EG706 MSc International Hospitality Management Assignment Sample
Module code and Title: EG706 MSc International Hospitality Management Assignment Sample
Introduction
Staff management and ethical employment in the industry of hospitality management are seen as flexible tools for managing Human Resources (HR) to get an optimum outcome, and different factors determine the productivity of such tools. The report is focussed on finding out the different managerial practices that are being carried out in the hospitality industry and challenges that sully occur to slow down the industrial output.
Reception, convenience management, staff allocation per floor, and accommodation amenities are all being studied and examined with academic citations to get an overview of the factors responsible for staff management. This report has been presented in two parts, the first part discusses the reward and staff management, while the second part critically evaluates ethical employment within the hospitality sector, using the framework of suitable authors.
1. Critical evaluation of reward management and staff motivation that develops the entire organisational action
Reward management impacting the hospitality industry
There is a proven correlation between reward management and the satisfaction derived from work performance, as many of the different companies in the hospitality sector usually thrive on employee retention strategies. One of the ways is to improve the job experience by providing work incentives, overpay bonuses, and various other rewards to hike the rate of efficiency in the employees. It is quite evident from the research findings that reward management often propels employees to have a better work environment and directs employees toward better authenticity (Samuel, 2021).
In the hospitality industry, the reward may be monthly bonuses, free medical and health insurance for the employees, or a luxury hotel trip to any chosen destination, with these added worker benefits. Reward management is the mechanism that is often targeted to let the employees have a better experience while being on the job and try out different work attempts to get the reward as it acts as a psychological propelling to let the employees achieve a better objective.
The question of the need for reward management often may arise, and the exact reason if the work environment is quite holistic or if too much reward makes the employees in the hospitality sector inefficient remains. Various research studies based on job flexibility and the allocation of different rewards need to be properly understood, as there has been an establishment on the relative correlation between employee operation and reward management (Victor and Hoole, 2017).
Company Example
The example of Four Seasons Hotel may be cited to understand the way the luxury hotel creates employee reward management and makes use of the different opportunities to train the employees for a longer period. The benefit of “complimentary staying” gets under the rulebook of the rewards program of this luxury hotel, as the best employee chosen according to the performance is granted better accommodation within the hotel (Refer to Appendix 1).
Another facility that is increasing benefit is the Four Seasons development periods, as in these time lapses, there are different mentorship ways granted to the employees for better performance, and the recruit receives these training modules that enable workers for in-company promotion (Four Seasons Jobs. 2022). The second company as an example may be cited, as the luxury resort of Chedi Andermatt offers different and exclusive reward management programs for the employees, such as various linguistic courses with varied training modules to choose from (The Chedi. 2022).
Use of reward management framework for the hospitality industry
A contingent payment framework is done to the model that is often used by the organisation to let the reward management be directed at a better system of management source, about the employee’s compromises or any kind of sacrifice being made. The contingent pay model has been listed to use the method of encouraging employees to tackle diverse roles within the hospitality industry and enable multiple roles to assume responsibilities with focused work (Ogbonnaya et al., 2017).
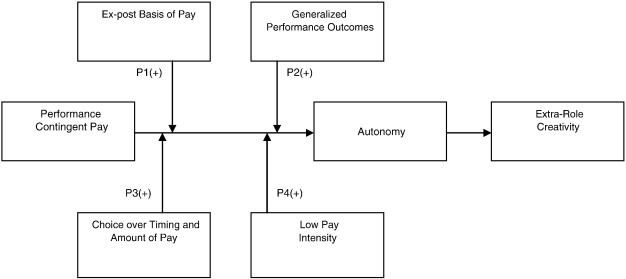 Figure 1: Contingent payment reward management framework (Source: Ogbonnaya et al., 2017)
Figure 1: Contingent payment reward management framework (Source: Ogbonnaya et al., 2017)
There are different staff roles that the company in the hospitality industry need to address, and all of these are taken care of depending on the framework that is used, where employee retention becomes if the contingent pay model is used, which is economical. The application of this model is rightly directed at employee retention by realising if the employee requires any kind of financial support as reward management, as many hospitality industry organisations offer maternity pay or vacation rewards based on employee records.
Staff motivation impacting the hospitality industry
Motivation for the staff is the psychological need that most of the employees need, and regarding this, the methods of motivating the employees need to be directly stated. There are multiple reasons why staff motivation is required in the hospitality industry, such as employees may feel out of place and discrimination on the payment may occur, which is also followed by rude behaviour or a negative attitude from the staff.
