MOD002405 Essay Sample
Introduction
To track the working processing and operations of a manager, the manager anchor is used, and the role of managers is the tasks and projects given to them and what they need to achieve. A lot of processing is present within an organization, and they have to be followed effectively to have the proper scope for the working. Managers have to create a path for themselves that will make the achievement present and also influence the working staff to be on the same path as them. Employees need to be provided with the proper communication and information about the projects by the manager to create a better environment that is created. Managers have a structure they follow so that the firm’s code of conduct and processing is smooth, which is an essential element for the business to develop. The report will discuss two strategies and structures for a manager with the help of Mintzberg’s and Fayol’s theories to better understand.
Critical review
Team anchor
Managers will have predefined duties for themselves, but it is essential to modify them when required so that there is stable development. As per Child, (2015), managers’ responsibilities are planning, controlling, organising, monitoring and coordinating. These aspects have to be understood and worked upon accordingly, but with these duties come challenges: mismatched skill sets, team conflict, scope creep, impractical deadlines, economic changes, budget restrictions, and data collection. These factors have to be analysed, and after that, there has to be the exemplary implementation of the resolutions developed. With the help of Mintzberg’s management theory, there is a better understanding that one can get of the team anchor. Mintzberg’s management theory has six elements: strategic apex, middle line, operating core, techno structure, and support staff (Mullins and Christy, 2013). The following report will discuss these aspects in detail while considering the team anchor.
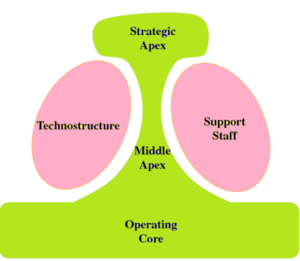
Figure 1: Mintzberg’s model of organizational structure
(Source: Mbaknol, 2022)
- Strategic apex
This is going to make the directors and senior executives of the company as the mission is well discussed with them, and then the objectives of the company are planned as per the aims. The firm’s managing team will be responsible for the achievement; therefore, they are also included in the working process. The relationship is well maintained from this aspect. In the opinion of (Acca global, 2022), the macro environment is well analysed per the company’s requirements; this way, smooth functioning is considered. There are a lot of responsibilities on the managers of a business, but they have to deal with the external factors which might impact the team’s overall achievement. Operations have to be monitored and controlled as per the plan so that a better working direction is included.
- Middle line
The operating core and the strategic apex are well linked from this mode which is that there is a reasonable interpretation of the roles, and then the expectations will be discussed. Conflicts might come at this stage between the employees and the managers, but there has to be a common ground that has been found in the relationship that they share (Mullins and Christy, 2013). A smaller business might not have a middle line in the company, which will make the processing slower. The middle management provides elements required by the team, but the budget is set as per the managers to ensure that no misuse is taking place.
- Operating core
Delivery of the activities takes place by the managers, and monitoring them is also essential, and the managers have to watch the staff. Carrying out the activities includes good communication and relationships with the employees that will make the operations occur. Managers need to understand the pressure of the middle line to ensure that good planning is being done for them in advance so that they are not having a lot of pressure on them (Schein, 2009). Managers have to ensure that the firm has a successful output from their decisions and planning for reaching the end goal.
- Techno structure
Managers need to plan a good delivery, training and development, human resources, and finances are essential. Budgeting can be a task for managers, so quality has to be impacted. The managers have to standardise the skills and ensure that all the employees are on the same page and that the best way of performance is being provided to them so that there is stable working (Drucker, 1974). Experience can be beneficial for the manager to make the right decisions for the overall growth to be considered. Analysing the effective way of processing is all on the manager and creating a stressful environment is unsuitable for the overall achievement of the targets.
- Support staff
Effectiveness in the direction and quality of work only comes in when a good understanding of the staff is being considered. The nature of the environment in which the staff is working has to be positive so that there is an exemplary output that they would be having. Importance is given to the attempts and input of the middle management to ensure a good process is followed (Mullins, 2013). The contribution of the upper and middle managers is the same. Still, the coordination has to be done well so that there is a better direction that the firm is witnessing.
Role of managers
Managers have many roles to play within a firm and must be structured well to complete all aspects. The environmental and organisational pressure is present on the managers: conflicts, resources, budget, deadlines, technical issues, uncertainty in the environment and changes. These pressures can be removed when they have the following skills: decision-making, organising, leading, communication, direction, coordination, listening, planning, and controlling. According to Bilton et. al. (2002), the roles of managers can be discussed with the help of Fayols’s theory which has five elements: planning, directing, coordination, organising and commanding. The following report discusses the roles of a manager with the help of this model for a better understanding.
