7021BMS Critical Review in Pharmacology
Introduction
The pharmacology chapter mainly develops in the 19th century and which is developed as a biomedical science. Biomedical science which is mainly applied to the principles of the scientific types of experiments depends on the therapeutic type of contexts. And these types of advancements in research techniques mainly propelled pharmacological understandings and research. Mainly in the field of medicine, the discovery of drugs is the main process. By this type of thing, here mainly discovered the medications of the new candidates. In this instance, the primary method for locating drugs is to identify drug classes derived from conventional treatments, like penicillin. In recent times, chemical libraries containing natural products, synthetic small molecule species, or extracts have been tested using living cells or entire organisms.In traditional pharmacology, substances must first be identified that possess therapeutic mechanisms of action that are desirable. Many purified proteins can now be quickly cloned thanks to the sequencing of the human genome. In large compound libraries, isolated biological targets thought to alter disease can be found using high-throughput screening. Reverse pharmacology is now used frequently. The effectiveness of these hits is evaluated first in cells and then in animals. Drugs can be defined as man-made, natural, or endogenous molecules that produce biochemical or physiological effects. Pharmacology is the branch of medicine, biology, and pharmacy that deals with drugs or the effects of drugs influence the cell. Organs, tissues, or organisms (these endogenous and exogenous bioactive species are sometimes referred to collectively as pharmacon). Specifically, the study of chemical-organism interactions that influence normal or abnormal biochemical function. Assuming substances have restorative properties, they are viewed as drugs. This field envelops all parts of medication synthesis and properties, capability, sources, amalgamation and plan, sub-atomic and cell instruments, organ or framework components, flagging or cell correspondence, collaborations, atomic diagnostics, synthetic science, treatment, and clinical applications. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics are his two primary areas of pharmacology. In contrast to pharmacokinetics, which focuses on how drugs affect organic frameworks, pharmacodynamics examines how drugs affect natural frameworks. While pharmacodynamics focuses on how chemicals interact with biological receptors, pharmacokinetics focuses on how chemicals are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted from biological systems.
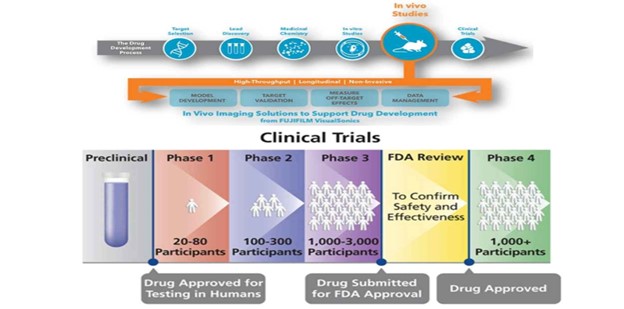
Figure 1: Overview of new drug discovery
(“Source: https://www.pharmatutor.org”)
Research aim and objectives
The research aim is mainly described to indicate the main purpose of the current developments and advancements in pharmacology and drug discovery research topics (Muttenthaler et al. 2021). The research aim is mainly needed to investigate all the factors and it is used to develop knowledge and theories. The research is mainly used to achieve the particular of that particular research project. The research objective mainly underlies the factors of the research aim. So the objectives of this research topic are given below.
- To discover the developments of the drugs.
- To investigate the improvement of drug discoveries.
- To analyze the important steps of drug discovery.
Research questions
The research question is mainly based on the current types of advancements and developments in drug discovery and pharmacology. Through the literature, here mainly interpret all the answers of that particular study. The research question is mainly used to address various types of problems related to that research topic. The research questions are given below.
- Are new types of technologies coming for discovering drugs?
- How the discovery of the drugs and the process of development are improved?
- What are the developments and advancements that come with pharmacology?
Research problems
Depending on that particular topic, the problem of the research comes into the picture. Various types of problems come at the time of developing or advancing pharmacology and drug discovery (Lee et al. 2019). At the time of doing this research, the rising pressure of cost, supply issues, and shortages in medicines. For this, the discovery of the drug is not improved day by day which can makes various types of problems. So improvement in the discovery of drugs is also necessary. Limitations of the animal models, heterogeneity of the population of the patient, length, and complexity are also modern types of challenges for drug discovery. For this type of thing development of the drugs is very difficult which is also a big problem for this improvement and development of the pharmacology and drug discovery research topic [Referred to Appendix 2].
