International Business and Strategy Assignment Sample
Essay Topic: Internationalization path of L’Oréal
Internationalization offers several opportunities to an organization, like enhanced visibility, greater market share, opportunities for sustain growth and development, as well as global success prospects. However, it also holds the potential to highlight certain challenges or milestones, like action while undertaking international operations, complexities in adaptation to local cultures and traditions, as well as lack of customer support to undertake business activities and options in other nations. Therefore, the present report is vital and crucial in highlighting the concept of internationalization by undertaking a case study analysis a well-developed and globally established cosmetics brand, L’Oréal.
It highlights the internationalization of the company or through different entry modes as per the macro environment in different nations. Additionally, it also includes the value chain analysis of the concerned corporation, while highlighting significant changes since the last decade. Lastly, it highlights potential threats or risk factors to the company as well as proposes certain recommendations or suggestions for mitigating the challenges in the near future course.
L’Oréal’s international growth and its motivations
Internationalisation is primarily referred to as the procedure of designing product in order to fulfil the needs and demands of users in different nations and designing them so they can be easily modified, to accomplish the goal or objective (Dmitrievna, 2021). Furthermore, it can be described as a company undertaking steps or initiatives to increase its footprint and capture greater market share outside of its own country of domicile, by branching out into global markets. The cosmetic brand, L’Oréal operates in over 130 nations across the globe. The consistent growth and development of the company as well as the share in the specific market is an outcome of its varied marketing strategies.
Also, the firm differs itself from its rival companies considering the terms of product design, packaging, brand logo/name, prices, sales promotion, advertisement, website, and its strong distribution network. The global success of the cosmetic brand revolves around the fact that the firm succeeded in reaching out to the customers in different nations of the world, across different income ranges as well as cultural patterns, thereby, providing them with appropriate product ranges they are worthy of (Dörner, 2019). L’Oréal is observed to sell its product range depending upon the demands and preferences of the customers as well as the country wants instead of keeping the product identical across the world. Additionally, the company has built a dozen of mega brands which are rooted in the local cultures as well as appeal to different customer segments across different nations. The principal motivator of L’Oréal includes consistent innovation, strong promotion and advertisement, attractive website for online sales, and successful fulfilment of customer demands and preferences in different nations as per their varied needs, requirements, and preferences.
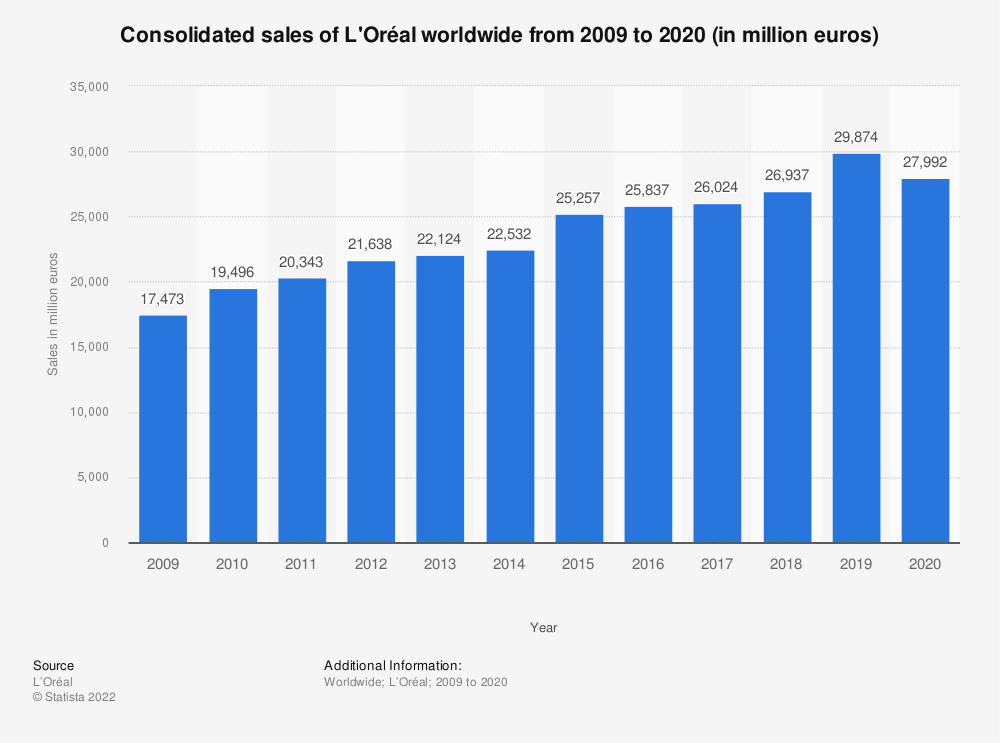
Figure 1 Consolidated sales of L’Oréal worldwide 2009-2020
(Source: Statista Research Department, 2022)
Considering the Uppsala Internationalisation Model, the brand, L’Oréal applied and integrated the four core concepts of market knowledge, market commitment, commitment decisions, and the current activities (Gilbert, 2021). In the initial stage, this model immensely supported laurels to initiate and consistently invest in one specific or in a few neighbouring nations, Like Germany, Switzerland, Italy, Belgium, Spain, and others. The model is based on the concept that instead of investing in different nations simultaneously, the brand must emphasise on carrying out its operations in specific nations cautiously, sequentially, and concurrently while also learning about the people of the firm operating in such international market. Therefore, L’Oréal implemented the framework while undertaking its international expansion, by applying its practical knowledge, learning from past experiences, and other vital skills (Igorevic, 2021). It also helps the cosmetic brand to ensure its overall cost efficiency, gain significant experience of different markets, and successfully penetrate into different nations.
