6BE005 The Strategic Business Assignment Sample
Module code and Title: 6BE005 The Strategic Business Assignment Sample
Section 1: The Strategic Environment
Introduction
IKEA is a popular multinational retail conglomerate specialised in selling modular furniture, kitchen tools, home accessories, and other home and professional goods and services. Founded in Sweden and headquartered in the Netherlands, IKEA has been the leading furniture retailer in the worldwide market since 2008. The company is known to offer modernist furniture and products to customers. The revenue listing of the company amounts to 41.9 billion pounds as of 2021 (Reuters. 2022). The company is a leading performer owing to the effective strategies of leadership and business management. The case for IKEA will extend and expand here.
Internal Analysis
The internal analysis is an important assessment to locate the effectiveness of a brand in the existing market. In this case, the analysis of the internal business practices and environments would commence for IKEA by using the SWOT analysis. It will locate the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats respectively.
SWOT Analysis for IKEA
| Strengths
● The customer knowledge of IKEA in any country or market is a major strength in the business (Rodrigues and Brandão, 2021). ● Clarity of vision is backed by the ability to communicate them to customers via unified teamwork. ● The company has a diversified portfolio of products being sold in the market. ● Consistency of product quality and standards have contributed in building IKEA’s reputation in retail. |
Weaknesses
● The quality of furniture and other products being sold have been noted to reduce the standards set initially. ● The standard product range has been constricting ever since IKEA has diversified the product range from furniture to other items (Sorge and Streeck, 2018). ● Negative publicity of the brand exists equally in the market due to ineffective services. ● Some ecological concerns have also been raised recently. |
| Opportunities
● IKEA holds many scopes to standardise the products and qualities with branding using the green model of business. ● The company can extend to ethical sourcing and production measures to attend trends of ethical purchases. ● The emerging markets in Asia and other continents offer a larger market opportunity which IKEA can explore. ● Online sales is a prominent channel where IKEA should invest. |
Threats
● The business model of IKEA is constantly being copied and used to produce better items by new and existing brands in the furniture retailing. ● Competition has also been rising in the market with an increasing demand for expensive items at affordable ranges. ● The concept of affordability of expensive furniture is not friendly for the business without diversification of promotions and after-sales. |
Table 1: SWOT Framework (Source: Created by Author)
Brief Analysing the points discussed in the strengths, the first advantage for IKEA comes from the brand reputation and name. The company has its own recognition for exclusive and modernised designs of furniture which appeal to customers internationally. These come along with the cost leadership model of pricing and business benefiting sales.
However, analysing the weaknesses, IKEA has many issues that diminish the brand identity. For example, the delivery systems and shipping quality is not fair which leads to product damages within the local communities (Hoekstra and Leeflang, 2020). Again, the diversification of business has triggered pressures leading to rapid mass production that tampers quality produce.
Having mentioned these, a major opportunity for IKEA is emerging from the newer markets situated in Asia and Africa. The rising economic standards help to capture these markets where cost effective products are in demand. Similarly, the approach for online expansion, awareness and branding can prove useful for IKEA locally.
Lastly, these opportunities also bring forth some risks and stakes. The competition has been increasing constantly with diversification of retailers offline and online. Amazon offers a major competition with other brands like Pepperfry offering quality items at standard prices. The pricing model is also outdated when compared to modern trends.
Justifications
Evaluate the model you have chosen – Compare and contrast it against other internal analysis models. What does it do well and not so well when analysing your businesses’ internal environment. (200 words)
The SWOT framework has always been considered an effective approach for market analysis. The purpose here is to list the strengths and weaknesses of a company which help to locate opportunities and threats eventually in the industry. For example, in this case, the strengths and weaknesses of IKEA has helped to identify the feasible choices to empower the brand and control the threats using early intervention. However, the overall representation is simplistic and legible.
The TOWS matrix, by contrast, is an advanced model of the SWOT but it makes the presentation complex and illegible to comprehend brand’s internal aspects. The briefing is a short and precise recognition on which underlying aspects of IKEA make the points mentioned worthy of consideration. However, analysing the same insights using McKinsey’s 7S model would have constricted the research.
