.
De Menezes, L.M. and Kelliher, C., (2017). Flexible working, individual performance, and employee attitudes: Comparing formal and informal arrangements. Human Resource Management, 56(6), pp.1051-1070.
Galbraith, J.R., (2014). Designing organizations: Strategy, structure, and process at the business unit and enterprise levels. John Wiley & Sons.
González-Rodríguez, M.R., Jiménez-Caballero, J.L., Martín-Samper, R.C., Köseoglu, M.A. and Okumus, F., (2018). Revisiting the link between business strategy and performance: Evidence from hotels. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 72, pp.21-31.
Handy, C. (1993) Understanding Organisations, (4th ed) Penguin, London.
Johnson, A., Nguyen, H., Groth, M. and White, L., (2018). Workplace aggression and organisational effectiveness: The mediating role of employee engagement. Australian Journal of Management, 43(4), pp.614-631.
Kansal, J. and Singhal, S., (2018). Development of a competency model for enhancing the organisational effectiveness in a knowledge-based organisation. International Journal of Indian Culture and Business Management, 16(3), pp.287-301.
Liu, S., Cheng, I. and Cheung, L., (2017). The roles of formal and informal institutions in small tourism business development in rural areas of South China. Sustainability, 9(7), p.1194.
Lumineau, F. and Schilke, O., (2018). Trust development across levels of analysis: An embedded-agency perspective. Journal of Trust Research, 8(2), pp.238-248.
Miles, R.E., Snow, C.C., Fjeldstad, Ø.D., Miles, G. and Lettl, C., (2010). Designing organizations to meet 21st-century opportunities and challenges. Organizational Dynamics, 2(39), pp.93-103.
Mullins, LJ (2016), Management and Organisational Behaviour, Pearson Education, Limited, Harlow, United Kingdom.
Syssner, J. and Meijer, M., (2017). Informal Planning in Depopulating Rural Areas: A resource-based view on informal planning practices. European Countryside, 9(3), pp.458-472.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services: