KB7032 Project Organisations & Information Management
Module code and Title: KB7032 Project Organisations & Information Management
Aim, Objectives, and Scope
Aim of the study is to understand the impact of information management over the success of a project.
Objectives
- To analyze about impact of implementation of information system in organisation settings
- To discuss knowledge management strategies and its installation in a project in organisation
- To highlight about influence of information system in project settings
Scope
The study aims to highlight the impact of different management processes within an organisation. Stakeholders apply an important role in improving the net business process. It includes paying closer attention across various activities and thus highlighting the contribution of expertise over the management process.
Comprehensive understanding of information and organizational needs to achieve
Stakeholder management is an essential element for any business organization for the success of the projects of the business and overall success of the organization. As opined by MacDonald et al.(2019), stakeholders may play a critical role in making or breaking the success of a project. Therefore, it is critical to gain the trust of the stakeholders and ensure that they are happy with the project to ensure a successful completion of the project. Thus as opined by Xu and Saxton, (2019), engaging stakeholders especially during the beginning of the project may have significant impact on uncovering the underlying risks and and increase their involvement within the project.
The organization therefore needs to keep the stakeholders engaged within a project such that analysis of various parameters may take place. The stakeholder has a significant contribution in providing expertise within a project and insights of the industry. As opined by George et al.(2019), the involvement of all the stakeholders during the gathering of the requirements of the project may contribute to missing out on any significant information that may be important for the project.. The stakeholders within an organization play a critical role in granting acceptance for any project. Therefore, as opined by Bacon et al.(2019), both the internal and external stakeholders need significant consideration for ensuring their success within the organization and for achieving the goals and objectives of the organization.
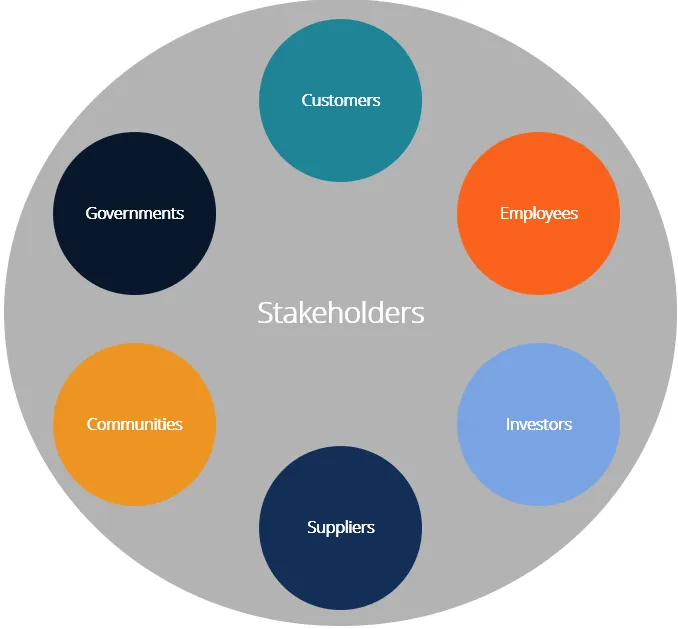 Figure 1: Different internal and external stakeholders of an organization (Source: Manaf et al.2018)
Figure 1: Different internal and external stakeholders of an organization (Source: Manaf et al.2018)
The organization’s success and development is partially dependent upon the stakeholders of the organization as they may have a significant role in influencing the success of any project. Thus, ensuring the engagement of both the internal and external stakeholders is critical for the success of the project. Stakeholders play an important role in the business process. In opinion of Ameer et al. (2022), understanding the management process helps in improving employee coordination. Inclusion of different activities such as employee engagement activity improves the communication process. Collection of necessary information about employees helps in improving the outcome of business. It also includes addressing requirements such as subconscious desire of employees or necessities. News of an organisation is the requirements that help in pushing the business forward. Overall problem understands the influence shared by different management strategies in a project of organisation.
