BSS052-6 Project and Operations Management Assignment Sample
1. Business case
1.1 The Business Case
The project that has been selected in this case is to construct an NHS Mobile service for the patients near the Luton campus. The National Health Service (NHS) in the UK is one of the premium healthcare initiatives by the government of the UK. Healthcare is publicly funded and aimed at improving the lives of the people. The major reason why this project may help the Luton community is that it will help raise awareness about the different health issues that can affect college students and how to detect such issues. According to Tereso et al. (2019), it will also help in preventing the spread of any kind of communicable diseases on campus. Also, keeping in mind the current pandemic out of which the UK has barely survived, it has become more than important to ensure regular check-ups of the university students who have just started college. The alternatives that were considered to this plan were to either develop a workshop program aimed at educating women on how to use the e-service platforms or develop a fund based on some specific charity.
1.2 Primary and Secondary Objectives
The primary objectives are:
- To help the students remember to conduct regular check-ups and ensure that the students are not infected by COVID 19 virus
- To inform the students about vaccination camps for those who are yet to receive the vaccination
The secondary objectives are:
- To create a healthy environment around the Luton campus
- To raise awareness regarding contraception methods and promote safe sex
- To help the students through reminders about appointments and taking pills in the desired time
- To help develop a “positive” attitude in the students regarding their health and make the students more aware of the potential dangers present in not conducting regular check-ups.
1.3 Expected benefits, estimated costs, resources required
There are several benefits linked to the start of new mobile healthcare service in the Luton area. One of the major benefits is linked with removing the disparity that is present in healthcare and also provides it to students at affordable prices. As per the view of Gordon et al. (2018), the major reason is that students are mostly jobless and have to survive on a limited income and therefore can afford a proper healthcare plan through this initiative. Another benefit is that it will help in bridging the gap that is present between accessibility and “healthcare” for students. Also, the start of this project will ensure that the students will be the main focus of the healthcare professionals. The consideration of a “patient-centric” approach as compared to a “clinical” approach will help in easier communication between the healthcare professionals and the students. Most importantly the start of this initiative may also help in garnering sponsors to help with the project.
The estimated cost of the project should be around 26500 pounds initially, as settled by the National Health Service. The high cost of the budget is because it includes the maintenance of a variety of resources which will acquire a high cost.
There are many resources required to initiate the process of developing a mobile healthcare service. Firstly, the NHS will need to develop a website and an app that the students can access through their mobile phones (Gul et al. 2017). A toll-free number will also need to be developed through which the students can access these services. The NHS will also need to develop and arrange for round-the-clock nurses and doctors who will help the students through emergencies. There also needs to be the presence of updated and modern technologies that will be tasked with directing automated responses, directing calls to hospitals during emergencies, giving reminders to the students, and so on. Each of these resources is needed to be managed within the given cost.
1.4 Stakeholder analysis
| INTERNAL STAKEHOLDERS | |||
| Name | Roles | Influence | Impact |
| Employees | Includes all the administrative staff such as the maintenance, social media manager, security, server security, etc. | Hold a very strong influence as involved in the day-to-day management of the service. | HIGH |
| Medical Staff | Includes the nurses, doctors, medical students, etc. | Strong influence as these professionals are tasked with helping the students | HIGH |
| EXTERNAL STAKEHOLDERS | |||
| Community | Includes the people residing in the Luton area which consists of students and also residents in that area | Low influence as not directly involved | LOW |
| Luton Corporation | Includes the media, Mayor of the town, local “partnerships,” members of different state councils, etc. | Low influence as not directly involved | LOW |
| Local Service Providers | Includes nursing care providers, the GPs of the area, dentists, etc. all of whom will have to stay available in this service. | High influence as they have to present and rush to aid if needed | HIGH |
| Commissioners | Includes NHS England under whom the service is being organized. | Moderate influence as they are the main brains behind this initiative and also associated with providing funds | MODERATE |
| Service Users | This includes the patients and their carers (if present). | High influence as they are the main receivers of the service | HIGH |
| External factors | This includes the NHS providers, Health Education England, the Ambulance services when required, etc. | High influence as they help provide support to the service | HIGH |
| Customer proxies | This includes voluntary council members who help patients when needed, Healthwatch officials who can be present at a moment’s notice, etc. | Moderate influence help provide support to the service | MODERATE |
Table 1: Stakeholders Analysis Matrix
(Source: Inspired by NHS, 2021)
1.5 Key risks, constraints, assumptions
The key risks that are associated while developing this project are the cost risks, which can arise due to wrong planning and cost estimation of the project. It also includes legal risks where the policies and programs have not been properly maintained and may lead to the stoppage of the project (Moshtaghianet al. 2020). Risks may also include performance risks where the project fails to deliver the promised results.
