107SAM Assignment Sample – Business and Management Statistics 2022
TASK- I
Introduction
The report aims to define the several attributes regarding the university students and develop the factors to ascertain the present relationship. With the university survey conducted on the university campus, it has been developed that the student factor regarding age, location, gender, and domicile would be ascertained within the scope of the survey.
The development of the survey in the educational expertise would lead to ascertaining the commuting time and requirements for the survey. The survey would be conducted based on 150 students aiming to manage the attributes and information for developing the quality. In this survey, the data has been estimated to contain fourteen attributes for structuring the data information and system in the survey.
Analysis of the data
From the data provided, it has been developed that the analysis of the university and students’ information would be initiated along with their domicile and country (Zend and Dong, 2019). The information contains the understudy’s reaction to the ascribes and factors identified with the college students alongside their home, gender, age, area of living arrangement, their work understanding, and instructive foundation. The examination of the example overview will help to assemble and a robust model that can be utilized in the estimation of specific credits identified with students in the college (Wu et al., 2020).
In the specific report, we must research the components such as age, gender, area, and their impact on the driving chance to Coventry University. With the ascertainment of the university, several attributes would be undertaken.
From the survey, it has been observed that the assessment of the factors has been done for about fourteen attributes that influence the survey. The defined survey is based on the several attributes present and developed regarding the different types of people commuting to the university (Valaskova, Kliestik, and Kovacoa, 2018).
The commutation would take a certain period which has been observed uniquely in the case of students with age, gender, and location criteria. This report aims to survey on the topic and build a forecasting model for ascertaining the attributes of the survey (Varivath and Brobbey, 2020). Several factors have been ascertained keeping in mind the differences in the age factor and location factors. Developing several attributes would help in determining the influential age and gender for the university traveling time.
Investigation Factors
Classification A being the student in the age section of 18-19 years, Classification B having a place with the students whose ages extend from 20-21 and finally the students of Classification C running in the age over 21 years. The quantity of students in the age section of 18-19 is 93 and the complete time they took to travel is 3407 mins while 13 students in the age section of 20-21 take around an aggregate of 518 mins. Computing the time taken by students in the distinctive age section, it tends to be distinguished that students in the age section of 18-19 take in normal, 33.58 mins while the students in the section of 20-21 take 38.07 mins.
These currently present an immediate connection between the age of a specific student and their movement time to the college. This implies the expansion in the age has an immediate relationship with an increment in the driving time (Valaskova, Kliestik, and Kovacoa, 2018). This can additionally be fortified by the way that the normal travel time of the students in the age section of over 21 is 50 mins. Therefore, an expanding age fragment infers a progressive increment in driving time.
This ascertains the age growth model formation in the survey suggesting the output regarding the based outcome. The attributes present the belongingness of students with the university based on its traveling time structure. This attribute would help in determining the accurate result from the several aspects brought in with the survey. Thus, the declining of the facts would help in estimating the attributes.
Conclusion
The data and information which has been assessed provide insight into the several attributes which can create and influence on the people. The required models and estimation generated through the statistics have helped in defining the various attributes of a human in selecting an experience. This report presents the time taking utility to the university with the aspects of location, age, gender and domicile, which has ascertained that the students who are the UK domiciled take little time in reaching the university whereas, the international students take more time in deciding for the route to take. Also, young students reach faster than older students which is a natural observation.
TASK – II
Background of the Analysis
A regression analysis has been conducted in the survey report which suggests the investigation for the accommodation to university reaching time assessment. This measures the timing of the students regarding their extra work which forms in between to delay in reaching the university (Sperka and Enright, 2019).
Coventry University would be assessed regarding the regression analysis of the time and would bring out the relationship between the given attributes. Using this analysis, the prediction assessment gets stronger which helps in predicting the relationship through the examples developed (Schroder et al., 2016). With the regression analysis, the two attributes would be ascertained and predict the dependence on each other by the implementation of several factors in the university.
Discussion
A relapse investigation is applied in the information of the number of hours worked in a low maintenance work way and the movement time to college to set up a relationship utilising Excel. For relapse work, the needy variable is set aside as the movement effort to college, while the time expended in work throughout the week is taken as a variable. This information helps in finding the relapse work in exceeds expectations (Sergi et al., 2019).
After finding the relapse work, the relapse condition can be distinguished which characterizes the connection between the two variables. It additionally exhibits the estimation of R square, which features the level of the fluctuation in the needy variable that is commonly clarified through the assistance of autonomous factors.
