MOD004160TRI:The future proof organization Sample
Introduction
Changes are taking place in technological utilisation within every organisation. Covid-19 pandemic outbreaks have increased pace of technological changes occurring within different organisations. This article published in “Harvard Business Review” is analysed within this assignment for understanding different steps required for future proofing an organisation. This article has evaluated details of before pandemic situations companies were aiming at improving their technological advancement in order to increase performance of their business. Moreover, incorporation of advanced technologies for different organisational functionalities has increased their sustainability. Different organisations are incorporating technological changes in various ways. This is providing them with diverse benefits and this is resulting in changes for their future provisions. Many companies are focussing on increasing efficiency of their workforce by technological advancement. In case of companies that are not considering these changes, they are not able to cope with changes facing them in future business environment. This assignment includes discussions on overview of this cover story, critical analysis of it, challenges identified within this article and its application on different business and non-business organisations.
Overview of cover story
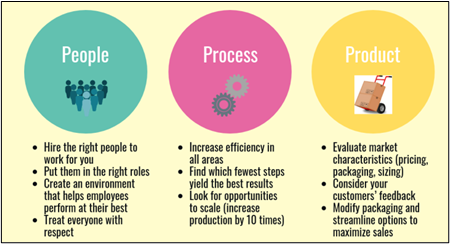
Figure 1: People, Process and Product of Business
(Source: Influenced by Morgan and Liker, 2020)
This cover story published in “Harvard Business Review” about ways of “Future-proofing your organisation” is focussed on strategies for technological advancement of organisations. These strategies defined within this review are aimed at making companies future ready through technological incorporation. Different conditions associated with organisational technological advancement are discussed within this cover story. Organisations were incorporating technological changes from before outbreak of Covid-19. Technological advancements are putting organisations way ahead of their competitors in a market. Technological changes are being made within different aspects of a business organisation. These include “people”, “production”, “process” and “management” also. Diverse types of benefits are being incurred by organisations through these technological advancements (HBR, 2021). Examples of technological advancement and its benefits are mentioned within this cover story.
Different companies used to employ a large number of employees for monitoring of organisational functionalities. This incurred high costs and also reduced productivity within these organisations. However, with incorporation of technological equipment such as “Artificial Intelligence (AI)” analytical tools within organisational functionality analytics have become easier (Stone et al. 2020). Only a few employees are required to operate analytical functionalities, that labour force can be employed in other work. This will benefit organisations with an increased productivity through technological incorporation. This cover story has also defined importance of identifying most important organisational roles. There are different types of functionalities that take place within an organisation. However, among these functionalities about 95% of functionalities can be impacted by management of 5% of organisational functionalities (HBR, 2021). This 5% functionality is very important for organisational performance and is required to be managed efficiently.
It is difficult to identify which functionalities are required to be focussed on. Technologies such as “Sensor” along with “big data analytics” are incorporated within different processes for monitoring organisational functionalities (Mikalef et al. 2020). These technologies define functions according to their respective importance and manage them efficiently. In order to achieve success, organisations are required to think of future changes and define functionalities to suit these changes. In case of changes in functionality of an organisation it becomes difficult for employees. In case organisational functionality does not change, then only 60% of organisational employees become enabled to manage organisational functionalities (HBR, 2021). However, in case of changes occurring, organisations are required to recruit new staff skilled for handling specific job roles.
Some organisations have focussed on incorporating technological changes by recruiting employees with suitable skills for embracing these changes taking place within organisation. Assessment of a large number of candidates and incorporation of a recruitment drive has enabled these organisations to recruit skilled employees (Börner et al. 2018). Their recruitment drives have been done based on results of analysis done by organisations on required operations changes. Recruitment of new and skilled employees enabled these organisations to operate these functions due to suitability of employees with new changes. “Ping An” have developed an system of recruiting employees by utilising technologies such as “Big Data” (HBR, 2021). This has enabled them to recruit employees at a significant low cost compared to traditional recruitment procedure.
Role of “Human Resource” management have also been focussed within this cover story in light of digital advancement incorporation within it. This has focussed on steps taken by organisations to enhance skill levels of their employees in order to prepare them for future. Benefits gained by these organisations such as prevention of cost of recruitment have been mentioned within this article. Moreover, focuses of organisations to enable technologies such as “Big Data” in preparing employees have also been discussed within this cover story (HBR, 2021). This provides ideas about role of technological advancement in aiding employees to embrace future organisational changes.
