BM533 Contemporary Economic Analysis Sample
Introduction
This assignment is totally based on the Familymart Groceries which is bothered about its fluctuation of performance in the competitive market. The theories of demand and supply along with their functions, shifts, movement in the market and their affecting factors are explained to the new recruited sales manager of Familymart Groceries for better comprehension.
The assignment also critically reviews two theories from the traditional view and two from the neo-classical view for comparing their impact in modern business practices. The microeconomic theories of demand and supply is discussed with some diagram and the situation of Familymart is also analysed.
Task 1
1.1 Explanation of the law of Demand, movement along the same demand curve and changes in demand curve with influencing factors
First of all, to understand the demand and is influencing factor of Familymart, the competitive market must be understood. Markets like the UK are group of buyers and sellers of some particular goods and services where the buyers try to determine the demand of some of the goods and the sellers determine the supply of the goods. The market total demand is achieved by joining all the individual demand in one graph.
The supply of the market is also determined through the same procedure to meet the intersection point between the demand curve and supply curve (corporatefinanceinstitute.com, 2021). At the intersection point of both lines, the market equilibrium point is achieved where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. In case of Familymart, the market is highly competitive due to presence of other grocery stores and supermarket chains in the UK.
In this case, the goods which are sold by Familymart are highly substitutable and they have several suppliers in the region. Increasing competitiveness has also been a huge influencer in the fluctuation of the sale of it.
Now the law of demand can be understood. The demand for any good or service is the amount of the good which the buyer is willing and able to pay for purchasing (economictimes.com, 2021). On the other hand, it again can be stated that in microeconomics, demand is the main influencer of market mechanism which represents the quantity of any such product produced and sold in the particular market which the buyer is willing to pay and has the same ability to purchase.
It should be noted that only the willingness does not necessarily represent the demand but the willingness along with its purchasing power necessarily does.
The first influencer of demand is in any market is the price of the product. From this view, the law of the demand forms. The law of demand tries to explain the mechanism of market where the market economy allocates its scarce resources to determine the price of goods and services for meeting the demand criteria inside the market which is seen in transaction. The demand curve can be shown in the diagram below.
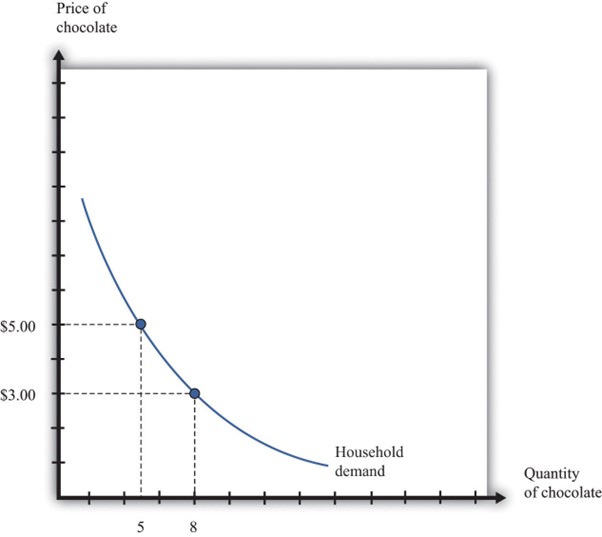
Figure 1: Demand curve
(Source: Pettinger, 2021)
The diagram shows the general demand of chocolate in any market. The quantity of the chocolate is measured in the horizontal axis and the corresponding price of the chocolates are measured in the vertical one. At price of $5, the quantity supplied is 5 units. On the other hand, at the price of $3, the quantity supplied is 8units. The combination of price and quantity forms some points of allocation which are joined by a single line representing the demand curve of the market.
This shows the highlighted portion of the traditional law of demand which is prevalent in both classical microeconomics and neo-classical microeconomics. The law of demand shows that the quantity of the demanded product fluctuates as the price of it fluctuates. The lower quantity is seen to have been demanded as the price is higher for the good. On the other hand, in case of lower pricing, higher amount of products are purchased increasing the demand.
The case can be explained in other words. People have some limited income but have unlimited wants. Though there is a margin between the wants and needs. According to their income, people try to fulfil their necessary needs which may satisfy him. The demand of goods vary on several factors. They also depend on the nature of the goods.
The income is the main factor widely accepted to impact the purchasing power of buyers in the market. The higher income leads to higher purchasing power and higher demand of goods regardless the price at that amount of goods demanded. The goods which changes their demand proportionately along their change in income of the buyers, are known as normal goods. Daily necessities like groceries and other are under this category.