The major constraints that can affect developing the project are the costs that are associated with the project, as oftentimes the budget provided may not be enough to develop the service. Another constraint is the quality of the service that is being provided should also be considered.
The assumptions that have been considered are:
- Availability of cheap labour sources during the pandemic
- The presence of a skilled workforce
- Presence of new and updated equipment
- Equal contribution of all the stakeholders in the project
1.6 Completion date, milestones
The date of completion is one important constituent when it comes to developing a project. The project will need to be completed within six months from the start date. The project will start in the first week of September 2021 and will need to be completed by the first week of March 2022. Hence, the entire project will need to be completed within 180 days.
The major milestones that will be achieved while the project is being conducted have been given below.
| Tasks | Roles | Time Frame |
| TASK 1 | Creating a budget and managing the funds | 10 days |
| TASK 2 | Development of the website and the toll-free number that will be used by the students to contact the service provider | 40 days |
| TASK 3 | Finalizing on the design of the website | 10 days |
| TASK 4 | Buying and Setting up of equipment | 40 days |
| TASK 5 | Implementing cyber security measures | 20 days |
| TASK 6 | Completing the legal procedures | 30 days |
| TASK 7 | Employing round the clock officials who will answer the calls | 30 days |
Table 2: Milestones Chart
(Source: Self-Created)
1.7 Key project personnel and roles
The key personnel who are involved while a project is being developed are:
- Project Manager, who is tasked with managing the entire project and ensuring the proper planning, execution, control, and monitoring of the project. This person is also tasked with providing updates and ensuring that the project gets completed on time.
- The Project Team consists of activities whose job is to work on different activities and ensure that the deliverables of the project are maintained.
- The financial team is tasked with the planning of the budget and the managing of the financial resources. It is the brains behind how to effectively manage the finances provided and not go over budget.
- Resource Manager, whose responsibility is to manage the “resource pools” effectively and work together with the project manager by ensuring that all the demands of the project are met.
2. Work Breakdown Structure
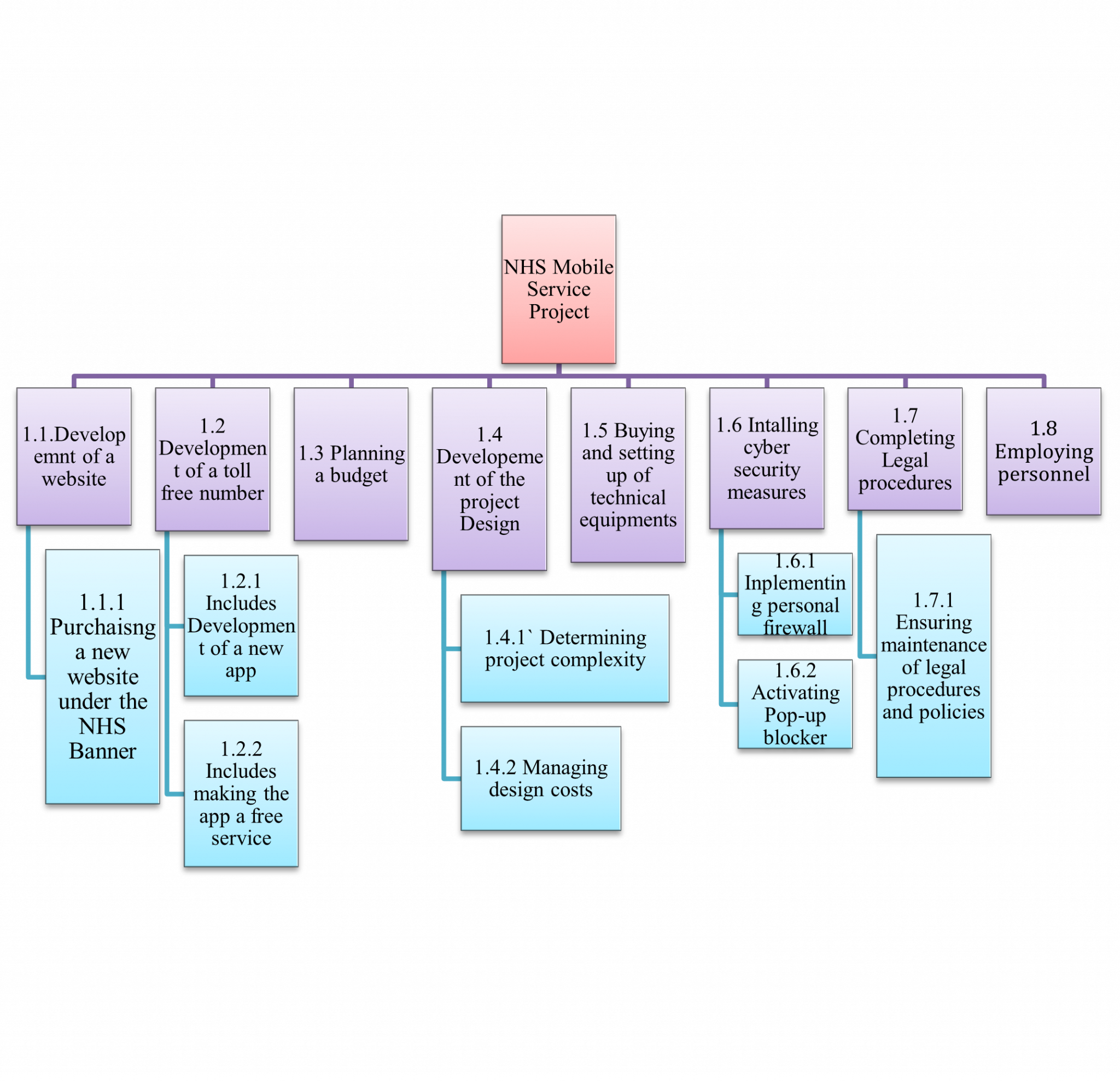
Figure 1: Work Breakdown Structure
(Source: Self-Created)
A look at the work breakdown structure shows that there exists eights steps that will need to be considered while developing the project. Each step also includes a few sub-steps which will need to be considered. It is based on this work breakdown structure that the Project manager will consider completing the project. The use of this structure from developing the website to employing officials in the NHS Mobile service will help the manager in completing the project on time.
