7028MAA Research Methods and Project Samples
Introduction
Background
The title of the study aims to identify “The Influence of Environmental Management Practices and Supply Chain Integration on Technological Innovation Performance.” Hence, the following study focuses upon the importance of technological innovation performance and the way it is influenced by environmental management practices and supply chain integration of an organisation. The development in technology and innovation has allowed organisations to extensively improve the effectiveness of their supply chains (Francisco & Swanson, 2018). However, with the use of technology and advanced methods, it has also been seen that the sustainability of the organisation reduces. Keeping this in mind environmental management practices have also been adopted by various organisations, which are aimed towards reducing their carbon footprint and using renewable energy in order to make their operations sustainable. Therefore, in order to use better environmental management practices and achieve a robust and effective supply chain management, organisations have turned to technological innovations and performance methods that help an organisation to achieve both the goals.
Significance of the study
The study is quite significant, as it would help in understanding the specifications of supply chain integration due to which organisations adopt technological innovations that aimed towards improving the performance of an organisation, which in turn helps in increasing the performance of the supply chain (Liu, Bruins & Heberling, 2018). The findings from the study would also help in gaining insights regarding environmental management practices due to which technological innovation can be undertaken by organisations to attain sustainability in their respective industries. Therefore, the focus of the study would be upon the technological innovations that help an organisation to achieve sustainability as well as develop a robust supply chain management. Adding to that, the study would also help in understanding the different strategies adopted by organisations in order to achieve sustainability and effective supply chain management practices (El-Kassar& Singh, 2019). Moreover, the key factors that influence an organisation to adopt technological innovation performance methods would also be identified that will be further help to understand the topic of study in a better way.
Apart from that, technological innovation performances also allowed organisations to have control over their production process effectively helping them in making their operations cost-effective and profitable. There are several organistaions in the global market that have been effectively utilising technological innovation performance methods to increase their effectiveness and achieve a competitive edge in their respective markets. For example, Amazon operating in the eCommerce industry has been using AWS (Amazon Web Services) to manage productivity, whereas, Tesla operating in the automotive industry and Google operating in the IT industry using essential technical aspects to support their production and service performances.
Literature Review
Technology for achieving sustainability
Technological innovation plays a very important role in Sustainable Development Goals. In these, the goal of the technology is to reduce the risk of environmental and ecological harm by creating sustainable products. Through the help of technology, it has become easier to access clean water with the help of efficient water purification and sanitation technologies. Technology is becoming the most fundamental factor in every sector of the world from industrial resources to e-commerce; technology has become a blessing for the entire population (Nasrollahi et al. 2020). Sustainability is widely dependable on the innovation of the technologies, which are related to energy. As the world needs to understand and minimise the use of fossil fuels, which is not good for the environment; thus, technology is giving its efforts to create less pollution in the world. Natural gas is one of the elements that produces less pollution in comparison to the uses of other fuels and oils. Increasing the efficiency of energy in the transportation system is a major improvement across the world. “Improving fuel efficiency” is one of the prime objective of some of the biggest automobiles organisation as it takes a step ahead of saving the environment as well as improving sustainability. Therefore, organisations like Tesla, Volkswagen, Renault, Honda, Hyundai, Kia, Mazda, Nissan, BMW, Toyota and others are working hard on technical innovation that can fulfil their above mentioned goal (Blanco et al. 2020). The following figure shows how the organisations are developing their automobile business by providing fully electric vehicles without the use of fuels.
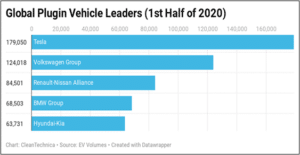
Figure 1: Fully electric vehicles sales of the organisation
(Source: Fuchs, 2017)
Manufacturing and mining have seen a huge revolution as technology has started to apply the cycle of reducing, reusing and recycling. This helps the industry to use the maximum of the materials for their production. The wastes of one particular segment have been used as a material of the other segment, by using this concept the industries are changing their ways of manufacturing and production. This helps the environment to breathe and expand. Sustainable technology is very essential for an organisation as it reduces the risks and improves the outcomes of a project (Niederhauser et al. 2018). Everyone wants to work in a place where the business has social and environmental standards.
Impact of technology and innovation on supply chain integration
Technology has changed the complete structure of the way people are working today. Technology has a huge impact on the supply chain integration of an organisation. It increased transparency as it improved digital communication in a much easier way. Technology helps to improve the relationship between the business and the customers. By enhancing the system of production and delivery, satisfaction of the customers can be increased by maintaining transparency amongst all who are related to the selling and purchasing cycle. Technology has developed the supply chain, as it was known before (Ganbold, Matsui & Rotaru, 2020). A few years back it was very simple to hide the errors, which are happening around the industry, but now the customers can check about their products immediately after they order something. Blockchain drives the supply chain transparency by reducing the risks and data errors. In the given figure, highest benefits that supply chain gets are by blockchain providing the tracking facilities, enhancing communication, improves logistics and enables transparency.
