PEOPLE AND ORGANIZATION MANAGEMENT SAMPLE
Introduction
People management is the process of managing people within an organisation to ensure that they are productive and motivated. It involves creating and maintaining an effective working environment, setting goals for employees, providing feedback and recognition, and encouraging collaboration . It also includes managing conflict, developing employees’ skills, and addressing issues related to diversity and inclusion. Organisational management is the practice of managing people, resources, and processes to achieve organisational objectives. It includes planning, organising, leading, and controlling an organisation’s resources to achieve its goals and objectives(Simic and Bardarova, 2019). It involves a wide range of activities, from recruiting and training employees to set goals and evaluating performance.
Statement 1
Factors of motivation and management style
There are so many that can motivate the team to work with someone’s organisation, such as job security, pay, and benefits, respect, work/life balance, career development, recognition, and autonomy. There are a lot of these depending factors that can significantly affect any organisation.
Job Security: Employees need to feel secure in their roles and have confidence that the organization will continue to be successful and provide them with employment. Job security is a motivating factor for employees to work with a team and for an organisation. When employees have job security, it provides a sense of security and stability that may be lacking in other aspects of their lives(Jyoti, 2019). This can lead to high levels of job satisfaction and motivation to work hard and stay with the organisation. Employees will feel like they are part of a team and be more likely to take initiative and contribute to the success of the organisation. Job security can also lead to better performance as employees are more likely to take risks and be creative due to the feeling of security. Long-term job security can also help with morale and employee retention. When employees know that their job is secure, they are more likely to stay with the organisation. This can lead to a greater sense of loyalty, which can lead to higher productivity and a better work environment. As stated by (Voorn et al., 2021) job security can also lead to a better work-life balance as employees can be sure that they will not be laid off or have to worry about the future of their job. As a project manager, his or her responsibility should be to take care of all these requirements of the employees so that it can be beneficial for the organisation.
Pay and Benefits: Money is the most obvious motivator and one of the most important factors in deciding whether to stay in a job or look for a new one. Pay and benefits are two of the most important factors in motivating people to work with and for an organisation. As stated by (Merenlender and Kremen, 2018), a person’s financial security and well-being are of paramount importance to them and, when an organisation provides a competitive salary, employees are more likely to feel valued and have a greater sense of loyalty to the company. Furthermore, if the salary package is attractive, it can be a powerful incentive for people to join a team or organisation. Pay and benefits can motivate the employees to connect with the organisation and give their full attention to the work field. It also encourages them to be loyal to the organisation and as a manager is the duty of the manager to take good care of these things so that the organisation can grow in the future.
Respect: Employees need to feel respected and valued in the workplace. They should feel that their contributions are acknowledged and appreciated. Respect is a powerful motivator in any team or organization. As per the views of (Mahapatro, 2022), it can create a sense of trust and security within a team, which can lead to greater collaboration, communication, and productivity. It can also inspire team members to strive to be their best and work together in order to achieve their goals. Respect can also create a sense of pride and belonging within an organization, which can lead to increased motivation and loyalty. Finally, respect can allow team members to feel heard and valued, which can lead to greater job satisfaction and a sense of accomplishment. Respect can be an important factor in motivating a team to work together and with an organization. It’s the manager’s duty that pays full attention to these factors to well balance the organisation well.
Work/Life Balance: Employees need to feel that their work-life balance is balanced. This includes having a reasonable number of working hours, having enough time for leisure activities and family life, and having access to suitable health and fitness facilities. As stated by (Massaro et al. 2018), work/life balance is an important factor in motivating a team to work with someone’s team and organisation. When employees feel that they have a healthy balance between their work and personal lives, they are more likely to be engaged in their work and committed to the organisation. A healthy work/life balance can also help to boost morale, reduce stress and create a more positive work environment that encourages collaboration and a spirit of teamwork.
Career Development: Employees need to feel that they have the opportunity to develop and progress in their careers. This includes access to training, mentoring, and other career development opportunities. As per the views of (Kraus-Hoogeveen et al. 2018), career development can motivate teamwork in an organisation by providing a clear path of growth and development for each individual team member. Having a career development plan in place can motivate team members to strive for advancement and to take ownership of their own careers.
