LCBS5001 Strategic Management Assignment
Introduction
Strategic management is basically a process for setting objectives, goals, and procedures for making a company more competitive in the marketplace. Thus, in the following report, the strategic management of Unilever would be analysed in detail. In the primary section of the report, the historical background and with the growth of the company would be discussed followed by its organisational culture and structure. Furthermore, an in-depth discussion would be presented with the present business level and corporate level strategies of Unilever. As the report progresses, a strategic analysis of the company would be developed using different tools such as PESTLE, SWOT, VRIO, and others. Through this, the competence of Unilever in terms of macro and micro environment can be determined thoroughly. Finally, certain recommendations would be provided to the company for further strengthening their strategic management for being more competitive and attractive from the point of view of both companies and customers respectively.
1.1 Historical background and growth of the chosen company
Unilever is a consumer goods organisation, which was established in 1929 and has gained extensive success in the international marketplace (Unilever, 2023). Considering the continuous success of the organisation Unilever is considered for this study. The organisation has a broad portfolio of different personal care as well as household products ranging from tea, and ice cream, to soap and others. The history of Unilever indicates that Lever Brothers and Margarine signed an agreement to create this organisation in 1929 (Unilever, 2023).
The vision statement of the organisation indicates that it is a global company with a global purpose that is extremely concerned with “making sustainable living commonplace”. The organisation has more than 400 brand names in over 190 nations globally (Unilever, 2023). Unilever has been able to make a truly global business as approximately 3.4 billion people around the globe are utilising its products in their daily lives (Unilever, 2023). Moreover, the turnover of the company in 2021 was approximately €52 billion with 58% in emerging markets (Unilever, 2023). Hence, Unilever is identified as one of the successful companies around the globe that started its journey as a British Dutch multinational company and has been operating in the international market.
1.2 Organisational culture and structure
The cultural attributes within Unilever are largely confronted within the concept of maintaining business integrity. It reflects the motive of Unilever management to create an effective workplace environmental by signifying respect and responsibility, integrity and pioneering as an integral part of ensuring a positive influence across their business value chain (Unilever, 2023). Apart from that, concise ethical standards are also considered by Unilever within their business culture with the code of business principles to determine the ethical behaviours. The people management approach within Unilever is also depicted through their cultural standings with regards to treat people with honesty, dignity, and fairness (Unilever, 2023). Workplace diversity is effectively maintained by Unilever along with fair and safe working environments for their employees.
A functional or divisional structure is maintained by Unilever where each respective business group under the company is completely responsible and accountable for their strategic concerns, growth, and others. The different business groups under Unilever include personal care and home care, beauty and wellbeing, nutrition, ice cream and others (Unilever, 2022). While moving away from current matrix structure, Unilever has been attentive to promote a clear visionary approach to consider functional structure by dividing up the business in accordance with the focus areas.
2. Current business-level and corporate-level strategies of the company
Unilever is employing a different variety of strategies in the market for increasing its competitive advantages and maximization of profits by leveraging on the positive changes that the company is attempting to bring to its organisational operations. In the aspect of understanding their strategies in detail, an understanding needs to be gained from the business level and corporate level strategies of the business.
Business level strategy
A business strategy is typically focused on attracting customers to a company for selling the products to make a profit. It is typically developed for assisting a company in being more competitive. In regards to Unilever, it can be noticed that for acquiring customers, the company is working forward towards building trust through increasing responsible practices and enhancing transparent communication. Additionally, the company is using different channels for reaching to a wider range of audiences (Unilever, 2023). The company has been following a competitive pricing strategy for attracting a wider range of customers. With rising aspect of inflation, the company is noticed to price aggressively for protecting from inflation (Jefferson and Carroll, 2022). Although, Unilever CEO, Alan Jope, has stated that with the increase in process, they would keep on investing competitively in research development along with marketing for protecting the brand health amidst the rising cost of living (Jefferson and Carroll, 2022). With this, the quality of the products can be maintained and retention of customers becomes possible, keeping in mind the profitability aspect of the company.