On the other hand, if the rise in the income of the lowers the demand of the good, it represents the characteristics of the inferior good. There are also the substitute goods that are distinguishable in nature appearance but identity in nature. The rise of one good may lead to rise of demand for another goods if the tow goods are close substitute. On the other hand, complementary goods are said to be those in which, if the price of one good rises, the demand of other falls. These all are the cases of the related goods for influencing the demand.
The taste and preferences also have been recorded to be responsible to change the structure of demand in the market highly. The tastes are based on the psychological forces that represents that if one buyer likes one product, they must purchase that more.
On the other hand, the expectations also keep impact on the demand such as, if one person expects his rise in income in the next month, he must save less in the current period and consume more of it. The number of buyers are also seen to have a good influence on the demand.
The movement along the demand curve represents the price fluctuation and this happens due to expansion or contraction of prices. The case can be analysed from the diagram below.
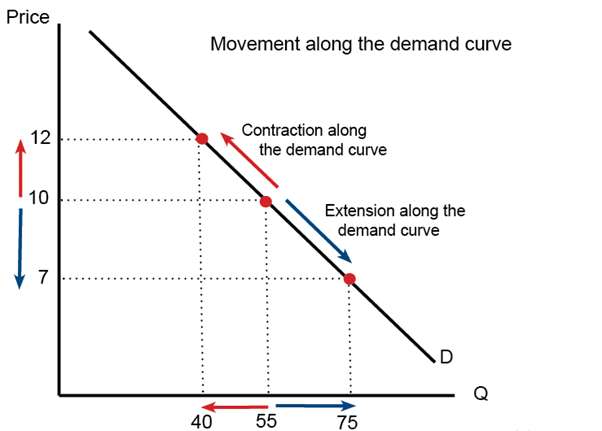
Figure 2: the movement along demand curve
(Source: Pettinger, 2021)
From the diagram it is seen that the change in price does not shift the demand curve rather the points of demand move along with it. In case of the contraction, from the diagram it can be seen that the rise of price which is to $12 from $10, leads to fall in quantity demanded 40 units from 55 units before. On the other hand, fall in price to $7 leads to rise in quantity to 75 units.
The shift in the demand curve can also be explained which is accompanied by other factors.
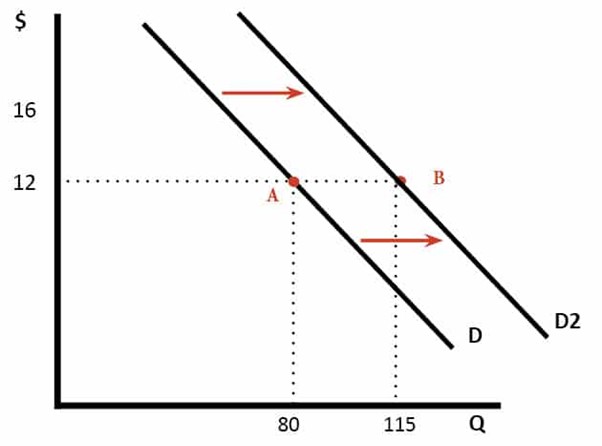
Figure 3: Shift in demand curve
(Source: Pettinger, 2021)
The shift or change in the demand curve occurs when the curve shifts rightward or leftward being influenced by other factors. The rise of income can be a case where the people get more purchasing power to buy their wanted good and services which raises the demand. In case of the diagram, after the change in income, the quantity demanded hiked from 80 to 115 units at the same price of $12.
The popularity of goods may fluctuate accompanied by the rise in the advertisement or change in the styles which again raises the willingness to buy and thus the demand curve shifts rightward. In case, if the price of the substitute goods rises, or the price of the complementary goods fall, the shift is obvious. The seasonal factors and taste and preference of consumers paly a big role in the shift.
1.2 Explanation of the law of Supply, movement along the same supply curve and changes in supply curve with influencing factors
The supply is the amount which the sellers are willing and able to sell in the market (Mankiw, 2020). The prices always play a crucial role in the determination of supply. The Familymart faces a competitive market with many buyers but the seller is the store itself. The law of supply states that in “ceteris paribus” or all the factors remaining same, if the price of the goods or services falls, the supplier will also reduce the supply. The supply curve and its characteristics can be explained from the diagram below.
