BSS057-6 Corporate Innovation and Entrepreneurship Assignment Sample
Module code and Title: BSS057-6 Corporate Innovation and Entrepreneurship Assignment Sample
1. Introduction
Two vignettes are given based on that two scenarios problems with data handling will be discussed in this session with consideration of TUI context and “data science hackathon”. As per Vignette A given scenario of difficulties in applying the learned session into organizational context and effectiveness of master classes provided by external trainers. Moreover, by describing the difficulties of these learning sessions, the problem associated with the application of learned discussion after the session can be described.
The application of a “TUI-based” learning session can be an effective one for better learning as it focuses on storytelling learning that increases creative thinking among learners. Furthermore, this learning system is ineffective for application after the session and this can be improved through learning sessions with more activity-based learning such as attribute analysis, brainstorming, analogy, superheroes, and role storming.
As per the given vignette B, different departments and communities of an organization take several data science techniques for record keeping and tracking any progress by using a “data science hackathon”. Moreover, they faced problems in managing departmental work with these techniques as most of the engineers, user interface do not use this properly, and this problem can be solved by implementing different systematic processes like design thinking and DPS.
2. VIGNETTE A
2.1 Critical analysis
“TUI-based learning” is efficient for increasing knowledge among learners to explain social and personal behavior in the organizational context but it has the difficulties of distractions of learners during learning sessions with the problems of inclusive learning. According to Beşevli et al. (2022), this process is not so efficient for increasing the efficiency of learning sessions for solving complex issues in organizations.
“Tangible User Interfaces (TUIs)” use the natural ability of individuals by storytelling or make different scenarios within the organization and it has difficulties adapting teachers’ techniques and students’ adaptability as they tend to forget the learning materials and cannot apply them during the original requirements (Deng and Cho, 2022). This problem can be fixed with the application of different teaching processes in the organization for increasing the sense of learning among employees and creating their responsiveness to solving any complex problems in the organization (Setozaki et al. 2018).
Theory application
“Brainstorming theory” can be applied to solving complex organizational problems by improving the realistic conceptualization of the employees. According to Victor et al. (2020), this theory allows the highest achievable performance of employees through learning sessions within the organization. This theory is built on four principles for increasing the creativity of all group members through the specific solution to a particular organizational problem.
“Quantity over quality”– Brainstorming focuses on creative thinking and ideas coming from learners instead of the quality of the ideas as these will be filtered at the last stage of the session. Thus, it encourages everyone to think about a given situation and find valuable solutions as per their ability (Paulus and Baruah, 2018). This improves the creativity of employees and makes responsiveness among all employees to face and find solutions to any organizational problem.
Withhold criticism- Learners should be encouraged to share their ideas with the trainers for evaluation of their effectiveness and efficiency in solving any problem. According to Zhai et al. (2020), this theory takes feedback from each student by removing any blocking during the session as these will be discussed after the session whose idea was most suitable and the problem with others. This improves competitiveness in the organization and improves the quality of employees by improving their creativity and problem-solving attributes.
Welcome, all crazy ideas- Trainers encourage all the team members to think out of the box for solving any given problematic situation and this opens doors for everyone to think and share their ideas. This influences the creation of more creative ideas for improving organizational performance and increases responsiveness among employees (Hidayanti et al. 2018).