The 7S model is used to predict all internal operations, without considering the links to the external business aspects. However, compared to both these models, SWOT analysis offers internal insights and also locates the most suitable measures for the company to extend operations looking for risks simultaneously. These have made the chosen model different and ideal.
External analysis
The external analysis is a significant part of the curriculum to understand the market conditions. In this case, the analysis would involve evaluation of the furniture retail market in the UK. For this purpose, the PESTLE analysis would find application to determine the socio-political, economic, technological, legal and ecological conditions.
External Analysis of the UK market using PESTLE Framework
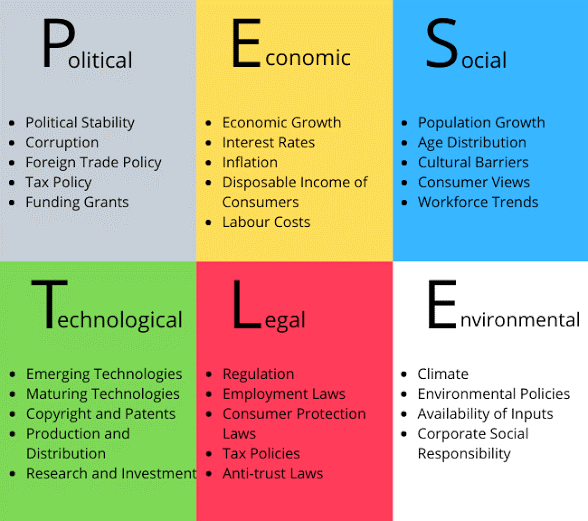 Figure 1: PESTLE Analysis (Source: ABLE Activator. 2022)
Figure 1: PESTLE Analysis (Source: ABLE Activator. 2022)
Political Factors
Assessing the political scenario of the United Kingdom, the country has a stable government with strict and effective implementation of government policies and controls. The country has a successful governance which is proven by the UK’s first rank in political stability in 2007 (Davies and Blanco, 2017). Being a powerful country, the governance system in the UK is both democratic and monarch. The democracy is parliamentary while monarchy is constitutional in the country. However, Brexit has imposed several uncertainties in the last three years triggering some complexities.
Economic Factors
It is easily claimed that the UK holds a stable economy as the GDP trends show a sound performance. The nominal GDP in the country is an approximate 2.744 trillion units, making it rank in the sixth position globally (Takahashi and Yamada, 2021). Similarly, per capita recordings have placed the UK in the first 20 highest per capita holdings worldwide. Again, the market is a diverse economy with equal opportunities for all forms of businesses to flourish and expand which also contrasts inflation.
Social Factors
Predictions of the population levels by the Office for National Statistics that the levels in the UK would rise by 2039 (Storey, 2018). As a result, the UK offers the largest consumer market in the world. It is also the hub for a wide range of profitable businesses like the real estate, fashion, tourism and health care. Health care systems and conditions are also consolidated in the UK which is traced from the rapid recovery faced here. Income levels are also higher.
Technological Factors
The United Kingdom is considered to possess the leading research and development centers of the world to break technological limitations in any field. The country’s economic stability allows many industries to invest heavily in the research and development of massive technologies. The UK is also a distributor of technological services to the world. Thus, inventions and developments add up to the finances of the UK. The British technologies have advanced to compete with Asian rivals like Japan, India, Korea and even American technologies.
Legal Factors
A strong legal structure operates in the UK which helps to control businesses under several acts. The Employment Act 1996 is issued to ensure employee welfare in terms of wages, holidays, pays, leaves and the rights of the staff. Similarly, the Equality Act 2010 helps to secure people from any form of discrimination or abuse in workplaces. There are individual laws for protecting the rights of minorities to make workplaces inclusive and clients more liberal for attending to the needs of globalisation.
Environmental Factors
Several environmental problems have emerged in the UK with developments. Consequently, the government has issued several regulations to ensure sustainable development and eco-friendly measures in all levels of operations. Here, voluntary and government organisations come together to ensure proper waste management and controls processes. They promote recycling and reuse tendencies and condemn plastic generation legally. The tourism industry generates heavy investments (around 127 billion pounds annually) to promote welfare activities across the United Kingdom which assist welfaring (Belke and Gros, 2017).