Furthermore, Unilever is creating high-end value for customers through increasing sustainability. Suitability has become such an aspect that is impacting the inclination of customers toward a brand. Thus, Unilever is increasingly attempting to work toward sustainability for attracting a wide range of customers that are inclined toward green practices. Every action undertaken by Unilever such as innovation, manufacturing, sourcing, and others is assisting in creating value for their stakeholders (Unilever, 2023). Additionally, the company has been working forth to enhance its competitiveness by being purposeful. The executive vice president of hair care at Unilever, Jean-Laurent has stated that if a company wants to be relevant in society, specifically keeping in mind the younger generation, being profitable and purposeful is the only way (Mainwaring, 2020). This mindset of the company also impacts getting employees into the company. Thus, the business level strategies undertaken by Unilever can be grasped in detail that is leading towards high-end profitability along with employee and customer retention.
Corporate level strategy
A corporate strategy is referred to a strategy that helps an organisation in determining the tentative markets that a company wants to enter and the way that can be achieved successfully. The corporate strategy is a larger aspect of a company that nurtures growth and overall operations in detail. In the aspect of Unilever, the aspect of diversification comes well under the notice for incorporating the corporate strategy. The company has both diversified its product range and also in terms of entering into different markets. The company has mainly diversified its product range into foods and refreshments, beauty and personal care, and home care (Seeking Alpha, 2022). The sales generated from beauty and personal care is approximately 40%, whereas 20% from home care and the rest 40% from food and refreshments (Seeking Alpha, 2022).
Additionally, the company has entered several markets around the world for getting a hold of a larger share of audiences. With regards to the exposure of the company in terms of geography, the sales from the largest share of Unilever in the US have accounted for only 20%; whereas more than 50% of the revenue is generated from emerging markets (Seeking Alpha, 2022). Thus, the diversification aspect of Unilever in terms of geographies and products for achieving growth of the company can be noticed in detail. The company is noticed to be in more than 190 countries around the world (Unilever, 2023.). Additionally, the company has introduced both mid-end and high-end products for acquiring customers from the middle to high class. The company has different brands under a single segment such as Vaseline, Dove, Sunsilk, and others under the beauty and well-being aspect (Unilever, 2023.). Different brands provide different price ranges as per the affordability of consumers; this impacts the operations of the company to a great extent.
This has impacted Unilever in satisfying the needs of a wider share of customers and also increases the revenue aspect. Thus, from this, it can be analysed that the corporate strategy of Unilever is to diversify products efficiently and enter emerging markets for increasing company awareness and maximization of profit. Furthermore, the corporate strategy is also focusing on cost-cutting for enhancing profitability. It has been noticed that through sourcing sustainability, the company has reduced costs by $1.5 billion since 2008 (Brown, 2021). Additionally, the cost reduction by shifting to green electricity has been immense. Through this manner, the company is optimizing cost reduction and downsizing unnecessary spending through different sustainable actions. Thus, the implication of both business and corporate strategy toward attracting consumers and increasing revenues and be understood in detail that can be noticed from the figure below.
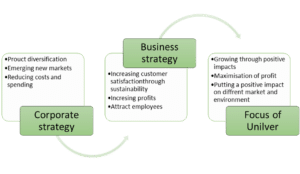
Figure 1: Strategic activity map of Unilever
(Source: Created by the researcher)
3. Strategic analysis
3.1 Micro/internal environment
According to Liang and Chen (2021), SWOT (Strength, Weakness, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis is a useful framework to analyse the internal environment of an organisation. Hence, this framework is considered to be used for the internal environment analysis of Unilever.
