7050SOH Assignment Sample : Globalisation and Health 2023
UNDERSTANDING THE IMPACT OF GLOBALISATION AND GLOBAL CHANGE ON THE RISE OF TUBERCULOSIS
The world around us is changing due to increasing globalisation. The boundaries no longer create the issues and challenges for the exchange of resources across the different nations. But the different factors of globalisation have led to the increase in the large number of diseases which is creating great issues for the people living around the world (Flew, 2018).
This essay would be focusing on explaining the impact of globalization and global change on health. The essay will give a brief discussion regarding key concepts such as globalization, global challenge and global health along with governance. Further, it will also analyse drivers and forms of global change and their relationship with globalization processes.
It will critically evaluate the effects and contemporary challenges of globalization for global public health. Lastly, it will also give information related to the role of different actors and global health partners and initiatives that aim to promote and protect health and issues of global health governance.
Mainly it will give the information related to challenges that are faced by global health agents at the time of reducing the burden of disease at a global level. For explaining this in detail the essay would be focusing on a case study related to tuberculosis.
Globalisation is a great event which is connecting the world with each other and has reduced the barriers related to the borders. The increasing globalisation is having both pros and cons on the entire world. Globalisation is affecting all the different areas and health of the world population is also a crucial area which is affecting due to globalisation (Shahbaz et. al. 2018).
The great development due to globalisation had created several new diseases and had affected human life in a negative manner. several diseases had increased due to globalisation. The globalisation of food production, businesses and all the diverse industries had created great issues and challenges for human health. If we just look at the negative impact of globalisation on human health, then it has created great issues by raising the number of infectious diseases.
In the modern world diseases such as malaria, plague, measles, HIV, hepatitis, diabetes, tuberculosis and many more. These diseases had increased to a greater extent across the globe after globalisation. The continuous development of the industries is leading the world towards more pollution and risk in other harmful factors which have increased the incidence of the chronic and infectious diseases across the globe. Tuberculosis is one of the common diseases which is being faced by the people across the globe (MacNeil et. al. 2020).
Every year billions of people are suffering from tuberculosis across the globe and around 23% of the world population is being affected due to tuberculosis. Due to this reason it is significant to understand the different factors which are increasing the incidence of Tuberculosis among the world population.
Tuberculosis is also known as TB that is a type of serious infectious disease that directly affects the lungs. The bacteria from which this disease is caused can easily spread from one person to another in the form of tiny droplets which are released into the air from sneezes and coughs. The main symptom of the disease is cough. Tuberculosis is mainly caused by a bacterium which is named mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Not only the lungs but it also affects the other parts of the body like the kidney, brain and spine. If the person who is having tuberculosis does not get treatment, then they can also suffer death. Tuberculosis includes three types of stages that are exposure, late and active disease. Mainly tuberculosis is identified by doing a skin test or TB blood test and also another type of testing is needed.
It has been identified that tuberculosis can be cured by antibiotics and develop permanent lung damage that in the worst cases moves it makes the large hole in lungs called cavities along with returning of Airways called Bronchiectasis.