Recognition: Employees need to feel that their contributions are noticed and rewarded. This could include awards, bonuses, and promotions, as well as verbal and written recognition. Recognition can be a powerful tool for motivating teamwork within an organization. It can be used to reward individuals and teams for achieving specific goals, meeting deadlines, or hitting targets. As stated by (Beckman and Liebowitz, 2020) it can also be used to recognise outstanding performance in areas such as customer service, innovation, and collaboration. Recognition can create an atmosphere of appreciation, foster a sense of belonging, and promote a sense of pride in the team’s accomplishments. Additionally, it can help to build trust within a team and encourage team members to strive for excellence. The manager and the management authorities should take into consideration this.
Autonomy: Employees need to feel that they have the autonomy to take decisions and have control over their work. Autonomy in the workplace can help to motivate teamwork in an organization by giving employees the freedom to make decisions and take initiative. As mentioned by (Serafimova et al. 2018) this can help to create a sense of ownership and responsibility, encouraging team members to take ownership of the tasks they are working on and work together to achieve their goals. Additionally, allowing employees to work independently can help to foster innovation and creativity, as well as increase morale, as employees feel they are making a difference and are being trusted to do their job. Now, these days there are varieties of management styles in the field but these are the most effective styles the management field such as “Autocratic”, “Democratic”, “Laissez-faire” and “Transformational”. The manager follows here the “Democratic” management style to lead the team. The democratic management style also referred to as participative management, involves giving employees a greater say in the decision-making process and allowing them to take a proactive role in their own development. As stated by (Mohelska and Sokolova, 2018) This style of management is based on the belief that employees are best motivated and enabled when their ideas and opinions are taken seriously and their input is valued. The “democratic management” style has a number of benefits for businesses. For example, by giving employees a greater say in how they do their work, businesses can foster a culture of collaboration and innovation. This can lead to better morale, higher productivity, and improved customer satisfaction. Additionally, it can help to create a more unified and cohesive team, as employees feel more connected to the goals and objectives of the business. Finally, it can help to reduce turnover, as employees are more likely to stay with a business when they feel that their voice is heard and their input is valued.
Financial incentives and productivity
Financial incentives are certainly one way to motivate a team, but it is not necessarily the most effective strategy. In addition to offering financial incentives, a project manager could also offer incentives such as flexible working hours, recognition for a job well done, or opportunities to take on additional responsibilities. As per the views of (Tollman et al. 2018) incentives that focus on recognition, personal growth, and career development can often be even more effective than financial incentives in motivating a team to work harder and increase productivity.
Argument for:
Financial incentives is a powerful way to motivate employees and increase productivity on a project site. Money is a universal motivator and offering bonuses, raises, or other types of financial rewards can help to motivate employees to work harder and be more productive. Financial incentives can also create a sense of loyalty, as employees who feel like they are being rewarded for their hard work are more likely to stay with the project.
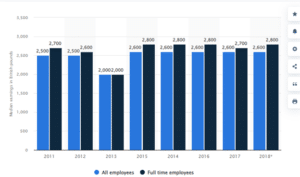
Figure 1: “Median incentives in the United Kingdom’s (UK) digital sector from 2011 to 2018 in GBP)”
(Source: Statista.com, 2022)
Argument against:
Financial incentives are not the only way to motivate a team and increase productivity. Other strategies, such as fostering a culture of collaboration, providing meaningful feedback, and recognizing good work can all help to build morale and encourage team members to work harder. Additionally, financial incentives can be expensive and may not always be feasible. Furthermore, over-reliance on financial incentives can lead to a short-term focus and can decrease long-term motivation.