To maintain the occupational level of decency and let the employees be responsible for the task, mental preparation is required and a system of job channelising is considerably required for the employees. Regular research studies on the corporate models that may be suitable for staff motivation are being discussed, where the direct determinants of staff monitoring or prediction of performance based on historical records have been observed (Chaghari et al., 2017).
In other words, sometimes the staff in the hospitality industry may feel burnt out, or the constant attending to different customers may land the employees without better human interaction into a state of psychological non-willingness. The reason for which staff motivation in the hospitality industry is required is the staff may need the Human Resource Manager’s perception and strength of mind to work forward without being overexposed to the regular monotonicity of the work. This staff motivation may be in the form of constant training schedules or creating weekly workshops where a guest appreciation of the employee of the week may be awarded.
Example from real life
The real-life example may let the reader understand better about the staff motivation and the career key to having a better hotel experience, as has been the case of Raffles Hotel. An employee in the Rafters Hotel shows that the staff motivation in the hotel had been of superior quality. Staff motivation in Raffles Hotel has been processed as one of the most reputable because of the multiple systems such as the staff training, or the direct way of onboarding the different people for a better job experience (Refer to Appendix 2).
Another example from the real-life scenario of Ritz-Carlton about the direct staff motivation may be cited for better example analysis, as the company often engages in the smooth transition from the incentives, with monthly bonus points and an astronomical appreciation of the staff, with weekly Human Resource activities meant for the employees (Optometric Business. 2022).
A research framework on staff motivation for better illustration
There is no discrete theory about staff motivation which is not a part of the Human Resource Management theory, and different types of theories that incline staff motivation have been discussed over a long space. The theoretical framework of McClelland’s Three Needs Framework has been duly refreshed in the recent analysis, where the three needs ladder is explained which forms the basic framework for better staff management.
The need to exercise comparative dominion, the need for gaining a sense of success and the need for better team affiliation and appreciation are the basic wheels of this model. The model of McClelland’s Three Needs had been attempted in various organisations multiple times, and no gender biases had been considered while the model had been developed by McClelland (KHURANA and JOSHI, 2017).
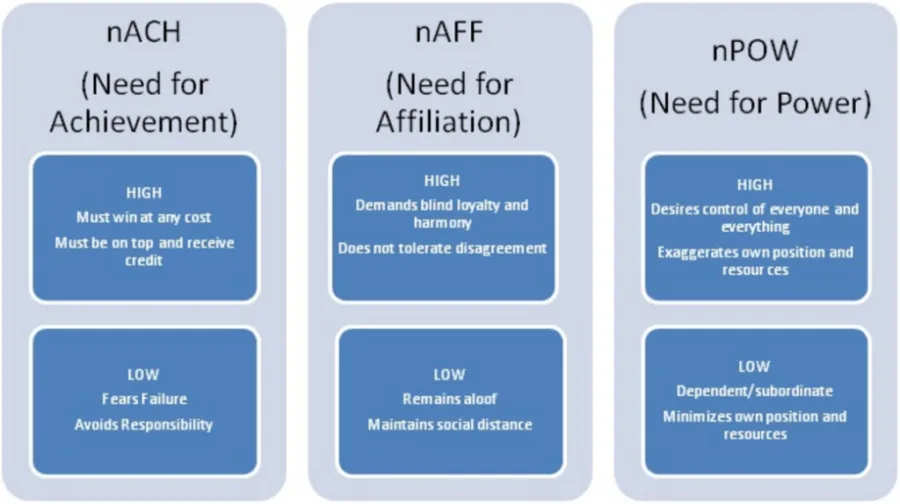 Figure 2: McClelland’s Three Needs Framework (Source: KHURANA and JOSHI, 2017)
Figure 2: McClelland’s Three Needs Framework (Source: KHURANA and JOSHI, 2017)
The application of the McClelland Three Needs model is useful for the direct application to measure if the staffs in the hospitality industry organisations are in the need of achievement, or the staffs need to be motivated for better affiliation.
2. Evaluation of ethical employment systems shaping the activities of international hospitality organisations
Shift work
The theory of deontology is regarded to be an ethical theory that might be prevalent within an organisational culture as it is focused on differentiating right from wrong and the real significance concerning the given theory is in deciding the moral intent of an action. According to research, the notion of deontological ethics might be further described as duty-based ethical theories and it is focused on the nature of action along with its motive to determine whether the same is correct or incorrect (Benlahcene et al., 2018).