3. Activity list and Gantt chart
Activity List
| Activity | Activity Description | Activity Duration | Preceding Activity |
| A | Developing website | 10 days | – |
| B | Publishing the website under NHS Banner | 20 days | A |
| C | Developing a toll-free number | 15 days | B |
| D | Designing and developing an APP | 15 days | B |
| E | Making the app a free service for the customer | 15 days | D |
| F | Budget Planning | 15 days | D |
| G | Developing project design | 15 days | D |
| H | Purchasing and setting up technical equipment | 20 days | C, E, F, G |
| I | Installing cyber security measures | 15 days | H |
| J | Completing legal procedures | 15 days | H |
| K | Ensuring management of legal procedures | 15 days | I |
| L | Employing personnel | 9 days | J |
| M | Closure | 1 days | K, L |
Table 3: Activity list
(Source: MS Word)
Gantt Chart
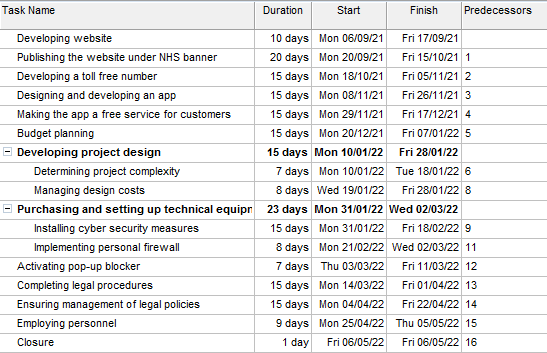
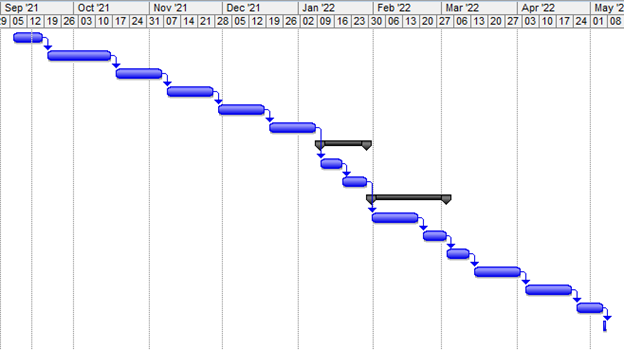
Figure 2: Gantt Chart
(Source: MS Excel)
Figures given above as the activity list and Gantt chart highlights the activities involved in this project. The project of establishing a mobile service for the NHS involves various activities which need to be conducted within provided deadlines to ensure successful completion of the project (Papke-Shields and Boyer-Wright, 2017). Various activities involved in this project are a development of a website that requires 10 days to complete. It involves publishing the website in an NHS banner which requires 20 days to complete. The activity of creating a toll-free number requires 15 days to complete and designing and developing an app is another activity that requires 15 days.
Making the app available to the customers free of cost following all the procedures requires 15 days to complete. Planning the budget for completing this project is a major activity of this project which requires 15 days. Development of project design comes after planning the budget of the project and it requires another 15 days to complete this activity (Vaníčková, 2017). The project involves several other activities and it takes 180 days in total to complete this project successfully.
4. Network Diagram and Critical Path Analysis
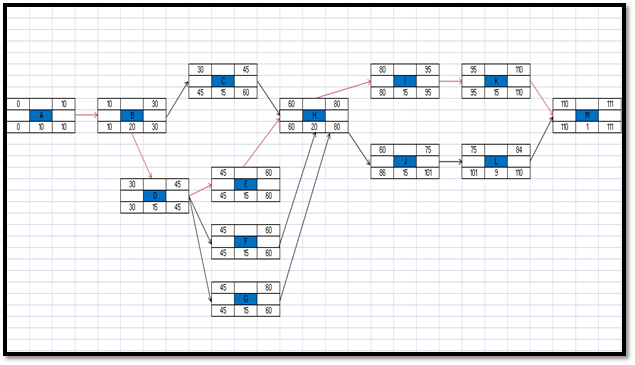
Figure 3: Critical Path and Network Diagram
(Source: MS Excel)
Critical path of the project is A-B-D-E-H-I-K-M
The figures network diagram and critical path showcase the interrelation between various activities involved in this project. It highlights how different activities of this project are in interrelation with each other and how one activity starts with the completion of its previous activity.
5. Budget
| Activity list | Budget |
| Developing website | 1500 Pounds |
| Publishing the website under the NHS banner | 1000 Pounds |
| Developing a toll-free number | 500 Pounds |
| Designing and developing an app | 2000 Pounds |
| Making the app a free service for customers | 1000 Pounds |
| Budget planning | 2500 Pounds |
| Developing project design | 3000 Pounds |
| Purchasing and setting up technical equipment | 5000 Pounds |
| Installing cyber security measures | 2000 Pounds |
| Completing legal procedures | 2500 Pounds |
| Ensuring management of legal policies | 1000 Pounds |
| Employing personnel | 4000 Pounds |
| Closure | 500 Pounds |
| Total | 26500 Pounds |
Table 4: Budget plan
(Source: MS Word)
The table of budget plans given above breaks down the budget required to finish the project of developing a mobile service for the NHS near Luton Campus. The project involves various activities and the table provided above breaks down the total budget into the expenditure of different activities of this project (Willumsen et al. 2019). The overall sum required to complete this project of setting mobile services for the NHS is 26500 British Pound Starlings.
