MBAG FIN 309 Merger And Acquisitions Amazon Assignment Sample
Here’s the best sample on MBAG FIN 309 Merger And Acquisitions Amazon Assignment.
Introduction to Amazon
Amazon is an American conglomerate that was found in 1994 by Mr. Jeff Bozos. It was started by an online bookselling website, but as the time had been passing, it diversified into different areas of products such as media, apparel, body products, consumer electronics, beauty products, gourmet food, groceries, health & personal care items, industrial & scientific supplies, kitchen items, jewelry, lawn & garden items, sporting goods, automotive and sporting goods etc (Aversa et al., 2017).
In this concern, Amazon provides the vital range of products and services to explore more than one segment at a single time period. It offers more than 480 million products by online services in the USA only so that it can serve the wide range of customers. Amazon has a wide geographic presence in more than 100 countries including urban & rural areas and male & female both. In order to diversify its business, Amazon has done many merger & acquisitions with different companies in its life to make it popular and expand its business whole the world. It has done a merger & acquisition with GeoWorks, HomeGrocer.com (1999), CDNow, Egghead Software (2002), Mobipocket.com, smallparts.com (2005), Zappos (2009), Goodreads (2013), Twitch (2014), Harvest.ai, Whole Foods Market, GameSparks, Body Labs (2017) and Ring (2018) etc (Sherer et al., 2016). These are different merger and acquisition that has been done to grab the opportunities for the next growth phase. When Amazon did its starting mergers that time it found these were profitable which motivated Amazon to participate in further merger & acquisition activities.
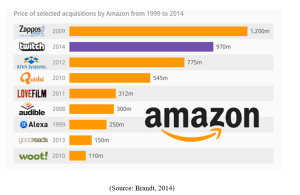
Figure 1: Acquisition by Amazon from 1999 to 2014
Segment Analysis
During the analysis of segment, it is found that Amazon’s segmentation includes a set of activities which are aimed to determine the particular segment of people like customers and produce products and services in order to attract this specific group (Loughran and McDonald, 2016). Being an online retail giant, Amazon deeply focuses on changes in the external marketplace as well as observes continuous increasing customer’s expectations. In this regards, Amazon adopts different types of segmentations such as geographic, demographic, behavioral and psychographic etc. In addition, Amazon acquired ten startups such as Harvest.ai, Thinkbox Software, Do.com, Souq.com GameSparks, Graphiq, Wing.ae, Body Labs, Goo Technologies and Blink Home etc in 2017. These companies were acquired to support the Amazon growth.
Amazon invested its largest amount in acquiring the online shoe retailer Zappos for &1.2 B in 2009, a supermarket chain the Whole Foods for $13.7 B in 2017 and smart doorbell & camera producing Ring for around $1 B in initial days of 2018 (Columbuc, 2018). Apart from these companies, Amazon also acquired e-sports streaming site named Twitch for $970M, and Kiva Systems the warehouse robotic for $775M in 2012. Due to this acquisition, Amazon has around 45,000 robots in its warehouse today.
Figure 2: Amazon’s most acquisitive year on record
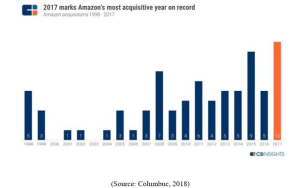
Further, Amazon reordered increased unit sale around 24% and 23% in 2016 and 2017 in comparison to the previous year that was less. This could happen due to Amazon’s merger with Whole Foods Market (Grant, 2016). It provides Amazon competitive edge by reducing prices for its customers which includes different shipping offers, availability of in-stock inventory and increased options for them etc due to increased sales.
Financial Segment Analysis
As per the financial analysis, Amazon business segment’s operating income and operating margin during 2016 are as follows:
| Segment | Operating Income | Operating Margin |
| North America segment | $2.4 billion | 3.0% |
| International segment | -$1.3 billion | -2.9% |
| AWS segment | $3.1 billion | 25.4%. |
Figure 3: Net Sales, 2017
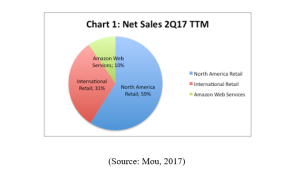
This table defines the operating profit of Amazon Business Segment. Accordingly, it is examined that Amazon enjoyed profit in North America segment as well as AWS segment but in the International segment, is has to face loss during 2016.
Financial Analysis of Amazon as Per the Year Ending 2017:
For analyzing the financial performance of Amazon, here are some ratios that are calculated to help the understand Amazon’s market in context of its shares and its market value. These ratios are as following:
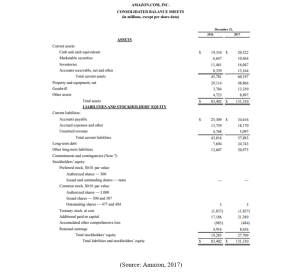
(Source: Amazon, 2017)
Liquidity Ratio:
Current ratio:
Current ratio defines the company’s ability to pay the short –term as well as long-term liabilities. In this, the current assets and current liabilities are considered. On the basis of calculation of 2017’s data, the current ratio of Amazon is 1.03 that means the company can pay its debts easily.
