Ethics & Governance: Individual Capstone Project
Executive summary
The purpose of this report is to present a research on Collins Foods Limited, an Australian public listed company in the area of governance and ethics. The interpretation of the company towards its governance approach highlights good governance perspective in terms of board composition and size and remuneration area which has contributed in the financial success of the company and its growth in Australia.
However, the governance in the area of reporting of social and environmental disclosure highlight crisis in this area and thus, is not consistent with the legitimacy theory. The ethical approach is analysed to be moral right which is a non- consequential approach. The report adopts the application of stakeholder theory and steward theory of corporate governance.
The purpose of the report is to research and present an interpretation of an Australian public listed company, (CKF) Collins Foods Limited for its intended disclosure to gain insight and find out the stance towards the governance and ethical approach. The vision of the company is to become top restaurant holding company by taking care of its employees and customers who in turn with take care of its business and the mission of the company is to establish Collins Foods Limited as a principal restaurant holding company that successfully operates premier brands where employee are proud to work and customers love to eat. The code of conduct in the company gives relevance to high standards of responsibility and ethical values in the workplace to conduct its business activities that the senior management (directors) and employees, consultants and contractors are expected to follow (Collins Foods Limted, 2018). The code of conduct of the company is regulatory as well as practical set of rules to behave in a business and guide the organisational member to adopt the desired approach to carry out the business activities. The company has faced struggle in the restaurant franchise industry for its operating restaurant chain, Sizzler in Australia which has led to the decision and action towards closing the operations of several Sizzler restaurants in 2016 in Australia. To stay in the leading position, the company has focused on the KFC restaurants performance and growth in Australia and has also focused in new acquisitions and purchase of Taco Bell franchise rights in Australia.
The history of Collins Foods Limited set in motion in year 1968 after the acquisition of Sizzler brand in year 1967 as Collins Foods International (Collins Foods, 2018). It founded by a James Collins. After the changes in menu selection and customer experience of Sizzler there was an increase in profitability and the company expanded to Asia in year 1992. There was acquisition of 42 KFC restaurants by Collins Foods Limited in year 2013 in Australia and the company was incorporated in Australia in year 2011 (Collins Foods, 2018). The company’s headquarters is in Hamilton in Queensland, Australia. In Australia, Collins Foods Limited has increased focus on KFC restaurants operations and has only limited Sizzler restaurants (around 20) (Financial Times, 2019). The revenue has increased by 14% ($282.49 million) and the underlying net profit after tax was increased to 3.7% ($17.4 million) (Business Insider, 2017).
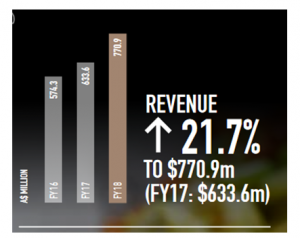
Figure 1: Financial Performance of Collins Foods Limited
(Source: ASX, 2019)
Collins Foods Limited is successfully operating in food service retail outlets for KFC restaurant chains (more than 225 stores) in Australia and KFC (over 65 stores) and Sizzler restaurant chains in Asia in 2016. Thus, Collins Foods Limited is successfully operating in the consumer services and restaurants industry.
For this report, the area of company background information, recent annual report, corporate governance statement, remuneration report, board composition, legitimacy theory and the different theories of corporate governance have been researched. There has been adoption and application of the stakeholder theory and stewardship theory of corporate governance for Collins Foods Limited.
Summary of corporate governance at Collins Foods Limited
Composition of the board
The board composition in Collins Foods Limited comprises of six directors where five of them are non-executive directors and one is executive director. The chairman is non-executive director and is an independent director. Thus, the board of this company includes a high number of independent directors which are four in number including the chairman and one is non-independent director (ASX, 2019). Thus, the ratio of independent to non-independent directors is 4:1 considering the non-executive directors.
It can be summarised that the composition of the board in this company consists of directors with diverse skills set and experience in the field of finance and capital markets, audit and accounting, legal, risk and compliance, mergers and acquisitions, operation, information technology, marketing, human resources and project management as stated in the director’s report of the company.
The experience of each director is also complementary to ensure the effective management and improve the performance of the company for long-term growth. It can be summarised that the structure comprising of six directors provide a good balance among the directors which is neither tow low nor high to provide them external perspective on different aspects of company and also provide them a level of independence (Mahadeo et al., 2012). Also, the high number of independent directors highlight that the board composition is to make certain that an independent judgement is promoted on different decisions.