Diverse functionalities regarding management of human resources are performed by HR managers of an organisation. Therefore, technological inclusion for these activities has been mentioned. Inclusion of technologies for management of employees would improve capabilities of HR managers. Mention of technologies such as analytical tools using AI and many more have been done within this article. Incorporation of technologies such as AI have increased after Covid-19 outbreak for analytical and decision-making purposes.
Technological awareness of employees is very essential for technological advancement of organisations. Moreover, this is necessary for making employees ready for future changes such as technological advancements and introduction of new techniques. Importance of this has been discussed within this cover story also. Lastly, this article highlighted importance of focusing on changes that are about to come in future. Making changes according to future requirements of organisation will enable organisations as well as employees to be ready for accepting these changes. Mention of organisations such as “Service Now” has also been included within this cover story (HBR, 2021). This organisation focussed on improving employee engagement with organisation and making their work procedure easier.
Challenges Identified in cover story
Identification of important functionalities
A variety of organisational functions are performed within an organisation regularly. Different employees perform different duties as per their responsibilities. Technological incorporations are done for improving different organisational purposes. However, defining of most important organisational functionalities is an important task for organisations to ensure success of their operations. This task has been found to be challenging for many organisations due to lack of opportunities of analysing their tasks. These organisations not being able to clearly define their organisational functionalities and specifying their most important procedure often face failure (Bugwandeen and Ungerer, 2019). This challenge is required to be addressed in order to increase future proofness of organisations through digital inclusion.
Selecting appropriate employees according to different jobs
Employees working within an organisation are responsible for performing different responsibilities. Moreover, these employees possess different skills according to their specific job roles. In order to enable employees to work within an advanced technological environment it is required to provide them with training. This includes high cost and time required to train employees for specific job roles (Rozario et al. 2019). Moreover, changing environment would require multiple training sessions. This results in recruitment of employees possessing required skills for specific job roles. This provides significant benefits to organisations by improving productivity. However, this recruitment procedure for selecting appropriate employees for their specific job roles is posed as a challenge to different organisations. Interviewing different candidates and analysing their skills to find out suitability with a job role is required to be done efficiently by organisations.
Costs of recruiting new employees due to changes in work functions
Some organisations that are going through organisational changes and are incorporating changes in their functionality become concerned about employee preparedness. Strategy of recruiting skilled employees for specific job roles is often considered by organisations for meeting with their future objectives. However, recruitment is a lengthy process, which includes analysis of skills of a large number of employees and selection of them. High costs oriented with recruitment procedures are defined as a significant challenge to different organisations (Hmoud and Laszlo, 2019). These organisations are finding solutions to this issue for reducing costs oriented with recruitment procedure and improving its efficiency.
Management of HR functions
Figure 2: People, Process and Product of Business
(Source: Influenced by ThiHoa et al. 2021)
“Human resource management” within an organisation includes diverse functions such as “recruitment”, “training of employees”, “management of wages”, and “guiding employees through organisational changes”. These varieties of tasks require active participation of HR managers with these tasks. Due to large scale of each of these tasks it becomes difficult for HR managers to manage these tasks (ThiHoa et al. 2021). Organisations are finding different ways of solving this issue and increasing efficiency of HR managers in performing their duties. It is essential for organisations to include digital technologies for providing assistance to HR managers in management of these tasks.
Increasing technological awareness of employees
Main aim of “future proofing of organisations” is to enable organisations to embrace changes that are about to take place. These changes are mainly oriented with technological advancement and incorporation of new technologies within organisational functionality. In order to make an organisation “future proof” it is essential to incorporate with advanced technologies and comply with present technological trends prevailing within business market (Nambisan et al. 2019). Moreover, incorporation of further advanced technologies is also being done by organisations for improving their sustainability and being ready for upcoming changes. However, a big challenge is faced by these organisations during incorporating these advanced technologies within their functionalities that is preparedness of employees. Advanced technologies such as “Big data”, “Internet of Things (IoT)”, “Machine learning” and “Artificial Intelligence” are very new concepts for employees. In order to enable these employees to be able to utilise these technologies they are required to be made aware about functionalities of these technologies. This has been found to be a significant challenge for these organisations.