Scatter plots distinguish critical association between two factors and this basic association between the two factors is otherwise called connection (Rossi, Wright and Anderson, 2013). When the information focuses are accepted to be near one another they sense to show a solid relationship.
Disperse plot is a factual device which assists with breaking down various highlights of the example review, shaping examples and featuring anomalies that would be covered up if the information were simply in a table (Reiss, 2013). The disperse plot made with go time to the college on the flat side and hours take a shot at the vertical hub present with a straight line which is the pattern line which features the type of connection between the factors.
The relapse condition which can be acquired from the relapse examination of the movement time to college a normal time of work in seven days. In this relapse condition, the movement time to college is utilised as the reliant variable while the time expended in work throughout the week is utilised as a free factor (Plonsky and Ghanbar, 2018). The relapse condition taxi is distinguished utilising the relapse line, which is likewise the best fit line for the information. It is generally a normal where all the focuses line up. The relapse condition is essential in making the future forecasts from your information, it is likewise gainful in the signs of past conduct.
Regression equation:
| y=-0.0218x+15.858
R² = 0.0037
|
Here, y refers to and feature a reliant variable and x mirrors the autonomous variable. There exist different focuses in the disperse plot which are not on the pattern line as these are known as the blunder or the leftover information focuses (Naveed and Iqbal, 2016). Lingering esteem figures the separation, for example, vertical in nature between the assessed estimation of y and real estimation of for example contrast in these two information focuses speak to continuing esteem which is spoken to by the hole between the point and the line (Hayter, Ramussen and Rooksby, 2020).
In simple words, it helps in the estimation of the vertical separation between the anticipated point on the line and the genuine information point and based out of the example study (Hiranti and Olorungbohunmi, 2019). The incline for the given condition is – 0.0218, which features the adjustment in the factors and its connection (Montogomery et al., 2012).
If the length of the hours worked increments by 60 minutes, we foresee the movement time to college will increment by around 0.0218 (Stats Direct, 2020). The slant of the best-fit line or the connection line features the connection between the reliant variable (y) and its changes for a unit increment in the free factor.
Slope Interpretation
Slope interpretation is the anticipation of the time travelled which defines the basis to calculate the structure of the survey. If the term of the hours worked is 0 seconds, at that point, we anticipate the time travelled is 15.858 (Statistic Solutions, 2020). So also, an expansion in the hours worked increment from 1 to 2 refers to an expansion of 15.88 mins in the time travelled.
Intercept
From the survey, the intercept has been ascertained to be the coefficient factor of several determinations of multiple records. R-squared, for the most part, investigates the information focused which are situated around the best-fitted relapse line (Sperka and Enright, 2019). The R-squared is additionally named as the coefficient of assurance, or the coefficient of numerous assurances for the most part in the different relapse with huge informational indexes with various variable focuses and factors (Hiranti and Olorungbohunmi, 2019).
R-squared refers to what could be compared to the change for a needy variable that is for the most part clarified by an autonomous variable in the straight relapse. R-squared discloses the degree to which the fluctuation or change of one variable clarifies the difference of the other variable. R-squared is commonly esteemed somewhere in the range of zero and one and a low R-squared figure is commonly a negative image for the awful forecast model condition, for the most part, a higher R-squared shows a model which is better fitted to make sensible expectations (Seeing Theory, 2020).
R-squared in the given example is 0.0037 which in nature refers to that the connection between the hours worked and the time taken to head out to the college. These speak to a low connection coefficient that implies that they do not clarify the qualities of one another. These characterise that the watched variety can be distinguished not exactly a solitary rate utilising the model info esteems. Using the information in the relapse condition, we can evaluate the long periods worked by students at a specific college (Misuri et al., 2019). Putting the estimation of one variable will help in the estimation of the other variable utilising the relapse condition.
From the following equation,
y=-0.0218x+15.858
If the time spent on the movement to the college is around 15 minutes, at that point placing the incentive in the condition,
15= – 0.0218x+15.858
0.0218x=0.858
X= 39 mins
This suggests when the time taken to head out to the college is around 15 mins that on a normal that student work low maintenance for around 39 hours all through the whole week. This condition helps in the ward or the free factor on the off chance that the time taken in the movement excursion to the college is around 20 minutes, at that point placing the incentive in the condition,
20= – 0.0218x+15.858
0.0218x=5.858
X= 268 hours
This infers when the time taken to head out to the college is around 20 mins that on a normal that student word for around 268 hours all through the whole week. The qualities determined in the entireties indicates the conceivable inconsequentiality of the relapse model to characterise and evaluate the relationship (Valaskova, Kliestik and Kovacoa, 2018). The factors in the specific relapse model can be named to be not measurably critical as it displays a lower connection between the hours worked in a week and the movement time to the college (Lumen learning, 2020).