Literature Review
This part is mainly defined as reducing the problems of the current developments and advancements in pharmacology and drug discovery research topics. So the problems are reduced through the various types of relevant journals, relevant secondary sources, and articles. So it is given below.
According to Prathumsap et al. 2022, In both healthy and diseased myocardium, the balance of cardiac parasympathetic and sympathetic activity is closely linked to mitochondrial function, cellular oxidative status, and immunoregulation. Doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity (DIC) is characterized by cardiac autonomic neuropathy, mitochondrial and cellular dysfunction, and other key pathophysiological features (Prathumsap et al. 2022). They tested the hypothesis that acetylcholine receptor activation-based autonomic modulation effectively reduces its DIC. Rodents were separated into control gathering and doxorubicin bunch. They treated the rats in the DOX group for 30 days by evenly dividing them into four intervention groups. Vehicles, Muscarinic and Nicotinic Receptor Agonists, and the Composite mAChR Agonists Group. The heart was analyzed for its biochemical and functional properties. This indicates that AChR agonists improved mitochondrial and cardiac function to protect the heart from DIC. A decrease in inflammation, apoptosis and mitochondrial oxidative damage came along with this. Eminently, PNU and BET applied cardioprotection through various atomic pathways.
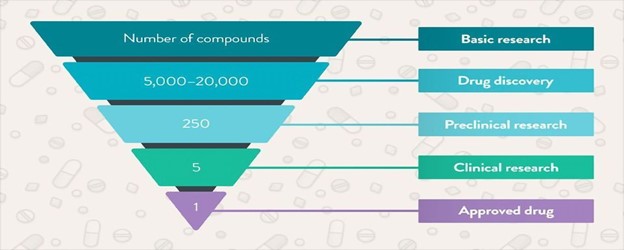
Figure 2: Exploring the process of drug development
(“Source: https://assets.technologynetworks.com”)
According to Bonaventure et al. 2021, New viral infection regulators can be identified using genome-wide screening. New HIV-1 inhibitors were discovered through CRISPR/Cas9 screening in this instance. They envisioned the “RNA” helicase “DDX42” as a novel viral replication inhibitor using this strategy.DDX42 was recently demonstrated to be a non-processive helicase that can bind to G-quadruplexes and other “RNA” optional designs without revealing its capabilities. According to their findings, “DDX42” fatigue naturally extends the time it takes for “HIV-1 DNA” to be assembled and contaminated in cell lines and base cells. When “DDX42” was overexpressed in comparison to a dominant-negative mutant, “HIV-1” infection decreased (Bonaventure et al. 2021). However, the general nonspecific effects on target cells that were confirmed by “RNA-seq” are inconsistent with the fact that “DDX42” does not prevent infection by three negative-strand RNA viruses. However, diseases caused by LINE-1 retrotransposition, other retroviruses, and positive-strand “RNA” infections like “CHIKV” and “SARS-CoV-2” were significantly reduced by “DDX42”. In proximity ligation and bridging RNA immunoprecipitation assays, “DDX42” was found in close proximity to viral elements, indicating a specific interaction with fragile viral RNA. This strongly suggests that the viral ribonucleoprotein complex is directly affected by “DDX42”. For the first time, their findings indicate that their “DDX42” now appears to play a significant new role in the body’s natural antiviral defenses.
According to Yao et al. 2022, In mouse plasma stoma, the long non coding RNA (lncRNA) PVT1 was discovered to initiate a variety of translocations for the first time. Along with human lncPVT1, the well-known MYC ontogeny can be found on chromosomes. LncPVT1 has been linked to the dysfunctional physiological processes of cancer cells, including DNA damage, and to the regulation of these physiological mechanisms in previous research. It has been discovered that LncPVT1 aids in the growth of various types of cancer (Yao et al. 2022). Chemotherapy and radiation significantly reduce the efficacy of tumor therapy by inhibiting steaminess (for cancer stem cells, CSCs), hypoxia, epithelial transition (EMT), and repair associated with the dysfunctional physiological processes of cancer cells, which include DNA damage. In some cancers, it was recently discovered that lncPVT1 alters chemo resistance and radio resistance. The mechanisms by which lncPVT1 regulates cellular radio resistance and chemo resistance are discussed in this summary. It is anticipated that lncPVT1 will be a potent anti-tumor target and sensitizer for chemotherapy and radiotherapy due to its high expression in malignant tumors and its sensitizing effect on these treatments. However, additional research is required [Referred to Appendix 1].