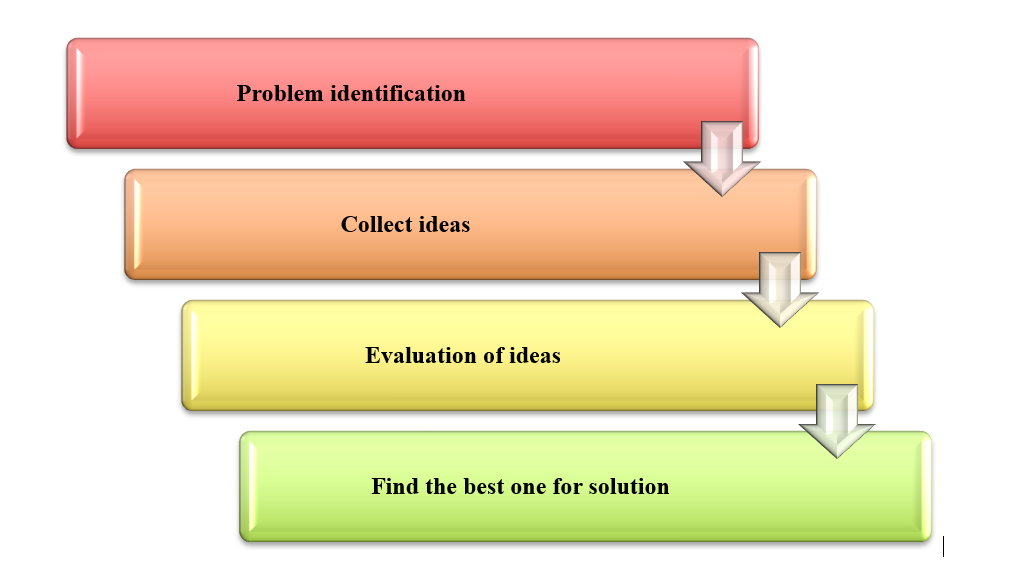 Figure 1: Steps of brainstorming (Source: Self-created)
Figure 1: Steps of brainstorming (Source: Self-created)
Refine, combine, and improve ideas- After taking everyone’s’ views and ideas trainers develop the most suitable strategies by taking individual ideas or connecting with others for solving organizational problems. Thus, everyone gets interested in giving creative ideas to solve organizational problems and improve their performance so that their ideas can be selected at the end of the session (Maysaroh et al. 2021). This increases employee engagement and performance of the organization by focusing on inclusive learning with external learners.
Brainstorming does not allow any criticism; instead, it encourages everyone to think as much more about their capability for participating in organizational improvement through their creative ideas. Thus, it increases the ability of the employees to solve any problem with their creativity and gives cancer to everyone to share their perspective of the problem (Ed.gov, 2018). The main principle of this theory is that everyone should have an equal chance of participating in the decision-making process in the organization.
Analysis
TUI learning context is quite hard to implement in the organization it is a higher chance of distraction and is not adopted by most experienced employees. Moreover, this requires more patience, and employees may not be so responsive during and after the training session thus it is a waste of time and cost within an organization.
According to Liani et al. (2018), brainstorming is more beneficial than these techniques as this process includes every employee in the decision-making procedure. Brainstorming generates more innovative ideas for improving problem-solving criteria within an organization with the help of its employees. Thus, this theory increases the performance of employees and increases innovation in the organization by improving creativity among employees.
The main difficulty with the application of this theory is trained and experienced trainers for the feedback-giving session, as they should not give any feedback for the ideas coming from employees. The trainers should give required aid and assistance to the employees for increasing their innovative knowledge so that all employees can participate in the session (Masoumifard, 2021). Thus, this increases employee participation and engagement in the organization and solves any problems easily with the effort of everyone within the organization.
2.2 Conclusion
This process introduces different perspectives of complex problems and opens the door for innovation with proper ideas of implementation coming from employees. This reduces the cost of operation as employees think of innovative techniques of working and increase employee engagement as they also get the chance of sharing their knowledge and showing its application. Moreover, the given problem is an application of learning theories in the real organizational context as most of the employees do not focus on their improvement and creatively think with the learning session with TUI learning.
Hence, brainstorming features can implement in the organization with the help of organizational or external trainers for improving the performance of its employees. Thus, the organization can solve any complex problem with the innovative and creative ideas of its employees. All the features and principles of the brainstorming techniques have been given here for this analysis so that organizations can implement these techniques for increasing creativity in the organization.