Justification
Having addressed the external analysis of the UK using PESTLE framework, the importance of usage is clarified further. It is crucial to note here that the above analysis gives a range of insights on the most feasible approach for a wholesome market analysis. It does not merely address the UK retail sector but provides a complete evaluation of social, political, economic, technological, legal and ecological aspects which are linked to IKEA’s business.
For example, the political stability is an advantage for IKEA to build trade relations outside the country. Similarly, the economic performance is a major determinant for the purchasing tendencies. Similarly, the social dynamics help to locate the likeness of customers towards new items that IKEA launches.
However, using Porter’s five forces, a limited microenvironmental asessmern would only generate. The latter is only based on five selected competitive forces for IKEA in retailing. However, it would be applicable for macroeconomic aspects like international trade or services. Hence, PESTLE offers clearer insights on the processes in the UK affecting globally.
Section 2: Strategic Decision Making
The importance of Strategic decision making
The concept of strategic decision making refers to research and sequencing of analysis to plan vital business activities. It is a crucial process that helps companies to maintain proper planning having researched on markets and expansion goals simultaneously. Several frameworks are applied to generate a clearer insight like Ansoff matrix.
Strategic decision-making theory.
Ansoff Matrix
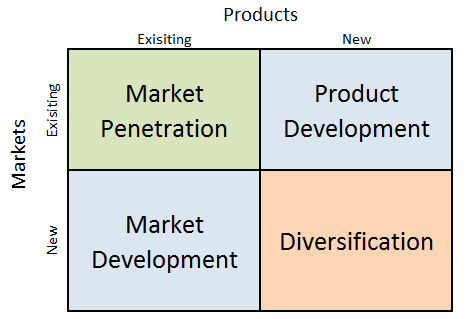 Figure 2: Ansoff Growth Matrix for IKEA (Source: Research-Methodology. 2022)
Figure 2: Ansoff Growth Matrix for IKEA (Source: Research-Methodology. 2022)
Market Penetration
It is noted that IKEA utilises an aggressive market entry strategy in selling existing items to the prevalent buyers. It includes an extensive use of the catalogues which help customers to see a diverse range of existing designs of furniture to select the appealing one besides generic promotions.
Product Development
One of the major strategies for IKEA’s growth is product development. The company invests amply in redesigning existing items. The home improvement and furnishing chain has built more than 9500 products in range with additions of more than 2500 annually (Research-Methodology. 2022). Some of these are in-house while some are extracted from supplier transactions.
Market Development
Market development is an extensive procedure for IKEA in the retail sector. The company operates more than 400 stores in 50 global markets (Research-Methodology. 2022). It uses short, medium and longer plans for entering new markets. Automatically, branding plays a critical role in acquiring the efficiency for drawing customers.
Diversification
IKEA has used diversification only occasionally until recent times to create new and exquisite furniture and sales models. A major example of such plans is the restaurant chain built within IKEA’s furniture stores. The cost advantage of furniture stores have risen undoubtedly but restaurants are failing.
Bowman’s Clock Model
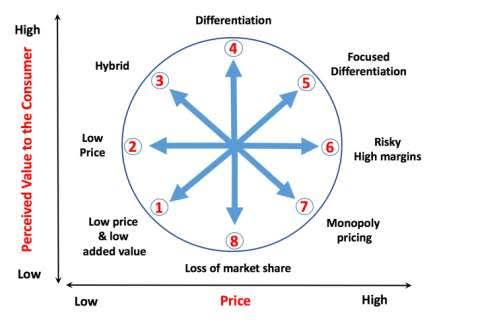 Figure 3: Bowman’s Strategy Clock (Source: Modern Ghana. 2022)
Figure 3: Bowman’s Strategy Clock (Source: Modern Ghana. 2022)
The strategy clock by Bowman is an effective tool that is applicable in complementing the generic strategies of Porter in businesses. Applying the framework in the case of IKEA, one can deduce the prominence of flat pack furniture and modular designs in making customisation and assembling customer-friendly. The products that IKEA delivers are easily unpacked and settled by household members in the UK, making it a preferred furniture retailer. Again, initially, IKEA focused heavily in the low price and low value position (Burt et al., 2021). However, bearing the vision for bettering everyday, IKEA expanded the business from home decor to full-fledged furniture sales and distribution throughout the UK and the worldwide. The focused differentiation level is easily conceived for IKEA during the business shift and expansion of product portfolios. The furniture has been steady for IKEA making it a unique brand image in the customer groups. However, IKEA faces high risks due to competition.