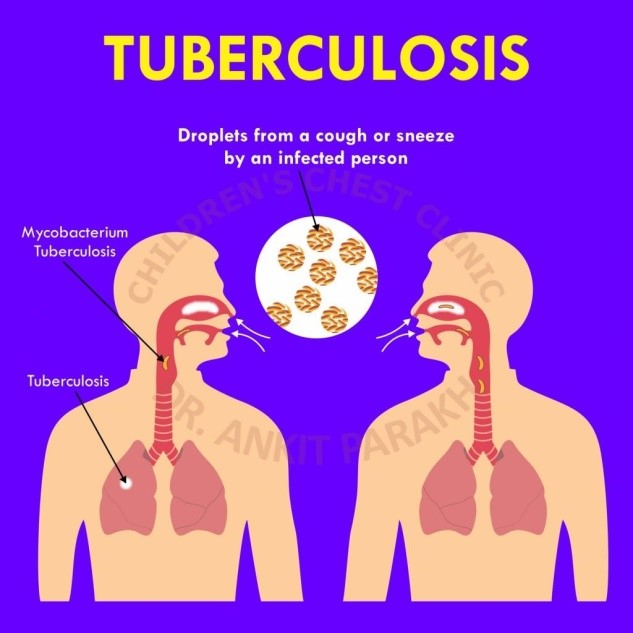
Figure 1 Tuberculosis
(Source: Dr. A. Parakh, 2020)
Tuberculosis is caused because of Mycobacterium tuberculosis; it is a bacterial disease that mostly affects the lungs. This bacterial disease has a tendency of spreading from person to person through the medium of air. When people affected by tuberculosis cough or sneeze, they release the germs into the air, if a normal person inhales these germs it is likely for him/her to get infected (MacNeil et. al. 2020). 10% of the infected individuals who have low immunity are likely to develop active disease of the virus.
Due to increasing globalisation the communication, collaboration and interaction among the individuals had increased to a greater extent. Because of this the infectious diseases had increased significantly. The migration of people from one nation to another has increased the risk for infectious diseases to a greater extent. When the people belonging to different nations connect with one another then it affects the diseases by favoring the global spread of different infectious diseases.
Active Tuberculosis is a type of disease in which the bacteria are rapidly increasing in or multiplying two different organs data present in the body. The symptoms of this type of TB are cough, chest pain, weight loss, weakness, fever, sweating at night and chills. The person who is suffering from this kind of disease can easily spread it to the other by sneezing or airborne transmissions through the air (Ismail et. al. 2018).
For this, the treatment which is used is known as multidrug treatment which is mainly dependent upon the local public health regulations. In this military, TB is also a type of active disease which mainly occurred at the time when bacteria escaped to go in the bloodstream. In this, they can easily spread over the body into the form of tiny nodules that can easily affect organs at once.
On the other hand, it is also known as a type of TB debt that can easily be rapidly fatal. Active Tuberculosis shows symptoms which include site specific symptoms, weakness, fever, and weight loss. While talking about active pulmonary TB disease, the most common symptoms are chest pain and persistent coughing. In persons suffering with immunosuppression the virus tends to spread out of the lungs resulting in extra pulmonary TB (Churchyard and Swindells, 2019).
The symptoms may vary depending upon the infection sites like lymph nodes, osteoarticular and pleura areas. People infected with this virus have 5-10% risk of lifetime falling ill along with TB. But those suffering from immunosuppression such as HIV, diabetes and malnutrition, or the ones who consume tobacco generally are the ones who are at higher risk of falling ill (Lai et. al. 2021).
When a person results in developing active TB disease, the symptoms may be very mild for months, this may lead to delay in seeking care and resultantly the infected person may have spread the virus to many other individuals.
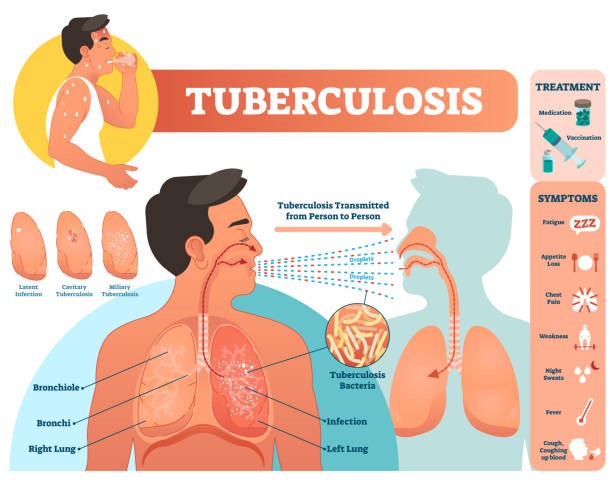
Figure 2 Latent TB infection
(Source: iStock, 2021)
Latent TB infection is a type of infection that is in the form of TV which does not develop any type of over it disease. In this, the person has no symptoms regarding chest pain and other things. Further, it is also not identified by chest X-ray. But on the other hand, it can be only identified by tuberculin skin test R interferon-gamma release assay. It also has different types of risk that can easily escalate to active disease. The risk of the illness can also be increased by medications (Bongomin, 2020).