6. Risk Register
| Risk Log
Status/Version: Date: Project: Author: Distribution: |
|||||||||
| Ref. | Date | Risk Description | Probability (P) | Impact (I) | Risk Rating (P*I) | Action | Responsible person | Review date | Status |
| 1. | 07/09/2021 | Operational risk | 1 | 1 | 1 | Proper planning and execution of operations. The project manager needs to provide a clear description of the objectives and requirements of the project to their team to mitigate operational risks from the project (Murianaand Vizzini, 2017). | Project Manager | 08/09/2021 | |
| 2. | 09/09/2021 | Communication risk | 2 | 2 | 4 | Creating mobile services involves the creation of apps that requires the proper development of software. It is significant for the project management team of the NHS to have effective communication throughout the department to ensure proper management of communication risks and the establishment of software for the mobile application (Kušar and Šelih, 2017). | Project Manager | 10/09/2021 | |
| 3. | 11/09/2021 | Management risk | 3 | 3 | 9 | Establishing proper risk mitigation strategies prior to initiating the project in order to ensure that any type of risk cannot halt the project (Stanitsas et al. 2021). The risk management team and their manager are responsible to identify and mitigate the risks at their initial stages to avoid severe damage to the project. | Management team | 12/09/2021 | |
| 4. | 12/09/2021 | Strategic risk | 4 | 4 | 16 | Establishing mobile services for a healthcare organization can be a critical process that requires strategic analysis as it may consist of strategic risks (Wang et al. 2017). It is significant for the project manager of an NHS project to determine its possible strategic risks prior to the project and develop mitigation strategies to avoid the risk of project failure. | Strategic Management team | 13/09/2021 | |
| 5. | 14/09/2021 | Legal Risk | 5 | 5 | 25 | Establishing a new service requires legal permissions and regulations to be followed ethically. The management team of the NHS has to hire legal expertise to provide them valuable legal advice to establish their mobile services for their organization effectively (Boy et al. 2021). | Legal advisor | 15/09/2021 | |
| Establishing mobile services for a healthcare organization can be a critical process that requires strategic analysis as it may consist of strategic risks (Wang et al. 2017). It is significant for the project manager of an NHS project to determine its possible strategic risks prior to the project and develop mitigation strategies to avoid the risk of project failure. | |||||||||
Table 5: Risk Register
(Source: MS Word)
The risk register table provided above highlights various types of risks which can be observed at the time of developing the project. This project involves the development of mobile services for the NHS that can provide health check-up facilities through mobile applications to its patients. Creating mobile services for a large number of employees and patients requires agile software development that can mitigate all the loopholes of the project. This can be achieved by mitigating all the risks related to the project.The table evaluates risk ratings of the various risks involved in the project to analyse the severity of the risks involved in this project.