Adapting to future requirements
Incorporation of digital technologies is changing work procedure of organisations. Along with this, new innovative ideas are utilised and variations are being introduced within services or products offered by an organisation. These changes within offerings by organisations are also giving rise to changed requirements by customers. Changes of customer requirements are being identified within not only type of products but also within scale of their demands. These changes are often faced by organisations as challenges due to their incapability to meet with customer requirements (Bals et al. 2019). “Woodsire energy” faced difficulties managing their diverse operations such as “Decision-making” within organisation. Moreover, increase in capabilities of organisations will also enable them to address further market requirements that might arise in future. This will increase sustainability of organisations and also enable these organisations to constantly improve their productivity. Organisations are finding different ways to cope with these changing requirements of their organisational capabilities.
Mitigation of challenges provided in cover story
Different organisations are developing different strategies for solving issues oriented with making their organisations digital proof. This cover story of “Future-proofing your organisation” has discussed different mitigation techniques employed by different organisations for solving these issues. These strategies for solving such challenges include utilisation of diverse technologies. Issues of inclusion of a large number of employees required for maintaining inventories and managing product supply have been identified within this cover story. Solutions of this challenge have been provided to be incorporation of “Predictive analytics” along with “real time point of sale”, “logistic data” and “data of manufacturing” (HBR, 2021). These technologies are enabling companies to be aware about requirements of supply at different stores and supply accordingly.
Issues of defining important organisational procedures and focussing on them have been solved by “Woodside Energy” through their realisation of necessity of enhancement of conventional procedures (HBR, 2021). This company utilised “Sensor technologies” along with “Big data analytics” for improving their decision making procedure and making it faster. Moreover, utilisation of “machine learning and AI technologies” has been done by this company in defining their most important tasks and focusing on their enhancement. Implementation of these technologies improved productivity and safety within work sites of Woodside Energy.
Issue of selection of suitable employees according to job roles is also a significant issue that requires a solution. “Chemistry group” provided solutions to this issue by defining different requirements for different job roles. Along with basic requirements of every job role information about “skills required for them”, “traits” and “behaviours” have been suggested to be provided for solving such issues. Issues arising due to higher costs of recruitment are solved by “Guardian”, according to this cover story through digital transformation of their “technologies” “process’ ‘ and “data”. Enhancement of working ability of their employees will enable them to perform 60% of their future duties.
Effective management of HR duties have been identified to be a significant challenge. This challenge has been addressed by “Ping An”, largest insurance company of China (HBR, 2021). This company hires a large number of employees every year. In order to solve issues with recruitment of employees have been solved by it through utilising “big data” and “AI” technologies (Bag et al. 2021). These technologies are aiding in recruitment as well as management of efforts of development. Some organisations also focussed on development of their employees through training and enhancing their skills. This enabled employee to be ready to adapt to technological changes. For example, “USAA”, a financial service provider is one such company that is increasing technological awareness of their employees. Moreover, their employees are supported by “machine learning algorithms” (HBR, 2021). These utilise AI drive analytics to assist their employees in analysing damage caused to a vehicle. Being able to cope up with technological changes, employees could perform their job roles efficiently within changing pattern of work of their organisation.
Issues oriented with adaptation to future challenges have also been provided with solutions by some organisations. For instance, “ServiceNow”, a software and service based company solved this issue through employee retention and encouragement of employees (HBR, 2021). It defined most important aspects of their organisation and focussed on them rather than focussing on not so important tasks such as fancy interiors. This enabled it to work on most critical factors of their business and enhance their productivity by enhancing those (Moeuf et al. 2020). Besides this, organisations are incorporating technologies such as “machine learning algorithms” for enabling employees to cope with future changes occurring within organisational functionality.
Critical analysis of cover story
Cover story “Future-proofing your organisation”, published within “Harvard Business Review” has been focussed on technological advancements and different strategies incorporated by organisations to become ready for future changes. Diverse solutions developed by various organisations for solving these issues have also been discussed within this cover story. Utilisation of advanced technologies such as “AI” and “Big Data” has been discussed within this article with examples for solving organisational issues. These insights have provided proper ideas about steps required for making organisations ready for future changes. However, this cover story only focussed on positive sides of technological advancements yet failed to address challenges that are faced by organisations in incorporating technologies. Biggest issue with technological advancement is oriented with high costs associated with it. Companies irrespective of being business or non-business organisations face difficulties in management of funds for technological advancements. Another issue that is faced during technological advancement that also has not been mentioned within this article is technological availability.