The relapse model contains a free factor that is factually immaterial and exhibits a sensibly lower R-squared worth. The measurable criticalness demonstrates the relative changes in the free factors which associate with shifts in the needy worth. A decent R-squared worth connotes that the model introduced clarifies a decent and huge extent of the fluctuation or changes in the reliant variable (Lee et al., 2019). This variable produces a certainty with the conditional fluctuations. The survey would lead in estimating the several factors to ascertain the university task and begin with a proper regression calculation for the future analysis.
TASK- III
Introduction
A system outline in management the board shows the general span of the undertaking exercises and their conditions between exercises in a graphical portrayal as a table. The system outline distinguishes the request for work where these should be finished utilising coherent connections between various related exercises (Kyalheim, 2020).
System chart, for the most part, helps in characterising the best and ideal way for finishing the exercises and the task, and it is additionally valuable in arranging and booking of the grouping of various works (Valaskova, Kliestik and Kovacoa, 2018). Alongside estimating the progressing execution and mirroring the proposed and acknowledged changes, the drawing of the system outline needs certain estimates which ought to be taken sequentially first being the readiness of the rundown of the exercises remembered for the task and their reliance on different exercises (Kott, 2007).
After the rundown of exercises shave been assessed the following most significant thing is the estimation of the time timetable of every one of the above-expressed exercises. These estimations and suppositions depend on measurable approach and experience. At that point booking calculations are done to get a gauge of the most punctual beginning and finish times for every action, to recognise basic way and to demonstrate the measure of slack on non-basic ways (Hiranti and Olorungbohunmi, 2019). These, when shaped, are assessed all the time to gauge in the opportune development of these exercises inside the expressed timeframe.
Discussion and Analysis
The system diagram which is readied utilising the information from the table has been used to recognise the best basic way for the specific undertaking. The table gives a rundown of 11 distinct exercises which are to be finished in the whole undertaking. These exercises have a reliance on the first movement, for example, the following movement must begin once the past action or the depending action have been finished (Hayter, Ramussen and Rooksby, 2020).
These exercises likewise have an alternate period in a week for specific exercises to be finished. These exercises will accordingly help in giving the most ideal and the base time taken to finish the general various exercises of a task. The undertaking here comprises of dispatch of the specific item whose earlier exercises have been clarified with their pertinent time to look a comprehension of the general time which is required to dispatch the item in the market.
Table: 1
| Activity | Description | Proceeding Activity | Duration (in weeks) |
| A | Approval of training budget | 1 | |
| B | Training of service staff | A | 9 |
| C | Training of sales staff | A | 3 |
| D | Sales promotion to distributors | C | 4 |
| E | Distribution to distributors | D | 2 |
| F | Distribution to retailers | E | 4 |
| G | Advertising brief | A | 2 |
| H | Advertising contract | G | 1 |
| I | Illustrations and text | H | 4 |
| J | Printing | I | 4 |
| K | Product Launch | B, F, J | 1 |
| (Refer to Excel Sheet )
|
Utilising the table above for the development of system chart, dispatch of the item can be drawn, where the sum of what exercises have been swaggered in a graphical way referenced in index 1.
Alongside the system outline, a technique which is utilised in the planning exercises in management is the Precedence Diagramming Method (Gwon et al., 2020). The starter step in this is the arrangement to take a shot at the breakdown of the general structure as, this separating of various initiates helps in completing the exercises on schedule.
The Precedence chart technique catches diverse advance which is the forward pass computation and the retrogressive pass figuring alongside skim. The advances pass computation species and feature the base timespan in which every one of the exercises can be properly performed and it connotes the base span of the management. The retrogressive pass estimation, as a rule, decides the most recent timeframe by which every action can be finished without expanding the general least term (Daoud, 2017).