Statement 2
Concept of project culture
Project culture is a set of values, norms, and beliefs that govern the behavior of a project team. It includes expectations for how the team works together and how it interacts with other teams, stakeholders, and customers. As stated by (Sumadi and Ma’ruf, 2020) It can also include how it solves problems, develops new ideas, and communicates information. Project culture is essential for successful project delivery and should be discussed and agreed upon by the project team. There are four stages of management that affect the most in any organisation’s management such as planning, organising, leading, and controlling. Planning involves setting objectives and determining the best way to achieve them. It includes establishing an overall strategy for achieving the objectives, as well as developing specific plans and procedures to implement the strategy. Establishing a vision and setting goals for a team or organization. Developing strategies and objectives to achieve these goals. Organizing involves establishing the structure and division of labor that will enable the organisation to achieve its goals. In the views of(Strakova et al. 2019), this includes determining what tasks need to be done and who should do them. Structuring a team or organisation by assigning tasks and roles, allocating resources, and setting timelines. Leading involves motivating and inspiring employees to perform their best. It also involves guiding, training, and developing employees in order to help them reach their full potential. Inspiring, motivating, and guiding personnel to reach the goals set. Controlling involves monitoring performance and taking corrective action when necessary. It also involves setting standards and evaluating performance against those standards to ensure goals are being met. As stated by (Pagh, 2020) monitoring performance and ensuring that goals are met. Making adjustments to strategies and objectives as necessary.
Project culture is a set of values, beliefs, and behaviors that exist in an organization and shape the project environment. As stated by (Kurtipek and GÜNGÖR, 2019) it is the shared understanding and acceptance of how projects should be managed and how people should interact with each other. It includes the norms and expectations of how people should behave, how they should make decisions, and how they should communicate with each other. Project culture is an important factor in the success of any project and is closely linked to people and organization management. Project culture starts at the top and is shaped by the organization’s leadership. It is up to the leader to set the tone and develop a culture in which people feel comfortable and motivated to work on projects. As per the views of (Irfan et al. 2019) leaders can foster a culture of collaboration, trust, and openness by setting clear expectations, providing clear communication, and offering feedback and recognition.
Project culture also depends on the team members’ attitudes and behaviors. Team members must be willing to work together and respect each other’s ideas and opinions. They must be open to learning new skills and knowledge and be willing to take on new tasks and responsibilities. Team members must also be willing to take risks and be open to trying new things. Project culture should be nurtured and reinforced on a regular basis.
Role of project manager in designing and shaping structure of the project culture
Project manager plays a vital role in every organisation’s individual different projects. The project manager is typically the person responsible for leading the team and overseeing the project from start to finish. They are responsible for setting deadlines, managing budgets, tracking progress, and ensuring the project meets its goals. The project manager’s responsibility is complete every individual project, and clear every difficulty that comes into the path. The project manager plays a very vital role in every organisation.
Project managers play a critical role in the design and implementation of effective project culture. A project manager is responsible for defining the project objectives, creating a plan for success, and maintaining the project culture so that it meets the goals of the organization. The project manager is the leader of the project and is responsible for setting the tone for the project culture. They must have a deep understanding of the project objectives, the team dynamics, and the organization’s culture. The project manager has to be able to create a vision for the project and communicate this vision to the team. The project manager should also be able to create a shared sense of purpose and commitment among the project team. The project manager needs to also be flexible and adaptive in their approach to the project culture. It is important that they recognize that the project culture may need to be adjusted as the project progresses. As new challenges arise, the project manager should be prepared to adapt the project culture to meet the goals of the organization. The project manager should also motivate and inspire the team to work together toward achieving the project objectives. As stated by (Xu et al. 2019) they should be able to foster communication among the team, encourage collaboration, and support the team members in their development. The project manager should also be able to recognize and reward team members.
The project manager plays an important role in the structure of any project. They are the bridge between the stakeholders and the team members, and in turn, the key to building a successful project culture.
Project managers are responsible for setting the tone for the project. They must be able to effectively communicate expectations, set goals, and clearly define roles and responsibilities. At the same time, they must develop relationships with the team and stakeholders. By setting the standard for the project, project managers can establish a strong project culture that is based on collaboration, trust, and respect. The project manager’s leadership style will also shape the culture of the project. They must be able to motivate the team and foster an environment of open communication. They must provide guidance and support, as well as empower the team to take ownership of the project. They must also be able to handle difficult situations and be willing to take risks. As per the views of(Castro and Guimaraes, 2020) Project managers must also be able to recognize the needs of the team and provide them with the resources to succeed. This could include giving the team access to the latest technologies, providing proper training, and ensuring there is enough time and resources available to complete the project successfully. Finally, project managers must be able to handle conflict and be confident.