Porter’s Generic Strategies
The generic strategies of Porter are effective measures to analyse the business model of IKEA in current markets. First, the cost leadership paradigm is highly reflective in IKEA’s brand values and ethos (Trendafilov, 2018). It aima to make products accessible for a wide range of people in the market at affordable ranges without compromising reh qualities. Even though, the diversification strategies have reduced the standards of product qualities in IKEA, it has retained the brand differentiation as a furniture retailer in the worldwide market. An important observation here is in terms of competitive excellence which comes from the business model of IKEA. It also generates from the product designing that producers retain to motivate differentiation of items. These help to make the brand still demanding among customers across boundaries.
Impact on Strategic decision making.
Evaluate the main considerations that effect strategic decision making. In order to do this effectively you will need to refer to the internal and external analysis that you carried out in part 1.
Impact of IKEA’s Internal Environment on Business Strategies
There is no doubt in accepting the connection between IKEA’s internal environment and the decisions issued in the business. However, analysis of internal capacities enables IKEA to run operations despite facing problems that reduce brand strengths. One must note that several internal factors combine to create the business system (About.ikea.com. 2022). The value chain comes first which involves primary and secondary activities of IKEA. Applying Porter’s Value Chain framework, it is observed that IKEA’s main goal is to promote motivational sales by listening and learning about demands and requirements.
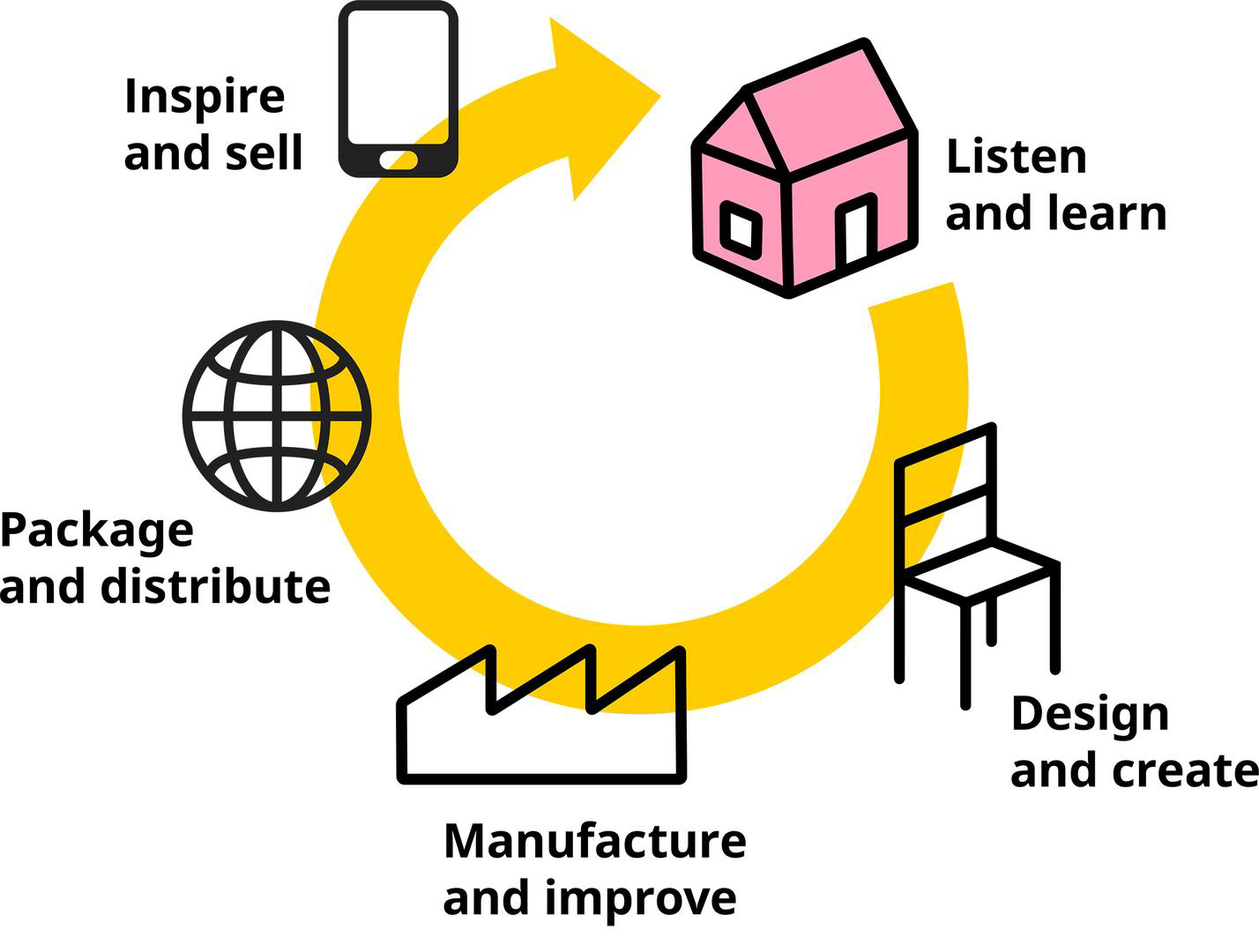 Figure 4: Value Chain Practices of IKEA (Source: About.ikea.com. 2022)
Figure 4: Value Chain Practices of IKEA (Source: About.ikea.com. 2022)
It is also conclusive from the figure that IKEA’s furniture designs and manufacturing are all based on internal resources and capabilities (About.ikea.com. 2022). Thus, the core intention for all primary and secondary choices is to listen and design items that meet most demands in the market. Now, for this purpose, there should exist the abundance of internal capacities like human skills, teamwork and communication to interact and learn about needful data. The SWOT analysis above states the branding and portfolio marketing which come from these value-based activities. Not only that, the organisational structure and culture immensely affect the internal possibilities of IKEA in strategic responses. For example, the company has a clan culture with a hierarchical structure to sustain a steady flow of commands. However, the model is hybridised to accommodate the needs for team contributions in value analysis.