Various risks related to this project are communication risks, strategic risks, legal risks, operational risks, and general risks related to the project. AS argued by Demirkesen and Ozorhon, (2017), it is significant for the entire management team of this project to contribute significantly to mitigate these risks. For instance, the project manager is responsible for mitigating operation-related risks, whereas the risk manager is responsible to mitigate project-related risks at their initial stage as it can damage the entire project and its outcome if not rectified at the initial stages. Similarly, the project manager looks after the strategic risks related to this project to mitigate the risks on time and a general manager takes help from legal expertise to deal with the legal risks and regulations of the project. Mitigation of risks related to this project can enhance the potential of this project. (BSS052-6 Project and Operations Management Assignment Sample)
7. Quality plan
| Measures | Product ID | Quality Method | Frequency | Target | Plan | Source of Data |
| Effect of defect removal | 1 | Audit | At the completion of each iteration | 99 % with 5% tolerance | Proper analysis and investigation of the reasons for deviation by analysing the severity of the defect, its origin, and the efforts spent on it. Work product review reports can help a project management team to analyse the efficiency of defect removal. | (Defects removed/ defects found)* 100 |
| Requirement Volatility Index | 2 | Inspection Check | Monthly | 99% with 3% tolerance
|
Changing request logs is one of the most common plans for removing project requirements volatility. It can also be achieved by resulting in effort estimation which can help to evaluate the requirement volatility. |
Changes Requested/ total requirements)* 100 |
| Schedule Variance | 3 | Inspection cross check | Monthly | 0% variance with 10% tolerance | MS Project for forecast baseline is one of the most favourable plans for determining the quality of schedule variance of a project. | Schedule of the project |
| Customer Service Index | 4 | Audit | Pre-project and post-project frequency | 95% with 10% variance | Comparison of the index before and after implementation can help to analyse the quality of customer services provided to the customers of the NHS. | Surveys |
| Major Defects per business process | 5 | Mathematical Check | Monthly | 0% with 20% tolerance | Inspection by a quality manager can help an NHS to analyse major defects per business processes in NHS project development of mobile services. | Defect Log |
Table 6: Quality plan
(Source: MS Word)
The table above shows the quality plan of this project of building mobile services for the NHS near Lutron Campus. The quality plan of this project involves various measures, units in which the measures are evaluated, frequencies, plans, and source of data. The first measure of a quality plan of this study is the effect of defect management which has been measured in percentage. The frequency of this measure has been measured at the end of each iteration process. The target unit of this measure is 99% with 5% of tolerance and the plan to achieve this measure is to analyse proper reasons for deviations along with the severity of the effect. Proper data to evaluate the effect of defects that occurred in this project can be achieved by dividing the defect removed by the defects found and then multiplying the sum into 100.
The second measurement is the requirement volatility which is observed at a monthly frequency and has a target of 99% with 3% tolerance. Changing the effort log and estimating the efforts are major plans for achieving this measure. Schedule variance, customer service index, and major defects are other measures of quality planning of this project. The frequencies of all these measures are observed monthly (Susilowatiet al.2021). The targets of these measures are 0% with 10% tolerance, 95% with 10% tolerance, and 0% with 20% tolerance respectively. Plans for achieving these measures are MS project, comparison of an index, and inspection by project manager respectively. These measures can be achieved with the help of a defect log, surveys, and scheduling the project.
8. Critical discussion of Lessons learned from the project
After working on the project to create an NHS mobile healthcare service near the Luton campus aimed at looking after the welfare of the students has taught me a lot of aspects about project management. However, I have also come across several issues while developing this project. The following recommendations will help in reducing those issues observed.
Recommendation 1: Need for Communication
One of the major issues I found was the lack of communication present between the stakeholders and also between the team members involved in developing the project. The presence of miscommunication hampers the development of the project (Chandra, 2017). This can be improved by maintaining transparency in the projects and conducting regular meetings with the stakeholders. It can also be made easier by using project management tools that help in keeping everyone updated.
Recommendation 2: Need for accountability
The issue of accountability was also very much observed by me while developing this project. The lack of accountability of a few team members caused snags and delays as these people failed to understand and maintain their roles in the project. This issue can be mitigated by regular briefing and updates from the team members, and using a project management tool that tracks the members’ progress (Chawla et al. 2018).
Throughout the project, I was also able to learn certain hard skills like ITIL and PRINCE 2. The use of ITIL helped me gain a better understanding of how to standardize the different procedures required while conducting a project. It also helped in teaching me how to improve efficiency. The use of PRINCE 2 taught me how to emphasize dividing up the projects and make them more manageable and easier to control (Hughes et al. 2017). I learned that the use of this method is flexible and hence can be put to use easily.