According to Salloway et al. 2021, DIAD, also known as dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease, manifests itself decades before clinical symptoms appear due to predictable biological changes; it is possible to test interventions to slow disease progression at both the asymptomatic and symptomatic stages. Participants with her DIAD took part in a multi-arm, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of solanezumab in both the asymptomatic and symptomatic stages of the disease. Transporters of the change were given to three gatherings: They took medication or a placebo every day for four to seven years. A mental endpoint was the primary outcome (Salloway et al. 2021). Clinical, cognitive, imaging and fluid biomarker measurements were among the secondary outcomes. Gantenerumab was given to 52 participants with a single mutation, solanezumab to 52, and placebo to 40. Multiple measures of cognitive decline increased more in the solanezumab-treated group, but subsequent biomarkers remained unaffected. The total percentage of patients in the gantenerumab group experienced amyloid-related imaging impairment and edema, compared to 2.5 percent in the placebo group and 0 percent in the solanezumab group. It significantly reduced tau and slowed the rise of neurofilament light chains. Gantenerumab and solanezumab didn’t slow mental deterioration in suggestive DIAD. In no disorder did mental deterioration happen. Participants experienced relief from their symptoms before the intended dose was reached.
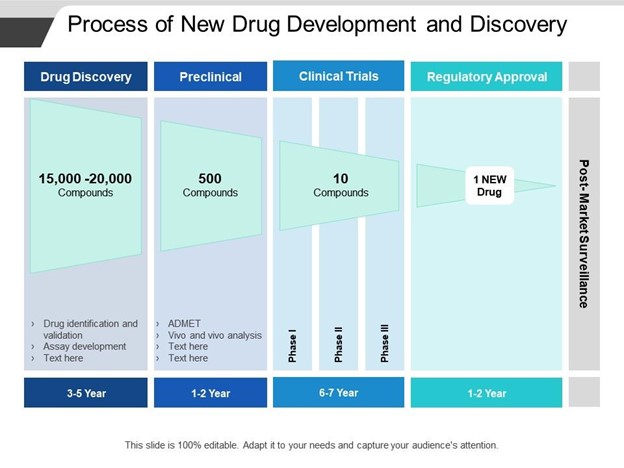
Figure 2: The process of new Drug Development
(“Source: https://www.slideteam.net”)
According to Tang et al. 2022, Not only does drug-induced cardiotoxicity increase cardiovascular disease mortality and morbidity, but it also slows the development of new drugs. In preclinical cardiac safety assessments, comprehensive proper arrhythmia risk drug testing has been utilized for more than 15 years. In any case, not as much examination has been finished on different systems of cardio toxicity (Tang et al. 2022). The majority of the FDA’s black box warnings about adverse cardiovascular events are known to be caused by issues with mitochondria, a common type of “cardiotoxicity”. “Preclinical cardio toxicity” safety studies have not yet been evaluated. Drug-induced “mitochondrial toxicity”, a high-throughput cardiomyocyte screening method, and its potential integration into preclinical safety pharmacology are the topics covered in this overview. The experts emphasize the importance of using essential adult human cardiomyocytes for the evaluation of “mitochondrial morphology” and capability as well as the necessity of new cardiovascular security testing stages that incorporate mitochondrial harmfulness and “proarrhythmia risk” evaluation with heart health evaluation.
Literature Gap
This part of the research is mainly underlying the section of literature review. A gap means missing information; here literature gap is mainly described as the missing information in the literature review section (Mak and Pichika, 2019). The Section of literature review does not address a variety of issues through a variety of related articles and journals in the Literature Review Section. These details were not provided by the authors in the literature review. Literature reviews cannot solve the current issues that arise during the drug development process. The literature review section does not discuss this or the difficulty of the drug discovery process. The major risks and the future of drug discovery are also not mentioned in the above section. So these are the main gaps or the missing information in the literature.
