7069SOH – Managing and Planning Resources in Healthcare Organisations Assignment Sample 2023
Coursework 1
Introduction
Healthcare funding model has significantly impacted the service and care provided to the people in various parts of the world. Patients now have an increased access to better healthcare facilities along with increased assistance to the healthcare professionals as well to provide adequate care to the patients in need. A proper and efficient funding model significantly increases the overall health condition of the country.
In different countries, their respective healthcare model may differ depending upon the suitability and facility being accessible to their home countries. Financial support and proper administration is increasingly becoming important in such cases. In this present study, a discussion is conducted on the Healthcare funding models of the UK and Australia.
The study will also evaluate the points of difference in the two countries’ models and attempt to understand the impact of these models on the care of patients and health in their respective countries.
Healthcare models
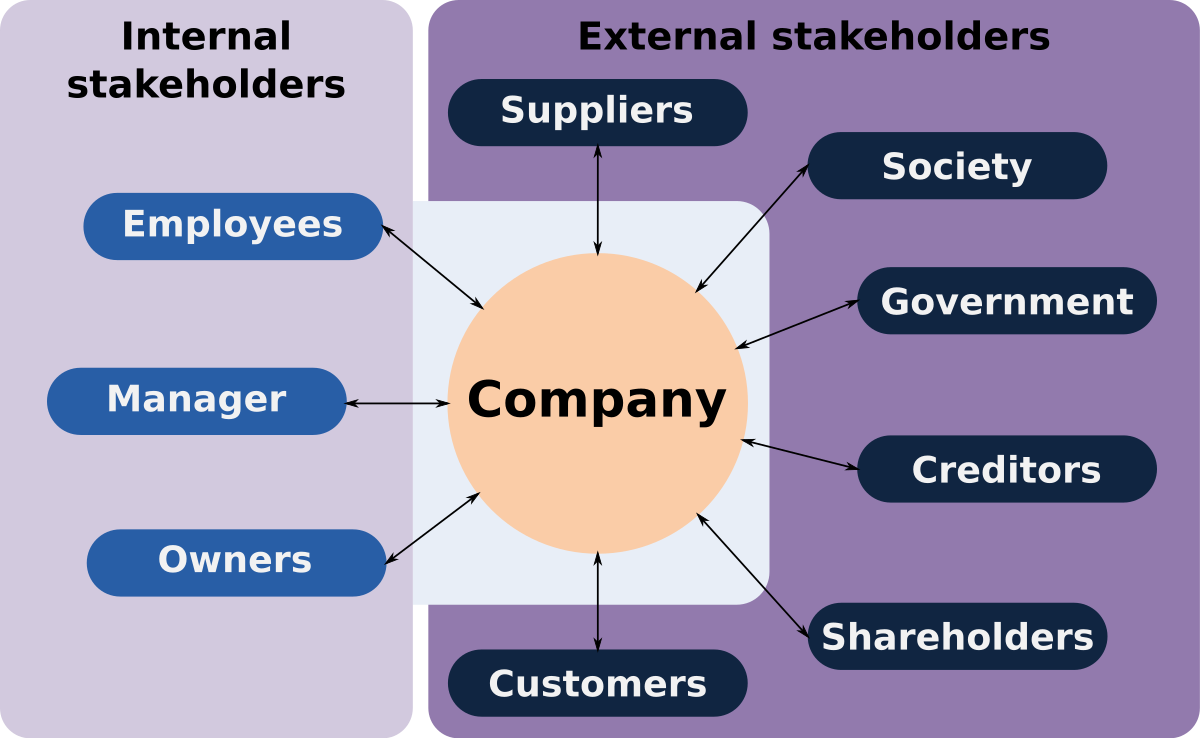
Countries have recognized the need for developing an exhaustive healthcare system to regulate and organize adequate health resources and provide proper care and treatment to patients in need. They have adopted various models to suit their particular system and maximize services to patients.
Broadly, there are four widely accepted models of healthcare systems which have been adopted by different countries suiting their needs. The Beveridge Model of healthcare provides a centralized model of healthcare. It places the government as a single payer to the healthcare units providing all provisions and services for the citizens to avail free healthcare facilities to all the taxpaying citizens. This system is used by the UK.