2.3 Recommendation
The application process of these brainstorming techniques should be incorporated through a few distinguished steps such as identification of the problem, framing of the problem, and practicing the brainstorming after the warming-up session. Thus, employees can know more about the problem, they can find a solution more easily, and their creativity encounters the problem situation to find a suitable solution.
This increases the performance of the organization but at the initial stage, the organization should train employees through training sessions by external trainers. Moreover, this process of learning requires enough understanding from employees to figure out the situation for finding out an innovative solution and the organization should have a transparent system of data flow. Thus, employees have the knowledge of the overall operation within the organization and they can think freely without any boundaries and generate creative ideas to solve complex problems.
3. VIGNETTE B
3.1 Critical analysis
As per the given applications of data security and the learning process, there were several difficulties faced by organizations to solve organizational issues. Such as during the implementation of the “Northern regional hackathon” in 2021 there was the problem of not the participation of the whole IT team and thus it could not be applied in the scenario of most of the northern regions. Moreover, during the application of the “Data Science Hackathon,” there was a lack of participation of software engineers and other user interfaces that was also one reason behind its failure (Happonen et al. 2022).
Hackathon are effective tools for assisting exports in solving a crisis or problem with efficient and innovative policies by a collaboration of other experts (Nolte, 2019). The concept of this technique is to bring everyone together and gather everyone’s perspective for solving an issue instead of bouncing back on others’ perspectives and thus problem solving becomes easier.
Although, this implementation requires efficient participation of everyone; due to not participating different working groups the implementation of Hackathon failed in these two cases. As per the other situation, using “light bulb lab” only describes internal issues of the organization and ignores external issues. The main concept of this principle is comparing two ideas on their cost, appearance, and brightness after the application for implanting in the organization to solve problems (Oosterkamp et al. 2019).
Thus, it ignores any external issues and does not consider more ideas coming from employees and other groups. Hence, it is not so efficient for using them in an organization to solve internal issues efficiently as it ignores everyone’s participation. The marketing department has used the “annual forum” as a platform for ideas and knowledge sharing by the employees for improving customer services by fulfilling their demands.
This forum has been quite successful in the past for improving customers’ experiences as most of the employees like to share their ideas but some of them did not recognize this process. This is one of the main reasons behind its difficulties in further implementation (Avila-Merino, 2019). The IT department organized highly technical meetings for introducing innovation within the organization but most people do not have the idea of it.
According to Sanchez-Romero et al. (2019), these meeting contents were highly technical that are not understood by most of the employees from other departments thus these cannot be implemented in a lucid form of innovation. Hence, this is not an efficient way of improving innovation and technological advancement within the organization. However, employees are the main players who will be working with the newly developed system for operating tasks.
After all, these trial applications the strategy-making group has implemented an “innovation forum” for monthly observation but it is also field due to a lack of collaboration among a different working group within the organization. Hence, not all employees can take part in the innovative knowledge sharing in this monthly forum and the strategy failed to solve organizational issues.
Theory application
The most suitable theory applied to solve organizational issues by motivating all employees to participate in the decision-making process and the knowledge-sharing process is the “creative problem-solving theory (CPS)”. This is a seven-step process of identifying a problem with finding a proper solution with the increasing engagement of all employees through inclusive learning and training for focusing on improvement of their creativity.
According to Graesser et al. (2018), this technique refers to breaking down a probe for easier understanding of employees to generate creative ideas from them for finding out the solution. All the seven steps of this technique have been achieved through two types of thinking processes such as “Divergent Thinking” and “Convergent Thinking” (Iom.int, 2018). The first phase follows a divergent type of thinking process that generates many optional ideas from employees and the second phase follows a convergent type of thinking for evaluation of those options to find the best one.