Utilisation of technologies such as “Big data” and “AI analytics” has been mentioned within this cover story. “Big Data” and “AI” driven tools are complex pieces of technology. Development of “Big Data” requires collection of past and present organisational data and incorporation of them within a single place (Wang et al. 2020). This is very difficult for any organisation. On the other hand, “AI” engines are required to be developed and trained with proper commands to enable proper functionality by them. Such tasks associated with preparing these technologies are very complex and require a high level of technological knowledge and skills. Often this is found to be posing a significant challenge for an organisation. However, this challenge has no mention within this cover story. Enhancement of recruitment procedures through incorporation of “AI” technologies have been discussed within this cover story (He et al. 2019). However, issues such as failure of these technologies to analyse different abilities of candidates have not been discussed within this cover story. Inclusion of this information within discussions of this report would have helped in proper understanding of challenges oriented with future preparations of organisations.
Theoretical analysis
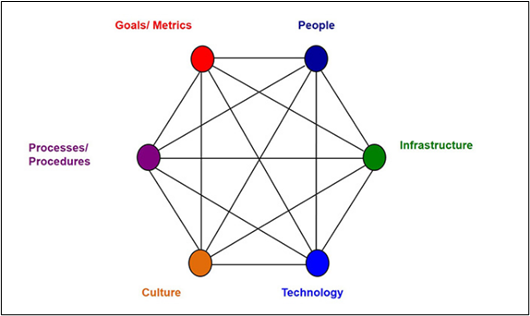
Figure 3: Systems theory and Technological orientation
(Source: BUSINESS.LEEDS, 2021)
Discussions within this Cover story included information about technological advancements, impact of such advancement on people and its benefits on organisations. It can be said that most suitable theory for this cover story is “Systems theory” as it states that every aspect of an organisation is interrelated with other aspects of that organisation. According to “Socio-technical Systems theory”, organisations are made of sub-systems including “goals”, “people”, “infrastructure”, “technology”, “culture” and “process” (BUSINESS.LEEDS, 2021). These sub-sections are defined to be interacting with each other in nature. This framework states relationships present within these aspects of organisation such as “people with required skills are recruited within organisation”. These people work for fulfilling organisational objectives. Organisational work process is followed by people which includes usage of technologies. These technologies are operational within organisational infrastructure. Moreover, these are utilised following cultural values prevailing within an organisation.
This information associated with this framework is significant of efficiency of organisational performance through only collaboration between social as well as technological aspects of it. In order to incorporate any technological changes within organisations, advancement of both people oriented with an organisation and its technologies are required to be done simultaneously (Teece, 2018). Strong involvement of employees is required along with technological incorporations and for making it successful. Moreover, proper understanding of changes taking place within an organisation is also required to be developed among employees. This will prepare them to embrace technological changes within organisation. Along with this other aspects of an organisation such as tasks of that organisation are also required to be incorporated with elements of change.
Application of this article on business and NGO business organisation
Critically analysing “Future-Proofing Your Organization” article, it has been identified that technology is needed in bringing change over business operations or any innovations in an organisation. Pandemic created issues in business operations and it has created challenges in performing business operations smoothly. Therefore, a lot of critical challenges were eliminated because of implementation of technology in business operations. In times of COVID-19, there was a requirement of new capabilities, which would help businesses to survive in economic unstability. This article has helped understand that digital technology was helping businesses to transform and make new opportunities to rebuild business in global pandemic era (Scoblic, 2020). Running a business properly and especially a non-profit one, this article has helped implement new strategies to their businesses, which have helped them to understand where they were lacking in their business management.
Critical roles need to be understood by every business management, which can help them to identify different threats that their business can face in near future. As suggested by Williamson (2021), understanding critical roles would help them to gain an insight on potential issues that can be inflicted upon non-profit and leading business both. Pandemic has changed assumptions of importance of a role in a company as every employee is of importance in time for running a business properly and accurately. Therefore, different skills are needed to create a good business operation that would help in achieving success for meeting goals of business. Both profit and non-profit organisations are testing impact of big data science and digitisation of business to implement new strategies and competitiveness in production operations (Morkunas et al. 2019). Engineers had most reliable role in business infrastructure of both profit and nonprofit organisations, which has created scope in rebuilding and shaping future of both businesses during time of pandemic.