Powerful stakeholder management involves tracking the productivity and efficiency of an organisation through maximising accountability and transparency within the business operations. Thus, as per the views of Bacon et al. (2019), keeping communications aligned with the interests of the stakeholders may contribute to obtaining fruitful outcomes. Businesses exist to meet the needs and expectations of the stakeholders as it may contribute to the business to obtain profit for the investors as well as the owners. Hence, it is critical for an organisation to achieve stakeholder success. As per the views of Derakhshan et al. (2019), the stakeholders’ success will ultimately contribute to the success of the organisation and may have a critical impact on the reputation of the organisation in the market. Therefore, the following steps may ensure fulfilling the requirements and needs of the stakeholders of the organisation:
- Prioritising the stakeholders based on the power and interest within the organisation
- Engagement of the stakeholders in the different decision-making processes
- Communicating the stakeholders about the potential risks and challenges within the project
- Continuous demonstration of the competence of the organisation
Therefore, a stakeholder may have a critical influence on the project and may therefore be critical behind the success or failure of the organisation. As per the views of MacDonald et al. (2019), the organisation must fulfil the needs of the stakeholders to increase the sales and profit rate of the organisation in the market. Therefore, the stakeholders may play a critical role in attaining a competitive advantage in the market over the potential rivals. The potential internal stakeholders within the organisation include project sponsors, team, owners, and any individual that has input within the project. However, the external stakeholders include customers, vendors, Government, auditors, shareholders, and others. Therefore, as opined by Nasr et al. (2019), the organisation needs to identify the strategies of both the internal as well as the external stakeholders to maintain a balance within the project and thus contribute to the success of the stakeholders and ultimately the success of the project and organisation.
Strategic importance of knowledge and organizational learning at different levels
Organizational learning is a process through which an organization may undergo significant improvement over a certain time through experience and development of knowledge. As opined by Antunes and Pinheiro, (2020), organizational learning is critical for all the organizations as the retention, creation, and development within the organization may contribute to significant strengthening of the organization. The importance of organizational learning includes:
- Decreased turnover rates
- Increased job satisfaction
- Increased efficiency, profits and productivity within the organization
- Development of leaders at different levels
- Increase in adaptability throughout the organization.
Organizational learning therefore, contributes to development of a learning culture that may help in implementation of competitive learning within the organization. As opined by Oh, (2018), four major levels of organizational learning are as follows:
Individual
Organizational learning may have significant contributions to individual growth and development that may have a critical role in improving the efficiency and improvement of overall performance. Therefore, as opined by Basten and Haamann, (2018), the individual growth within an organization is closely associated with organizational learning and may have a significant contribution in personal growth and development.
Group or team
Organizational learning is a great way of learning in groups or teams as it helps in understanding the importance of moving with the team. As opined by Fischer et al. (2020), organizational learning may significantly contribute to the growth and development of the team through helping and supporting each other under critical and uncertain situations. Therefore, organizational learning may imbibe the essence of empowerment through working in teams and may help in development of leadership qualities within the individuals.
Organizational
The organizational level learning is a critical level of learning where the organization experiences significant growth along with the growth and development of the employees within the organization. As opined by Kompen, et al.(2019), embedded systems learning enables organizational learning directly through the system and includes workflow systems, learning management systems, and operational and process systems.
Inter-organizational level
Organisational learning is critically important for retention, creation, and transfer of knowledge within the organisation that may substantially contribute to the strengthening of the organisation as a whole. As stated by George et al. (2019), conceiving, acting, and reflecting are the three main actions that need significant consideration by the organisation. Thus, these actions may have a significant contribution to knowledge creation, knowledge transfer, and knowledge retention. Organisational learning at different levels may have a significant contribution to upgrading the skills of the existing employees thereby leading to a significant increase in the efficiency of the employees. As opined by De Weger et al. (2018), the increase in efficiency of the employees may have a significant contribution to the increase in efficiency and productivity of the organisation. Thus, organisational learning at different levels may imbibe a positive impact on the productivity of the organisation on a long-term basis.
Organisational learning has a direct impact on the growth and development of the organisation within the domestic as well as international market. As per the views of Vargas et al. (2019), the competition is growing extensively and to survive in the market it is essential to keep upgrading with the changing trends in the market. Thus, organisational learning may contribute to coping with the changing trend and demands of the customers in the market. Thus, as stated by Antunes and Pinheiro, (2020), learning is a process that never stops and is a continuous process that may result in continuous improvement. For instance, technology has taken over the corporate world.