In that context, it might be stated that organisations are also required to adhere to such theories of moral actions while ensuring they are implementing ethical practices for the workforce. In that context, determining relevant shift work for the employees is one such practice that further assesses whether or not the same is integrating moral actions for their workforce or not. On a broader note, providing a flexible shit time within the hospitality industry is one of the moral duties that the organisations working within the hospitality industry are required to do.
It needs to be mentioned that making individuals work beyond the normal working hours is perceived as an unethical practice which is also against the official regulations of some countries, especially the UK in which no employee might work beyond the official working hours.
The UK government mandated that an individual is prohibited to work beyond 48 hours a week and the given law is known as the working time regulations or the working time directive (Gov. uk. 2022). Therefore, it might be stated that the majority of the hospitality organisations based within the UK adhere to these rules which influences their organisational behaviours.
Unsociable hours
Unsociable working hours are also similar to shift work which is the prospect of working beyond the traditional working hours such as the 9-5 shift and it is one of the most common aspects of working among shift workers. The same is also an unethical practice that is considered as unethical practice since it is known to impact the physical and mental health of people and for that, the organisations might experience increased turnover which could negatively impact their operational activities.
Henceforth, every organisation in any given industry including the hospitality industry has developed a robust Human Resource or HR department that further looks after the given matter to ensure that employees are not experiencing any implications at work and obtain a significant amount of job satisfaction.
In that context, the theory of consequentialism is applicable as it focuses on the wrong and right aspects of consequences that actions bring and therefore, it might also be implied that such unsociable working hours would bring negative consequences within the hospitality industry and prevent them from being an ethical enterprise.
Consequentialism attempts to evaluate the merits of two fundamental forms regarding moral theoretical framework through the means of mutual comparison attempting to obtain the implications along with the tendencies of each theory by taking them individually (Slote, 2020).
Zero hours
There are different types of work contracts based on the opportunities and real-life case examples where a contractual agreement formed between the employment-providing companies and staff takes place, which occurs just by on-spot recruitment. In a more distinct case study, the zero-hour employment system operates if the company has agreed on various terms with the employee, and all of these do not spill over or breach the employment contracts.
A more sensible way to discuss the issue is that the zero-hour contracts must not have any employment rate that is below the industry standard and does not include the potentiality of undermining the current market standard rate of payment (GOV.UK. 2022). As for the different hospitality industries in different nations, the UK labour standard and zero-hour policy may be reviewed, where different works do not have the maintenance of zero-hour or branching employment terms clearly (Koumenta and Williams, 2019).
Modern-day slavery or pay
Underpayment or being exploited in the hospitality industry has been a common case to focus upon as all of these are included within the framework of the legislation to monitor, or overview. Most of the time, modern-day slavery and unethical standards are being practised which has not been reviewed or oppressed people even after revolting, the hospitality organisations do not exactly review the work climate.
Modern-day slavery may take the form of excessive working hours, exploitation of different employees on overtime without any payment, below standard payment and a few more disasters. Modern slavery is usually defined as the worker’s psychological exploitation, which includes any form of forced or tortured verbal or physical hurt, use of strict manipulation and excessive risks associated (Crane et al., 2022).
The lack of job security or the use of debt bondage that may essentially endanger the working system of an employee and create a more chaotic sense is a way of modern-day slavery, as many of the people suffer from this process over a longer period in the hospitality industry (The Freedom Hub. 2022).
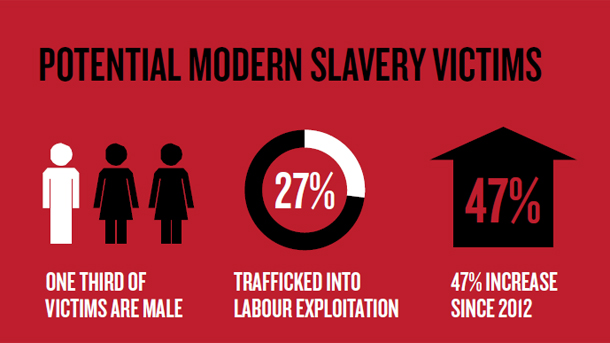 Figure 3: Modern-day slavery information in the current global perspective (Source: The Freedom Hub. 2022)
Figure 3: Modern-day slavery information in the current global perspective (Source: The Freedom Hub. 2022)
Overtime issues and psychological evaluation
The question of overtime arrives in the case where there is a constant imposition of working hours without the essential criteria of paying the workers or making the hospitality industry workers go through a lot of different cases where there are different kinds of overtime occurring.