The Bismarck model of healthcare provides for healthcare insurance for all employees by the employers in a privatized system of healthcare. National model of health insurance is a take on the first two models. It provides a centralized insurance system furthered by private providers. The out-of-pocket model provides for a creation of a medical system for the less developed areas to provide free medical facilities and services to those of the vulnerable and lower income group.
Healthcare Model in the UK
Healthcare in the UK has received much admiration due to its well organized and equipped healthcare system. They ranked the best healthcare provider in 2017 due to their diligence and high quality care provision. UK uses a centralized model of healthcare. It places the government funded organization and healthcare system, National Healthcare Service (NHS), known as a single provider to the healthcare units providing all care and services for the citizens to avail free healthcare facilities.
According to Dhariwal and Bouchet (2018), this facility is available to all the taxpaying citizens of the UK who can avail quality care and service form these government funded hospitals. The NHS is funded by the taxpaying citizens and thus obtains means and resources to fund and manage the healthcare systems of the country.
Along with this, the country also has developed some public funded hospitals and healthcare units. There are also provisions regarding health insurance for employees for employees receiving private hospital care (Fletcher et al. 2020).
Healthcare model in Australia
Australia has a slightly unique model of healthcare than other countries. The healthcare system in Australia is funded by Medicare. This is a national healthcare insurance system which provides Australian citizens a scheme to avail medical facilities when in need. This facility of availing an insurance scheme is provided to all the permanent citizens of Australia. The funding of this medicare insurance policy is approximately a part of 2 percent of the governmental levy.
According to Dixit and Sambasivan (2018), along with this, Medicare also helps the citizens of Australia by covering medical expenses in private healthcare organizations of up to 75 percent. Along with the private healthcare institutions, this Medicare scheme provides 100 percent coverage to all permanent citizens availing Medicare care and treatment in the public healthcare units.
Medicare in Australia is also funded by general taxpayers’ money along with the funds provided by the federal government of Australia in supporting and improving the healthcare systems of the country. Australia also has developed many community healthcare hospitals to promote healthcare facilities to the lower income groups by covering them through this medical insurance facility (Lacaze, Tiller & Winship, 019).
Relation between the two systems
The healthcare system in the UK is a centralized model of healthcare. It places the government funded organization and healthcare system, National Healthcare Service (NHS), known as a single provider to the healthcare units providing all care and services for the citizens to avail free healthcare facilities (Atella et al. 2019).
This facility is available to all the taxpaying citizens of the UK who can avail quality care and service form these government funded hospitals. In the case of Australia, however, the healthcare system in Australia is funded by Medicare. This is a national healthcare insurance system which provides Australian citizens a scheme to avail medical facilities when in need.
According to Bond et al. (2019), This facility of availing an insurance scheme is provided to all the permanent citizens of Australia. Both the countries levy general taxation of the public to fund these programs and provide improved quality of care and treatment to the patients.
Impact in delivering care
Healthcare models are extremely crucial for the development of a comprehensive and safe system for providing efficient healthcare services to patients along with a steady development and growth in the overall health of a society. Countries have recognized the need for developing an exhaustive healthcare system to regulate and organize adequate health resources and provide proper care and treatment to patients in need.
Many authors are of the opinion that centralized provisions and systems of healthcare funding can result in governmental debts (Gille, Smith and Mays, 2021). Moreover, they suggest that investing in these models can also influence a lowered quality of care than privatized facilities. This system, though, has proved to be effective in providing immediate and adequate care to the patients form the lower income groups, who could avail to Medicare schemes in Australia as well as receive proper care in the UK healthcare system.
Conclusion
The present study discussed the healthcare funding systems of UK and Australia, evaluated the points of difference in their model and studied the impact of these models on the care of patients.