| Strength | Weakness |
| ● Market capitalisation of Unilever is US$ 127.02 Billion (Companies Market Cap, 2023)
● Unilever has a strong market presence, which is in approximately 190 countries (Unilever, 2023) ● The company also has a global base of customers ● The organisation has a diversified portfolio of consumer goods |
● Products are not significantly unique and they are easily imitable
● Unilever has been providing a great focus on sustainability, which sometimes became the reason for loss (Carroll, 2022) ● Due to difficulties with quality and safety of products, the company has experienced product recalls (Economic Times, 2022) |
| Opportunities | Threats |
| ● The organisation has chances to increase its market share in developing nations, where there is the opportunity for expansion
● Unilever is in a significant position to benefit from the increasing consumer demand for environmentally friendly as well as sustainable goods |
● Extensive market competition
● Political unrest and economic ambiguity may have impacts on the organisation in certain of the nations, where it operates the business; such as the UK market |
Table 1: SWOT analysis of Unilever
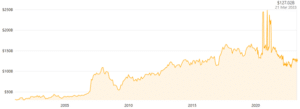
Figure 2: Unilever’s market capitalisation
(Source: Companies Market Cap, 2023)
Based on the above internal environmental analysis of Unilever considering the SWOT analysis framework, strengths of Unilever have been determined by its current market presence, consumer base, and product diversification, which ensures financial success. Even the organisation has the opportunity to expand its business in new foreign markets and wholesale consumer demand regarding sustainable products. However, the organisation has been facing challenges due to product recalls due to quality and safety issues (Economic Times, 2022). Moreover, P&G (Procter & Gamble), Nestlé, and other retailers of consumer products are the main competitors of the company (Anupama et al. 2022). Economic uncertainty in countries like the UK is imposing threats to the business operation of Unilever as consumers are expanding less on daily goods (Arab News, 2022). Hence, considering the overall internal analysis it is observed that Unilever needs to be focused on improving the quality of products and dealing with market competition.
Apart from that, to analyse the internal environment of Unilever; specifically evaluate the resources and capabilities of Unilever that are ensuring its competitive advantage the VRIO framework is considered.
| Resources | Valuable | Rare | Imitable | Organised | Competitive advantage |
| Global market presence | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Long-term |
| Product diversification | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Sustainable competitive advantage | |
| Marketing | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Temporary competitive advantage | |
| Customer support | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Competitive | |
| Human resource | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Long-term |
Table 2: VRIO analysis
Based on the VRIO analysis, it is observed that the market presence, product diversification, and human resource of Unilever are valuable and organised that are ensuring competitive advantage and long-term success of the business. The organisation provides a great focus on human resources by considering employees at the heart of the business, which is ensuring its long-term competitive advantage (Unilever, 2023). However, the product portfolio and customer support system of the company can be improved as they are not rare; although, they are ensuring the competitiveness of the company.
3.2 Industry level analysis
In order to contact industrial level analysis of a business the use of Porter’s 5 forces analysis is extremely beneficial (Anastasiu et al. 2020).
| Factors | Impact | Analysis |
| Bargaining power of customers’ | High | Customers in the global consumer goods sector have a significantly high bargaining power. This is because customers in this particular sector prefer to buy from companies that provide quality products at reasonable prices (Neger and Uddin, 2020). In addition, there are several companies in this sector that are offering the same products just like Unilever which is also influencing the bargaining power of customers significantly. |
| Bargaining of suppliers | Moderate | Suppliers in the consumer goods sector globally can have influences on the supply accessibility of businesses. Moreover, in this sector the availability of suppliers is adequate around the globe as companies can consider global as well as local suppliers as well in terms of producing and offering consumer goods (Tien, 2019). Hence, the bargaining power of suppliers for Unilever is moderate. |
| Threat of new entrants | Moderate | Due to the demand for consumer goods investors or new companies can find it attractive to invest in this particular sector (Mariani and Wamba, 2020). It requires a significant amount of money to make a powerful presence like Unilever; which makes the threat of new entrances not significantly impactful to Unilever. However, due to low switching costs and growing demands for consumer goods, the rate of new entrants in the sector is moderate. |
| Threat of substitutes | Low | In recent years, the preference of customers to use organic items has been increasing (Unnamalai and Gopinath, 2020). Hence, this can impose a threat to a company like Unilever in terms of offering daily goods. However, product pricing matters to customers and organic items can be expensive, which reduces consumers’ preferences towards organic substitutes of daily goods. Therefore, the threat of substitutes for Unilever is low. |
| Competitive rivalry | High | As mentioned above, there are several companies such as P&G, Nestlé, and other retailers, that are imposing extensive competitive rivalry with Unilever (Anupama et al. 2022). |
Table 3: Porter’s 5 Forces of Unilever
3.3 Macro/general environment
According to Abdullah et al. (2022), PESTLE is one of the most significant frameworks for the macro environmental analysis of a company. Hence, this framework is considered to be used for analysing the macro environment of Unilever.
| Factors | Analysis | Impact |
| Political | ● Unilever has been operating in different countries around the globe and the political stability of those countries is impactful for its business.