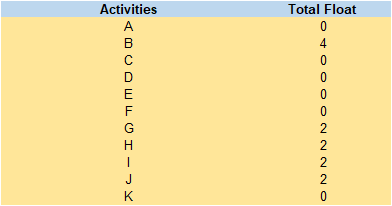
The total float is the measure of time that a movement can be deferred without postponing the management rivalry at a predefined date. The exercises delivering an all-out total float which is zero is the basic way in the system chart. These have been recognised in the development of the system outline and can be clarified utilising the reference section. The ES or the Early Start in informative supplement 2 aides on the distinguishing proof of the base time in which management can be expressed while LS speaks to the poor start. In our count of the system outline, solid start number is for the help in comprehension is composed at the upper left corner of movement box, and early completion is introduced on the upper right corner (Hayter, Ramussen and Rooksby, 2020)
. A poor start and the late completion shows the most recent time a specific movement on a system way can begin and finish (Austic and Merlo, 2017). Likewise, Late beginning number or the LS is composed at the base left corner of various movement, and late completion on the base right corner (Seeing Theory, 2020). The all-out total float is the measure of time in weeks in this specific case is a movement that can be postponed without influencing the end date of the task.
The basic way is in the general arrangement of the exercises in a specific task which is finished inside the time for management to finish inside the expressed due date. Any action on the basic way cannot begin until when its first movement is finished (Hayter, Ramussen and Rooksby, 2020). If action is late by a multi week, at that point the entire undertaking will bring about deferral of the multi week (Daoud, 2017). Encouraging start in the task when included with the term of a movement results into the early completion.
At the same time, late completion when deducted from the term computes poor start. After the count of the early stars and poor start alongside the all-out total float, we can work out to locate the basic way through the system chart. The basic way is the arrangement of various exercises inside the system chart with zero absolute total floats.
The basic way for the concerned task, for example, the undertaking of management dispatch can be assessed utilising the most ideal and the base time wherein the task can be finished. The basic way for the specific task is
Action A – Activity C – Activity D – Activity E – Activity F – Activity K
The time which it takes to finish the task utilising the above way is the 15 weeks. These ways have been concealed in dark to separate this basic way in different ways. This basic way contains action which it has an all-out total float of 0. The all-out total float speaks to the time inside which a movement can be deferred without influencing the fulfilment date of the specific undertaking. The absolute total float for every one of the movements is tried in the table beneath:
Table: 2
(Refer to Excel Sheet )
The total span for the above undertaking is that management which has a general rationale to dispatch the item and it contains various exercises which the organization needs to bring about in a sequential request to guarantee convenient fulfilment of every movement (Aiello and Bonanno, 2016). The system chart help in the foundation of the basic way which will at that point help in the least time in which the task is finished. Following the basic way in the specific undertaking, the base time in which the task can be finished is 15 weeks (Austic and Merlo, 2017). This guarantee that all the exercises have been finished a convenient stage with an affirmation of the general estimation of various exercises.
Conclusion
The dispatch of specific management considers the opposition of various exercises which are interdepend on every one of the exercises and these can be assessed utilising the system chart as this will furnish with the base prong outline in which the specific undertaking is finished, completing the former action. Utilising the vital of solid start, poor start, early completion, late completion, and all-out total float we can recognise the basic way which guarantees the base time where the item can be propelled. The time in which the specific item can be propelled is 15 weeks, which guarantee the convenient way of the culmination of all the former action.
Reference List
Aiello, F. and Bonanno, G., (2016). Efficiency in banking: a meta-regression analysis. InternatIonal revIew of applIed economIcs, 30(1), pp.112-149. 10. Sajad, M., Sadiq, M.,
Austin, P.C. and Merlo, J., (2017). Intermediate and advanced topics in multilevel logistic regression analysis. Statistics in medicine, 36(20), pp.3257-3277
Daoud, J.I., (2017), December. Multicollinearity and regression analysis. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 949, No. 1, p. 012009). IOP Publishing.
Fedorov, V.M., Grebennikov, P.B. and Frolov, D.M., (2020). Russian Arctic seas, sea ice extent, annual, interannual and long-term variation, insolation, insolation contrast, correlation and regression analysis. Evaluation, 24(3), pp.38-50.
Gwon, J.S., Toh, G.M., Kim, W.S. and Park, J.H., Industry Univeristy Cooperation Foundation Hanyang University, Hyundai Motor Co and Kia Motors Corp, (2020). Method for predicting clamp force using convolutional neutral network method. U.S. Patent Application 16/691,308.