L’Oréal’s pattern of growth in term of mode of entry and geographical entrance
Considering the strategy of internationalization or entry mode used by L’Oréal, it has been observed that the company adopt different entry modes of strategies for different nations. For an example it used the entry mode of establishing its subsidiaries in Brazil, in the year 1959 because of its speed, ability to coordinate with different departments, and for adopting the local culture of Brazil (Sergeevna, 2021). However, it encountered certain issues like high development cost and political issues in the nation. Later, it entered China by exporting its beauty products and selling them to the local agents. Yet, the company encountered problems of little control over technology, marketing, lack of coordination, and a proper distribution channel in China, and faced a dramatic loss. Nonetheless, a significant change introduced by L’Oréal my establishing its subsidiary brand, Maybelline, offered it a significant boost in the Chinese market after a few years.
Therefore, the internationalisation strategy adopted by L’Oréal is universalisation (Santos et. al. 2018). The company tends to capture, understand, and respect differences while undertaking its international expansion. It aims at providing tailor made beauty as well as to fulfil the aspirations of its customers across the globe. It is strategically concentrated, however, operationally decentralised, by empowering its local teams which guarantee that the company is close and relevant to its consumers in each nation. Therefore, different strategies or modes of market entry have helped L’Oréal to guarantee its successful international expansion in different nations.
L’Oréal’s value chain activities
The primary activities of L’Oréal highlight the inbound logistics operations, which include receiving, storing, and disseminating the inputs of different products, with the help of artificial intelligence further, the company emphasises on customer loyalty, trust, and CSR initiatives. Additionally, the operations of the cosmetics brand include gathering of raw materials and development of product (Prgić, 2019). The company has 37 cosmetic plants with each having different technologies. The company has established its policy for production of products very close to the market, thereby, maintaining good supplier relationships.
Moreover, the outbound logistics of L’Oréal include delivery of manufactured products to the retailers, suppliers, outlets, stores, and consumers. The company uses its excellent transportation and distribution network to ensure easy availability and accessibility of its products in different nations. Considering the marketing and sales activities of L’Oréal, the company adopt different marketing or promotional techniques (Withisuphakorn et. al. 2019). The company launches 500 new products every year and guarantees that its marketing strategies are successfully aligned with its business strategy and objectives. Lastly, in the service stage, L’Oréal guarantees that the customers are satisfied with its products, obtain feedback from them through different social media platform, and guarantees immediate response to their issues.
Observing the secondary activities of L’Oréal, the company has integrated modernised technologies, like AI, machine learning, cloud computing, and other digital platforms to guarantee smooth operational flow, customer satisfaction, and superior products (). Further, considering the dimension of HRM, the company recruits around 1 lakh employees across its outlets, subsidiaries, stores, and other launches across the globe. It primarily emphasises on recruiting skilled, talented, and highly competent employees who respect the organisation, its policies, and its objectives.
Additionally, the procurement stage of the company highlights its purchase of raw material from its suppliers at the best price (Andersen, 2019). It includes supplies, laboratory equipment, machinery, office equipment, and other raw materials for the cosmetics. Lastly, L’Oréal has a strong form infrastructure, concerning its organisational structure and chart, which is headed by its chairperson, Jean Paul Agon, being followed by four managers and other executives or leaders working under him.
Changes in the value chain configuration of L’Oréal are significantly noted in its technological integration and the concept of industry 4.0. The brand is getting closer to a fast fashion approach. Additionally, it aims at restructuring its operational flow or its value chain to further shorten the time to market while providing broader product ranges as well as maintaining quality standards. The company has recently transformed its methods of packaging, purchasing, manufacturing, and supply chain, thereby seeking to harness new technologies (Lefebvre, 2020). These include the Internet of Things or IOT, Virtual or augmented reality, connected objects, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing in order to boost overall efficiency and flexibility.