For protecting this illness, US employees have made different types of treatment that is in the form of preventive therapy. If we look at the positive impact of the globalisation, then it can be said that it has improved the treatment which is being provided to patients across the globe. Due to increasing globalisation different International firms are working for the betterment of health of people across the border. Because of globalisation the large organisations are working to help the poor section of the society to fight against the serious diseases.
It can be said that globalisation has strengthened the health system and this is helping in addressing the major health issue including tuberculosis. Due to higher incidence of tuberculosis the global healthcare organisation focuses on solving the issues related to the different diseases. The most common symptom of the disease is cough along with sputum and also blood at some times, weakness, weight loss, sweats at night, fever.
Rapid molecular diagnostic test is recommended by WHO as an initial diagnostic test for people having symptoms of TB, as they have a high rate of diagnostic accuracy which results in major improvements in the early stages of the disease.
Globalisation is a complex concept which has changed the way in which the world connects with one another. It has changed the nature of human interaction among the people. Globalisation has affected all the different factors such as social, political, environmental, cultural and technological (Smith et. al. 2020). Along with all these factors globalisation had affected healthcare to a greater extent and had raised a lot of health issues due to the environmental influence of globalisation on the world.
With the ongoing globalisation it can be estimated that it would be having a crucial impact on the rise of infectious diseases. Global migration and globalization have resulted in affecting the epidemiology of TB in both developed and developing countries. It is also to be known that inadequacy of treatment has led to the emergency of multidrug-resistant strains of the disease.
The rise in cases all across the globe is not only concerned with rising in HIV infection but also many other reasons including the disparities in wealth, lack of health services, free movement of people all across the world, reforms in the health system, and lack of commitment of the government towards providing health care facilities to the poorest countries.
To understand the linkage between health and globalization mainly in the context of increasing cases of TB, it is important to understand the term Globalization itself, it is defined as a set of global procedures that are responsible for changing the human interaction with social spheres like cultural, economic, social and political.
It is observed that globalization is an act that is very necessary for human beings as it is known to be a social animal but it results in the interaction of individuals all across the world resulting in the spreading of contagious diseases that may lead to very negative consequences for the economic, social and political sphere of the society (Sigler et. al. 2021).
There is a need to develop a deep understanding of the interplay it plays between pathogen, host, and environment. Basically, the increase in mobility has shown its impact on the increase in the livelihood of these viruses from one country to another. A rise in TB cases is noticed in some developing countries because of the increasing dependence of countries on each other in terms of trade, business, tourism or education. Globalization may show its effects on determinants of health broadly.
The increasing mobility of the population is an important factor which is affecting the health of the population. It is not to be disputed that the world is changing constantly in different ways, thus it shows both positive as well as negative impacts on the health of humans (Bert-Dulanto et. al. 2021). However, talking about 2 decades ago it is obvious that earlier people were born and brought up at the same place where they were born because traveling was a rare scenario at that time and it was also not easily affordable.
At present due to spatial dimensions across the borders, there is an increased rate of traveling mainly due to business, tourism, pleasure, studies. It is to be noted that 2 million people travel international borders for one or the other reason. It is observed by statistics that 175 million people were living out of their home countries in 2000 which reflects an increase of 100 million in 1995.
Technology has made it easier for man to travel from one place to another and it has been seen from figures that it is convenient to shift from one place to another due to high-speed trains, automobiles, and long flights. With these technological advancements, the rate of transfer of diseases also expanded on a high scale.
