7BSP0333 Principles of Project Management
Introduction (7BSP0333 Principles of Project Management)
Stakeholders play a significant role in the development of an organization. There is a requirement for effective participation of stakeholders in improving services and future opportunities. The report is going to focus on stakeholder analysis in the management of a project. Project managers face multiple challenges in delivering a project effectively such as strategic risk, market risk, communication gap, and financial risk. Effective and efficient planning in a project assists to reduce the impact of risks.
Stakeholder Analysis
1. Stakeholder Analysis in the context of project management
Effective project management assists an organization to develop a number of opportunities. The innovation hub is focused on building a cooperative environment for scientific technologies and knowledge development. As per the opinion of Blázquez et al. (2021), there is a requirement for appropriate project management in order to build an effective work environment. Effective work environments assist an organization in enhancing the productivity level of employees. Active participation of stakeholders assists to maintain the quality of services. The innovation hub is focused on providing the services of clinical labs, business development centres, and scientific workshops.
In building an effective innovation culture, there is a requirement of investors, owners, mentors, government, employees, technology management, financial manager, quality manager, suppliers, customers, and Human Resource management. As stated by Rambaree et al. (2021), every stakeholder has different responsibilities in a project. The analysis of stakeholders assists in allocating responsibility effectively. The owner of the innovation hub needs to build an effective relationship with suppliers in order to get enough material on time. Project management of the innovation hub project needs to understand the requirements of project effectively before implementing a strategy or planning. Active participation of stakeholders assists to bring innovative ideas in order to maintain uniqueness and competitive advantages.
Stakeholder analysis assists the project management to remove multiple barriers such as supply risk, financial risk, and customer risk. Stakeholder analysis can assist the management of innovation hubs to build trust, identify risks, plan, requirements of the project, and manage expenditure. As per the opinion of Kalbaska et al. (2017), there is a requirement of effective stakeholder analysis in order to build a healthy work environment, implement strategy, and develop future opportunities. As stated by Sapapthai et al. (2020), there are multiple elements of stakeholder analysis such as identifying the stakeholders, investing the roles, desire, internet, and identifying the conflict of relationship among all stakeholders. Effective management is essential in every project in order to get a positive outcome. The analysis of stakeholders assists a project to complete a project within time.
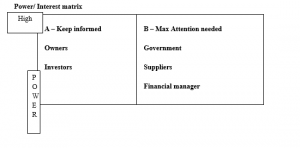
2. Table with at least 8 key stakeholders for this project
| Stakeholders | Importance of stakeholder | Likely position | Ability to influence project (very high, high, medium, low, very low) | Predictability of behaviour | Actions were taken to operate stakeholders |
| Investors | A – Keep informed | The investors play a significant role in the development of the innovation hub. The investors can financially support the work process. | Very high | The behaviour of the stakeholder can be predictable due to effective communication. | The owner will conduct meetings with investors to define the concept of investment. |
| Financial manager | B – Max Attention needed | The financial manager can support the project by estimating the cost on the basis of loss, profit, and investment. | High | The behaviour of the stakeholder can be predictable due to regular conversation. | There is a requirement to monitor the work progress and conduct meetings. |
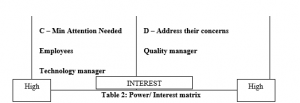
| Employees | C – Min Attention Needed | The employees can support the project effectively by increasing the productivity level. As stated by Melloni et al. (2020), employees’ motivation and effective relationships with management are essential in order to build an effective environment. | Very high | The behaviour can be predictable due to effective conversation. | There is a requirement to monitor work performance of employees and provide feedback every week. |
| Suppliers | B– Max Attention needed | Active participation of suppliers can support the project by delivering enough material and reducing the impact of quality risk. | High | The behaviour of suppliers can be predictable due to meetings. | The management will conduct meetings with suppliers and build healthy relationships. |
| Quality manager | D – Address their concerns | Quality managers can support the innovation hub project by analyzing the quality of services effectively. | Medium | The behaviour of Quality manager can be predictable due to daily monitoring of the work process. | Management will monitor the work process and conduct meetings with quality manager. |
| Government | B – Max Attention needed | Government can support and oppose the project by implementing acts and regulations (Ul and Curry, 2021). | Medium | The behaviour of government can be unpredictable due to implementation of new legislation. | The owner will conduct meetings with government to inform the work process. |
| Owners | A – Keep informed | The owners can support the project effectively by monitoring work processes. | High | The behaviour of owner can be predictable due to board meetings. | There is a requirement for a board meeting. |
| Technology manager | C– Min Attention Needed | Technology managers can support the project effectively by monitoring the functions of technologies (Colclough, 2021). | Medium | The behaviour of technology managers can be predictable due to effective communication. | Management will conduct meetings with technology manager. |
Table 1: Stakeholder analysis (Source: Jayasena et al. 2019)
3. Challenges and suggestions of project management
Communication with stakeholders is one of the major challenges in project management. Lack of effective communication tools is responsible for this communication gap between a project manager and stakeholders. As cited by Teo and Loosemore (2017), cultural and moral values may differ between stakeholders and project managers and different types of conflict arise during executing project management plans. Project managers have created specific goals for an organization for a particular period but lack of clear success criteria has created different managerial issues. Sometimes project managers have spent more money than forecast due to uncertainty that affected profitability of stakeholders and they never considered more expenses than predetermined budgets.