● In 2021, the worldwide political stability index was approximately -0.07 points (The Global Economy, 2023). |
Moderate |
| Economical | ● The global market size of the FMCG industry is predicted to touch an estimated $265.9 billion by 2028 (Parashar, 2023).
● Economic uncertainty in some countries like the UK and the increasing cost of living is reducing purchasing abilities of customers (Arab News, 2022). |
Moderate |
| Social | ● Consumer spending globally is US$ 44 trillion each second (The World Counts, 2022).
● Customers are willing to spend more on eco-friendly and sustainable products (Forbes, 2022). |
Positive |
| Technological | ● Updates technologies such as QR codes, RFID technology, NFTs, and big data analytics have been utilising in this sector.
● FMCG sector is utilising technology to increase its efficiencies (Moneylife, 2021) |
Positive |
| Legal | ● The “Prevention of Food Adulteration Act, 1954” (Gov, 2023)
● “Essential Commodities Act, 1955” (Legislative, 2023). |
Moderate |
| Environmental | ● Businesses are forced to reduce their environmental impacts and improve sustainability across their operations (Bocken et al. 2022)
● Ban of single-use plastic for environmental protection |
Negative |
Table 4: PESTLE analysis of Unilever
Considering the above macro environment analysis of Unilever, it is observed that the social and technological factors are influencing its business positively. This is because the emergence of updated technologies has made it easier to improve business operations, which is helping Unilever to improve its customer service, which further ensures improved customer experience. However, economic uncertainty in countries like the UK is reducing consumer spending, which has the ability to reduce the sales rate of the company in the nation (Arab News, 2022). Moreover, social factors such as customers’ willingness to spend more on sustainable as well as eco-friendly products have been influencing the business of Unilever in a positive manner. However, Unilever has been focused on building environment sustainability and safety into every product innovation; although, it has a limited sustainable product range (Unilever, 2023). Unilever can ensure increasing product portfolios that are concerned to be eco-friendly or sustainable to ensure its business growth in this particular sector.
4. Strategic Recommendation
With reference to the overall strategic analysis of Unilever, a set of recommendations are provided below with an intention to develop the company business strategy furthermore for the future-
Empowerment of sustainability
Unilever management is strongly recommended to improve their focus on the provision of sustainable offerings and services for their potential consumers. The strategic analysis of Unilever has eventually highlighted the need to become eco-friendly or sustainable to obtain business growth opportunities by overcoming the barriers of limited sustainable product range (Unilever, 2023). The conceptualisation of green supply chain management as well as sustainable corporate governance framework is also suggested for Unilever in this regard. The context of the triple bottom line theory can be highlighted in this regard, which looks forward to focus on 3 respective areas for achieving business success including people, profit, and planet (Laosirihongthong et al. 2020). By improving sustainable product portfolios, Unilever would be able to empower the accountability and credibility of their services and offerings throughout the competitive market based on which the chances of profit enhancement could also be increased by them by focusing on both the environment and consumer demand.
The strategic analysis also highlighted cost reduction behaviour from the perspective of Unilever by transforming their focus towards green electricity. In this case, preference of the renewable energy sources for entire business operations is also recommended for Unilever to further improve their focus on sustainability (Qazi et al. 2019). Unilever would also be able to comply with the future trend of green business through this initiative, which may also empower their chances of business expansion and competitive growth.
Improvement of research and development
The management of Unilever will have to look to expand their focus towards research and development opportunities. The topmost reason behind referring to this strategy highlights to efficiently prevent and abide the need for product recall related incidents, which has also become one of the most significant weaknesses of Unilever (Economic Times, 2022). It has also been raising questions regarding the quality and safety of Unilever products and offerings. Proper research and development would enable Unilever management to avoid the need for product recall along with maintaining quality standards, which may also add a greater value to their brand recognition in the market. In this regard, the systems management theory can be taken into concern. According to theoretical understanding, business success usually depends on interrelation between the subsystems, synergy, and others (Kumar, 2020). The managers within an organisation should be attentive to evaluate appropriate patterns for determining the best management approach through collaboration for ensuring success. The context of improving research and development operations can also be highlighted as the determination of best management approach from the perspective of Unilever due to which the company would be able to improve their product quality for avoiding the occurrence of product recall.