Rapid urbanization: This affected people of developing countries in large numbers as they tend to travel from rural to urban cities in order to achieve economic prosperity. This lead to overcrowding of urban towns which is itself a reason for developing this disease in urban places along with it the houses that they leave behind are of a poor standard and contain poor ventilation which may result in these type of air-borne diseases.
The poor section of the society is at higher risk of the diseases and due to this reason it is important to focus on the health and wellbeing of the poor section of the society (Hayward et. al. 2018). The poor section of the society is working under different working conditions and due to this reason they are at a higher risk of infectious diseases.
Especially the risk of airborne diseases had significantly increased. Due to this reason it is essential to focus on ensuring that the people need to pay attention to these diseases. The incidence of tuberculosis among the poor section of society is important.
Poverty: Due to increasing globalisation the difference between the rich and poor had increased due to it. This is also a major factor which had led to the rise in the diseases across the world. It is not to be ignored that growth and development are a result of economic globalization which has led to the growth of economies and increasing wealth and resources for people in order to access and buy health (Heinze, 2020).
But in other words, it also resulted in poverty, unemployment, poor living standards, which increases the risk of diseases like TB. Major sections of the society living in the urban areas are at more risk of tuberculosis. Due to increased globalisation the migration had increased to a greater extent. Because of this reason the occurrence of tuberculosis is more seen among the people living in the developing nations.
Although tuberculosis is a major issue in both the developed and developing nations, it is more common in the developing nations. Usually in the developing nations the individuals are living and working under poorly ventilated and crowded places.
Because of this reason the risk for infectious diseases increases. Also the companies do not pay attention to the working conditions of the people that are living and working under poor conditions. Due to this reason the poor peoples are at more risk of these diseases.
Impact of industrialization on healthcare is also a major reason behind the rise of different diseases across the globe. Industrialization has resulted in increased migration and free movement of people across the borders. Individuals suffering from latent TB infection are likely to make a high percentage of TB cases in developing countries.
This poses threat for developing countries along with developed ones because of global migration where people cross borders to meet different purposes like business meetings, leisure, refugee or as asylum seekers. Increasing industrialisation is also a major reason behind the increasing risk of the infectious diseases. Due to increasing globalisation and industrialisation the level of population is increasing which is enhancing the risk of airborne diseases.
Increasing industrialisation is also a major reason behind the increasing risk of the infectious diseases. Due to increasing globalisation and industrialisation the level of population is increasing which is enhancing the risk of airborne diseases (Stamenovic, 2018).
Tuberculosis is a significant socioeconomic factor due to which it is having a major impact on the entire world. The people belonging to different nations are at higher risk of these diseases because there are different socioeconomic factors which are being considered as a major reason for the spread of the disease. Hygiene is a crucial factor which is having a significant influence on the health and wellbeing of the peoples of the world (Lim et. al. 2021).
For a human being it is essential to live in a clean and hygienic place which can help them in reducing the risk of several infectious or the spreadable diseases. When the people are not living in a better surrounding then it affects their health and wellbeing negatively. If the people are living under better conditions, then the risk for spreadable disease such as tuberculosis.
For this it is important for the world health organization to focus on the treatment of tuberculosis and should focus on reducing the incidence of Tuberculosis. The healthcare organisations operating at both global and national level need to focus on working effectively for reducing the negative impact of this disease on the health of the people across the globe.
Limited access to healthcare is also a significant factor which is affecting the health of the people at global level. Due to the increasing globalisation the healthcare issues are increasing at a faster rate. Along with this the difference between the rich and poor section of society or the economic inequality is also a crucial factor which is affecting the increasing cases of Tuberculosis across the globe.
Not all people are having better resources to get high quality treatment and due to this factor they are at higher risk of major diseases. It is essential that all the people living across the globe both rich and poor, need to have better accessibility to health care. Providing better healthcare to all the people living around the world is a major global challenge which is being faced at global level (MacNeil et. al. 2019).