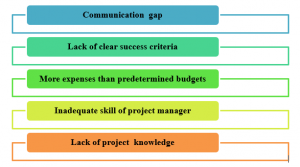 Figure 1: Challenges of project management (Source: Teo and Loosemore, 2017)
Figure 1: Challenges of project management (Source: Teo and Loosemore, 2017)
Inadequate skill of project manager and its entire team affects performance of project that is a major challenge to execute business activities seamlessly. Performance of a project improves when every team member feels that responsibility to ensure the entire project. Most project goals are set by project managers and there was least contribution of stakeholders that sudden involvement of stakeholders in a project has affected the whole project. As opined by Cooper and Sommer (2018), stakeholders provide unrealistic deadlines to project managers that affect quality of projects and extra pressures reduce efficiency of work. Lack of knowledge about a particular project of stakeholders affects decisions of the project manager that creates more complex situations during executing a project. Lack of efficient structure
Recommendations and suggestions for project management
Project managers have to implement efficient and effective communication tools to remove communication gaps among stakeholders and project managers. As cited by Xia et al. (2018), success criteria of business must be prepared by collaborative contributions of project managers and stakeholders that will provide a brief knowledge about the project and there will be least chance of an argument. Project managers have to prepare an accurate budget and must have to consider upcoming uncertainties for accurate forecasting and profitability of the project. It was suggested to make project decisions with a collaborative approach of project managers and stakeholders.
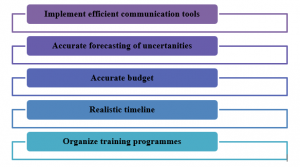 Figure 2: Suggestions of project management to deal with challenges (Source: Eskerod and Ang, 2017)
Figure 2: Suggestions of project management to deal with challenges (Source: Eskerod and Ang, 2017)
Project team must be prepared based on the skills of team members. Tasks of the project must be allocated on the basis of skills of team members that will increase efficiency of the project. A predetermined structure must be maintained in the project that will help to increase control over the project. As opined by Eskerod and Ang (2017), stakeholders directly participate in decision making before starting a project that will improve relationships among project managers and stakeholders. Timeline of the project must be prepared based on project difficulties and future uncertainties that will reduce pressure among team members and the quality of the project will be improved. Project managers have to organize training programmes that will increase efficiency of team members and provide a proper understanding of project structure. Proper understanding of structure will remove conflicts among team members.
Conclusion
Based on the above discussion it can be concluded that active participation of stakeholders in a project assists to implement a strategy effectively. Every industry such as food, clothing, retail, and technology faces multiple challenges due to the crisis of COVID 19 such as service risk, material risk, quality risk, and pricing risk. Majority of organizations are focused on implementing technology in order to provide effective services in post-covid situations. Moreover, it can be stated that the management of the innovation hub is needed to focus on the analysis of stakeholders in order to provide effective quality of services. Effective management can assist the organization in managing every task efficiently.
References
Blázquez, L., García, J.A. and Bodoque, J.M., 2021. Stakeholder analysis: Mapping the river networks for integrated flood risk management. Environmental Science & Policy, 124, pp.506-516. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1462901121002094
Colclough, S., 2021, November. The Costs, Benefits and Stakeholder Analysis of an Irish Social Housing Deep Energy Retrofit Case Study. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 2069, No. 1, p. 012110). IOP Publishing. Available at: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/2069/1/012110/meta
Cooper, R.G. and Sommer, A.F., 2018. Agile–Stage-Gate for Manufacturers: Changing the Way New Products Are Developed Integrating Agile project management methods into a Stage-Gate system offers both opportunities and challenges. Research-Technology Management, 61(2), pp.17-26.Available at: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/08956308.2018.1421380
Eskerod, P. and Ang, K., 2017. Stakeholder value constructs in megaprojects: A long-term assessment case study. Project Management Journal, 48(6), pp.60-75.Available at: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/875697281704800606
Jayasena, N.S., Mallawaarachchi, H. and Waidyasekara, K.G.A.S., 2019. Stakeholder analysis for smart city development project: an extensive literature review. In MATEC Web of Conferences (Vol. 266, p. 06012). EDP Sciences.Available at: https://www.matec-conferences.org/articles/matecconf/abs/2019/15/matecconf_iconbee2019_06012/matecconf_iconbee2019_06012.html
Kalbaska, N., Janowski, T., Estevez, E. and Cantoni, L., 2017. When digital government matters for tourism: a stakeholder analysis. Information Technology & Tourism, 17(3), pp.315-333. Available at: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40558-017-0087-2
Melloni, G., Turetta, A.P.D., Bonatti, M. and Sieber, S., 2020. A Stakeholder Analysis for a Water-Energy-Food Nexus Evaluation in an Atlantic Forest Area: Implications for an Integrated Assessment and a Participatory Approach. Water, 12(7), p.1977. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/767476
Rambaree, K., Sundström, A., Wang, Z. and Wright, S.A.I., 2021. Qualitative stakeholder analysis for a Swedish regional biogas development: A thematic network approach. Sustainability, 13(14), p.8003.Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/1192558
Sapapthai, S., Leelawat, N., Tang, J., Kodaka, A., Chintanapakdee, C., Ino, E. and Watanabe, K., 2020. A Stakeholder analysis approach for area business continuity management: A systematic review. Journal of Disaster Research, 15(5), pp.588-598. Available at: https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jdr/15/5/15_588/_article/-char/ja/
Teo, M.M. and Loosemore, M., 2017. Understanding community protest from a project management perspective: A relationship-based approach. International journal of project management, 35(8), pp.1444-1458.Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0263786316301302
ul Hassan, U. and Curry, E., 2021. Stakeholder Analysis of Data Ecosystems. The Elements of Big Data Value, p.21. Available at: https://library.oapen.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.12657/50023/978-3-030-68176-0.pdf?sequence=1#page=40
Xia, N., Zou, P.X., Griffin, M.A., Wang, X. and Zhong, R., 2018. Towards integrating construction risk management and stakeholder management: A systematic literature review and future research agendas. International Journal of Project Management, 36(5), pp.701-715.Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S026378631731308X
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