Organisation learning is an important aspect as without it the entire work process can get affected. In opinion of Danijela et al. (2022), organisational learning includes understanding efficiency of a work process or improving the job satisfaction rate. It also includes development of leaders at various levels. Lack of organisational learning affects the adaptability of employees with the organisation. Organisation learning also focuses on boosting individual growth as an employee of the business. Organisational learning includes different aspects such as impact of employee behaviour, employee coordination and impact of the working environment over productivity (Letícia Barbosa Gomes et al. 2022). Organisational learning reflects the entire workflow system and thus works on various mergers or acquisition of the company.
Organisational learning involves a collaborative learning process that may contribute to the growth of the employees as well as the organisation collaboratively. The several benefits of organisational learning are as follows:
- Boosting the confidence and morale of the employees
- Increase in the degree of productivity and efficiency
- Encourages accountability and shared ownership
- Development of a culture that promotes adaptability and knowledge sharing
- Attainment of competitive advantage in the market
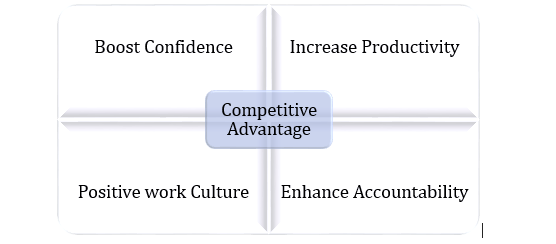 Figure 2: Benefits of Organisational learning (Source: Created by the Author)
Figure 2: Benefits of Organisational learning (Source: Created by the Author)
Therefore, these factors are critical for an organisation and may have a critical role in making a difference within the organisation.
Skills on how to organize and implement support information systems in project settings
For execution of a project, successfully it is critical to efficiently manage and implement the strategies for maintaining a balance and meeting deadlines of the project. As opined by Oh, (2018), continuous monitoring, improvement and efficient management is required for successful implementation of a project. Therefore, the several steps for management, organization, implementation for supporting information systems in the project settings are as follows:
Setting early expectations
Setting early expectations may help the employees and other staffs understand the quality of work expected from them, along with the efficient distribution of responsibilities.
Following a template
Following a template may contribute to an efficient working process and may help in providing a roadmap for the steps required for successful implementation and completion of the project.
Continuous review of progress against a project plan
Reviewing the progress against the project plan will contribute to identification of mistakes and monitoring the quality of the process involved in the project.
Set up of deadlines
Setting up deadlines may be critical for completion of the project within an expected time-period and may have a significant contribution in increasing the efficiency of the employees.
Development of efficient filing system
Documentation may be critical for keeping a track of the project and may help in preserving the important information associated with the project.
Researchers use various skills for the organization and execute support information systems in project settings such as operations management and decision-making. According to the views of Gajdzik and Wolniak, (2022), decision-making is significant in a business entity in making sure that the business authorities are required to make decisions every time. Besides these, data presented, compiled, and collected in a usual path supports managers recognize the organizational position and take proper decisions. As commented by Ryohei Matsumura, et al. (2022), operations management is another skill to organize and implement support information systems in project settings. In this context, it is useful for conducting daily operations in a business organization. According to the views of Oyemomi, et al. (2019), besides these, operations management and daily tasks are important to follow up or keep records on inventory, creditors, and supplies made more convenient with the assistance of the information system. Besides these customer interactions are other helpful skills in this context that assist in making the interaction between the potential consumers within a project operation. Apart from that, team collaboration, as well as strategic initiatives skills, helps organizations in the interaction between various people involved in a specific project.
Systems implementation within a project helps in understanding how to build the information system within the project such that maximum stability and productivity is attainable for the project. According to Basten and Haamann, (2018), the information system is critical for operational management. It alsoensures maintenance of quality standards within the project setting. Hence, organisation of information within a project is critical for controlling the flow of data within the project, planning, management, monitoring, and execution of the project with efficiency. Thus, the information system may be managed within a project through the following steps:
- Determining the critical role of information
- Assigning roles and responsibilities for managing the working of information system within the project
- Development of information resources along with transparent policies
- Performing Audit of the information
- Linking with the management processes
- Optimisation of the operations of the information system within the project
These factors may therefore contribute to a critical understanding of the organisation process for the information system within the project. Thus, as per the views of Oh, (2018), system implementation is significantly important for making it available for the use within the project. Information systems may therefore have a critical role in the storage of data, documenting, keeping records, and revising histories that are critical to the project.0020The benefits of organising and implementing an information system within the project settings are as follows:
- Reduction of communication gaps between the project heads and employees
- Significant tracking of the operational steps within the project
- Increase in the transparency of operations within the system
- Identification of risks and challenges within the project
- The smooth functioning of the project
- Meeting the deadlines of the project with increased efficiency
These factors may therefore be critical for the completion of the project and efficient organisation and implementation of the project may have a critical contribution in turning it into a reality. As opined by Naqshbandi and Tabche, (2018), efficient organisation and implementation of the information systems within the project may have a substantial influence on the reduction of overall costs involved within the project. Thus, the information system reduces costs and increases reliability and surveillance within the project, which may be beneficial for the outcomes of the project.