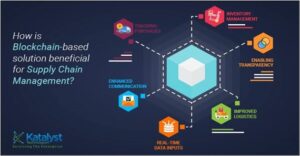
Figure 2: Blockchain-based Supply chain
(Source: Dutta et al. 2020)
Technology has made the supply chain process faster and simpler. The involvement of technology in an organisational transport system and warehouse helps the business to ensure that everything is going well with proper data capture, monitoring resources and improving labour management. Technology helps in providing visibility to the business to check the errors and resolve them immediately. The process of integration saves time as well as reduces the mistakes, which are done manually. OBSL’s CALIDUS software changes the whole supply chain. CALIDUS TMS helps in optimising and reducing the driver miles and is able to capture the correct information (Gao, Calderon & Tang, 2020). This software also helps in checking the quality and the products, which are delivered or despatched through the system only. Technology has evolved throughout the decade and it effectively affected the supply chain integration by enhancing the operational process.
Technology is a concern for environmental management practices
Technology is playing a crucial role in innovation in the world as well as it is generating harmful substances for the environment as well. The revolution in industries has brought a huge development of technology in the world. Technology is making everything easy and simpler but on the contrary, it is negatively affecting the environment and damaging the natural earth (Zhironkin&Cehlar, 2021). It is damaging the world in two ways, one is by polluting and the other one is by depletion of natural resources. Technology has become so convenient for the population that they do not even bother to use natural resources as it takes more time and hard work. Harmful qualities of gases such as carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitric oxide, sulfur dioxide and methane are the gases that are released in the environment by the emerging industries, as a result, it influences climate change (Cheng et al. 2021). The burning of fossil fuels, mass agriculture, power stations and the waste material of the industries are polluting the air as well as the water. Consequently, it is negatively affecting nature, human beings, animals and increases global warming. Dumping the waste into the water leads to the degradation of aquatic life. The depletion of natural resources includes deforestation, mining for fossil fuels, soil erosion, overconsumption and contamination of the resources (Moletsane& Venter, 2018).
Triple bottom line theory

Figure 3: Triple bottom line theory
(Source: Tseng et al. 2020)
The triple bottom line theory is a framework that can be utilised by organisations in order to use technological innovations to achieve sustainability in their business operations. The triple bottom line theory indicates that an organisation can utilise environmental-friendly operations while also conducting CSR activities aimed towards the development of the society in which they operate (Birkel& Müller, 2020). However, the theory also indicates that these actions of the organisation need to be profitable there for helping to achieve the three objectives of the triple bottom line theory that are people, profit and planet. Organisations that are able to achieve these three objectives based on the triple bottom line theory can attain total sustainability in their market operations, which is a major part of their environmental management practices (Braccini&Margherita, 2019). This also benefits the supply chain integration due to which technological innovation performance methods can be adopted for further enhancing the ability of the organisation to achieve the objectives of the triple bottom line.
Research questions
- What is the significance of technological innovation performance?
- How environmental management practices does aimed towards achieving sustainability influence technological innovation?
- To what extent do integrations in supply chain management influence technological innovation?
- How effective are technological innovation performance methods for organisations in terms of their overall competitiveness and sustainability?
- What are the different ways, which can be utilised to improve innovation performance that can help in achieving sustainability and improve supply chain integrations?
Methodology
The research questions addressed in the above chapter would be met with the help of secondary research methods. This would involve the study of a range of different secondary sources, which would help in identifying the influence of environmental management practices and supply chain integration on an organisation’s technological innovations (Mohajan, 2018).
In terms of research methods, the researcher would adopt positivism research philosophy because it helps in achieving and analysing data and information in a more scientific manner. The positivism research approach is quite relevant to the topic of study and the kind of data that would be collected (Basias & Pollalis, 2018). In order to understand aspects related to technological innovations, it is necessary to adopt a scientific approach for analysing information and theory presented by different authors.
Apart from that, a deductive research approach would also be adopted by the researcher, which would help in achieving the answers to the research question and addressing it with the help of realistic conclusions. The reason for choosing a deductive research approach for the topic because it helps in formulating a theory based on which the hypothesis of the study is formed leading to further observations and finally achieving confirmation if the theory that was formed initially can be accepted or rejected (Janis et al. 2020). Considering that the study would be based upon hypothesis analysis a detective research approach suits the requirement of the research.
Furthermore, a descriptive research design would also be adopted which would help the researcher to focus upon specific aspects that are linked with the topic of study and research questions. The descriptive research design is quite beneficial for studying qualitative data and this makes the research approach and design more appropriate.