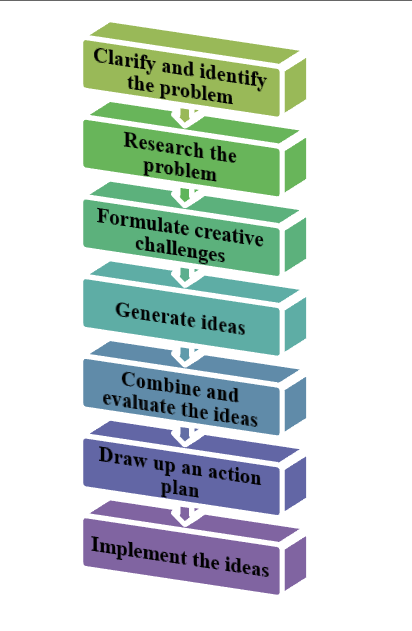 Figure 2: Seven Steps of CPS (Source: Self-created)
Figure 2: Seven Steps of CPS (Source: Self-created)
The first step of this technique is the identification of the problem for setting criteria for judging the potentiality of all probable solutions. The next step is to research the problem to increase understanding of the problem so that employers can draw a clear view of the problem (Ummah and Yuliati, 2020). The next step is developing creative challenges corresponding with the issues and this should be quite simple and concise.
The next step is the generation of ideas through brainstorming of employees and writing down all ideas and after that, all these ideas are combined to find the best solution. After finding the solution, the next step is its evaluation for solving the problem and drawing up an action plan for its application as the change includes the risk to manage the workforce during a changed situation. After all the evaluation, the last step is the application of the solution that comes from different ideas of employees.
Analysis
CPS is one of the most effective techniques for finding an appropriate solution to any internal or external issues of an organization with the assistance of all employees. Thus, it improves employee engagement and increases responsiveness among employees, and potentially solves the problem of participation of all employees.
Furthermore, these techniques motivate all employees to share their innovative ideas to solve complex problems and thus encourage them to be more efficient in the selection of their ideas. According to Nordin and Osman (2018), this is the simplest but effective way to critically analyze organizational problems and create awareness among employees. All given problems faced by different sectors of organizations can use these techniques for increasing the effectiveness of innovative ideas of all employees and increasing responsiveness among all departmental employees.
3.2 Conclusion
All the given sceneries have been described for finding out difficulties faced by those departments for finding out solutions for organizational issues. As per the given cases, it is obvious that employee participation is the most effective way to find out the best solution for any problem as they must have enough knowledge and capability to understand the problem or issue for finding out the solution. This signifies employee knowledge and capability to handle any situation with the organization and demonstrate collaboration in an organization.
3.3 Recommendation
As per the previous discussion, it is obvious that employee participation is the most efficient way to solve any complex issue and using CPS increases responsiveness among employees. This CPS increases the effectiveness of employees and finds easier solutions to any issue of the organization through active partition and ideas sharing among employees.
The organizations are recommended to encourage all employees for participating in these sessions of decision-making and define the challenges available within the organization. Thus, employees can be more active to participate in creative knowledge sharing and solve critical issues of organizations through such techniques.
Reference list
Journals
Avila-Merino, A., 2019. Learning by doing in business education. Using hackathons to improve the teaching and learning of entrepreneurial skills. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, pp.22(1).
Beşevli, C., Göksun, T. and Özcan, O., 2022, June. Designing Physical Objects for Young Children’s Magnitude Understanding: A TUI Research Through Design Journey. In Interaction Design and Children (pp. 109-122).
Deng, Q. and Cho, D.M., 2022. A Study on the Cognitive Potential of Pre-school Children with AR Collaborative TUI. Journal of Korea Multimedia Society, 25(4), pp.649-659.
Graesser, A.C., Fiore, S.M., Greiff, S., Andrews-Todd, J., Foltz, P.W. and Hesse, F.W., 2018. Advancing the science of collaborative problem solving. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 19(2), pp.59-92.
Happonen, A., Nolte, A., Bystriakova, N., Santti, U. and Kärhä, K., 2022. Study on Hackathons for New Innovation Seed and Business Model Development Needs in Digitalization Driven Sustainability, Circularity and Environmentally Friendly Solutions Demanding Digitalizing Societies. New Innovations in Economics, Business and Management Vol. 4, pp.1-29.