References
Atella, V., Belotti, F., Bojke, C., Castelli, A., Grašič, K., Kopinska, J., … & Street, A. (2019). How health policy shapes healthcare sector productivity? Evidence from Italy and UK. Health Policy, 123(1), 27-36. http://eprints.lse.ac.uk/90582/1/Street_How%20health%20policy%20shapes_2018.pdf
Bond, C., Brough, M., Willis, J., Stajic, J., Mukandi, B., Canuto, C., … & Lewis, T. (2019). Beyond the pipeline: a critique of the discourse surrounding the development of an Indigenous primary healthcare workforce in Australia. Australian journal of primary health, 25(5), 389-394. https://www.publish.csiro.au/PY/pdf/PY19044
Dhariwal, M., & Bouchet, C. (2018). PMD66-COMPARING THE LONG-TERM IMPACT ON HEALTHCARE RESOURCES AND COSTS DUE TO SINGLE-PIECE ACRYLIC INTRAOCULAR LENS (IOLS) IMPLANTATION DURING CATARACT SURGERY: A COST-CONSEQUENCE ANALYSIS FROM UK HEALTHCARE SYSTEM PERSPECTIVE. Value in Health, 21, S254. https://www.valueinhealthjournal.com/article/S1098-3015(18)34817-4/pdf
Dixit, S. K., & Sambasivan, M. (2018). A review of the Australian healthcare system: A policy perspective. SAGE open medicine, 6, 2050312118769211. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/2050312118769211
Fletcher, E., Campbell, J., Pitchforth, E., Freeman, A., Poltawski, L., Lambert, J., & Hawthorne, K. (2020). Comparing international postgraduate training and healthcare context with the UK to streamline overseas GP recruitment: four case studies. BJGP open, 4(3). https://bjgpopen.org/content/bjgpoa/4/3/bjgpopen20X101034.full.pdf
Gille, F., Smith, S., & Mays, N. (2021). What is public trust in the healthcare system? A new conceptual framework developed from qualitative data in England. Social Theory & Health, 19(1), 1-20. https://www.research-collection.ethz.ch/bitstream/handle/20.500.11850/395771/1/Gilleetal.2020.pdf
Lacaze, P., Tiller, J., & Winship, I. (2019). Healthcare System-Funded Preventive Genomic Screening: Challenges for Australia and Other Single-Payer Systems. Public health genomics, 22(3-4), 140-144. https://researchmgt.monash.edu/ws/portalfiles/portal/312963609/296210488_oa.pdf
Coursework 2
Executive Summary
Ensuring a proper healthcare provision is extremely crucial for the development of a comprehensive and safe system for providing efficient healthcare services to patients along with a steady development and growth in the overall health of a society. The present report will discuss the Australian healthcare system and evaluate their processes and management and organization in the healthcare system.
It can be said that Healthcare is the most important for every country in this world. It helps to develop safety and security for the people who are living in that country. Healthcare plays an important role in determining the county’s development as well. Further it can be seen that the healthcare sector of Australia needs a proper priority setting in the organizations.
Introduction
Healthcare is extremely crucial for the development of a comprehensive and safe system for providing efficient healthcare services to patients along with a steady development and growth in the overall health of a society. It is primary that all citizens of any country regardless of their social, cultural and economic background have access to better and advanced healthcare facilities along with adequate assistance from the healthcare professionals.
A proper and comprehensive healthcare system provides increased care to patients as well as the healthcare professional to provide adequate care to the patients in need. Countries have recognized the need for developing an exhaustive healthcare system to regulate and organize adequate health resources and provide proper care and treatment to patients in need.
It is also crucial that these systems thus developed are managed and well resourced for continually providing efficient care to the patients and for improving the quality of overall health of the citizens. The present report will discuss the Australian healthcare system and evaluate their processes and management and organization in the healthcare system. The report will also discuss decision making processes along with the planning and management of various aspects for improving the quality of care in different sectors
1. Priority setting and decision-making processes
Management of healthcare is one of the primary aspects in providing an efficient and adequate care and treatment to the patients in need with a timely deliverance. Any healthcare organization assumes the responsibility of managing and delivering proper and efficient care to the patients entrusted under their care. Proper and efficient care provision also needs support in the form of funds along with care from professionals to effectively provide a more nuanced service to the patients.
For this purpose resource allocation and scheduling has gained the centre stage in the management in the healthcare sector. Resource allocation is an extremely important aspect in any healthcare practice (Bertram et al. 2021). The managers in the healthcare systems have the most important role of determining the resource allocation based on the needs and priorities of their individual organization.