Conclusion
Here mainly conclude that the most important aspect of drug discovery is that identify the small types of potent compounds which is mainly selective to bind with the target of interest with a level of high affinity. Another thing is that there are various types of processes are coming into the picture in the process of drug discovery. But the main three major processes of drug discovery are that discovery and development, then the second step preclinical types of research, then the clinical research. After that review that drug and then monitor the post-market safety of the drug. There are various types of techniques are come for discovering the drugs and the improvement of the drugs. So the process of discovering the drug development process is improving day by day through the identification of the target and validation, Screening & development of assay and lead optimization process are also needed for the improvement of the drug discovery. So these are the main outcomes of this research topic. Over the course of the past century, drug discovery has contributed more to medical advancement than any other aspect of science, starting with chemistry and moving on to pharmacology and clinical science. The discovery of new drugs has greatly benefited from the development of molecular biology, particularly genomics. Monoclonal antibodies and recombinant proteins have significantly expanded our therapeutic options. Utilizing tools from both genomics and bioinformatics will be able to examine the genetic basis of multifactorial diseases and select the most promising drug targets, expanding the range of treatment options. The institutional foundations of this interdisciplinary endeavor are being challenged by the dramatic increase in the complexity of drug discovery. The pharmaceutical industry’s discovery arm has been replaced by the biotechnology sector. In order to bridge the gap between academia and big pharmacy, biotech companies have evolved into potent tools for technology transfer.
Reference List
Journals
Bonaventure, B., Rebendenne, A., de Gracia, F.G., McKellar, J., Gracias, S., Labaronne, E., Tauziet, M., Valadão, A.L.C., Bernard, E., Briant, L. and Gros, N., 2021. The DEAD box RNA helicase DDX42 is an intrinsic inhibitor of positive-strand RNA viruses. bioRxiv, pp.2020-10.
Devine, P.N., Howard, R.M., Kumar, R., Thompson, M.P., Truppo, M.D. and Turner, N.J., 2018. Extending the application of biocatalysis to meet the challenges of drug development. Nature Reviews Chemistry, 2(12), pp.409-421.
Gajdács, M., 2019. The concept of an ideal antibiotic: implications for drug design. Molecules, 24(5), p.892.
Henninot, A., Collins, J.C. and Nuss, J.M., 2018. The current state of peptide drug discovery: back to the future?. Journal of medicinal chemistry, 61(4), pp.1382-1414.
Lee, A.C.L., Harris, J.L., Khanna, K.K. and Hong, J.H., 2019. A comprehensive review on current advances in peptide drug development and design. International journal of molecular sciences, 20(10), p.2383.
Mak, K.K. and Pichika, M.R., 2019. Artificial intelligence in drug development: present status and future prospects. Drug discovery today, 24(3), pp.773-780.
Muttenthaler, M., King, G.F., Adams, D.J. and Alewood, P.F., 2021. Trends in peptide drug discovery. Nature reviews Drug discovery, 20(4), pp.309-325.
Prathumsap, N., Ongnok, B., Khuanjing, T., Arinno, A., Maneechote, C., Apaijai, N., Chunchai, T., Arunsak, B., Shinlapawittayatorn, K., Chattipakorn, S.C. and Chattipakorn, N., 2022. Acetylcholine receptor agonists provide cardioprotection in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via modulating muscarinic M2 and α7 nicotinic receptor expression. Translational Research, 243, pp.33-51.
Salloway, S., Farlow, M., McDade, E., Clifford, D.B., Wang, G., Llibre-Guerra, J.J., Hitchcock, J.M., Mills, S.L., Santacruz, A.M., Aschenbrenner, A.J. and Hassenstab, J., 2021. A trial of gantenerumab or solanezumab in dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease. Nature medicine, 27(7), pp.1187-1196.
Tang, X., Wang, Z., Hu, S. and Zhou, B., 2022. Assessing Drug-Induced Mitochondrial Toxicity in Cardiomyocytes: Implications for Preclinical Cardiac Safety Evaluation. Pharmaceutics, 14(7), p.1313.
Yao, W., Li, S., Liu, R., Jiang, M., Gao, L., Lu, Y., Liang, X. and Zhang, H., 2022. Long non-coding RNA PVT1: A promising chemotherapy and radiotherapy sensitizer. Frontiers in Oncology, 12.