Conclusion
The study came to the conclusion that people and organisation management is that it is essential for companies to have proper management of their people and organisations in order to remain competitive and successful. People and organisation management involves setting objectives, measuring performance, recruiting and retaining the right people, developing and improving processes and procedures, and ensuring equitable and fair treatment of employees. Proper management of people and organisations can lead to increased productivity, improved morale, and better customer service. Proper financial incentives can bring numurios number of benefits to an organisation. Companies should ensure they are properly managing their people and organisations in order to remain competitive and successful.
Reference List
Bardarova, S. and Simic, I., 2019. Managers’ role in achieving balance between people and organization. Contemporary economic trends: Technological development and challenges of competitiveness.
Bhalla, V., Caye, J.M., Lovich, D. and Tollman, P., 2018. A CEO’s guide to Talent Management today. Boston Consulting Group. Retrieved.
Blom, R., Borst, R.T. and Voorn, B., 2021. Pathology or inconvenience? A meta-analysis of the impact of red tape on people and organizations. Review of Public Personnel Administration, 41(4), pp.623-650.
Boskov, T., Zezova, A. and Serafimova, M., 2018. Career management and new organization perspectives. Calitatea-acces la succes (Quality-Access to Success), 19(165), pp.110-113.
Castro, M.P. and Guimaraes, T.A., 2020. Dimensions that influence the innovation process in justice organizations. Innovation & Management Review.
Dal Mas, F., Renaudin, M., Garlatti, A. and Massaro, M., 2018, November. Towards a social Knowledge Management in a knowledgeintensive public organization. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Intellectual Capital, Knowledge Management And Organisational Learning ICICKM 2018 (pp. 40-48).
Jyoti, K., 2019. Green HRM–people management commitment to environmental sustainability. In proceedings of 10th international conference on digital strategies for organizational success.
Knies, E., Leisink, P. and Kraus-Hoogeveen, S., 2018. Frontline managers’ contribution to mission achievement: A study of how people management affects thoughtful care. Human Service Organizations: Management, Leadership & Governance, 42(2), pp.166-184.
Kremen, C. and Merenlender, A.M., 2018. Landscapes that work for biodiversity and people. Science, 362(6412), p.eaau6020.
Kurtipek, S. and GÜNGÖR, N., 2019. Determination of the perceptions of sport managers on the concept of organization: A metaphor analysis study. Journal of Education and Training Studies, 7(2).
Liebowitz, J. and Beckman, T., 2020. Knowledge organizations: What every manager should know. CRC press.
Mahapatro, B.B., 2022. Human resource management. PG Department of Business Management.
Mangla, S.K., Sharma, Y.K., Patil, P.P., Yadav, G. and Xu, J., 2019. Logistics and distribution challenges to managing operations for corporate sustainability: study on leading Indian diary organizations. Journal of Cleaner Production, 238, p.117620.
Mohelska, H. and Sokolova, M., 2018. Management approaches for Industry 4.0–the organizational culture perspective. Technological and Economic Development of Economy, 24(6), pp.2225-2240.
Nisar, T.M., Prabhakar, G. and Strakova, L., 2019. Social media information benefits, knowledge management and smart organizations. Journal of Business Research, 94, pp.264-272.
Pagh, J., 2020. Managing Context Collapses: The Internet as a Conditioning Technology in the Organization of Practices. International Journal of Communication (19328036), 14.
Rehman, S., Sami, A., Haroon, A. and Irfan, A., 2019. Impact of sustainable leadership practices on public sector organizations: a systematic review of past decade. Journal of Public Value and Administrative Insight, 2(3), pp.1-5.
Sumadi, S. and Ma’ruf, M.H., 2020. IMPLEMENTATION OF THE CONCEPT AND THEORY OF MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS IN EFFORTS TO IMPROVE QUALITY. International Journal of Economics, Business and Accounting Research (IJEBAR), 4(02).
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

