SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT
Introduction
The present reporting on deficiencies and other health issues along with the preventable deaths in hospitals indicates inadequate nurses in hospitals (Eyeberu et al. 2021). Based on the provided case study it is further determined that the staff members in the hospitality business are an essential factor that further contributes a lot towards the growth of the hospital (Suresh et al. 2020). It is further determined that the number of patients in comparison to the ratio of nurses across NHS Hospitals has increased to a great extent. Apart from that, it is also observed that the percentage of morality has enhanced (Brouwer, 2019). The growth of the hospital somehow depends on how the patients are been cared for by the staff members of the hospital. Furthermore, the paper involves the necessary description with respect to the satisfaction of the patients with hospital care and nurses in England. It is further identified that though the administrative department of the nation has announced safe nurse staffing to provide maximum satisfaction to the patients the nation has observed substantial variation in nursing (Lasater et al. 2021). Based on the provided illustration it is opined that the paper involves necessary details regarding the satisfaction level of the patients and the loops in RN nursing that the hospital faces. Therefore, it can be said to drive out authenticated and reliable information in the context of the field of nursing the detailed analysis of the paper is very essential (Bautista et al. 2021). Recently it is notified that due to the inadequate activity of the staff members of the hospital and uncaring nurses deficiency in the hospitals has been seen. Further to analyze the paper in detail and to provide reliable information patient survey data from 2010 has been interpreted. The reason behind an interpretation of patient survey data is to illustrate the rates given by patients for their care (Russell et al. 2021). Moreover, quantitative research methodology has been implemented to provide authenticated details.
Main body
Robustness
Research problem
Concerning the provided case study it is determined that the main issue of the research paper is to determine the viewpoint of the patients of England in the context of the staff members of the hospital. The increasing death rates and other health issues can also be considered as the reason why these staff members and their policies are being questioned (Vogel et al. 2021). Another problem of the research paper is to determine the association between the confidence level of the patients and the staff members of the hospital such as nurses, doctors, RN staffing and others. It further also provides necessary information in context to the experience of the patients in NHS by interpretation of the survey report of NHS Adult Inpatients.
Purpose significance of the study
Based on the provided case study and the further report it is perceived that the main purpose behind the research is to evaluate and determine the satisfaction level of the patients of NHS hospital with its nurses and other staff members. In other words, it can be said that the paper involves necessary details in accordance with the impact of nurses on the satisfaction level of the patients. Nurses are further determined or referred to as the greatest power that can improve the experience level of the patients. Hence, it can be said that nurses in the hospitality business play a significant role and the experience of the patients somehow depends on the ability and empathy level of the nurses (Cribb et al. 2022).
Literature review
Illustration in context to the importance of nurses to meet the satisfaction level of the patients
Based on the provided case study it is determined that nurses play an essential role in the hospital as the growth of the hospital is dependent upon the activity of the nurses. Further, it is also determined that due to the work done by the nurses their satisfaction level and their confidence fluctuate. The nurses not only provide physical support to the patients but also play a central role in the hospitality business. They further give psychological and emotional support to the patients as well as their family members. In hospitals providing maximum satisfaction to the patients is very essential and crucial and based on the satisfaction of the patients the quality of the healthcare sector or the quality of the hospital is determined (Karaca and Durna, 2019).
It is further determined that the satisfaction level of the patients further creates an impact on the clinical outcomes of the hospitals (McHugh et al. 2021). Apart from that it further also creates an effect on patent retention and the claims of medical malpractice. Therefore, based on the provided description and further observation it can be said to drive out essential information in context to the work done by the staff members of the hospital and to examine the health care quality it is very essential to analyze the satisfaction level of the patients. Further, it is percieved that it is very essential to provide maximum satisfaction to the patients as the healthcare experience quality of the patients depends on patient satisfaction (Abidova et al. 2020).
Description with respect to the relationship between the patients and the staff members of the hospital
Moreover, it is determined from further observation that to make the hospital productive and profitable it is very crucial to build a healthy relationship between the patients and the staff members of the hospital. The relationship between the nurse and patients is determined to as a helping relationship (Manzano and Ayala, 2021). Along with care, it is further essential for the nurses and other staff members of the hospital to build effective interaction with the patients and their family members. Along with that it further requires healthy communication, respect in the context of ethical values and empathy to stimulate introspection and behavioural charge (Mtawa et al. 2021).
Moreover, it is also notified that building a healthy relationship with the patients is essential to facilitate cooperation. Apart from that, it is ordained that a good or sound relationship with the patients further obliges the nurses or other staff members of the hospital to gain essential information in context to the unique health needs of the patients (Seo et al. 2021).