I was also able to develop certain soft skills through the phase of the project like learning how to work in a team and developing my leadership skills. Teamwork helped me learn more about coordination and cooperation and helped in increasing my efficiency. Learning leadership qualities taught me how to be more responsible and lead a team. It also taught me about the various ways how a leader influences and encourages its team members to work better.
As the project was being conducted I also learned a great deal about my strengths and weaknesses and the effect they had on my working style. The major strengths that I found were my ability to be perceptive about the needs of the project. I also found that when it came to making critical decisions, I was able to be calmer and more focused compared to my peers. I also found that my strengths lay in the knowledge of different project management tools that helped my peers greatly. However, I also came across several weaknesses, one of which was my ability to properly communicate with others. I also found that I was not very proficient when it came to time management. I also found that I often felt restless which made it difficult to concentrate on the tasks at hand.
Reference List
Afzal, A. and Gauthier, J.B., 2017. Project management and practitioners in the health sector: From the Quebec healthcare system perspective to pm literature review. Available at: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01579996/file/PROJECT%20MANAGEMENT%20AND%20PRACTITIONERS%20IN%20THE%20HEALTH%20SECTOR.pdf
Borkovskaya, V., 2018. Project management risks in the sphere of housing and communal services. In MATEC Web of Conferences (Vol. 251, p. 06025). EDP Sciences. Available at: https://www.matec-conferences.org/articles/matecconf/pdf/2018/110/matecconf_ipicse2018_06025.pdf
Boy, W., Imani, R. and Noviani, N.T., 2021, April. Identification of constraint factors on the contract quality plan for the BatangKuranji sediment control development project, Padang City. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science (Vol. 708, No. 1, p. 012091). IOP Publishing. Available at: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/708/1/012091/pdf
Chandra, N., 2017. Do Project management competencies influence the project performance? An Insight at Philips Healthcare. Wageningen University and Research Centre. Available at: https://edepot.wur.nl/425751
Chawla, V., Chanda, A., Angra, S. and Chawla, G., 2018. The sustainable project management: A review and future possibilities. Journal of Project Management, 3(3), pp.157-170. Available at: http://m.growingscience.com/jpm/Vol3/jpm_2018_6.pdf
Demirkesen, S. and Ozorhon, B., 2017. Impact of integration management on construction project management performance. International Journal of Project Management, 35(8), pp.1639-1654. Available at: http://www.projcp.com/Readings/180329%20Integration%20management.pdf
Gordon, A. and Pollack, J., 2018. Managing healthcare integration: Adapting project management to the needs of organizational change. Project Management Journal, 49(5), pp.5-21. Available at: https://www.academia.edu/download/57159572/Gordon___Pollack__2018.pdf
Gül, M., Güneri, A.F. and Güneş, G., 2017. Project management in healthcare: A case study for patient flow evaluation in an emergency room using fuzzy cpm and fuzzy pert. Sigma, 8(1), pp.41-51. Available at: https://eds.yildiz.edu.tr/ArticleContent/Journal/sigma/Volumes/2017/Issues/1/YTUJENS-2017-8-1.1716.pdf
Hughes, D.L., Dwivedi, Y.K. and Rana, N.P., 2017. Mapping IS failure factors on PRINCE2® stages: An application of interpretive ranking process (IRP). Production Planning & Control, 28(9), pp.776-790. Available at: https://bradscholars.brad.ac.uk/bitstream/handle/10454/18078/57-32507.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y
Kušar, M. and Šelih, J., 2017. Challenges in BMS quality plan development. Life-cycle of engineering systems: Emphasis on sustainable civil infrastructure, pp.1526-1531. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Matej-Kusar-2/publication/314457981_Challenges_in_BMS_quality_plan_development/links/5b35faf00f7e9b0df5d865ec/Challenges-in-BMS-quality-plan-development.pdf