Priority setting is a crucial aspect in any decision making on the subject of allocation of essential resources and funds. Priority setting is one of the most crucial factors to be considered is the aims and objectives of the particular organization. The leaders and management authorities need to take proper care and due diligence while making decisions along with being fast and effective.
According to Smith et al. (2017), a clear and effective goal setting clarifies the aims and objectives of the organization and helps the leaders and managers to make informed and effective decisions in the interest of the organization as well as the patients and other stakeholders. To help the executive authorities in the decision making process, they need to consider several principles and set their priorities for the organization, affecting a seamless transition process (Barasa et al 2017).
Priority setting is extremely crucial in the healthcare sector. Providing patients with the choice of opting for proper and adequate facilities and options, increases the satisfaction and results in an increased reception of the treatment and care for the patients along with having an impact on their overall health and well being in a radical manner (Odu, 2019).
Providing standardized options for the patients is also impacted by the attitude and priority building of the leaders in the healthcare system. Making informed and exhaustive decisions from a point of view of care can significantly increase the quality and provision of care for the patients.
In the present situation of pandemic, it has become extremely crucial that leaders and executive authorities in the healthcare system make necessary adjustments and take effective decisions since there is a dire scarcity of resources. According opt Littlejohns et al. (2019), priority setting will also help the healthcare professionals to deliver proper and adequate care to the patients
The healthcare system in Australia is driven by Medicare insurance systems. Australia has a slightly unique model of healthcare than other countries. The healthcare system in Australia is funded by Medicare. This is a national healthcare insurance system which provides Australian citizens a scheme to avail medical facilities when in need.
This facility of availing an insurance scheme is provided to all the permanent citizens of Australia. The Australian parliament has also taken certain health initiatives to improve the quality of healthcare and make it a priority (Németh et al. 2019). Furthermore, the present situation of the Covid-19 pandemic has induced the healthcare system to rethink its approaches and provide adequate care and treatment to the patients in need.
The increased demand for an improved quality of healthcare system is reflected in change in the processes and attitudes of the overall system in the country. In this process, the Australian healthcare system has also taken initiatives to provide an advanced and increased system for management and administration of the public hospitals in the country (Wong et al. 2018).
Along with this, the healthcare system of Australia has also made commitments to deliver increased service and care as well as raising awareness on the issue of breast cancer, and providing immunization and screening to the people. In this process, the country has also set up many community healthcare hospitals to promote healthcare facilities to the lower income groups by covering them through this medical insurance facility.
The government funder scheme of medicare plays a great role in supporting and improving the healthcare systems of the country. Priority setting for the country in their healthcare system has helped them to deliver an increased and more personalized care to the patients in need along with allocating necessary resources and professionals to deliver these care and treatment to the needy patients (Pratt, 2019).
Increase in emergency services along with other provisions have significantly increased the overall health and wellbeing of the community and made Australia emerge as one of the best healthcare providers.
2. Workforce planning and development in the healthcare sector of Australia
Workforce planning and development is required for every healthcare sector around the world so that they can deliver adequate treatment to the patients care. Workforce planning provides healthcare sectors with proper members of staff who have adequate skills in them. When any organization will have sufficient numbers of staff in their healthcare organization then they can provide excellent healthcare facilities to the citizens of the country.
In the opinion of Lai et al. (2018), for successful workforce planning the healthcare sector needs to have an evidence-based workforce plan in their hospital. A successful evidence-based plan must consolidate a complete financial planning structure and also a proper performance and activity plan.
According to Windsor et al. (2017), healthcare organizations of Australia must adopt workforce planning and resource planning to deliver exceptional healthcare facilities to the patients of Australia. Thus if they implement resource management and workforce planning into their healthcare sectors then they can provide support to the departments of healthcare.
Further, the implementation of resource management and workforce planning can also benefit their services and also can improve the ward of their hospitals. Therefore, to develop proper workforce planning in their healthcare sectors they must introduce staff implementation policies they must have flexible hours for the healthcare professionals. In addition to this, they must also implement human resource matters in their organizations and also provide facilities for taking leaves.