Study design
Based on the requirement of the paper and the provided case scenario it is determined that the quantitive research method is being implemented in the further section of the paper to determine the association between doctors and nurses and patients. Further, it is also determined that the cross-sectional data is determined or utilized in the paper to evaluate the satisfaction level of the patients with nurses and the healthcare activities of the hospital. The quantitative study further depends on the type of design that is being used to evaluate and analyze the paper. Based on the further illustration that has been provided it is opined that regression and coefficient method has been used to illustrate the survey report. Therefore it can be said that the statistical method has been incorporated to illustrate the pattern of a topic and the relationship between different variables (Douma and Weedon, 2019).
Methods
As per the provided description, it is opined that the Quantitative research method has been focused to drive out authenticated and reliable resources or information in context to the provided topic (Solarino and Aguinis, 2021). Main reason behind the implication of Quantitative research methodology is to focus on the statistical and numerical analysis of the collected survey data. Along with that, the quantitative method obliges to create a great focus on objective measurements. Another reason that has been determined or identified behind the implication of such a method to drive out reliable details is to attain greater knowledge with respect to the satisfaction of the patients (Drossman and Ruddy, 2020).
Philosophical underpinnings
As per the observation, it is determined that Quantitative Philosophical underpinnings indicate that the social world can not be illustrated from the viewpoint of the individual (Ronkainen and Wiltshire, 2021). It is further observed that most of the quantitative data is underpinned by post-positivist and positivist understandings in context to the facts and nature of the world. It further ordains that the derived data set can be easily measurable. In other words, it can be said that Philosophical underpinnings are determined or illustrated as something that is considered to be served as a foundation. The reason behind the identification of the philosophical basis is to drive out sustainable and realistic philosophical underpinnings (Reid et al. 2021).
Theoretical framework
As per the provided case study, it is determined that the European Unions Seventh Framework program has been emphasized (Downes and Loveless, 2018). Apart from that it is also ordained or perceived that the National Institute of nursing research and the national institute of health have been emphasized to drive out a piece of essential and effective information with reference to the provided topic. Moreover, another theory that can be emphasized to drive out the necessary information is the patient satisfaction theory. According to the analysis of the proposed theory, it is determined that the satisfaction level of the patients is further considered as the outcome of the agreement between the expectation of the patient and the actual care provided by the hospital (Helaß et al. 2022).
Aim and hypothesis
The primary aim of this research is the identification of the satisfaction level of the patient by hospital care and nurses in the context of England. In this regard, this research has developed hypotheses for the purpose of proving and unproven the topic of this research. These hypotheses are presented below:
Null hypothesis: The satisfaction level of patients will not be influenced by their confidence in their nurses and episodes of missed nursing care. (p>0.05)
Alternative hypothesis: The satisfaction level of the patient is directly related to episodes of missed nursing care and confidence. (p<0.05)
This study has determined whether the null hypothesis has been accepted or rejected. In this way, the impact of nursing care on the satisfaction level of the patient can be identified.
Sampling
Sampling is one of the key factors for a quantitative study that can be used for the purpose of collecting responses quantitatively as per the viewpoint of Al-Ababneh, (2020). This study has collected responses through sampling techniques. Over 66000 patients are selected who were discharged from 161 NHS trusts located in England. In addition to this, “Nurse survey data” has been collected from “medical care and surgical direct care” for 2963 inpatients in a sample of 31 of the same NHS trusts located in England. It is recognised that the survey of around 12581 of a total of 66348 patients from the 31 NHS trusts was discharged due to comprising 46 different hospitals. Furthermore, 5311 patients among these 12581 patients were admitted to general medicine wards. This analysis helps to identify that this study has selected a “random sampling technique” for the purpose of collecting samples. In this regard, this research has used a few funding options to conduct surveys such as “European Union’s Seventh Framework Program (223468)”, “National Institute of Nursing Research”, and “National Institutes of Health (R01 NR014855)”.
In this regard, this research does not consider patients as participants in the initial design although they are engaged in the survey process actively. In this way, the researchers have become able to identify whether the experience of patients is good or not regarding care provided by nurses in England.
Furthermore, it is observed that this study has implemented the interview process by including patients while pilot testing. In this regard, this research has provided opportunities for the patients for describing their experience in one page regarding inpatient questionnaires as well as on the aspects which are essential for them. Therefore, it is stated that this study has undertaken patients anonymous while on the other hand primary focus of this study is the identification of experiences of patients regarding nursing care.