Sensor technology was built to combine with access to low cost computing power and its big data analytics to make faster decisions by using a vast range of data sources that are accessible. Therefore, it can be said that impact of this article and its practice number one has helped in attaining big data scientists for both profit and non-profit organisations, which has assisted in sustaining in business industry.
In second practice of this article, it has been showcased that hiring skilled employees are very important to improve performance in business operations. Therefore, both profit and non-profit organisations have been able to identify candidates that can take on new tasks efficiently. Based on an analysis of Demirkan et al. (2020), new tools and techniques have been utilised to analyse employees and their behavioural perspective with training sessions. This has allowed organisations to develop talent management and create proper recruitment strategies so that business needs can be met. Thus, both profit and non-profit organisations have been able to use behavioural perspective and critical analysis of personality tests to understand employee capability. Both of these organisations encouraged employees to adopt and learn about new mind set or behaviours through training sessions which would help them to achieve new transformation (Vanclay, 2020). Non-profit organisations do not have effective capital to hire employees by influencing them with proper salary therefore, these organisations need to use their communication skills properly so that candidates are influenced to take up jobs.
In third practice, it is understood that management development is very important in rebuilding business structure. Therefore, it has been understood that in times of pandemic there was a lot of job retention, which created a scope for hiring skilled employees that have vaster knowledge on technology and other business analytics tools. As suggested by Lew et al. (2020), recruiting new candidates can be an issue for non-profit organisations as recruiting new efficient candidates can be expensive. Businesses need to concentrate on having digital transformation within organisation to focus on improving different technological advances so that business performance can be easier. Implementing data analytics have helped both profit and no profit organisations to collect data and develop products according to customer trends suggested by data analytics (Wamba-Taguimdje et al. 2020). It is also told in this article that cutting off management development such as, “budget, training session and educational programmes” is not a smart move for achieving a positive future of an organisation. Thus, in pandemic era these new tricks have helped businesses to gain new opportunities in improving their working method so that efficient working methods can be implemented while performing business operations.
Fourth practice has suggested that HR function in management is important because frequent interaction among employees would not be cost effective for future of an organisation. Using technology has helped profit and non-profit organisations to track their employee performance and implement HR practice in their team management to reward employees accordingly. It has been observed by Kotsantonis and Serafeim (2019), employee performance needs to be appreciated so that they would be able to work with motivation. Thus, non-profit organisations have been able to reward their employees by motivating them and it has helped them to achieve efficiency in their working environment and business operations. Focusing on narrative of future candidates wants from a company helps in identifying that an employee’s needs help in achieving good management practice in an n organisation.
Conclusion
From analysing “Future-Proofing Your Organization”, it can be concluded that critical understanding of business practices and its method, which would attain success in business operations. This article has defined six practices, which would help businesses to improve their working procedure so that their business operation can be easier. Thus, it has assisted in understanding that technology is a major part for transforming a business into effective business management. Six practices has helped in undermining employee rewards, HR practice, engaging employees more with tech has helped in accomplishing a more data driven and strategic method in business operations. Implementation of technology would help in breaking down barriers of traditional methods of business infrastructure, which would help in attaining success for business operations and future of an organisation.
References
Bag, S., Pretorius, J.H.C., Gupta, S. and Dwivedi, Y.K., (2021). Role of institutional pressures and resources in the adoption of big data analytics powered artificial intelligence, sustainable manufacturing practices and circular economy capabilities. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 163, p.120420.
Bals, L., Schulze, H., Kelly, S. and Stek, K., (2019). Purchasing and supply management (PSM) competencies: Current and future requirements. Journal of purchasing and supply management, 25(5), p.100572.
Börner, K., Scrivner, O., Gallant, M., Ma, S., Liu, X., Chewning, K., Wu, L. and Evans, J.A., (2018). Skill discrepancies between research, education, and jobs reveal the critical need to supply soft skills for the data economy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(50), pp.12630-12637.
Bugwandeen, K. and Ungerer, M., (2019). Exploring the design of performance dashboards in relation to achieving organisational strategic goals. South African Journal of Industrial Engineering, 30(2), pp.161-175.