Hidayanti, W.I., Rochintaniawati, D. and Agustin, R.R., 2018. The Effect of Brainstorming on Students’ Creative Thinking Skill in Learning Nutrition. Journal of Science Learning, 1(2), pp.44-48.
Liani, E., Hamdani, D. and Risdianto, E., 2018. Penerapan Model Problem Based Learning dengan Metode Brainstorming untuk Meningkatkan Kemampuan Pemecahan Masalah Siswa di SMAN 3 Kota Bengkulu. Jurnal Kumparan Fisika, 1(2 Agustus), pp.20-24.
Masoumifard, M., 2021. Comparison of the Effect of two Teaching Methods (Brainstorming and Group Discussion) by E-Learning Method on the Rate of Learning and Interest in Group Work in Social Studies Course for Third Grade Students in Tehran. Iranian journal of educational sociology, 4(4), pp.10-18.
Maysaroh, W., Mulyono, M. and Kurniasih, A.W., 2021. The mathematical communication ability based on student’s self-confidence in Problem Based Learning models with brainstorming techniques. Unnes Journal of Mathematics Education, pp.10(3).
Nolte, A., 2019, August. Touched by the Hackathon: a study on the connection between Hackathon participants and start-up founders. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM SIGSOFT International Workshop on Software-Intensive Business: Start-ups, Platforms, and Ecosystems (pp. 31-36).
Nordin, N.M. and Osman, K., 2018. Students’ generated animation: An innovative approach to inculcate collaborative problem solving (CPS) skills in learning physics. Journal of Education in Science Environment and Health, 4(2), pp.206-226.
Oosterkamp, E.B., Bruinsma, A., Sauter, E., Wolfert, J., Sundmaeker, H. and Campos, A.R., 2019. D2. 1 Regional challenges: An Overview of Regional Challenges that were organized in the first period of the project, p.212.
Paulus, P.B. and Baruah, J., 2018. Enhancing creativity in E-Planning: recommendations from a collaborative creativity perspective. In New approaches, methods, and tools in urban E-Planning (pp. 192-222). IGI Global.
Sanchez-Romero, J.L., Jimeno-Morenilla, A., Mora, H. and Pujol-Lopez, F., 2019, April. Using Physical Activity Monitors in Smart Environments and Social Networks: Applications and Challenges. In The International Research & Innovation Forum (pp. 231-241). Springer, Cham.
SETOZAKI, N., SUZUKI, K., IWASAKI, T. and MORITA, Y., 2018. Development and Evaluation of the Usefulness of Collaborative Learning on the Tangible AR Learning Equipment for Astronomy Education. Educational technology research, 40(1), pp.71-83.
Ummah, I.K. and Yuliati, N., 2020. The Effect of Jumping Task Based on Creative Problem Solving on Students’ Problem Solving Ability. International Journal of Instruction, 13(1), pp.387-406.
Victor, A., Aarthy, S.L., Sujatha, R. and Srivani, A., 2020, December. E-Brainstorming Engenders Synergy Based on Ontology. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 981, No. 4, p. 042089). IOP Publishing.
Zhai, Y., Ye, Q., Lu, S., Jia, M., Ji, R. and Tian, Y., 2020, August. Multiple expert brainstorming for domain adaptive person re-identification. In European Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 594-611). Springer, Cham.
Websites
Ed.gov, 2018, “The Effect of Using Brainstorming Strategy in Developing Creative Problem Solving Skills among male Students in Kuwait: A Field Study on Saud Al-Kharji School in Kuwait City”. Viewed on: 15.08.2022, https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1083780.pdf
Iom.int, 2018, “Creative Problem Solving”. Viewed on: 15.08.2022, https://www.iom.int/sites/g/files/tmzbdl486/files/staff-welfare/creative_problem_solving.pdf
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:


1 Comment