Ethical consideration
According to McCauley et al. (2019), ethical consideration is one of the key factors for a quantitative study as it has included several key elements based on which researchers and the participants have become able to provide consent towards the study. In this regard, the research of Roher et al. (2021) stated that ethical consideration in research is referred to the set of principles that provide guidance to the designs and practices of research. Based on this analysis, it has been represented in this study that ethical consideration can be helpful in identifying whether the participants are satisfied with the study or not. It has consisted of “voluntary participation”, “confidentiality”, “informed consent”, and many others (Alkaraki et al. 2020). In the context of this research, it is observed that samples are collected from patients and inpatients from NHS trusts in England. Therefore, it is stated that there is a requirement to provide confidentiality. In addition to this, it is recognised that this study has collected approvals from “The University of Pennsylvania Institutional Review Committee (IRB)”. Based on this analysis, it has been represented in this research that this study has successfully maintained the ethics of this research.
Data collection
The method for collecting data plays a significant role in a quantitative study as per the viewpoint of Mikalef et al. (2019). On the basis of this identification, it is stated that the selection of an appropriate method for collecting data can be helpful in identifying the satisfaction level of patients regarding taking care by nurses. In the context of this study, data are collected in a quantitative way. The quantitative method of collecting data helps to gather data from the survey participants (Barrett and Twycross, 2018). Due to this reason, this research has selected a quantitative method for collecting data from patients and inpatients from NHS trusts in England. In addition to this, it is observed that all the data collected for this study were from NHS trusts and RN.
Data analysis
According to Cathala and Moorley (2018), the analysis of data varies between different studies on the basis of the design used by the researchers in a quantitative study. On the basis of this analysis, this research has selected a quantitative method for the purpose of collecting and analysing data in an effective way. This research has also discussed that descriptive study is the proper design for a quantitative study to get a better outcome. In this regard, the research of Jordan et al. (2021) stated that descriptive design for research can be beneficial in investigating one or more variables of a study. In the context of this study, there are two variables such as the satisfaction level of patients and nursing care. Therefore, it is stated that the use of descriptive design can be useful to make an investigation regarding the impact of nursing care on the satisfaction level of patients.
Findings
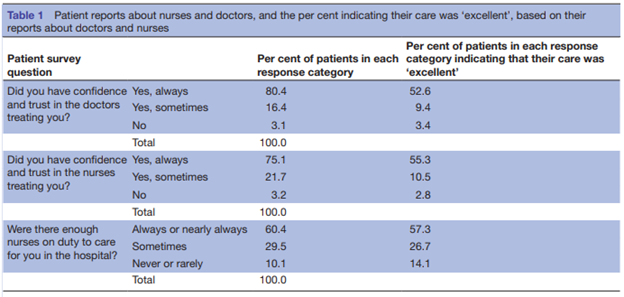
Figure 1a: Patient report regarding nurses and doctors
(Source: Provided)
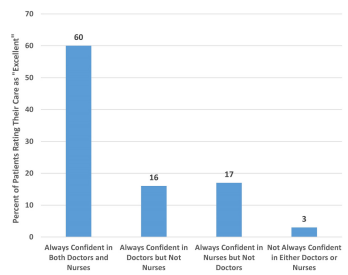
Figure 1b: Patient report regarding nurses and doctors
(Source: Provided)
Figure 1a and Figure 1b represent the responses of patients about nurses and doctors. These figures have shown that 60% of total respondents have always had confidence in both the nurses and doctors. In addition, 16% of total respondents have confidence in doctors however not nurses. 17% of total respondents have confident only in nurses while on the other hand, 3% of total respondents do not confidence in both doctors and nurses.
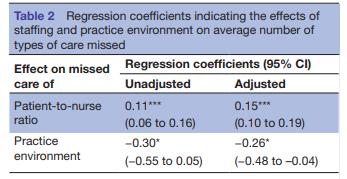
Figure 2: Regression coefficients
(Source: Provided)
This figure represents the “regression coefficient” that helps to identify that the “patient-to-nurse” ratio stands at 0.15 and the practice environment stands at -0.26 regarding adjusted. On the other hand, these factors stand at 0.11 and -0.30 regarding unadjusted respectively.