Remuneration report
The remuneration of the company is set in accordance with the corporation act under section 300A to determine the value of remuneration of non-executive directors, the managing director and chief executive officer (CEO) as per the condition of the performance. Also, towards the governance of remuneration for directors and executives the company takes input from shareholders, proxy advisors, tax advisors, external remuneration consultants, lawyers and Remuneration and Nomination Committee members. The remuneration mix consists of Long Term Incentive performance metrics and Short Term Incentive performance metrics. Thus, the total remuneration package of these key management personnel includes fixed remuneration plus target Long Term Incentive plus target Short Term Incentive (ASX, 2019). The board and committee fees and ́the superannuation (compulsory contributions) forms the part of remuneration structure of non-executive directors.
It can be said that short term incentive plan provides an effect to remuneration to deliver the business plan leading to higher returns for shareholders where the targets serve to adjust the employing activities cost and risk in the situation of poor performance. The remuneration determination for directors and executives are made at the end of the measurement period and after the audit of the accounts of the company.
To determine the likely orientation of the board of the company, the steward theory of governance can be applied that considers the company executives as stewards that focus their efforts on maximising the wealth for the shareholders and earn and secure profits. According to Abdullah & Valentine (2009), the satisfaction and motivation of the executives is based on the success of the company when it is attained for the financial period. It can be analysed from the recent annual report of Collins Foods Limited that there is high focus on the position of the key executive for the responsibility and authority in the planning activities as well as for directing and controlling the company activities to act in parallel to ensure that the returns of the shareholders get maximised. It is analysed that the key management personnel share common goals of company growth and effective management of capital to grow profits. The presence of independent directors in the company makes the board not too controlling and has a guidance role to improve the corporate credibility, manage risk and empower executive to increase the likelihood of high performance. Thus, these improve the functioning of the governance standards in Collins Foods Limited. It can be analysed that the relationship among the directors of the board and the executives involves a process of shared decision making, mentoring role and also involves training. This suggests a stakeholder- stewardship orientation of board in the company.
In addition, the stakeholder theory approach can also be applied for Collins Foods Limited that argues that shareholders along with other stakeholders’ such as suppliers, customers, community, government, etc. that also have a major stake in the company and are affected by the company success or loss (Wagner et al., 2011). Under this, the executive have obligations towards the different stakeholders including shareholders that they receive a fair return which is also to operate in an ethical and responsible way under the corporate social responsibility. This is to ensure that the needs of the different stakeholders are meet which includes business practices that consider the sustainability principle for the community and the environment. Thus, the board of directors take responsibility towards the interest of key stakeholders for implementation of ethical ways in their corporate practices. Also, the presence of majority of non-independent directors in the company points towards the diversity on the board of directors with the purpose to improve the board performance. Thus, it can be analysed that the board composition is organised in way to ensure good governance practices and also ethical and responsible governance to manage the different stakeholders. This also points that the board orientation in Collins Foods Limited suggests a stakeholder- ethical branch orientation.
However, among these two board orientation Collins Foods Limited it can be determined that the stakeholder-stewardship is the most likely orientation of its board. This can be reflected from the composition of the Collins Foods board which comprises of majority of non-independent directors that are engaged in protecting and earning profits for the shareholders, and focus is on the role of top management personnel that are integrating the goal of growth and capital flow management for the success of the company. Collins Foods Limited placed relevance to the structures that empower the directors and executives and offer a board structure that provides a high level of autonomy based on the trust factor. It also recognises the position of key management personnel so that they are able to act in an autonomous way with the focus on company growth and shareholders’ returns and also management of capital to minimise costs under the stakeholder-stewardship orientation of the board.
Interpretation of company communications using Legitimacy Theory
The legitimacy theory provides a mechanism that offers supports to the companies in meeting their social contract through disclosures related to social and environmental (Archel et al., 2009). This helps to recognise the company objective for long term survival. The use of legitimacy Theory is for the understanding and analysis of Collins Foods Limited communications. It can be analysed that the moderate size of the board in Collins Foods ensure an effective coordination, communication skills, and decision making process. However, from the voluntary social and environmental disclosure it can be interpreted that the corporate communications in Collins Foods Limited is not in steady with the legitimacy theory. The corporate social and environmental practices have not been disclosed much as a part of their social and environmental reporting. However, there the voluntary disclosure is mainly associated to financial performance of the company.