Effect of the UK’s External Environment on IKEA’s Business Strategies
The impact of the social and political scenario of the UK remains undeniable on any business function across any industrial field across the chosen country. Analysing the PESTLE insights, one can comment on the feasibility of the UK politics that helps IKEA to expand in the country and abroad. The government’s support is a major advantage for the company to expand the business using cost leadership and product diversification (Trendafilov, 2018). It is the main supporting unit for IKEA’s strategic alliances issued with global companies to improve sales and services. The successful partnership with Apple for executing automatic and augmented systems in home decor and furnishing tools comes from the legal support in trade from the government (Chylinski et al., 2020). The market is also responsible for the large-scale economic inflow in IKEA from the worldwide business and local services. Another important aspect to note here is the abundance of possibilities using the product development partnership with LEGO. The collaboration is issued to design offshore production units for which international relationships are crucial determinants. It is worthy to claim that the overall system relies heavily on external rather than internal environments. The reason is that external factors are key influencers in internal stability. Be it skills, employee management, finances and other value-based approaches that the company issues, all functions linked to the market conditions outside IKEA.
Evaluating the success of a current business strategy
It is important to discuss the major strategies that IKEA has applied and explored in the industry since the last few decades. The first approach is the low pricing model and low value basis for attaining market awareness. IKEA has focused on building a cost leadership approach for pricing and product deliveries across all regions and communities (Trendafilov, 2018). Similarly, it has applied strategic alliances in market promotions, stability and promotions respectively. Lastly, the company has been diversifying the product basis to expand user conveniences in one-stop retailing across different target groups. The marketing strategies listed have also included corporate changes to ease the operational logistics of IKEA in the UK. Similarly, the company has been able to issue several initiatives to develop a better insight on brand among target buyers.