Capability to embed adopted knowledge management strategies to host and project organizations
Implementation of knowledge management strategies within an organization aims to develop changes within the management strategy. In accordance with the journal opinion of Radcliffe, et al. (2018), the identification of significant processes within knowledge management aims to increase the operational efficiency of the organization. Knowledge management platforms across different departments of the business help to share information with employees. As said by Michels, et al. (2020), Successful implementation of knowledge management strategies aims to improve job efficiency. Adoption of knowledge management strategies focuses on identifying any form of problems within the document process. Effective solution to the problem significantly drives the process of adoption of knowledge management strategies in order to host a project organization.
Knowledge management initiatives also include involvement of leadership strategy as well. One significant goal in terms of leadership strategy includes the active participation of every member of the team. According to journal discussion, assessment of current stature helps to evaluate the gap between the current organization states to desired organization state. Adoption of knowledge management strategies helps to identify problems within the business. According to the views of Ryohei Matsumura, et al. (2022), it also significantly includes solutions in terms of target users of the business. Knowledge management strategies also help to implement knowledge management tools within the business process. It also helps in the collection of valuable information for implementation. It maintains a competitive advantage within the highly competitive business environment as well.
Adoption of knowledge management strategies within project organizations helps to address the fragmented structure existing within the system. It also significantly considers obstacles in the path of implementation of knowledge management strategies. Different forms of Knowledge management strategies such as research and insight libraries as well as learning management systems help to improve activities within the knowledge management process. Knowledge management strategies help to store analyses as well as organize different techniques within the knowledge management strategy. According to a journal discussion of strategies of knowledge management such as “intelligent techniques” or “knowledge work system” helps to improve the collaborative flow.
Development of the ability for embedding knowledge management (KM) may be critical for planning to strengthen the operations and projects carried out within the organisation. Thus, as per the views of González-Valienteet al. (2019), the implementation of appropriate knowledge management strategies may have a critical role in benefiting the stakeholders as well as organisation. Hence, the development of strategies for knowledge management may contribute to the following:
- Increasing understanding and internal awareness about knowledge management
- Develop a strong business for getting optimum benefits for the organisation
- Gathering resources for the implementation of strategies
- Communication of efficient knowledge management practices and the plans for achievement of goals
- Tracking the processes within the organisation
 Figure 3: Impact of KM Strategies (Source: Created by the Author)
Figure 3: Impact of KM Strategies (Source: Created by the Author)
Embedding an adopted knowledge management strategy is critical for hosting and project organisations. As stated by Barley et al. (2018), building a KM strategy may help in efficient planning that may contribute to the attainment of competitive advantage by the organisation. Therefore, governance, technology, management, application, culture, and content management are some of the key components of KM strategy. As per the views of Dabićet al. (2019), it is essential to make the employees understand the importance of knowledge management for hosting and management of the projects within an organisation. Therefore, developing the ability to embed the adopted KM strategy requires critical thinking, communication, identification, networking, adopting best practices, and the development of appropriate policies. Thus, implementation of developed knowledge management may take place as follows:
- Establishment of the objectives and goals
- Development of a strategy for change management
- Involve significant leadership practices
- Assessment of the current status critically
- Establishment of the core capabilities
- Development of a roadmap
- Implementation of the roadmap
Therefore, embedding adopted KM strategies to host and project organisation may have a significant influence on the satisfaction, morale, and happiness of the employees within the workplace. Thus, as stated by Veer-Ramjeawon and Rowley, (2020), the development of the ability to embed KM strategy is highly critical and requires significant skills and knowledge for efficient implication. The ability to embed KM strategy may foster innovation and cultural changes that may help increase the engagement of the employees along with the evolution of the organisation. As per the views of Sklyaret al. (2019), the ability to embed KM strategy may develop within an individual through assessment, monitoring, tracking, and strategic thinking that may ultimately provide significant benefits to the project, employees associated with the project, and the organisation.