Furthermore, to improve their workforce every healthcare sector must have self-assessment tools that can help them to provide feedback, which is provided by the public after taking services from their organization. Thus after analyzing the feedback and recommendations from the public they can understand their drawbacks and can improve those in order to provide excellent services.
In the opinion of Maier et al. (2018), to develop a sufficient workforce in any healthcare sector the healthcare organizations must analyze their staff that are already working in their organization. After analyzing the feedback from the public, the healthcare organization will be able to understand whether the staff failed to meet the expectation of the patient or not. In addition to this if they also comprehend whether the staff can provide adequate patient care to the public or not.
Thus, if they find out that they failed to deliver adequate patient care and also failed to meet the expectation then they can provide skills development programs for them. Healthcare organizations must thoroughly analyse the skills of their staff for providing proper healthcare facilities to the public. The healthcare system of Australia also must focus on providing support to the healthcare professionals such as doctors, nurses and others. They must also improve in the healthcare facility that they are providing to the public and must be made that more transparent for them.
According to Loomes, Owens& McCarthy (2019), the healthcare system of Australia is facing challenges at present and that is the reason the Australian health workforce has adopted few strategies to improve their healthcare system.
The Healthcare Workforce Australia (HWA) also focuses on providing healthcare to the aboriginals of Australia. However, the aboriginals get deprived of many facilities that are provided by the government of Australia. Therefore, the government of Australia focuses on providing adequate healthcare facilities for them by recruiting new staff and healthcare professionals for them.
The Healthcare Workforce of Australia (HWA) has adopted an evidence-based approach for their healthcare organizations so that they can provide excellent services to the public of Australia. The HWA has implemented a new strategy for improving workforce plans for their healthcare organizations.
The plan consists of recruiting new healthcare professionals into their organizations. Furthermore, by providing training to the existing healthcare professionals and staff so that they can have proper skills for providing excellent services to the public. They have also organised training programs for the doctors so that they are able to improve themselves and that can result in improved services to the citizens of Australia.
The healthcare sector of Australia will also implement oral healthcare facilities in their healthcare system by recruiting oral healthcare practitioners. In this new plan of the workforce, the Australian healthcare system primarily focused on the NSW community. They have also focused hugely on the Aboriginal workforce program that will benefit the Aboriginal community of Australia.
Therefore, to provide sufficient healthcare services to the aboriginal community the Australian healthcare system must recruit more healthcare professionals and staff in their organizations. A study conducted by (Cortis& van Toorn (2020), shows that the Australian healthcare sector still needs almost 3% of employment in the healthcare sectors in order to provide healthcare to the aboriginals’ community of Australia.
In the opinion of Woolley, Larkins & Sen Gupta (2019), the commonwealth department of health of Australia is planning to develop some strategies that can benefit the healthcare organization of Australia. The strategies include the collaboration of healthcare organizations with another medical workforce.
This strategy also includes implementing an advisory committee in the healthcare sectors that will guide the healthcare organizations in every way possible. This medical workforce and advisory committee will consist of medical professionals, medical students and also medical specialists.
3. Human resource and talent management in the healthcare sector of Australia
Human resource management plays a most important and vital role in assuring that the healthcare organization is providing the finest healthcare services to the patients of the county. The human resource management works with various medical institutions for recruiting and hiring medical professionals for the healthcare organizations. Human resource management also ensures that the healthcare organization has sufficient staff and medical professionals.
They help the healthcare organization in hiring and managing healthcare workers in their organizations. However, the healthcare sector must ensure that every staff and professionals have proper skills. If they don’t possess any then they must organize skill development programs for them. Human resource management also helps healthcare organizations in adopting new policies and also assists them in implementing that.
Hunan resolve management is needed for every healthcare organization. According to (Mousa & Othman (2020), the primary focus of human resource management is to hire a proper workforce for the healthcare management so that they can provide excellent healthcare facilities to the patients.
Human resource management helps the healthcare organization in improving healthcare facilities for the patients and also ensure that the patients of Australia are not getting deprived of that facility. In the opinion of Grover et al. (2018), it can be understood that every healthcare organization must have human resource management in their organization in order to provide the finest healthcare services to the patients.