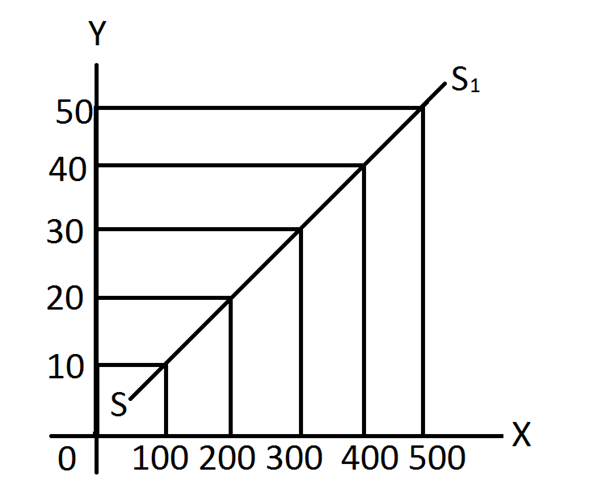
Figure 4: Supply Curve
(Source: Agarwal and Agarwal, 2021)
From the above diagram, it can be seen that when the demand of the consumers rise overtime, the price also rises. In case of higher price, the revenue also rises which encourages the suppliers to raise the supply of new goods and services. In any competitive market like the UK, the demand automatically settles to a competitive price.
The law of supply work along with the law of demand to determine the market price of the goods and services. Adding individual supply curve can lead to achievement of the market supply curve. The diagram above shows the quantity of certain goods or services in the horizontal axis whereas the vertical axis measure the corresponding price of it. As the price rises, the supply of the goods rises and the supply curve is upward sloping and it may be linear or non-linear.
The input prices influence the supply highly. For example, the supply of grocery goods require several inputs like man power, supply chain, goods from retailers and others. The related prices of those inputs impact on the overall supply. The number of sellers also play a crucial role where the supplier is only Familymart.
In case of change of price, the movement along the supply curve is prominent as higher price tends to higher supply. The extension or contraction in the supply curve can be named after the movement of the points of supply represented in the diagram below.
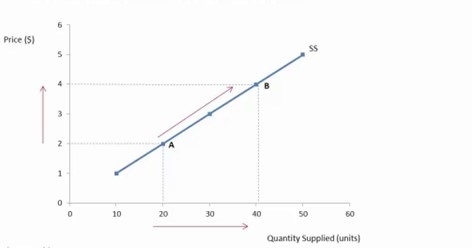
Figure 5: moving along supply curve
(Source: Maharjan, 2021)
On the other hand, shift of supply curve happens when the non-constant factors create some effect. In case of the shift, the introduction of new technology can be recognised as a factor that increases the supply at the same price seen in the diagram below.
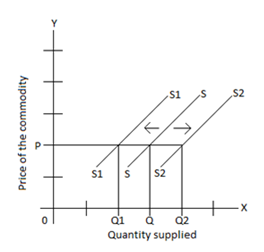
Figure 6: Shift in supply
(Source: Maharjan, 2021)
Task 2
Analysis of economic models from two centuries
From the beginning of the economic evolution, the most important question has been arose till date, how the economy and its theories can accompany the business well-being in the modern and advanced scenario. In case of modern business practices, many microeconomics and macroeconomic theories are obtained from the 21st century and 20th century theories of contemporary economics.
In the year 1944, the game theory was introduced. Von Neumann and Morgenstern published the Game theory and the Economic behaviour which created gave a huge opportunity to work with the cardinal utility (economicsonline.co.uk, 2021).
The psychological motivation was basic idea of the game theory. The theory undertakes several players as the unit players and their preferences of progression is recorded. This method identifies each player’s preference as well as the remaining and preferable moves and strategies for any real life situations. The game theory is based on the expectation or probability to predict the probable chances of occurring any favourable event.
The game theory was just an excellent approach to address many economic problems of prediction and mathematical models along with the econometric ones. The imperfect competition was not handled by previous entrepreneurs efficiently and this problem was solved after the invention of this theory (Azar, 2019). In any market process, the steady state equilibrium and its occurrence could be more predictable using the game.
In modern business, the game theory is beneficial for modelling the behaviour of the economic agents who are competing in the market. The economic gain must be decoded through several business choices and strategic movements which is easier in practice due to the use of Game theory. The price of goods and services have been more flexible and the incomplete information problem which was prevalent in the Keynesian economics was quite eradicated through Game. The price fixing and understanding the oligopolistic behaviour is also facilitated by the same (Aumann, 2019).
On the other hand, another theory of microeconomics in the 20th century is the Marginalism. Basically the marginalism is the description of the analysis of economic method and the theory of value. The main focus of this theory is the individual who have their decision on the margin (econlib.org, 2021).
According to Mosselmans (2017), in terms of economics, the value of any goods or services can be generated as per the availability or scarcity of the product or the additional utility of the extra unit of the product is provided on that. This case involves the water diamond paradox. The question has been prevailing on the tendency of preference of non-essential goods over essential goods by the people.
This is the value in exchange vs value in use paradox (Gryshova et al. 2019). In the diamond-water paradox, it is seen that the diamond is highly luxurious good that has no daily need. On the other hand, water is essential for human being to live. It should be noted that individuals choose between the increments of the goods where they use the method to identify the value of additional one unit of water along with one unit of additional diamond.