However, in the 1990s, the operations and business strategies of L’Oréal essentially revolves around accomplishing economies of scale, whereas, presently, the company is principally focused on redesigning its value chain, ranging from its suppliers to consumers, with efficiency and flexibility as the recurring themes.
Advantages of the current internationalization strategy adopted by the company
The giant cosmetics brand, L’Oréal, has chosen an exceptional strategy considering its international expansion or globalisation. This is the strategy of universalisation. It implies that the company aims at the procedure of globalisation which captures, develops a better understanding, as well as respect differences in nations, on the basis of culture, local preferences, demands, and skin requirements of the customers (Goxe and Viegas Pires, 2019). The firm emphasises on providing tailor-made beauty in order to fulfil the aspirations of its target consumers across different nations. This factor is considered to be the vision of L’Oréal. Additionally, the company creates and produces cosmetic products at the local level, thereby, guaranteeing that its formulations successfully adapt to the preferences and needs of its consumers, wherever they live.
For this purpose, L’Oréal has developed and established a worldwide network of research and innovation as well as marketing hubs, each for its strategic markets, including Japan, the United States, China, Brazil, South Africa, and India. Not only this, to further complement its work in development, the giant cosmetic brand has a global industrial presence, which guarantees that the product innovations are brought to the market efficiently and quickly (Baptista, 2020). Therefore, the strategy of universalisation has offered significant advantages to L’Oréal, concerning the selection and adoption of different entry modes in international markets as per the macro environmental situations in different countries.
Potential Threats and Recommendations
The external corporate environment across different nations highlights certain potential threats for the giant cosmetics brand, L’Oréal. These threats are further highlighted below.
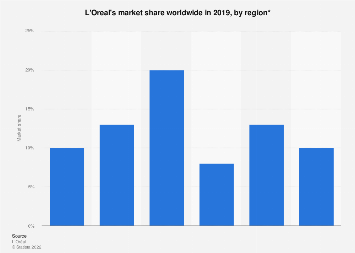
Figure 2 Loreal’s market share worldwide by region 2019
(Source: Statista Research Department, 2022)
Dynamic cosmetics industry: The Cosmetics industry encounters challenges with constant advancement being demanded by the customers. It is highly difficult and complicated for the organisations to keep up with the emerging trends, product attributes, and fast changing customer preferences (Adida, 2021). Not only this, increasing competition and intense rivalry across the global cosmetics industry further holds the potential to significantly impact the profitability and operations of the giant cosmetics company, L’Oréal. The ongoing addition of products is a potential threat to the company.
Cash Crunch: L’Oréal is a well-established brand operating across the global platform, and has established several sub-brands, which further implies that the company has to divide its cash into different segments. As a consequence, in a situation when the economy slumps, then the company might face a serious issue or challenge. This is because one or the other country always encounters economic problems, which can eventually result in stopping cash flow to the company from that particular nation (Almeida, 2018). This eventually results in adversely affecting overall cash flow as well as the management of working capital for the brand. Although, the economy of the European as well as the Asian countries is overall poor, which has resulted in a cash crunch for L’Oréal as well as potential danger looms during economic slumps.
Therefore, the company is recommended or suggested to guarantee effective and maximum utilisation of its integrated technologies, artificial intelligence, and internet of things in order to sport or identify the emerging trends concerning project attribute and customer preferences. Not only this, L’Oréal can also conduct market surveys or researches in order to gain feedback or insights about what products or specific product attributes the customers actually want considering the cosmetics and beauty care brands (Igorevic, 2021). It will eventually result in helping the company to produce goods or products which are actually based on the demands, needs, skin requirements, and preferences of the customers, thereby, developing and retaining a strong competitive advantage for the firm in the global cosmetics industry.
Although, there is not a particular approach to economic slump in certain countries or nations and it effect on the cash flow of the company. Yet, the company can detect early signs of economic decline in certain nations by market research or use of its extensive technologies. Later, the company can manage its cash flow prior to economic slump in nation, which will eventually minimise the effect of such economic declines on the overall cash flow and working capital management of the cosmetics brand, L’Oréal.
Evaluation of literature and sources
The evidences used for developing and accomplishing the above study include undertaken researches and studies by authors associated with internationalisation or globalisation. In addition to this, the authorised web page and website of the concerned cosmetics brand, L’Oréal, has been accessed to gain actual information or insights about its strategies and business activities. Additionally, published journals and articles associated with internationalisation within the cosmetics industry have been accessed to extract relevant data/information as per the requirements of the study and the subject.