All the healthcare organisations operating at different levels are working effectively for reducing or limiting the impact of Tuberculosis on human health. From this perspective it can be said that if the individuals are not having better access to healthcare and are not having good quality treatment for the diseases then it affects them significantly. Along with this there are different factors related to lifestyle which are having an impact on tuberculosis and increasing the risk of tuberculosis among the world population.
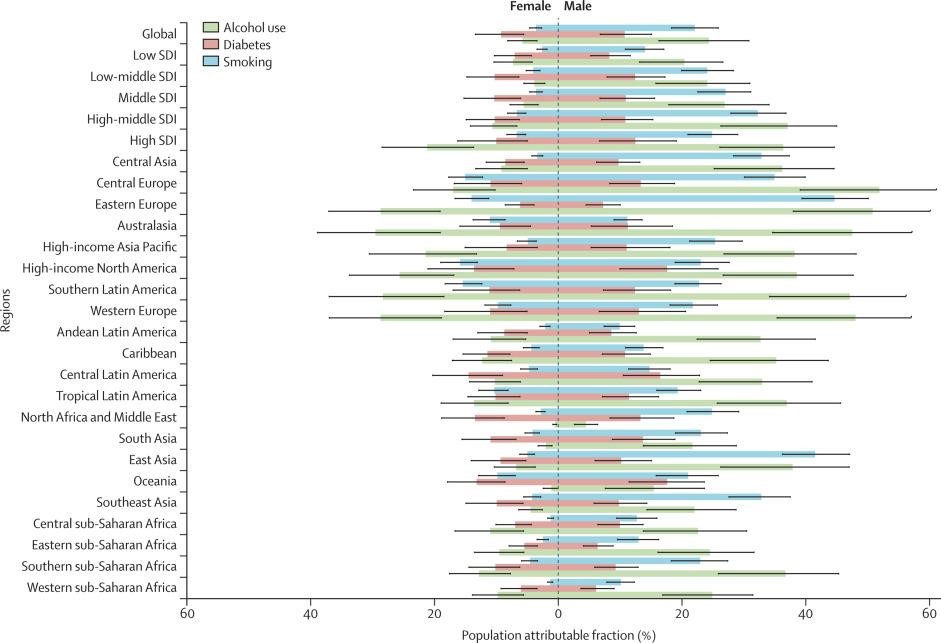
Figure 3 Tuberculosis deaths
(Source: Lancet, 2021)
The above graph is giving the information regarding the population that is in attributable fraction of all the age group of tuberculosis deaths that is because of alcohol use, smoking, diabetes and bidi among men and women in 2019. Tuberculosis death because of unsafe sex was 82-47%, because of drug is 5-59% and partner violence is 8-04%. In this the highest was seen in Africa and Oceania.
The data is mainly based upon the male and female of all the age groups who suffer from tuberculosis through smoking, alcohol and diabetes. From this it can be said that not only globalisation is affecting tuberculosis but there are different major factors related to the lifestyle of the individuals which is affecting tuberculosis. Thus it can be said that only globalisation cannot be blamed for the increasing cases of globalisation across the world.
If we look into the positive side, then it can be said that globalisation has led to a positive influence on global health by working effectively on it. Concern for human health is increasing due to the integration of the different determinants related to globalisation. Globalisation has contributed to health improvement to a greater extent. The knowledge related to healthcare has expanded due to globalisation Because of this more concern is being given to human rights and healthcare.
The low cost Healthcare technologies is a positive impact of globalisation which is adding value to all the people living across the globe. Due to globalisation different healthcare organisations are working effectively and together to reduce the impact of healthcare issues on human health (Reid et. al. 2019).
At global level different organisations are working to reduce tuberculosis at a global level because it is a common healthcare issue faced by the peoples living around the world. With regard to above mentioned issues different measures and programs are being initiated by the health ministry in order to control the spread of these diseases globally:
Training of TB medical staff and TB specialist: Proper and training to be provided to TB clinicians to be efficient in Detecting high index cases of immigrant’s who are reported with fever, cough, or weight loss. Initiating proper diagnosis and providing appropriate drug treatment and strict recommendations to complete the course. It may be operated well when a full-fledged training is provided to the TB physicians (Turner, 2018).