In terms of limitations, there are quite a few for instance the study is not based upon any specific industry or company due to which a wide array of data and information needs to be considered (Alase, 2017). In fact, technological innovation processes may vary from one industry to another depending upon the requirements and feasibility and this can lead to diverging results. This is one of the limitations, which has been taken into consideration. Apart from that, there are also sources that could lead to biased theories and interpretations therefore a critical analysis would be done upon all the data and information that would be collected in order to eliminate any kind of biases by comparing and contrasting the views of different authors and sources.
Additionally, a number of different ethical considerations should be taken into account carrying out the research. All the data and information that would be collected from secondary sources would be cited accordingly to acknowledge the sources (Ngozwana, 2018). This would also help in ensuring that the study is evidence-based and has no false information and representations. Furthermore, the researcher would also avoid any kind of biased approaches towards achieving the conclusions of the study. Moreover, detailed information that would be collected would not be shared for any kind of commercial purpose or personal financial gains.
Data collection
In terms of data collection and gathering, different industries and organisations operating in the global market would be taken into consideration. In this regard, the chosen organisations would be the ones that have utilised technological innovation performance improvement methods for achieving sustainability in their environmental management practices while also utilising supply chain integrations (Bretschneider et al. 2017).
Furthermore, in order to ensure that in-depth data regarding the topic of study can be collected a range of different published journal articles and news reports case studies would be taken into consideration. This would not only bring in the scope of sources that can be utilised for collecting data and information but would also help in conducting an in-depth analysis (Archibald et al. 2019).
In terms of ethical and confidentiality issues, it can be stated that since the study would be only considering secondary data and information the chances of confidentiality is quite low. This is due to the fact that all the information that would be collected would already be available on internet sources therefore they are accessible to the general public. As a result, confidential data will not be taken into consideration or collected in any form; thereby, eliminating any kind of ethical issues that can arise due to the leak of confidential data (Flynn, Albrecht & Scott, 2018).
Discussion
The hypothesis considered for the following research are-
H0: Environmental management practices and supply chain integration influence technological innovation performance
H1: Technological innovation performance is not influenced by an organisations environmental management practices or supply chain integration
The research would be based on the above-mentioned hypothesis and based on this a number of objectives have been formed that would further help in addressing the research questions of the study.
Objectives
- To analyse impacts of environmental management practices over and Organisations technological innovations
- To identify if supply chain integrations can influence and trigger technological innovations in an organisation
- To find out the different ways organisations use technological innovation performance improvements to achieve sustainability
- Address the research questions and I understand the influences of environmental management practices and supply chain integration over an organisations market operations
The research questions and research objectives are specific and this would help the researcher to specifically identify data and information and analyse them to address the research questions (Basias & Pollalis, 2018). This would also help to guide the researcher in terms of identifying the most appropriate methods for analysing the data. Considering any changes in the research hypothesis or research questions the analysis would be adjusted based on the changes that have been made to the scope of the study.
References
Alase, A. (2017). The interpretative phenomenological analysis (IPA): A guide to a good qualitative research approach. International Journal of Education and Literacy Studies, 5(2), 9-19. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://www.journals.aiac.org.au/index.php/IJELS/article/viewFile/3400/2797
Archibald, M. M., Ambagtsheer, R. C., Casey, M. G., & Lawless, M. (2019). Using zoom videoconferencing for qualitative data collection: perceptions and experiences of researchers and participants. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 18, 1609406919874596. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1609406919874596
Basias, N., & Pollalis, Y. (2018). Quantitative and qualitative research in business & technology: Justifying a suitable research methodology. Review of Integrative Business and Economics Research, 7, 91-105. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://sibresearch.org/uploads/3/4/0/9/34097180/riber_7-s1_sp_h17-083_91-105.pdf
Birkel, H. S., & Müller, J. M. (2020). Potentials of industry 4.0 for supply chain management within the triple bottom line of sustainability–A systematic literature review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 125612. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652620356584
Blanco, C. F., Cucurachi, S., Guinée, J. B., Vijver, M. G., Peijnenburg, W. J., Trattnig, R., & Heijungs, R. (2020). Assessing the sustainability of emerging technologies: A probabilistic LCA method applied to advanced photovoltaics. Journal of Cleaner Production, 259, 120968. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652620310155