In addition to this, use of excellent data sources, strong evidences, as well as authorised publications further ensure the use of quality information and actual insights about the concerned cosmetics company, L’Oréal. Additionally, the examples used for the brand concerning its entry mode of internationalisation, universalisation strategy, and other aspects guarantee superior quality of the entire study to its recipients or readers.
Hence, it can be concluded from the above report that internationalisation is a highly complex procedure. However, it ensures geographical diversification, Enhanced visibility of the brand name, as well as its products, and higher customer or market base across the globe. The above is reflected the case study analysis of an established cosmetics brand, L’Oréal. It highlighted the internationalisation strategies of L’Oréal, its value chain activities, as well as included potential threats to the company in the macro-environment of different nations.
References
Adida, A., (2021). L’Oréal digital consumer operating system. Managing Digital Transformation: Understanding the Strategic Process, pp.146-155.
Almeida, J.M.L.D., (2018). How to improve the process of sales’ prevision for the pharmaceutical division of L’Oréal? Development of a new model to analyze the gap betweensell-In and sell-out (Doctoral dissertation).
Andersen, M.L., (2019). L´ Oreal SA-consumer goods (Doctoral dissertation).
Azoulay, E., (2020). Using artificial intelligence to diversify the recruitment process at L’Oréal. Le journal de l’ecole de Paris du management, (2), pp.16-22.
Baptista, G.D.M.A., (2020). The importance of an analytical approach to e-commerce: the case of L’Oréal luxe division (Doctoral dissertation).
Dmitrievna, K.K., (2021). Transformation of Business Sustainability Strategies of FMCG Companies in the 21st Century on the Examples of Unilever and L’Oréal.
Dörner, N., (2019). L´ Oreal SA-consumer goods: a beautiful company at a luxurious price (Doctoral dissertation).
Flament, F., Zhang, Y., Yu, Z., Jiang, R., Houghton, J., Sarda Duthil, L., Arcin, V., Daniel, R., Perrier, J.C., Niviere, J. and Moyano, G., (2021). Developing an Artificial Intelligence (AI)‐based descriptor of facial appearance that fits with the assessments of makeup experts. Skin Research and Technology, 27(6), pp.1081-1091.
Gilbert, J., (2021). How L’Oréal adopted new technologies to scale personalisation, adapt to new customer demands and evolve into the top beauty tech company. Journal of Digital & Social Media Marketing, 9(2), pp.102-110.
Goxe, F. and Viegas Pires, M., (2019). Because It’s Worth It? A Critical Discourse Analysis of Diversity: The Case of L’Oréal. In Responsible Organizations in the Global Context (pp. 97-116). Palgrave Macmillan, Cham.
Igorevic, B.S., (2021). Advanced Analytics for Prediction of Customers’ Preferences: L’Oréal Case.
Lang, J., (2020). Working out Financial Analysis of a Selected Company in Cosmetic Industry.
Lefebvre, V.L.F., (2020). French cosmetics in China, a success story for L’Oreal: new opportunities in Brazil?.
O’Rourke, J.S., (2019). L’Oreal USA: Do Looks Really Matter in the Cosmetic Industry?. In Management Communication (pp. 318-322). Routledge.
Prgić, S., (2019). Human Resources Management function analysis in L’Oréal (Doctoral dissertation, University of Rijeka. Faculty of Economics and Business).
Santos, R., Au-Yong-Oliveira, M. and Branco, F., (2018, September1). L’Oréal and its innovative differentiated positioning process in the beauty industry. In European Conference on Innovation and Entrepreneurship (pp. 717-XII). Academic Conferences International Limited.
Sergeevna, V.N., (2021). Advanced Analytics for Prediction of Customers’ Preferences: L’Oréal Case.
Sevilay, U.L.A.Ş., (2020). Augmented Reality in Luxury Brand Communication in The Digital Transformation Process: L’Oreal Example. OPUS Uluslararası Toplum Araştırmaları Dergisi, 15(21), pp.12-33.
Wadhwaa, B. and Chaihanchanchai, P., (2021). The The Role of Online Influencer’s Characteristics in Attitude towards the Brand and Purchase Intention: A Case Study of L’Oréal. Communication and Media in Asia Pacific (CMAP), 4(2), pp.21-32.
Withisuphakorn, P., Batra, I., Parameswar, N. and Dhir, S., (2019). Sustainable development in practice: Case study of L’Oréal. Journal of Business and Retail Management Research, 13(Special).
Online:
Statista Research Department, (2022). [Online:]. Accessed through:< https://www.statista.com/statistics/243986/consolidated-sales-of-loreal-worldwide/ >
Statista Research Department, (2022). [Online:]. Accessed through:< https://www.statista.com/statistics/243955/market-share-of-loreal-by-region/ >
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