Enhancement of surveillance: Coordinated reporting of TB, MDR-TB, XDR-TB cases at national and international and local levels. Information concerned with these kinds of diseases should not be withheld, fearing isolation of goods and trade with other countries. Corporation should be made by all countries in order to overcome from the impact of any such disease. Corporation will guarantee rapid identification problem and suggest protective measure in order to overcome.
Economic empowerment: This may be practiced by empowering poor or developing countries in assessing healthcare resources and uplifting them to eradicate poverty. Empowerment of patients may be done by providing them loans to fight from the disease.
Campaigns for public awareness: To educate and facilitate people with the seriousness of disease and need for early diagnosis. This may be done by providing training and education programs with the help of radio, television, media.
Providing Infection control unit: Government should confirm availability of necessary equipment and professionals to scan and check at entry and checkpoints of immigrants to diagnose any severe disease at checkpoints to provide proper screening in order to safeguard the place.
From the above mentioned discussion it can be said that globalisation is having a significant impact on all the different factors associated with the health of the people. It has created both the opportunities and challenges for the healthcare of the people around the world. On the basis of the challenges it can be said that it has increased infectious diseases to a greater extent. Along with this Tuberculosis being a significant infectious disease had also increased to a greater level due to globalisation.
It can be said that globalisation has affected different factors which have led to the increase in the diseases and especially Tuberculosis. The incidence of Tuberculosis has increased because of different factors associated with globalisation. The increasing interactions, communication, poor working conditions, lack of access to healthcare and several other issues had developed due to globalisation (Kavanagh et. al. 2020).
Along with this both the developed and developing nations are having higher incidence of tuberculosis. Especially the poor section of the society is at more risk of the diseases.
On the other hand, if we look at the positive factors related to globalisation then it can be said that healthcare is improving due to globalisation. There are different organisations which are working effectively for addressing the major healthcare issues which are faced across the globe. Tuberculosis is an important disease which is affecting the people at a global level. Due to this reason there are different types of healthcare organisations which are working effectively for reducing the incidence of this disease (ResearchGate, 2021).
These organisations are focusing on reducing the causes and the risk factors which are leading to the rise of tuberculosis at the global level. Different programmes and initiatives are being developed around the world for solving the health issues faced by the peoples. From this it can be concluded that globalisation is having a significant impact on Tuberculosis. Both positive and negative impacts of globalisation are represented in the essay. It can be said that it is important to pay attention to this disease.
All the firms operating at global level need to work with each other to reduce the issues related to tuberculosis so that it can be managed and its risk can be reduced. Thus it can be said that globalisation is a major event which has affected all the factors associated with tuberculosis and its implications on human health.
References
Bert-Dulanto, A., Alarcón-Braga, E.A., Castillo-Soto, A. and Escalante-Kanashiro, R., (2021). Predicting mortality in pulmonary tuberculosis: a systematic review of prognostic models. Indian Journal of Tuberculosis.
Bongomin, F., (2020). Post-tuberculosis chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: An emerging public health concern. PLoS Pathogens, 16(8), p.e1008742.
Churchyard, G.J. and Swindells, S., (2019). Controlling latent TB tuberculosis infection in high-burden countries: A neglected strategy to end TB. PLoS medicine, 16(4), p.e1002787.
Flew, T., (2018). Post-globalisation. Javnost-The Public, 25(1-2), pp.102-109.
Hayward, S., Harding, R.M., McShane, H. and Tanner, R., (2018). Factors influencing the higher incidence of tuberculosis among migrants and ethnic minorities in the UK. F1000Research, 7.
Heinze, J., (2020). The impact of globalisation on poverty and inequality in the Global South. E-International Relations.
Ismail, M.B., Rafei, R., Dabboussi, F. and Hamze, M., (2018). Tuberculosis, war, and refugees: spotlight on the Syrian humanitarian crisis. PLoS pathogens, 14(6), p.e1007014.