SAFe Criteria Analysis of IKEA’s Business Strategy
| Strategies | Suitability | Accessibility | Feasibility |
| Strategic Alliance | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Low Pricing and Value Model | ✓ | ✓ | × |
| Product Diversity | ✓ | × | × |
Table 2: SAFe Test for IKEA’s Strategies (Source: Created by Author)
Applying the SAFe criteria, it is deduced that the chosen marketing strategies have not fulfilled all criteria of IKEA’s branding. A prominent cause of this is highlighted in the SWOT framework that product diversification has led to loss of product quality and standards. Complaints on the low pricing model are also noted which have reduced customer visits in IKEA over the last few years. The competition in the furnishing world and retail, as discussed previously, has been a major loss to IKEA with the stakes listed. Therefore, the company needs a new approach to improve the performance in the UK.
The first strategy to choose here is social media marketing. Experts have noted a rising trend in social media marketing for alliances and for global expansion. Reports show that online social media advertisements of Amazon have increased revenues by 87 per cent in 2021 (more than 7.9 billion dollars) (CNBC. 2022). The next strategy to accommodate is specialisation and differentiation. IKEA already has a specialised identity of furniture retail. The differentiation needs to evolve on grounds of modernising designs and product qualities. It can help to build customer interests given that items made revive the standard quality which had existed beforehand.
Reference List
ABLE Activator. 2022. Business Theory Analysis: PESTLE – ABLE Activator. [online] Available at: <https://activator.bg/2021/11/24/pestle/> [Accessed 13 July 2022].
About.ikea.com. 2022. Breaking down the IKEA value chain. [online] Available at: <https://about.ikea.com/en/about-us/the-ikea-value-chain> [Accessed 13 July 2022].
Belke, A. and Gros, D., 2017. The economic impact of Brexit: Evidence from modelling free trade agreements. Atlantic Economic Journal, 45(3), pp.317-331.
Burt, S., Dawson, J., Johansson, U. and Hultman, J., 2021. The changing marketing orientation within the business model of an international retailer–IKEA in China over 10 years. The International Review of Retail, Distribution and Consumer Research, 31(2), pp.229-255.
Chylinski, M., Heller, J., Hilken, T., Keeling, D.I., Mahr, D. and de Ruyter, K., 2020. Augmented reality marketing: A technology-enabled approach to situated customer experience. Australasian Marketing Journal (AMJ), 28(4), pp.374-384.
CNBC. 2022. CNBC. [online] Available at: <https://www.cnbc.com/amp/2021/07/29/amazons-ads-business-posts-87percent-growth.html> [Accessed 13 July 2022].
Davies, J.S. and Blanco, I., 2017. Austerity urbanism: Patterns of neo-liberalisation and resistance in six cities of Spain and the UK. Environment and Planning A, 49(7), pp.1517-1536.
Hoekstra, J.C. and Leeflang, P.S., 2020. Marketing in the era of COVID-19. Italian Journal of Marketing, 2020(4), pp.249-260.
Modern Ghana. 2022. [online] Available at: <https://www.modernghana.com/amp/news/855211/customer-loyalty-the-bowmans-clock.html> [Accessed 13 July 2022].
Research-Methodology. 2022. IKEA Ansoff Matrix – Research-Methodology. [online] Available at: <https://research-methodology.net/ikea-ansoff-matrix/> [Accessed 13 July 2022].
Reuters. 2022. [online] Available at: <https://www.reuters.com/article/ikea-climate-idAFL1N2TY0ZF> [Accessed 13 July 2022].
Rodrigues, C. and Brandão, A., 2021. Measuring the effects of retail brand experiences and brand love on word of mouth: a cross-country study of IKEA brand. The International Review of Retail, Distribution and Consumer Research, 31(1), pp.78-105.
Sorge, A. and Streeck, W., 2018. Diversified quality production revisited: Its contribution to German socio-economic performance over time. Socio-Economic Review, 16(3), pp.587-612.
Storey, A., 2018. Living longer: how our population is changing and why it matters. Office for National Statistics: London, UK.
Takahashi, H. and Yamada, K., 2021. When the Japanese stock market meets COVID-19: Impact of ownership, China and US exposure, and ESG channels. International Review of Financial Analysis, 74, p.101670.
Trendafilov, D., 2018. Design incorporated: IKEA as personal experience. Punctum. International Journal of Semiotics, 4(1), pp.165-178.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