Embracing inquisitive thinking, and professional reflexivity for project organizations
Professional reflexivity is useful for denoting activities that treat attention back to the project stakeholders and enhance a circular connection between the object and subject. According to the views of Gomes, (2018), on the other hand, non-reflection activities are those that differentiate an object from a subject, generated by influence, in a temporal or linear connection. In this context, every style rests on a various epistemology and guides to various paths of knowledge searching. As commented by Archer-Brown and Kietzmann, (2018), research can use quantitative or qualitative techniques in a particular project using focus groups, observations, and surveys are usually considered methodical issues. In this context, project managers influence the participants of their project by contaminating both the outcome and procedure. On the other hand, reactivity is not present as the issue which needs to be overcome or minimized but as a mandatory element in knowledge creation. Besides these, it is always practical within the project object and involved people within the project share the encounter. As cited by Oliva and Kotabe, (2019), it affects the research in becoming the collaborative making of knowledge rather than the knowledge exploration supposed to exist.
There are particular issues within project operation that are usually unique to the participants within a project. According to the views of Martins, et al. (2019), there are some contingency and iterations plans that need development. In this context, consideration of the leader for a project organization is significant in enhancing the project performance through training and development of the participants within that project.
Inquisitive thinking acts as a mental exercise that is an outcome of curiosity that may have a critical impact on making the mind stronger to a significant extent. As per the views of Neveuet al. (2019), inquisitive thinking makes the mind think beyond what one can imagine and makes the mind observant of innovative and new ideas. Hence, a curious mind may lead to anticipate new ideas beyond the imagination and thinking of the mind. As opined by Odendaal and Levänen, (2019), inquisitive thinking may enable an individual to celebrate mistakes, and always has a “never give up” attitude that makes them different and unique from others. Thus, inquisitive minds may help in getting more knowledge of different topics due to a never-dying urge of curiosity. An inquisitive person always tries to get a piece of in-depth knowledge about the topic of interest and may choose extreme mediums to get to the details of the topic. Hence, embracing inquisitive thinking may promote fostering new ideas for the project organisations and may imbibe positive impacts on the project.
Reflexivity is critical for evaluating one’s own beliefs, practices, and judgments during the project that may have a significant influence on the research. Hence, as per the views of Kuhnke and Jack-Malik, (2019), professional reflexivity gives rise to urges that help in developing strategies to analyse own values, assumptions, and beliefs, to understand complex relations with others or within a project. Thus, as per the views of Marusinetset al. (2020), this may have a significant contribution to increasing personal efficiency and performance within the project along with inspiring others to do better at the workplace.
Reflective practices in project management may enable experience, analysis, and action that may be critically applied by the professionals to improve their technical skills within the project. As stated by Masood and Egger, (2019), reflexivity may have a significant contribution in assessing professional performance to make improvements that may contribute to improving abilities and knowledge about the project. Therefore, embracing inquisitive thinking and professional reflexivity may have a critical impact on the productivity, and efficiency of the project that may help in enhancing the success rate of the project.
Methodology
As per research objectives, the study aims to hold a qualitative research process on the given topic. The output of the study aims to understand the influence of industrial practice over employee growth. It also includes understanding the influence of different government policies.
Recommendations
Solution of problem
One primary solution of the problem is conduction of qualitative study of the topic. It helps in clearing the concept and thus reflects about necessary changes needed for industrial development.
Improvement of research Process
One primary step in improving the research process includes identification of right and appropriate research methods and strategy . In view of Deep et al. (2022), selection of the right research strategy improves the net quality of the research process. It also includes selection of the right research design and research approach.
Conclusion
The study concludes that development of understanding regarding organisational learning and organisational behaviour helps in improving the working process. It concludes that a coordinated working approach improves the outcome of various business activities. Improving knowledge base also helps in devising necessary solutions for the work process. It also includes development of understanding regarding different knowledge sharing activities.