BUSINESS.LEEDS, (2021) Socio-technical systems theory. Available at: https://business.leeds.ac.uk/research-stc/doc/socio-technical-systems-theory [Accessed on: 30/09/2022]
Dahlman, C. and Westphal, L., (2019). Technological effort in industrial development–an interpretative survey of recent research (pp. 105-137). Routledge.
Demirkan, S., Demirkan, I. and McKee, A., (2020). Blockchain technology in the future of business cyber security and accounting. Journal of Management Analytics, 7(2), pp.189-208.
HBR, (2021) Future-Proofing Your Organization. Available at: https://hbr.org/2021/09/future-proofing-your-organization [Accessed on: 30/09/2022]
He, J., Baxter, S.L., Xu, J., Xu, J., Zhou, X. and Zhang, K., (2019). The practical implementation of artificial intelligence technologies in medicine. Nature medicine, 25(1), pp.30-36.
Hmoud, B. and Laszlo, V., (2019). Will artificial intelligence take over human resources recruitment and selection. Network Intelligence Studies, 7(13), pp.21-30.
Kotsantonis, S. and Serafeim, G., (2019). Four things no one will tell you about ESG data. Journal of Applied Corporate Finance, 31(2), pp.50-58.
Lew, A.A., Cheer, J.M., Haywood, M., Brouder, P. and Salazar, N.B., (2020). Visions of travel and tourism after the global COVID-19 transformation of 2020. Tourism Geographies, 22(3), pp.455-466.
Mikalef, P., Krogstie, J., Pappas, I.O. and Pavlou, P., (2020). Exploring the relationship between big data analytics capability and competitive performance: The mediating roles of dynamic and operational capabilities. Information & Management, 57(2), p.103169.
Moeuf, A., Lamouri, S., Pellerin, R., Tamayo-Giraldo, S., Tobon-Valencia, E. and Eburdy, R., (2020). Identification of critical success factors, risks and opportunities of Industry 4.0 in SMEs. International Journal of Production Research, 58(5), pp.1384-1400.
Morgan, J.M. and Liker, J.K., (2020). The Toyota product development system: integrating people, process, and technology. Productivity press.
Morkunas, V.J., Paschen, J. and Boon, E., (2019). How blockchain technologies impact your business model. Business Horizons, 62(3), pp.295-306.
Nambisan, S., Wright, M. and Feldman, M., (2019). The digital transformation of innovation and entrepreneurship: Progress, challenges and key themes. Research Policy, 48(8), p.103773.
Rozario, S.D., Venkatraman, S. and Abbas, A., (2019). Challenges in recruitment and selection process: An empirical study. Challenges, 10(2), p.35.
Scoblic, J.P., (2020). Learning from the future. Harvard Business Review, 98(4), pp.38-47.
Stone, M., Aravopoulou, E., Ekinci, Y., Evans, G., Hobbs, M., Labib, A., Laughlin, P., Machtynger, J. and Machtynger, L., (2020). Artificial intelligence (AI) in strategic marketing decision-making: a research agenda. The Bottom Line, 33(2), pp.183-200.
Teece, D.J., (2018). Dynamic capabilities as (workable) management systems theory. Journal of Management & Organization, 24(3), pp.359-368.
ThiHoa, N., Hang, N.T., Giang, N.T. and Huy, D.T.N., (2021). Human resource for schools of politics and for international relation during globalization and EVFTA. Ilkogretim Online, 20(4).
Vanclay, F., (2020). Reflections on Social Impact Assessment in the 21st century. Impact Assessment and Project Appraisal, 38(2), pp.126-131.
Wamba-Taguimdje, S.L., Wamba, S.F., Kamdjoug, J.R.K. and Wanko, C.E.T., (2020). Influence of artificial intelligence (AI) on firm performance: the business value of AI-based transformation projects. Business Process Management Journal, 26(7), pp.1893-1924.
Wang, J., Yang, Y., Wang, T., Sherratt, R.S. and Zhang, J., (2020). Big data service architecture: a survey. Journal of Internet Technology, 21(2), pp.393-405.
Williamson, B., (2021). Making markets through digital platforms: Pearson, edu-business, and the (e) valuation of higher education. Critical Studies in Education, 62(1), pp.50-66.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