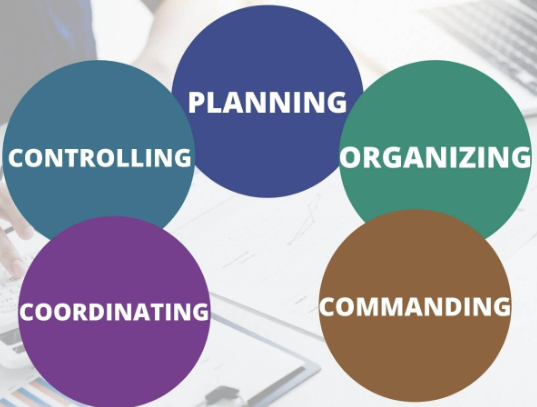
Figure 2: The five functions of Fayol’s management
(Source: Jones, 2021)
- Planning
Managers have to plan for all the processing that would be taking place within the firm. Author Anjali, (2019), suggests that the trends coming in the market are also being evaluated by the managers as per the capabilities of the staff so that the right actions are being taken. Tasks have to be well distributed, which will make the entire activities take place, and that is an excellent plan for the business. Transitions are also taking place within the firm so that there is a better sense of direction being given out.
- Organizing
In order to have influence over the workforce, the managers’ level of attention to the structure they are considering needs to be respected. Hierarchy has to be followed, which increases performance there and a good match in the demand is also present. The needs of the workers also have to be considered, which makes them able to give in their best and enable the manager to achieve the targets (Dillon, 2014). Activities have to be followed well so that there is a good increase in controlling that would be there and make the considerations present.
- Commanding
There has to be a good influence level in the manager so that they can make the workers’ efforts higher. The involvement of the workers comes from the manager, and value has to be gained for respect and work. Quality of skills and knowledge has to be higher for a manager to solve the issues and ensure that the managers are healthy command for the implementations. This way, the direction and communication of the managers and team members would be higher, which is very important for cost saving.
- Coordinating
Managers have to coordinate all the functioning that is taking place between the management and the staff. Facilities and resources must reach out to the team from time to time. The observation level of the managers has to be purposeful so that they can make the changes when required (Coffey, 2010). There has to be a suitable address that all the departments are getting for the achievements that they have to gain.
- Controlling
There are predefined plans management has, and living to these aspects is essential for the business. Products and services must be of high quality so that they can deal with the clients as well. Obtaining the best from the staff has to be there, and this aspect can be gained from controlling (Thompson, 2010).
Conclusion
From the above report, it can be analysed that understanding the suitable model is very important for the manager to have to be able to gain exemplary achievements. There are goals and targets which are put in front of the manager and without having the proper structuring for it’s them, there are going to be negative consequences. Businesses have to make the processing higher, and managers help the firms get the correct information and communication of the strategies being used so that the outcomes will be positive. Managers must value the employees’ capabilities and responsibilities, ensuring a positive environment followed for the best results. The roles of the manager are predefined, and they have to be valued by them to make the processing smooth. Without a code of conduct for the manager, there is no control, which could lead to a mishap in the firm.
References
Bilton, T., Bonnett, K., Jones, p., Lawson, T., Skinner, D., Stanworth, M. and Webster. A., (2002). Introductory sociology. 4th ed. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 196-201.
Child, J., (2015). Organization: contemporary principles and practice. 2nd ed. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons. Available through: Anglia Ruskin University Library Website <http://libweb.anglia.ac.uk>Chs. 4, 5.
Coffey, V., (2010). Understanding organisational culture in the construction industry. London: Spon Press.
Dillon, M., (2014). Introduction to sociological theory. Theorists, concepts, and their
applicability to the twenty-first century. 2nd ed. Chichester: Wiley Blackwell. Pp.377-381. (You may find this slightly obscure) and pp.441-446.
Drucker, P.F., (1974). Management: tasks, responsibilities, practices. London: Routledge.
Mullins, L., (2013). Management and organisational behaviour. 10th ed. Harlow: Prentice Hall/FT. Ch. 18.
Mullins, L.J. and Christy, G., (2013). Management and organisational behaviour. 10th ed. Harlow: Pearson. London: Pearson. Available through: Anglia Ruskin University Library website <https://library.aru.ac.uk> Ch. 17.
Mullins, L.J. and Christy, G., (2013). Management and organisational behaviour. 10th ed. Harlow: Pearson Education Limited. Ch.13.
Schein, E.H., (2009). The corporate culture survival guide. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons, Inc. Chs. 1, 2, 3, 6, 8.
Thompson, J., (2010). Strategic management: awareness and change. 6th ed Andover: South-Western Cengage Learning.
Acca global, (2022). Mintzberg’s theory on organisations. [Online]. Available through <https://www.accaglobal.com/gb/en/student/exam-support-resources/fundamentals-exams-study-resources/f1/technical-articles/mintzberg-theory.html#:~:text=Mintzberg%20believes%20that%20structures%20are,large%2Dscale%20production%20and%20manufacturing.>.
Anjali, J., (2019). Henri Fayol’s 14 principles of management. [Online]. Available through <https://theinvestorsbook.com/henri-fayols-14-principles-of-management.html>.
Jones, A., (2021). The five functions of Fayol’s management. [Online]. Available through <https://bvop.org/journal/five-functions-fayol-management/>.
Mbaknol, (2022). Mintzberg’s model of organizational structure. [Online]. Available through <https://www.mbaknol.com/strategic-management/mintzbergs-model-of-organizational-structure/>.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