Moreover, there are various factors that can actually affect healthcare organizations. Human resource management helps healthcare organizations in planning proper structure so that they can achieve success. Therefore, it can understand that human resource management (HRM) is essential for every healthcare organization.
In the opinion of Baum, T. (2018), talent management is important for every healthcare organization because it helps the organization to have proper accountability. When any organization will have talented healthcare professionals who have proper skills then they are able to deliver the finest healthcare services to the public of Australia.
Talent management also helps in promoting positive work culture in an organization. When any patient will hear about the positive culture in a healthcare sector then they will automatically prioritise that particular healthcare organization. According to Mohammed, Baig&Gururajan (2020), there are more than seventy thousand medical practitioners working in the healthcare system of Australia at present.
Furthermore, talent management can also help organizations overcome the challenges that are faced by the healthcare sector. It can be understood that talent management is very important for healthcare management. It also assists healthcare organizations to fill up the skill gaps that are missing in the healthcare industry. Talent management also helps healthcare organizations in effective skilled practice.
Therefore, the more skilled healthcare professionals the more effective and excellent services can be provided by the healthcare organizations. Talent management can help the organizations in many ways such as in case of emergency the skilled professionals can help and assist them and can reduce the waiting time for the patients.
In the opinion of Mohammed, Hafeez-Baig & Gururajan (2018), talent management can also help organizations in advisory and strategy development in their organizations. Furthermore, talented management can help the healthcare organization in focusing on hiring and recruiting more efficiently and can also help in improving employment in the healthcare organizations.
Talent management can further help the healthcare sectors in creating engagement and also assist the healthcare organization in solving any problem or crisis if it ever happens in an organization.
Recommendations for improvement of the healthcare system of Australia
The healthcare organizations of Australia must improve themselves in some aspects. In the opinion of Kravariti& Johnston (2020), the sectors where healthcare of Australia needs to improve themselves are, firstly the healthcare sectors need regulations to improve the healthcare service. Secondly, they need to improve themselves in the decision-making ability of the healthcare services.
Thus, if they will have proper decision making quality in their healthcare system then they can implement more adequate healthcare policy in their organizations. Proper decision making helps any organization to grow their business and help them to attain success in a limited time. Thirdly, the improvement that is needed for the healthcare sector in Australia is that they must focus on encouraging cost-effective investment in order to provide excellent healthcare to the public of Australia Heng et al. (2018).
However, the cost plays an important role in the healthcare system, if the cost of the healthcare is high then it will be difficult for the general people to take the facility. If the healthcare system will be low then it can affect the financial structure of the healthcare organizations. Therefore, to make cost-efficient healthcare facilities for the public the healthcare organizations must have proper financial plans and policies.
Fourthly the healthcare system of Australia must focus on the workforce and also must be focused on flexibility. When any organization will have an adequate workforce then it can provide more efficient services to the public. The more proper workforce in a healthcare organization the more effective and efficient they can work and provide healthcare services to the public of Australia.
In the opinion of Kritchanchai, Hoeur & Engelseth (2018), to provide a proper workforce the staff and healthcare professionals must have flexibility in their working time so that they can provide proper services to the patient care. Furthermore, the skills play an important role thus, the healthcare sector of Australia must have skill development training programs for the staff and healthcare professionals and also the specialist.
Fifthly, the improvement that is needed for the healthcare organizations of Australia is that they must provide more effective health insurance for the public. Thus, it can assist the general public of Australia to take the facility of healthcare services. Sixthly, the healthcare sector of Australia needs to improve in their human resource management and also in their talent management.
Thus, it can result in a more efficient and adequate workforce and skilled staff and professionals in the healthcare organizations. Lastly, the healthcare sector of Australia must improve in providing adequate information regarding their healthcare system or insurance policies. Talent management also helps the organizations to create a positive culture and ensure that all the staff that are working in that working are happy.
Conclusion
After analyzing and discussing the research paper about managing and planning the healthcare system in Australia it can be concluded that every healthcare sector needs a proper priority setting in the organizations. Furthermore, every healthcare organization must have a decision-making plan in their organizations.