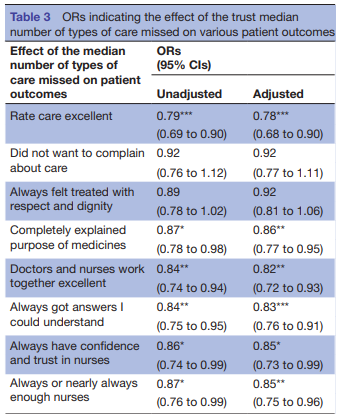
Figure 3: Impact of trust median number
(Source: Provided)
This table represents the implication of the trust median number in the context of the type of care missed regarding the outcomes of patients. It is identified from this figure that “Rate care excellent” stands at 0.79. In addition to this, “Did not want to complain about care”, “Always felt treated with respect and dignity”, “Completely explained the purpose of medicines”, “Doctors and nurses work together excellent”, “Doctors and nurses work together excellent”, “Always have confidence and trust in nurses”, and “Always or nearly always enough nurses” stands at 0.92, 0.89, 0.87, 0.84, 0.84, 0.86, and 0.87 respectively.
Discussion
Figure 1a a 1b helps to identify the satisfaction level of patients regarding both nursing and doctor care. It is observed from this data that a maximum number of patients are satisfied with both nurses and doctors. However, the primary focus of this research is the identification of the satisfaction level of patients regarding nursing care. In this regard, it is observed that there are a few numbers of patients who are satisfied with nursing care. Therefore, it is stated that a null hypothesis has to be accepted by this study.
“Regression coefficient” helps to identify the impact of a variable on other variables as per the viewpoint of Kafle (2019). On the basis of this identification, it is stated that the “regression coefficient” can be helpful in identifying the impact of staffing as well as practice environment on the average number of care missed types. Figure 2 has represented the use of the “regression coefficient”. This figure helps to recognise that there is a significant implication of the environment of staffing and practice on the average number of types of care missed. In this regard, it is observed that there are several types of care that are missed by nurses such as “oral hygiene”, “pain management”, “skincare”, and many others. Based on this identification, it is represented that the patients are not satisfied with nursing care.
Figure 3 shows the impact of the “trust median number of types regarding care missed” on the outcomes of different patients. Through this finding, it is stated that there is a significant implication of trust median numbers on the outcomes of patients. Based on this analysis, it has represented that there is a lack of confidence in patients regarding nursing care.
Conclusion
This research covers the identification of the satisfaction level of patients with the care of nurses in England. For the purpose of proving or unproven the research topic, this research has developed two hypotheses. It is identified that this research has collected information from survey participants who are patients and inpatients of NHS trusts in England. The result of this study shows that the null hypothesis is accepted which represents less confidence of patients in nursing care.
Reference list
Abidova, A., Silva, P.A.D. and Moreira, S., 2020. Predictors of patient satisfaction and the perceived quality of healthcare in an emergency department in Portugal. Western Journal of Emergency Medicine, pp.1-12.
Al-Ababneh, M.M., 2020. Linking ontology, epistemology and research methodology. Science & Philosophy, 8(1), pp.75-91.
Alkaraki, A.K., Khabour, O.F., Alzoubi, K.H., Al-Ebbini, L.M. and Altaany, Z., 2020. Informed consent form challenges for genetic research in Jordan. Journal of multidisciplinary healthcare, 13, p.235.
Barrett, D. and Twycross, A., 2018. Data collection in qualitative research. Evidence-Based Nursing, 21(3), pp.63-64.
Bautista, J.R., Zhang, Y. and Gwizdka, J., 2021. Healthcare professionals’ acts of correcting health misinformation on social media. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 148, p.104375.
Brouwer, S., 2019. The auditory foreign-language effect of moral decision making in highly proficient bilinguals. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development, 40(10), pp.865-878.
Cathala, X. and Moorley, C., 2018. How to appraise quantitative research. Evidence-based nursing, 21(4), pp.99-101.
Cribb, A., Entwistle, V. and Mitchell, P., 2022. Talking it better: conversations and normative complexity in healthcare improvement. Medical humanities, 48(1), pp.85-93.
Douma, J.C. and Weedon, J.T., 2019. Analysing continuous proportions in ecology and evolution: A practical introduction to beta and Dirichlet regression. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 10(9), pp.1412-1430.
Downes, J.F. and Loveless, M., 2018. Centre right and radical right party competition in Europe: Strategic emphasis on immigration, anti-incumbency, and economic crisis. Electoral Studies, 54, pp.148-158.
Drossman, D.A. and Ruddy, J., 2020. Improving patient-provider relationships to improve health care. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 18(7), pp.1417-1426.
Eyeberu, A., Shore, H., Getachew, T., Atnafe, G. and Dheresa, M., 2021. Neonatal mortality among neonates admitted to NICU of Hiwot Fana specialized university hospital, eastern Ethiopia, 2020: a cross-sectional study design. BMC pediatrics, 21(1), pp.1-9.