Braccini, A. M., & Margherita, E. G. (2019). Exploring organizational sustainability of industry 4.0 under the triple bottom line: The case of a manufacturing company. Sustainability, 11(1), 36. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/11/1/36/pdf
Bretschneider, P. J., Cirilli, S., Jones, T., Lynch, S., & Wilson, N. A. (2017). Document review as a qualitative research data collection method for teacher research. SAGE Publications Ltd. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://methods.sagepub.com/case/document-review-qualitative-research-data-collection-method-teacher
Cheng, Y., Awan, U., Ahmad, S., & Tan, Z. (2021). How do technological innovation and fiscal decentralization affect the environment? A story of the fourth industrial revolution and sustainable growth. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 162, 120398. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040162520312245
Dutta, P., Choi, T. M., Somani, S., & Butala, R. (2020). Blockchain technology in supply chain operations: Applications, challenges and research opportunities. Transportation research part e: Logistics and transportation review, 142, 102067. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc7522652/
El-Kassar, A. N., & Singh, S. K. (2019). Green innovation and organizational performance: the influence of big data and the moderating role of management commitment and HR practices. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 144, 483-498. Retrieved on 19 July from:https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Sanjay-Singh-132/publication/322227706_Green_innovation_and_organizational_performance_The_influence_of_big_data_and_the_moderating_role_of_management_commitment_and_HR_practices/links/5c1df01d458515a4c7f05b1e/Green-innovation-and-organizational-performance-The-influence-of-big-data-and-the-moderating-role-of-management-commitment-and-HR-practices.pdf
Flynn, R., Albrecht, L., & Scott, S. D. (2018). Two approaches to focus group data collection for qualitative health research: Maximizing resources and data quality. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 17(1), 1609406917750781. Retrieved on 19 July from:https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1609406917750781
Francisco, K., & Swanson, D. (2018). The supply chain has no clothes: Technology adoption of blockchain for supply chain transparency. Logistics, 2(1), 2. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://www.mdpi.com/2305-6290/2/1/2/pdf
Fuchs, C., (2017). Information technology and sustainability in the information society. International Journal of Communication, 11, p.31. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://ijoc.org/index.php/ijoc/article/view/6827
Ganbold, O., Matsui, Y., & Rotaru, K. (2020). Effect of information technology-enabled supply chain integration on firm’s operational performance. Journal of Enterprise Information Management. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/JEIM-10-2019-0332/full/html
Gao, L., Calderon, T. G., & Tang, F. (2020). Public companies’ cybersecurity risk disclosures. International Journal of Accounting Information Systems, 38, 100468. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1467089520300361
Janis, I., Alias, M., Zulkipli, M., & Muhammad-Sukki, F. (2020). Using Illustrations to Make Decisions on the Most Appropriate Qualitative Research Methodology: The Industry 4.0 Scenario. International journal of qualitative methods, 19, 1609406920907247. Retrieved on 19 July from:https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1609406920907247
Liu, T., Bruins, R. J., & Heberling, M. T. (2018). Factors influencing farmers’ adoption of best management practices: A review and synthesis. Sustainability, 10(2), 432. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/10/2/432/pdf
Mohajan, H. K. (2018). Qualitative research methodology in social sciences and related subjects. Journal of Economic Development, Environment and People, 7(1), 23-48. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/85654/1/MPRA_paper_85654.pdf
Moletsane, R. I., & Venter, C. (2018, August). Electronic waste and its negative impact on human health and the environment. In 2018 International Conference on Advances in Big Data, Computing and Data Communication Systems (icABCD) (pp. 1-7).IEEE. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8465473/
Nasrollahi, Z., Hashemi, M.S., Bameri, S. & Taghvaee, V.M., (2020). Environmental pollution, economic growth, population, industrialization, and technology in weak and strong sustainability: using STIRPAT model. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 22(2), pp.1105-1122. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10668-018-0237-5
Ngozwana, N. (2018). Ethical Dilemmas in Qualitative Research Methodology: Researcher’s Reflections. International Journal of Educational Methodology, 4(1), 19-28. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1170655.pdf
Niederhauser, D.S., Howard, S.K., Voogt, J., Agyei, D.D., Laferriere, T., Tondeur, J. & Cox, M.J., (2018). Sustainability and scalability in educational technology initiatives: Research-informed practice. Technology, Knowledge and Learning, 23(3), pp.507-523. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10758-018-9382-z
Tseng, M. L., Chang, C. H., Lin, C. W. R., Wu, K. J., Chen, Q., Xia, L., & Xue, B. (2020). Future trends and guidance for the triple bottom line and sustainability: a data driven bibliometric analysis. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1-25. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11356-020-09284-0
Zhironkin, V., & Cehlar, M. (2021). Analysis of the Negative Impact of Hydraulic Fracturing Technology on the Environment. In E3S Web of Conferences (Vol. 278, p. 01009).EDP Sciences. Retrieved on 19 July from: https://www.e3s-conferences.org/articles/e3sconf/abs/2021/54/e3sconf_sdemr2021_01009/e3sconf_sdemr2021_01009.html
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