It can be interpreted for the corporate communications towards non-disclosure of social and environmental information in the annual report thus, the company is not justifying the continued business operations in relation to the environment and within the society and also do not provide a response towards the expectation of the community in relation to the corporate behaviour. Thus, according to Mahadeo et al. (2011), the non-disclosure of social and environmental information the company is not fulfilling the accounting functions or reporting thus, it is not explaining the legitimacy of the company existence in concern to the legitimacy theory. Thus, it can be analysed that Collins Foods Limited can gain legitimacy effect through social and environmental reporting or disclosures (Milne & Patten, 2002) as it ensure that the company is operating within the norms of their society and report of the activities that a society expects from the corporate conduct. Thus, it can be analysed that by non-adoption of legitimacy theory perspective, the company can be perceived as a less ethical enterprise where it is operating and also put a question on the rationale behind adoption of code of ethics for self-interest or to act in a responsible manner.
It can be analysed that the ethical approach of the company is likely to be moral –rights approach as the company information highlight focus on the equal treatment of workers under law and human rights (Citeman, 2010), health and safety of workers, and respect for each other under the law and company code. This ethical approach is a non-consequential approach (Simola et al., 2010). The ethical approach in the company focuses on the health and safety of workers, fair remuneration and asserts compliance to the environmental regulation for restaurant operations. Thus, it can be said that under this ethical approach the moral decision are concerned toward the rights of the affected stakeholders under the law and codes and these basic right and autonomy is not taken away in the decision making in Collins Foods Limited.
It can be concluded that there good governance in relation to the broad composition, size , diversity and remuneration of key management personnel however, there is issue in the area of reporting of the social and environmental disclosure in the company’s annual report. It can be concluded that the steward theory of governance is most applicable which suggest a stakeholder-stewardship orientation of board in the company. The ethical approach is moral –rights considering the focus of the company top management personnel. It can be concluded that the non-disclosure of social and environment information in the annual report of Collins Foods Limited does not provide an evidence of company that legitimate the continued existence of the company.
Abdullah, H., & Valentine, B. (2009). Fundamental and ethics theories of corporate governance. Middle Eastern Finance and Economics, 4(4), 88-96.
Archel, P., Husillos, J., Larrinaga, C., & Spence, C. (2009). Social disclosure, legitimacy theory and the role of the state. Accounting, auditing & accountability journal, 22(8), 1284-1307.
ASX. (2019). Collins Foods Limited 2018 Annual Report. Retrieved from: https://www.asx.com.au/asxpdf/20180726/pdf/43ws7lsdg17447.pdf
Business Insider. (2017). Collins Foods shares are tanking as KFC acquisitions drag on profit. Retrieved from: https://www.businessinsider.com.au/collins-foods-shares-are-tanking-as-kfc-acquisitions-drag-on-profit-2017-11
Citeman. (2010). Moral Rights Approach. Retrieved from: https://www.citeman.com/12952-moral-rights-approach.html
Collins Foods. (2018). About Us. Retrieved from: https://www.collinsfoods.com/about-us/
Collins Foods Limted. (2018). Key Policies. Retrieved from https://www.collinsfoods.com/investors/corporate-governance/key-policies/
Financial Times. (2019). Collins Foods Ltd. Retrieved from: https://markets.ft.com/data/equities/tearsheet/profile?s=CKF:ASX
Mahadeo, J. D., Oogarah-Hanuman, V., & Soobaroyen, T. (2011). Changes in social and environmental reporting practices in an emerging economy (2004–2007): Exploring the relevance of stakeholder and legitimacy theories. In Accounting Forum (Vol. 35, No. 3, pp. 158-175). Taylor & Francis.
Mahadeo, J. D., Soobaroyen, T., & Hanuman, V. O. (2012). Board composition and financial performance: Uncovering the effects of diversity in an emerging economy. Journal of business ethics, 105(3), 375-388.
Milne, M. J., & Patten, D. M. (2002). Securing organizational legitimacy: an experimental decision case examining the impact of environmental disclosures. Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal, 15(3), 372-405.
Simola, S. K., Barling, J., & Turner, N. (2010). Transformational leadership and leader moral orientation: Contrasting an ethic of justice and an ethic of care. The Leadership Quarterly, 21(1), 179-188.
Wagner Mainardes, E., Alves, H., & Raposo, M. (2011). Stakeholder theory: issues to resolve. Management decision, 49(2), 226-252.