The higher utility is the key of the theory. It is again seen that water is quite available but diamond is highly demanded due to its scarcity which make them expensive (Grafton et al. 2020). In business practices, the marginalism helps the sellers to charge right price according to the value of the people looking at the inverse relationship of price and quantity.
In the 21st century economic model, the asymmetric information model can be discussed. In this case, it is assumed or observed that the seller may have excess knowledge about the market than the buyers (Zambrano Diaz, 2019.).
The lack of information can lead to highly impact the price of goods and services of the market. The risk of occurrence of market failure is prominent if the asymmetric information is prevailed in the market. In business, it may be quite hazardous as in case of lending and borrowing, the borrower may not know the complete scenario. According to Wang et al. (2018), the other hand, the asymmetric information can lead to broken agreements in the business.
On the other hand, Milton Friedman proposed his social responsibility of business theory. In this theory, he proposed that business should be only focused on earning profit for their shareholders and that is the main social responsibility of it (Reavis et al. 2017).
Friedman expected that any corporate sector would construct any strategies for maximising their profit for their shareholders but the world has been changed a lot towards a complex one. In this case, the business which only try to invite the profit cannot sustain globally and that is the reason they have to take some social responsibility to reduce their carbon footprint which can raise the social welfare (Al Halbusi and Tehseen, 2017).
Conclusion
This assignment critically discussed about the demand side of the market incorporating the factors that are responsible for affecting the demand curve. The case of Familymart is focused on the fluctuation of sales which has been discussed in the envelop of supply mechanism.
The demand and supply shifts as well as the moving along the corresponding curve have been critically evaluated through diagram. On the other hand, in four economic theories, the game theory, the marginality theory, the Milton Friedman theory of corporate social responsibility and the asymmetric information theory was covered.
Reference List
Agarwal, A. and Agarwal, A., 2021. Principles of economics. SBPD Publications.
Al Halbusi, H. and Tehseen, S., 2017. Corporate social responsibility (CSR): a literature review. Malaysian Journal of Business and Economics (MJBE).
Aumann, R.J., 2019. Lectures on game theory. CRC Press.
Azar, O.H., 2019. The influence of psychological game theory. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 167, pp.445-453.
corporatefinanceinstitute.com, 2021. Demand Curve. [online] Corporate Finance Institute. Available at: <https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/economics/demand-curve/> [Accessed 16 December 2021].
econlib.org, 2021. Marginalism – Econlib. [online] Econlib. Available at: <https://www.econlib.org/library/Enc/Marginalism.html> [Accessed 16 December 2021].
economicsonline.co.uk, 2021. Game Theory. [online] Economics Online. Available at: <https://www.economicsonline.co.uk/business_economics/prisoners_dilemma.html/> [Accessed 16 December 2021].
economictimes.com, 2021. What is Law Of Demand? Definition of Law Of Demand, Law Of Demand Meaning – The Economic Times. [online] M.economictimes.com. Available at: <https://m.economictimes.com/definition/law-of-demand?from=desktop> [Accessed 16 December 2021].
Grafton, R.Q., Chu, L. and Wyrwoll, P., 2020. The paradox of water pricing: dichotomies, dilemmas, and decisions. Oxford Review of Economic Policy, 36(1), pp.86-107.
Gryshova, I., Shabatura, T., Girdzijauskas, S., Streimikiene, D., Ciegis, R. and Griesiene, I., 2019. The Paradox of Value and Economic Bubbles: New Insights for Sustainable Economic Development. Sustainability, 11(24), p.6888.
Maharjan, P., 2021. Movement along a Supply Curve and Shifts in Supply Curve – Businesstopia. [online] Businesstopia. Available at: <https://www.businesstopia.net/economics/micro/supply-curve-movement-shift> [Accessed 16 December 2021].
Mankiw, N.G., 2020. Principles of economics. Cengage Learning.
Mosselmans, B., 2017. Marginalism. The Wiley‐Blackwell Encyclopedia of Social Theory, pp.1-3.
Pettinger, T., 2021. Shift in Demand and Movement along Demand Curve – Economics Help. [online] Economics Help. Available at: <https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/581/economics/changes-in-demand/> [Accessed 16 December 2021].
Reavis, M.R., Tucci, J.E. and St Pierre, G., 2017. Corporate social responsibility and millennials’ stakeholder approach. Journal of Leadership, Accountability and Ethics, 14(4), pp.74-83.
Wang, H., Wang, X., Bu, F., Wang, G. and Pan, Y., 2018. How the asymmetric information creates bubbles in Stock market?. Open Journal of Social Sciences, 6(8), pp.202-215.
Zambrano Diaz, L., 2019. Asymmetric Information and Economic Development.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