Conceptualisation of cost leadership
The strategic analysis as mentioned above has highlighted the consideration of aggressive pricing from the perspective of Unilever to protect themselves from inflation (Jefferson and Carroll, 2022). In this regard, Unilever management is recommended to consider cost leadership strategy under the lights of Porter’s generic strategy framework. Cost leadership strategy looks forward to offer products with acceptable quality and features to the consumers at a comparatively low price (Al-Romeedy, 2019). However, the aspects of contingency management theory can be highlighted for this purpose. In accordance with this theory, leaders within an organisation should apply appropriate leadership traits to every kind of situation where leadership flexibility would be helpful for adapting to a changing environment (Cheng, 2020). Similar consequences can be certified from the perspective of Unilever where the company leaders should focus on formulating cost leadership strategy in order to ensure competitive growth opportunities ahead of the existing market rivals.
Apart from the mentioned suggestions and strategic concerns, Unilever should be attentive to further improve their focus on technology advancement and automation to support operational sustainability.
5. Conclusion
The overall report has highlighted the existing strategic analysis of Unilever with a focus on their corporate level strategy and culture. Along with the maintenance of business integrity as the prime cultural value, the existing business level strategy of Unilever reflects competitive pricing where the company is intending to create high end value for customers with the empowerment of sustainability. The corporate level strategy of Unilever has also highlighted diversification and cost reduction. However, the aspects like product recall have been the prime weakness of Unilever. With the existence of highly competitive rivalry in the industry, Unilever is recommended to improve their focus on sustainability through green supply chain, renewable energy sources and others along with empower research and development arrangements for avoiding product recall.
References
Abdullah, M.F., Zainol, Z., Thian, S.Y., Ab Ghani, N.H., Mat Jusoh, A., Mat Amin, M.Z. and Mohamad, N.A., (2022). Big Data in Criteria Selection and Identification in Managing Flood Disaster Events Based on Macro Domain PESTEL Analysis: Case Study of Malaysia Adaptation Index. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 6(1), p.25.
Al-Romeedy, B.S., (2019). Strategic agility as a competitive advantage in airlines–case study: Egypt air. Journal of the Faculty of Tourism and Hotels-University of Sadat City, 3(1), pp.1-15.
Anastasiu, L., Gavriş, O. and Maier, D., (2020). Is human capital ready for change? A strategic approach adapting Porter’s five forces to human resources. Sustainability, 12(6), p.2300.
Anupama, S., Dharmajan, D. and Nair, R., (2022). Fast Moving Consumer Goods sector in India–Tending towards oligopoly?. Arab Economic and Business Journal, 14(1), pp.17-30.
Arab News, (2022). Macro snapshot — UK consumers cut spending on less urgent items; Swedish economy bounces back, but slowdown ahead. [Online]. Available at: https://www.arabnews.com/node/2131501/business-economy [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Bocken, N.M., Harsch, A. and Weissbrod, I., (2022). Circular business models for the fastmoving consumer goods industry: Desirability, feasibility, and viability. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 30, pp.799-814.
Brown, A.B., (2021). Unilever finds short-term sustainability costs lead to long-term savings. Supply Chain Dive. [Online]. Available at: https://www.supplychaindive.com/news/unilever-supplier-sustainability-costs-savings/595388/ [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Carroll, N, (2022). Five challenges awaiting Alan Jope’s successor as Unilever CEO. Marketing Week. [Online]. Available at: https://www.marketingweek.com/five-challenges-new-unilever-ceo/ [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Cheng, Y., (2020). Contingent organisation-public relationship (COPR) matters: reconciling the contingency theory of accommodation into the relationship management paradigm. Journal of Public Relations Research, 32(3-4), pp.140-154.