Hayter, C.S., Rasmussen, E. and Rooksby, J.H., (2020). Beyond formal university technology transfer: Innovative pathways for knowledge exchange. The Journal of Technology Transfer, 45(1), pp.1-8. 13.
Hiranto, P. and Olorungbohunmi, L., (2019). CAPM: Correlation and Regression 10 Stocks Comparing With Market Index. Available at SSRN 3319147.
Kerzner, H., 2019. Using the project management maturity model: strategic planning for project management. John Wiley & Sons.
Kott, P.S.(2007). A model-based look at linear regression with survey data. The american statistician, 45(2), pp.107-112.
Kvalheim, O.M., (2020). Variable importance: Comparison of selectivity ratio and significance multivariate correlation for interpretation of latent‐variable regression models. Journal of Chemometrics, 34(4), p.e3211.
Lee, J.W. and Manorungrueangrat, P., (2019). Regression Analysis with Dummy Variables: Innovation and Firm Performance in the Tourism Industry. In Quantitative Tourism Research in Asia (pp. 113-130). Springer, Singapore.
Levine, H., Jørgensen, N., Martino-Andrade, A., Mendiola, J., Weksler-Derri, D., Mindlis, I., Pinotti, R. and Swan, S.H., (2017). Temporal trends in sperm count: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Human reproduction update, 23(6), pp.646-659.
Lumen Learning (2020) The Regression Equation | Introduction to Statistics. Available from: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/introstats1/chapter/the-regression-equation/ [Accessed 29 July 2020].
Menard,S .(2000). Coefficients of determination for multiple logistic regression analysis. The American Statistician, 54(1), pp.17-24.
Misuri, A., Khakzad, N., Reniers, G. and Cozzani, V., 2019. A Bayesian network methodology for optimal security management of critical infrastructures. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 191, p.106112.
Montgomery, D.C., Peck, E.A. and Vining, G.G., (2012). Introduction to linear regression analysis (Vol. 821). New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons.
Naveed, K. and Iqbal, M.S., (2016). Software Project Management: Tools assessment, Comparison and suggestions for future development. International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security (IJCSNS), 16(1), p.31.
Plonsky, L. and Ghanbar, H., (2018). Multiple regression in L2 research: A methodological synthesis and guide to interpreting R2 values. The Modern Language Journal, 102(4), pp.713-731.
Reiss, G., (2013). Project management demystified: Today’s tools and techniques. Abingdon: Routledge.
Rossi, P.H., Wright, J.D. and Anderson, A.B. eds., (2013). Handbook of survey research. Academic Press.
Schroeder, L.D., Sjoquist, D.L. and Stephan, P.E., (2016). Understanding regression analysis: An introductory guide (Vol. 57). Sage Publications.
Seeing Theory (2020) Regression Analysis. Available from: https://seeing-theory.brown.edu/regression-analysis/index.html [Accessed 29 July 2020].
Sergi, B.S., Popkova, E.G., Bogoviz, A.V. and Litvinova, T.N. eds., (2019). Understanding Industry 4.0: AI, the Internet of Things, and the Future of Work. Emerald Group Publishing.
Sperka, L. and Enright, E., (2019). Network ethnography applied: Understanding the evolving health and physical education knowledge landscape. Sport, Education and Society, 24(2), pp.168-181.
Statistic Solutions (2020) Multiple Regression – Statistics Solutions. Available from: https://www.statisticssolutions.com/regression-analysis-multiple-regression/ [Accessed 29 July 2020].
Stats Direct (2020) Regression and Correlation Methods in StatsDirect. Available from: https://www.statsdirect.com/help/regression_and_correlation/regression_and_correlation.htm [Accessed 29 July 2020].
Valaskova, K., Kliestik, T. and Kovacova, M., (2018). Management of financial risks in Slovak enterprises using regression analysis. Oeconomia Copernicana, 9(1), pp.105-121.
Variyath, A.M. and Brobbey, A., (2020). Variable selection in multivariate multiple regression. PloS one, 15(7), p.e0236067.
Wu, X., Geng, Z., Shi, Y., Pham, N., Fomel, S. and Caumon, G., (2020). Building realistic structure models to train convolutional neural networks for seismic structural interpretation. Geophysics, 85(4), pp.WA27-WA39.
Zeng, X. and Dong, J., (2019). Calculation in Seconds for Time-Parameters and Critical Path of the Network Diagram.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:


Thank you very much for sharing, I learned a lot from your article. Very cool. Thanks. nimabi