Moreover, this research paper also analyses the workforce and planning that are important and must be developed by the healthcare organization of Australia. This research has also comprehended the importance of human resource management in the healthcare system of Australia.
Moreover, this research paper also highlighted the importance of talent management in the healthcare sectors of Australia. Furthermore, this research paper also recommends some of the strategies and plans that can improve the healthcare system of Australia. Thus, it can provide the finest healthcare services to the public.
References
Barasa, E. W., Cleary, S., Molyneux, S., & English, M. (2017). Setting healthcare priorities: a description and evaluation of the budgeting and planning process in county hospitals in Kenya. Health policy and planning, 32(3), 329-337. https://academic.oup.com/heapol/article-pdf/doi/10.1093/heapol/czw132/10986917/czw132.pdf
Baum, T. (2018). Sustainable human resource management as a driver in tourism policy and planning: a serious sin of omission?. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 26(6), 873-889.Retrived on: 01.10.21, from:https://strathprints.strath.ac.uk/62581/1/Baum_JST2017_Sustainable_human_resource_management_as_a_driver_in_tourism_policy.pdf
Bertram, M. Y., Lauer, J. A., Stenberg, K., & Edejer, T. T. T. (2021). Methods for the economic evaluation of health care interventions for priority setting in the health system: an update from WHO CHOICE. International Journal of Health Policy and Management. https://www.ijhpm.com/article_4004_a9dc83d4dc218427186bb89305f3662a.pdf
Cortis, N., & van Toorn, G. (2020). Working in new disability markets: A survey of Australia’s disability workforce. Social Policy Research Centre, UNSW Sydney. https://doi. org/10.26190/5eb8b85e97714.Retrived on: 01.10.21, from:https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Natasha-Cortis/publication/341448295_Working_in_new_disability_markets_A_survey_of_Australia’s_disability_workforce/links/5ec1c955299bf1c09ac4b98d/Working-in-new-disability-markets-A-survey-of-Australias-disability-workforce.pdf
Grover, S. L., Teo, S. T., Pick, D., Roche, M., & Newton, C. J. (2018). Psychological capital as a personal resource in the JD-R model. Personnel Review.Retrived on: 01.10.21, from:https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Stephen-Teo-2/publication/325093367_Psychological_capital_as_a_personal_resource_in_the_JD-R_model/links/5afc24e3458515c00b6ec8f0/Psychological-capital-as-a-personal-resource-in-the-JD-R-model.pdf
Heng, A., Heal, C., Banks, J., & Preston, R. (2018). Transgender peoples’ experiences and perspectives about general healthcare: A systematic review. International Journal of Transgenderism, 19(4), 359-378.Retrived on: 01.10.21, from:https://researchonline.jcu.edu.au/54712/1/JCU_54712_Heng%20et%20al_2018_accepted%20version.pdf
Kravariti, F., & Johnston, K. (2020). Talent management: a critical literature review and research agenda for public sector human resource management. Public Management Review, 22(1), 75-95.Retrived on: 01.10.21, from:https://researchportal.port.ac.uk/portal/files/26228838/Talent_management.pdf
Kritchanchai, D., Hoeur, S., &Engelseth, P. (2018, January). Develop a strategy for improving healthcare logistics performance. In Supply Chain Forum: An International Journal (Vol. 19, No. 1, pp. 55-69). Taylor & Francis.Retrived on: 01.10.21, from:https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Duangpun-Kritchanchai/publication/322262033_Develop_a_strategy_for_improving_healthcare_logistics_performance/links/5f564a7d299bf13a31a8693f/Develop-a-strategy-for-improving-healthcare-logistics-performance.pdf
Lai, G. C., Taylor, E. V., Haigh, M. M., & Thompson, S. C. (2018). Factors affecting the retention of indigenous Australians in the health workforce: a systematic review. International journal of environmental research and public health, 15(5), 914.Retrived on: 01.10.21, from: https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/15/5/914/pdf
Littlejohns, P., Chalkidou, K., Culyer, A. J., Weale, A., Rid, A., Kieslich, K., … & Knight, S. (2019). National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, social values and healthcare priority setting. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 112(5), 173-179. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0141076819842846