Appendices
Appendix 1: PHASES OF DRUG DEVELOPMENT PROCESS
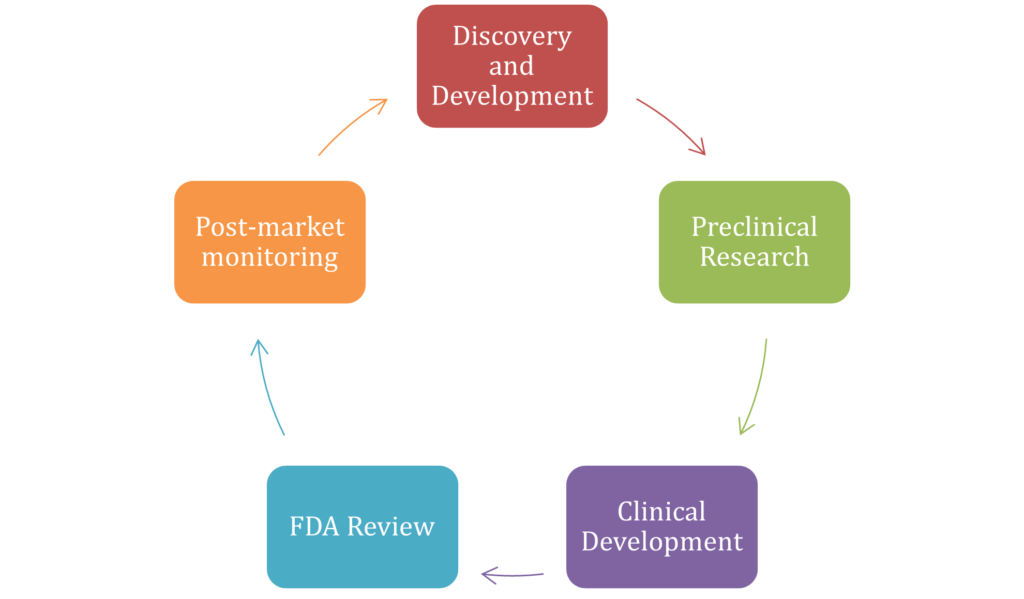
(Source: Self-created)
Appendix 2: DRUG DISSCOVERY RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT CYCLE
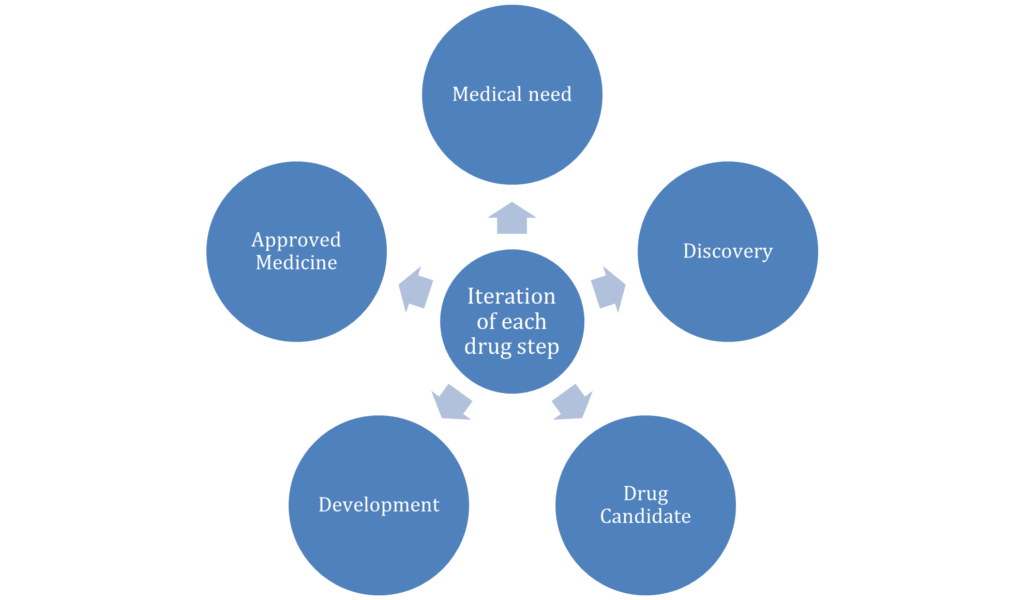
(Source: Self-created)
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