| 1 | Liquidity Ratios: | |
| A. | Current Ratio: | |
| Current Assets /Current Liability | 1.039977195 | |
| Current Assets | 60,197 | |
| Current Liabilities | 57,883 | |
Acid Test Ratio or Quick Ratio:
Acid test ratio is also called by the name of quick ratio. This ratio helps to measure the company’s ability to utilize its cash as well as quick assets to extinguish its current liabilities on an immediate basis. In this regards, the acid test ratio of Amazon is 0.76. that means the company can use its cash but also it needs to increase its cash within the organization.
| B. | Acid Test Ratio or Quick Ratio: | |
| Quick Assets/ Current Liability | 0.762745538 | |
| Quick Assets (Current Assets – Inventory – Prepaid Expenses) | 44150 | |
| Current Liabilities | 57,883 | |
Absolute liquidity ratio:
This ratio has the relationship between absolute liquid assets and current liabilities. In Amazon, it has the absolute liquidity ratio of 0.53. It means Amazon has less absolute liquid assets to pay its 100% worth of current liabilities.
| C. | Absolute liquidity ratio: | |
| Cash + Marketable Securities / Current Liability | 0.535321251 | |
| Cash | 20,522 | |
| Market Securities | 10,464 | |
| Current Liabilities | 57,883 | |
Profitability Ratio:
Profitability ratios define the company’s performance including operating margin, return on assets, return on sales, return on equity, gross profit margin and return on investment etc.
Return on Equity:
This return of equity ratio defines that Amazon has an 11% return on equity. It means Amazon does not use it investment properly. That is why it has less ROE in relation to book value of shareholder’s equity.
| A. | Return on Equity: | |
| Profit after Tax ÷ Net worth | 11% | |
| Profit after Tax | 3033 | |
| Net worth = Equity share capital, and Reserve and Surplus | 27,709 | |
Return on Assets:
Amazon has only 2% return on its assets that means the company does not have an appropriate investment in relation to its assets.
| B. | Return on Assets: | |
| Net Profit ÷ Total Assets | 2% | |
| Net Profit | 3033 | |
| Total Assets | 131,310 | |
Net Profit:
The calculation of Net profit shows that Amazon is enjoying the profit only 1.7% that is not enough for it. In this way, it has a need to hard to increase its profitability.
| C. | Net Profit: | |
| Net Profit ÷ Sales × 100 | 1.70% | |
| Net Profit | 3033 | |
| Sales | 177866 | |
DuPont Analysis:
After analyzing the profit margin, total assets turnover and financial leverage of Amazon, it is determined that the ROE of Amazon is 3%. In this way, it can be seen that the company generates average sales according to profit margin (Amazon, 2017). In addition, Amazon has assets turnover ratio 1.65 that also indicates its average sales in its business. At the same time, Amazon’s financial leverage is very low that means it has a less financial risk.
| Ratio | Formula | 2017 |
| Du Pont analysis | Profit margin*total assets turnover * financial leverage | 3% |
| Profit margin | 2% | |
| Total assets turnover | 1.65 | |
| Financial leverage | 0.89 |
Key Decision Making
Amazon adopts different decision-making strategies in order to take appropriate decision to increase its sale within the market and make its organization more profitable in comparison to other businesses. In this concern, Amazon did various merger and acquisition decisions that were included in its key decisions (Cardoso-Castro et al., 2018). The decision-making strategies make Amazon attractive and innovative while taking a decision within the business. It has different decision-making strategies for different departments so that they can manage every kind of functions like planning, organizing, staffing, directing, coordination and controlling over the operations.
Reference
Amazon, 2017. Annual Report. [Online] Available at: http://www.annualreports.com/HostedData/AnnualReports/PDF/NASDAQ_AMZN_2017.PDF. (Accessed: 31st July, 2018)
Aversa, P., Haefliger, S. and Reza, D.G., 2017. Building a winning business model portfolio. MIT Sloan Management Review, 58(4), pp.49-54.
Brandt, M., 2014. 5 Amazon Buys Twitch For $970 Million. [Online] Available at: https://www.statista.com/chart/2619/price-of-selected-acquisitions-by-amazon/. [Accessed: 30th July, 2018]
Cardoso-Castro, P., Swan, A. and Mendes, R., 2018. Exploring the key issues and stakeholders associated with the application of rainwater systems within the Amazon Region. Journal of Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues, 5(4).
Columbuc, L., 2018. 5 Acquisitions That Will Fuel Amazon’s Next Growth Phase. [Online] Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/louiscolumbus/2018/04/22/5-acquisitions-that-will-fuel-amazons-next-growth-phase/#2a287f1c65ba. [Accessed: 30th July, 2018]
Grant, R.M., 2016. Contemporary strategy analysis: Text and cases edition. US: John Wiley & Sons.
Loughran, T. and McDonald, B., 2016. Textual analysis in accounting and finance: A survey. Journal of Accounting Research, 54(4), pp.1187-1230.
Mou, J., 2017. Amazon: Built For Greatness, Not Built For Profitability. [Online] Available at: https://seekingalpha.com/article/4107984-amazon-built-greatness-built-profitability. [Accessed: 30th July, 2018]
Sherer, J.A., Hoffman, T.M., Wallace, K.M., Ortiz, E.E. and Satnick, T.J., 2016. Merger and acquisition due diligence part II-the devil in the details. Richmond Journal of Law & Technology, 22(2), p.4.
________________________________________________________________________________
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