References
Antunes, H.D.J.G. and Pinheiro, P.G., 2020. Linking knowledge management, organizational learning and memory. Journal of Innovation & Knowledge, 5(2), pp.140-149.
Archer-Brown, C. and Kietzmann, J., 2018. Strategic knowledge management and enterprise social media. Journal of knowledge management.
Bacon, E., Williams, M.D. and Davies, G.H., 2019. Recipes for success: conditions for knowledge transfer across open innovation ecosystems. International Journal of Information Management, 49, pp.377-387.
Barley, W.C., Treem, J.W. and Kuhn, T., 2018. Valuing multiple trajectories of knowledge: A critical review and agenda for knowledge management research. Academy of Management Annals, 12(1), pp.278-317.
Basten, D. and Haamann, T., 2018. Approaches for organizational learning: A literature review. Sage Open, 8(3), p.2158244018794224.
Carroll, N. and Conboy, K., 2020. Normalising the “new normal”: Changing tech-driven work practices under pandemic time pressure. International Journal of Information Management, 55, p.102186.
Dabić, M., Vlačić, E., Ramanathan, U. and Egri, C.P., 2019. Evolving absorptive capacity: The mediating role of systematic knowledge management. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 67(3), pp.783-793.
Danijela, C.L., Lalic, B., Delić, M., Gracanin, D. And Stefanovic, D., 2022. How Project Management Approach Impact Project Success? From Traditional To Agile. International Journal Of Managing Projects In Business, 15(3), Pp. 494-521.
De Weger, E., Van Vooren, N., Luijkx, K.G., Baan, C.A. and Drewes, H.W., 2018. Achieving successful community engagement: a rapid realist review. BMC health services research, 18(1), pp.1-18.
Deep, S., Bhoola, V., Vidhani, J. And Pradeep, R.H., 2022. Evaluating The Impact Of Constraints On Project Success: Empirical Study Of Highway Projects. Built Environment Project And Asset Management, 12(4), Pp. 684-700.
Derakhshan, R., Turner, R. and Mancini, M., 2019. Project governance and stakeholders: a literature review. International Journal of Project Management, 37(1), pp.98-116.
Fischer, M., Imgrund, F., Janiesch, C. and Winkelmann, A., 2020. Strategy archetypes for digital transformation: Defining meta objectives using business process management. Information & Management, 57(5), p.103262.
Fischer, M., Imgrund, F., Janiesch, C. and Winkelmann, A., 2020. Strategy archetypes for digital transformation: Defining meta objectives using business process management. Information & Management, 57(5), p.103262.
Gajdzik, B. and Wolniak, R., 2022. Smart Production Workers in Terms of Creativity and Innovation: The Implication for Open Innovation. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 8(2), p.68.
George, B., Walker, R.M. and Monster, J., 2019. Does strategic planning improve organizational performance? A meta‐analysis. Public Administration Review, 79(6), pp.810-819.
Gomes, J.M.V., 2018. Organisational Maturity and Information Systems and Technology Projects in Healthcare: The Mediation of Project Management (Doctoral dissertation, Universidade de Lisboa (Portugal)).
González-Valiente, C.L., Santos, M.L. and Arencibia-Jorge, R., 2019. Evolution of the Socio-cognitive Structure of Knowledge Management (1986–2015): An Author Co-citation Analysis. Journal of Data and Information Science, 4(2), pp.36-55.
Hofmann, P., Samp, C. and Urbach, N., 2020. Robotic process automation. Electronic Markets, 30(1), pp.99-106.
Kompen, R.T., Edirisingha, P., Canaleta, X., Alsina, M. and Monguet, J.M., 2019. Personal learning Environments based on Web 2.0 services in higher education. Telematics and informatics, 38, pp.194-206.
Kuhnke, J.L. and Jack-Malik, S., 2019. Two-eyed seeing, arts-based reflection and collaboration: Reflexivity tools for nursing practitioners working across cultures. European Journal for Qualitative Research in Psychotherapy, 9, pp.48-59.
Letícia Barbosa Gomes, F.F., Bouzon, M. And Diego De, C.F., 2022. An Analysis Of The Effects Of Stakeholders Management On It Project Risks Using Delphi And Design Of Experiments Methods. Benchmarking, 29(3), Pp. 713-734.