Loomes, S., Owens, A., & McCarthy, G. (2019). Patterns of recruitment of academic leaders to Australian universities and implications for the future of higher education. Journal of Higher Education Policy and Management, 41(2), 137-152.Retrived on: 01.10.21, from:https://ro.uow.edu.au/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1597&context=gsbpapers
Maier, C. B., Batenburg, R., Birch, S., Zander, B., Elliott, R., &Busse, R. (2018). Health workforce planning: which countries include nurse practitioners and physician assistants and to what effect?. Health Policy, 122(10), 1085-1092.Retrived on: 01.10.21, from:https://aura.abdn.ac.uk/bitstream/handle/2164/12710/1_s2.0_S0168851018302793_main.pdf?sequence=1
Mohammed, A. A., Baig, A. H., &Gururajan, R. (2020). An examination of talent management processes in Australian higher education. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management.Retrived on: 01.10.21, from:https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Atheer-Mohammed-11/publication/338707627_An_examination_of_talent_management_processes_in_Australian_higher_education/links/5e709af8a6fdccd76dcbd0ef/An-examination-of-talent-management-processes-in-Australian-higher-education.pdf
Mohammed, A. A., Hafeez-Baig, A., &Gururajan, R. (2018). Talent management as a core source of innovation and social development in higher education. In Innovations in Higher Education-Cases on Transforming and Advancing Practice (pp. 1-31). London: IntechOpen.Retrived on: 01.10.21, from:https://eprints.usq.edu.au/36091/1/Talent_Management_as_a_Core_Source_of _Innovation_a.pdf
Mousa, S. K., & Othman, M. (2020). The impact of green human resource management practices on sustainable performance in healthcare organisations: A conceptual framework. Journal of Cleaner Production, 243, 118595.Retrived on: 01.10.21, from:https://e-tarjome.com/storage/panel/fileuploads/2019-11-26/1574758102_gh9.pdf
Németh, B., Molnár, A., Bozóki, S., Wijaya, K., Inotai, A., Campbell, J. D., & Kaló, Z. (2019). Comparison of weighting methods used in multicriteria decision analysis frameworks in healthcare with focus on low-and middle-income countries. Journal of comparative effectiveness research, 8(4), 195-204. https://www.futuremedicine.com/doi/pdfplus/10.2217/cer-2018-0102
Odu, G. O. (2019). Weighting methods for multi-criteria decision making technique. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management, 23(8), 1449-1457. https://www.ajol.info/index.php/jasem/article/download/189641/178866
Pratt, B. (2019). Inclusion of marginalized groups and communities in global health research priority-setting. Journal of Empirical Research on Human Research Ethics, 14(2), 169-181. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1556264619833858
Smith, J., Keating, L., Flowerdew, L., O’Brien, R., McIntyre, S., Morley, R., & Carley, S. (2017). An emergency medicine research priority setting partnership to establish the top 10 research priorities in emergency medicine. https://emj.bmj.com/content/emermed/34/7/454.full.pdf
Windsor, J., Garrod, T., Talley, N. J., Tebbutt, C., Churchill, J., Farmer, E., & Smith, J. A. (2017). The clinical academic workforce in Australia and New Zealand: report on the second binational summit to implement a sustainable training pathway. Internal medicine journal, 47(4), 394-399.Retrived on: 01.10.21, from:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/imj.13356
Wong, J. Q., Uy, J., Haw, N. J. L., Valdes, J. X., Bayani, D. B. S., Bautista, C. A. P., … & Zeck, W. (2018). Priority setting for health service coverage decisions supported by public spending: experience from the Philippines. Health Systems & Reform, 4(1), 19-29. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/23288604.2017.1368432
Woolley, T., Larkins, S., & Sen Gupta, T. (2019). Career choices of the first seven cohorts of JCU MBBS graduates: producing generalists for regional, rural and remote northern Australia. Rural and remote health, 19.Retrived on: 01.10.21, from:http://unsworks.unsw.edu.au/fapi/datastream/unsworks:59598/binec814316-73ec-426c-8bc4-80da74859855?view=true&xy=01