Kavanagh, M.M., Gostin, L.O. and Stephens, J., (2020). Tuberculosis, human rights, and law reform: Addressing the lack of progress in the global tuberculosis response. PLoS Medicine, 17(10), p.e1003324.
Lai, C.C., Tehrani, B., Yungtum, G., Hsu, W.T. and Lee, C.C., (2021). Association between the use of statins and risk of tuberculosis: a real-world analysis. The Journal of Infectious Diseases.
Lim, V.W., Wee, H.L., Lee, P., Lin, Y., Tan, Y.R., Tan, M.X., Lin, L.W., Yap, P., Chee, C.B., Barkham, T. and Lee, V., (2021). Cross-sectional study of prevalence and risk factors, and a cost-effectiveness evaluation of screening and preventive treatment strategies for latent tuberculosis among migrants in Singapore. BMJ open, 11(7), p.e050629.
MacNeil, A., Glaziou, P., Sismanidis, C., Date, A., Maloney, S. and Floyd, K., (2020). Global epidemiology of tuberculosis and progress toward meeting global targets—worldwide, 2018. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 69(11), p.281.
MacNeil, A., Glaziou, P., Sismanidis, C., Date, A., Maloney, S. and Floyd, K., (2020). Global epidemiology of tuberculosis and progress toward meeting global targets—worldwide, 2018. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 69(11), p.281.
MacNeil, A., Glaziou, P., Sismanidis, C., Maloney, S. and Floyd, K., (2019). Global epidemiology of tuberculosis and progress toward achieving global targets—2017. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 68(11), p.263.
Reid, M.J., Arinaminpathy, N., Bloom, A., Bloom, B.R., Boehme, C., Chaisson, R., Chin, D.P., Churchyard, G., Cox, H., Ditiu, L. and Dybul, M., (2019). Building a tuberculosis-free world: The Lancet Commission on tuberculosis. The Lancet, 393(10178), pp.1331-1384.
Shahbaz, M., Shahzad, S.J.H., Mahalik, M.K. and Hammoudeh, S., (2018). Does globalisation worsen environmental quality in developed economies?. Environmental Modeling & Assessment, 23(2), pp.141-156.
Sigler, T., Mahmuda, S., Kimpton, A., Loginova, J., Wohland, P., Charles-Edwards, E. and Corcoran, J., (2021). The socio-spatial determinants of COVID-19 diffusion: the impact of globalisation, settlement characteristics and population. Globalization and health, 17(1), pp.1-14.
Smith, C., Burke, H. and Ward, G.K., (2020). Globalisation and indigenous peoples: threat or empowerment? (pp. xviii-24). Routledge.
Stamenovic, M., (2018). CHALLENGES OF ECONOMIC GLOBALISATION IN HEALTHCARE CONSIDERING HEALTHCARE COOPERATIVES AS RESPONSE. Economic and Social Development: Book of Proceedings, pp.243-248.
Turner, P., (2018). The changing landscape of healthcare. In Talent Management in Healthcare (pp. 15-37). Palgrave Macmillan, Cham.
Online
Dr. A. Parakh, (2020). Tuberculosis. [Online]. Available through: < https://www.ankitparakh.com/conditions-treated/tuberculosis/> [Accessed on 27th Oct 2021].
iStock, (2021). Tuberculosis Patient stock illustrations. [Online]. Available through: < https://www.istockphoto.com/illustrations/tuberculosis-patient> [Accessed on 27th Oct 2021].
Lancet, (2021). Global, regional, and national sex differences in the global burden of tuberculosis by HIV status, 1990–2019: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. [online]. Available through: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(21)00449-7/fulltext
ResearchGate, (2021). Framework for understanding effects of global change drivers. [online]. Available through: < https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Framework-for-understanding-effects-of-global-change-drivers-climate-change-altered_fig1_296468447>
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