Helaß, M., Greinacher, A., Götz, S., Müller, A., Gündel, H., Junne, F., Nikendei, C. and Maatouk, I., 2022. Age stereotypes towards younger and older colleagues in registered nurses and supervisors in a university hospital: A generic qualitative study. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 78(2), pp.471-485.
Jordan, J.J., Yoeli, E. and Rand, D.G., 2021. Don’t get it or don’t spread it: Comparing self-interested versus prosocial motivations for COVID-19 prevention behaviors. Scientific reports, 11(1), pp.1-17.
Kafle, S.C., 2019. Correlation and regression analysis using SPSS. OCEM J Manag Tech Soc Sci, 1(1), pp.126-132.
Karaca, A. and Durna, Z., 2019. Patient satisfaction with the quality of nursing care. Nursing open, 6(2), pp.535-545.
Lasater, K.B., Aiken, L.H., Sloane, D.M., French, R., Martin, B., Reneau, K., Alexander, M. and McHugh, M.D., 2021. Chronic hospital nurse understaffing meets COVID-19: an observational study. BMJ Quality & Safety, 30(8), pp.639-647.
Manzano García, G. and Ayala Calvo, J.C., 2021. The threat of COVID‐19 and its influence on nursing staff burnout. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 77(2), pp.832-844.
McCauley, D., Ramasar, V., Heffron, R.J., Sovacool, B.K., Mebratu, D. and Mundaca, L., 2019. Energy justice in the transition to low carbon energy systems: Exploring key themes in interdisciplinary research. Applied Energy, 233, pp.916-921.
McHugh, M.D., Aiken, L.H., Sloane, D.M., Windsor, C., Douglas, C. and Yates, P., 2021. Effects of nurse-to-patient ratio legislation on nurse staffing and patient mortality, readmissions, and length of stay: a prospective study in a panel of hospitals. The Lancet, 397(10288), pp.1905-1913.
Mikalef, P., Boura, M., Lekakos, G. and Krogstie, J., 2019. Big data analytics and firm performance: Findings from a mixed-method approach. Journal of Business Research, 98, pp.261-276.
Mtawa, N., Fongwa, S. and Wilson-Strydom, M., 2021. Enhancing graduate employability attributes and capabilities formation: a service-learning approach. Teaching in Higher Education, 26(5), pp.679-695.
Reid, A.J., Eckert, L.E., Lane, J.F., Young, N., Hinch, S.G., Darimont, C.T., Cooke, S.J., Ban, N.C. and Marshall, A., 2021. “Two‐Eyed Seeing”: An Indigenous framework to transform fisheries research and management. Fish and Fisheries, 22(2), pp.243-261.
Roher, S.I., Yu, Z., Martin, D.H. and Benoit, A.C., 2021. How is Etuaptmumk/Two-Eyed Seeing characterized in Indigenous health research? A scoping review. PloS one, 16(7), p.e0254612.
Ronkainen, N.J. and Wiltshire, G., 2021. Rethinking validity in qualitative sport and exercise psychology research: A realist perspective. International Journal of Sport and Exercise Psychology, 19(1), pp.13-28.
Russell, C.D., Fairfield, C.J., Drake, T.M., Turtle, L., Seaton, R.A., Wootton, D.G., Sigfrid, L., Harrison, E.M., Docherty, A.B., de Silva, T.I. and Egan, C., 2021. Co-infections, secondary infections, and antimicrobial use in patients hospitalised with COVID-19 during the first pandemic wave from the ISARIC WHO CCP-UK study: a multicentre, prospective cohort study. The Lancet Microbe, 2(8), pp.e354-e365.
Seo, W., Buyuktur, A.G., Verma, S., Kim, H., Choi, S.W., Sedig, L. and Park, S.Y., 2021, May. Learning from Healthcare Providers’ Strategies: Designing Technology to Support Effective Child Patient-Provider Communication. In Proceedings of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 1-15).
Solarino, A.M. and Aguinis, H., 2021. Challenges and best‐practice recommendations for designing and conducting interviews with elite informants. Journal of Management Studies, 58(3), pp.649-672.
Suresh, M., Yuvaprasanth, R., Nathan, R.A.R. and Amarnath, K., 2020, October. Employees stress level assessment: a case of apparel industry. In IOP conference series: Materials science and engineering (Vol. 954, No. 1, p. 012018). IOP Publishing.
Vogel, B., Acevedo, M., Appelman, Y., Merz, C.N.B., Chieffo, A., Figtree, G.A., Guerrero, M., Kunadian, V., Lam, C.S., Maas, A.H. and Mihailidou, A.S., 2021. The Lancet women and cardiovascular disease Commission: reducing the global burden by 2030. The Lancet, 397(10292), pp.2385-2438.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