Ma, X., Xiong, F., Olawumi, T.O., Dong, N. and Chan, A.P., 2018. Conceptual framework and roadmap approach for integrating BIM into lifecycle project management. Journal of Management in Engineering, 34(6), p.05018011. Available at: http://ira.lib.polyu.edu.hk/bitstream/10397/78061/1/Ma_Conceptual_Framework_BIM.pdf
Moshtaghian, F., Golabchi, M. and Noorzai, E., 2020. A framework to dynamic identification of project risks. Smart and Sustainable Built Environment. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Farzaneh-Moshtaghain/publication/340168888_A_framework_to_dynamic_identification_of_project_risks/links/5f74dbeba6fdcc00864b8cf5/A-framework-to-dynamic-identification-of-project-risks.pdf
Müller, R., Drouin, N. and Sankaran, S., 2019. Modeling organizational project management. Project Management Journal, 50(4), pp.499-513. Available at: https://biopen.bi.no/bi-xmlui/bitstream/handle/11250/2633658/Muller_Modelling_AM.pdf?sequence=1
Muriana, C. and Vizzini, G., 2017. Project risk management: A deterministic quantitative technique for assessment and mitigation. International Journal of Project Management, 35(3), pp.320-340. Available at:https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Cinzia-Muriana/publication/312875787_Project_risk_management_A_deterministic_quantitative_technique_for_assessment_and_mitigation/links/59d0a45a0f7e9b4fd7f9faf1/Project-risk-management-A-deterministic-quantitative-technique-for-assessment-and-mitigation.pdf
NHS., (2021), Home Page, Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/ [Accessed on 1st September, 2021]
Papke-Shields, K.E. and Boyer-Wright, K.M., 2017. Strategic planning characteristics applied to project management. International Journal of Project Management, 35(2), pp.169-179. Available at: https://fardapaper.ir/mohavaha/uploads/2017/10/papkeshields2017.pdf
Radujković, M. and Sjekavica, M., 2017. Project management success factors. Procedia engineering, 196, pp.607-615. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877705817331740/pdf?md5=5f61431ded9f936c77ffdfc5116c0e79&pid=1-s2.0-S1877705817331740-main.pdf&_valck=1
Stanitsas, M., Kirytopoulos, K. and Leopoulos, V., 2021. Integrating sustainability indicators into project management: The case of construction industry. Journal of Cleaner Production, 279, p.123774. https://www.academia.edu/download/64660997/1-s2.0-S0959652620338191-main.pdf
Susilowati, M., Kurniawan, Y., Prasetiya, H.P., Beatrix, R., Dewa, W.A. and Ahsan, M., 2021, March. How to manage scope, time and cost of project management plan to develop manufacture information system. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 1098, No. 6, p. 062006). IOP Publishing. Available at: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1757-899X/1098/6/062006/pdf
Tereso, A., Ribeiro, P., Fernandes, G., Loureiro, I. and Ferreira, M., 2019. Project management practices in private organizations. Project Management Journal, 50(1), pp.6-22. Available at: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/8756972818810966
Vaníčková, R., 2017. Application of PRINCE2 project management methodology. Studia CommercialiaBratislavensia, 10(38), p.227. Available at: https://sciendo.com/pdf/10.1515/stcb-2017-0021
Wang, X., Ren, A. and Liu, X., 2017, August. Researching on quantitative project management plan and implementation method. In AIP Conference Proceedings (Vol. 1864, No. 1, p. 020176). AIP Publishing LLC. Available at: https://aip.scitation.org/doi/pdf/10.1063/1.4992993
Willumsen, P., Oehmen, J., Stingl, V. and Geraldi, J., 2019. Value creation through project risk management. International Journal of Project Management, 37(5), pp.731-749. Available at: https://fardapaper.ir/mohavaha/uploads/2019/06/Fardapaper-Value-creation-through-project-risk-management.pdf
Assignment Services Unique Submission Offers:


At the beginning, I was still puzzled. Since I read your article, I have been very impressed. It has provided a lot of innovative ideas for my thesis related to gate.io. Thank u. But I still have some doubts, can you help me? Thanks.