Thai may be further illustrated by the case of the luxury hotel where the theory of incentives and employee motivation have been disregarded for overtime hours (Tan et al., 2020). The employees of luxury hotels, as is evident in the case of Hilton Hotels, where the different employees have been working overtime, with a psychological break in some cases (Refer to Appendix 3).
Conclusion
There had been so far no such amendments on a global basis that may monitor the different cases of overtime workers and this issue had been one of the red signals that the hospitality industry needs to notice and introduce employee psychological evaluation. From the above discussion, it may be concluded that the hospitality industry needs to modify or reconsider Human Resource Management with better rewards management, cut overtime and offer the employees better work relief.
References
Benlahcene, A., Zainuddin, R.B., Syakiran, N. and Ismail, A.B., 2018. A narrative review of ethics theories: Teleological & deontological Ethics. Journal of Humanities and Social Science, 23(7), pp.31-38.
Chaghari, M., Saffari, M., Ebadi, A. and Ameryoun, A., 2017. Empowering education: A new model for in-service training of nursing staff. Journal of advances in medical education & professionalism, 5(1), p.26.
Crane, A., LeBaron, G., Phung, K., Behbahani, L. and Allain, J., 2022. Confronting the business models of modern slavery. Journal of Management Inquiry, 31(3), pp.264-285.
Four Seasons Jobs. 2022. What to expect. Four Seasons Jobs. (n.d.). Retrieved November 17, 2022, from https://jobs.fourseasons.com/home/what-to-expect/
GOV.UK. 2022. Contract types and employer responsibilities. GOV.UK. Retrieved November 17, 2022, from https://www.gov.uk/contract-types-and-employer-responsibilities/zero-hour-contracts#:~:text=Zero%2Dhours%20contracts%20are%20also,have%20to%20give%20them%20work
Gov.uk. 2022. https://www.gov.uk/maximum-weekly-working-hours#:~:text=You%20cannot%20work%20more%20than,or%2040%20hours%20a%20week.
KHURANA, H. and JOSHI, V., 2017. MOTIVATION AND ITS IMPACT ON INDIVIDUAL PERFORMANCE: A COMPARATIVE STUDY BASED ON MCCLELLAND’S THREE NEED MODEL. Clear International Journal of Research in Commerce & Management, 8(7).
Koumenta, M. and Williams, M., 2019. An anatomy of zero‐hour contracts in the UK. Industrial Relations Journal, 50(1), pp.20-40.
Ogbonnaya, C., Daniels, K. and Nielsen, K., 2017. Does contingent pay encourage positive employee attitudes and intensify work?. Human Resource Management Journal, 27(1), pp.94-112.
Optometric Business. 2022. What the Ritz-Carlton teaches us about motivating staff. Review of Optometric Business. Retrieved November 17, 2022, from https://www.reviewob.com/what-the-ritz-carlton-teaches-us-about-motivating-staff/
Samuel, A.P., 2021. Reward Management And Organizational Performance Of Workers In Delta State. International Journal of Business and Law Research, 9 (2), 106, 113.
Slote, M.A., 2020. Common-sense morality and consequentialism. Routledge.
Tan, K.L., Sim, P.L., Goh, F.Q., Leong, C.M. and Ting, H., 2020. Overwork and overtime on turnover intention in non-luxury hotels: do incentives matter?. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Insights, 3(4), pp.397-414.
The Chedi. 2022. 5-star Swiss Alps Hotel: The chedi andermatt. The Chedi. (n.d.). Retrieved November 17, 2022, from https://www.thechediandermatt.com/
The Freedom Hub. 2022. Hotels and slavery: Many doors to hide behind. The Freedom Hub. Retrieved November 17, 2022, from https://thefreedomhub.org/blog/hotels-and-modern-slavery/
Victor, J. and Hoole, C., 2017. The influence of organisational rewards on workplace trust and work engagement. SA Journal of Human Resource Management, 15(1), pp.1-14.
Appendices
Appendix 1
https://fortune.com/2015/02/01/perks-four-seasons/
Appendix 2
https://www.tal.sg/tafep/resources/interviews/2019/what-motivated-one-employee-to-stay-for-46-years#
Appendix 3
https://www.overtimepaylaws.org/hilton-hotels-overtime-pay-lawsuit/
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