MacDonald, A., Clarke, A., Huang, L. and Seitanidi, M.M., 2019. Partner strategic capabilities for capturing value from sustainability-focused multi-stakeholder partnerships. Sustainability, 11(3), p.557.
Manaf, A., Purbasari, N., Damayanti, M., Aprilia, N. and Astuti, W., 2018. Community-based rural tourism in inter-organizational collaboration: How does it work sustainably? Lessons learned from Nglanggeran Tourism Village, Gunungkidul Regency, Yogyakarta, Indonesia. Sustainability, 10(7), p.2142.
Martins, V.W.B., Rampasso, I.S., Anholon, R., Quelhas, O.L.G. and Leal Filho, W., 2019. Knowledge management in the context of sustainability: Literature review and opportunities for future research. Journal of cleaner production, 229, pp.489-500.
Marusinets, M., Kominarets, T. and Fursenko, T.,2020, 3.2. DIDACTIC COMPONENT OF REFLEXIVE-PROFESSIONAL TRAINING OF THE TEACHER. Pre-school education in the context of new Ukrainian school‘s objectives, p.180.
Masood, T. and Egger, J., 2019. Augmented reality in support of Industry 4.0—Implementation challenges and success factors. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 58, pp.181-195.
Michels, C., Hindley, C., Knowles, D. and Ruth, D., 2020. Learning atmospheres: Re-imagining management education through the dérive. Management Learning, 51(5), pp.559-578.
Naqshbandi, M.M. and Tabche, I., 2018. The interplay of leadership, absorptive capacity, and organizational learning culture in open innovation: Testing a moderated mediation model. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 133, pp.156-167.
Nasr, A.K., Kashan, M.K., Maleki, A., Jafari, N. and Hashemi, H., 2020. Assessment of barriers to renewable energy development using stakeholders approach. Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues, 7(3), p.2526.
Neveu, P., Tireau, A., Hilgert, N., Nègre, V., Mineau‐Cesari, J., Brichet, N., Chapuis, R., Sanchez, I., Pommier, C., Charnomordic, B. and Tardieu, F., 2019. Dealing with multi‐source and multi‐scale information in plant phenomics: the ontology‐driven Phenotyping Hybrid Information System. New Phytologist, 221(1), pp.588-601.
Odendaal, A. and Levänen, S., 2019, The Way to Ippokampos: On Memory and Co-authoring. Remarks on a Visionary’s Journey, p.122.
Oh, S.Y., 2018. Effects of organizational learning on performance: the moderating roles of trust in leaders and organizational justice. Journal of Knowledge Management, 23(2), pp.313-331.
Oliva, F.L. and Kotabe, M., 2019. Barriers, practices, methods and knowledge management tools in startups. Journal of knowledge management.
Oyemomi, O., Liu, S., Neaga, I., Chen, H. and Nakpodia, F., 2019. How cultural impact on knowledge sharing contributes to organizational performance: Using the fsQCA approach. Journal of Business Research, 94, pp.313-319.
Radcliffe, V.S., Spence, C., Stein, M. and Wilkinson, B., 2018. Professional repositioning during times of institutional change: The case of tax practitioners and changing moral boundaries. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 66, pp.45-59.
Ryohei Matsumura, R., Asai, M., Nakai, H. and Suzuki, A., 2022. Analyzing the Development of a Remote Debate Program Using Video Annotation through a Systems Approach. Japanese Society and Culture, 4(1), p.9.
Sklyar, A., Kowalkowski, C., Tronvoll, B. and Sörhammar, D., 2019. Organizing for digital servitization: A service ecosystem perspective. Journal of Business Research, 104, pp.450-460.
Vargas, V.R., Lawthom, R., Prowse, A., Randles, S. and Tzoulas, K., 2019. Sustainable development stakeholder networks for organisational change in higher education institutions: A case study from the UK. Journal of Cleaner Production, 208, pp.470-478.
Veer-Ramjeawon, P. and Rowley, J., 2020. Embedding knowledge management in higher education institutions (HEIs): a comparison between two countries. Studies in Higher Education, 45(11), pp.2324-2340.
Xu, W. and Saxton, G.D., 2019. Does stakeholder engagement pay off on social media? A social capital perspective. Nonprofit and Voluntary Sector Quarterly, 48(1), pp.28-49.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