Companies Market Cap, (2023). Market capitalization of Unilever (UL). [Online]. Available at: https://companiesmarketcap.com/unilever/marketcap/ [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Economic Times, (2022). Unilever recalls Dove, some other aerosol dry shampoo brands over cancer risk. [Online]. Available at: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/new-updates/unilever-recalls-dove-other-aerosol-dry-shampoo-brands-over-cancer-risk/articleshow/95082711.cms [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Forbes, (2022). Consumers Demand Sustainable Products and Shopping Formats. [Online]. Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/gregpetro/2022/03/11/consumers-demand-sustainable-products-and-shopping-formats/?sh=4cddf4ad6a06 [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Gov, (2023). Far-reaching ban on single-use plastics in England. https://www.gov.uk/government/news/far-reaching-ban-on-single-use-plastics-in-england [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Gov, (2023). THE PREVENTION OF FOOD ADULTERATION ACT, 1954. [Online]. Available at: https://odishapolice.gov.in/sites/default/files/PDF/The%20Prevention_of_Food_Adulteration_Act_1954.pdf [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Jefferson, M., and Carroll, N., (2022). Unilever to price ‘aggressively’ to protect brands from inflationary pressures. [Online]. Available at: https://www.marketingweek.com/unilever-to-price-aggressively-to-protect-brands-from-inflationary-pressures/ [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Kumar, S., (2020). Relevance of Buddhist Philosophy in Modern Management Theory. Psychology and Education, 58(2), pp.2104-2111.
Laosirihongthong, T., Samaranayake, P., Nagalingam, S.V. and Adebanjo, D., (2020). Prioritization of sustainable supply chain practices with triple bottom line and organisational theories: industry and academic perspectives. Production Planning & Control, 31(14), pp.1207-1221.
Legislative, (2023). THE ESSENTIAL COMMODITIES ACT, 19551 ACT NO. 10 OF 1955. [Online]. Available at: https://legislative.gov.in/sites/default/files/A1955-10.pdf [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Liang, J. and Chen, A., (2021). Review on Social Welfare Crowdfunding in China Based on PEST-SWOT Model. Complexity, 2021, pp.1-11.
Mainwaring, S., (2020). Purpose At Work: How Unilever Leverages Growth and Acts on Advocacy. Forbes. [Online]. Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/simonmainwaring/2020/11/17/purpose-at-work-how-unilever-leverages-growth-and-acts-on-advocacy/?sh=70528f2205db [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Mariani, M.M. and Wamba, S.F., (2020). Exploring how consumer goods companies innovate in the digital age: The role of big data analytics companies. Journal of Business Research, 121, pp.338-352.
Moneylife, (2021). How the FMCG Sector is Using Technology to Increase Efficiencies. [Online]. Available at: https://www.moneylife.in/article/how-the-fmcg-sector-is-using-technology-to-increase-efficiencies/64198.html [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Neger, M. and Uddin, B., (2020). Factors affecting consumers’ internet shopping behavior during the COVID-19 pandemic: Evidence from Bangladesh. Chinese Business Review, 19(3), pp.91-104.
Parashar, A., (2023). How Paralleldots Is Utilising AI To Impact The FMCG Industry Parashar. Outlook India. [Online]. Available at: https://www.outlookindia.com/business-spotlight/how-paralleldots-is-utilising-ai-to-impact-the-fmcg-industry-news-261314 [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Qazi, A., Hussain, F., Rahim, N.A., Hardaker, G., Alghazzawi, D., Shaban, K. and Haruna, K., (2019). Towards sustainable energy: a systematic review of renewable energy sources, technologies, and public opinions. IEEE access, 7, pp.63837-63851.
Seeking Alpha, (2022). Unilever: Pricing Power And Diversified Revenue Exposure Support Solid Returns. [Online]. Available at: https://seekingalpha.com/article/4520232-unilever-pricing-power-and-diversified-revenue-exposure-support-solid-returns [Accessed 16 March 2023]
The Global Economy, (2023). Political stability – Country rankings. [Online]. Available at: https://www.theglobaleconomy.com/rankings/wb_political_stability/#:~:text=Political%20stability%20%2D%20Country%20rankings&text=The%20average%20for%202021%20based,countries%20where%20data%20are%20available. [Accessed 16 March 2023]
The World Counts, (2023). Every year we buy stuff worth 44 trillion USD or 1.4 million USD per second. [Online]. Available at: https://www.theworldcounts.com/economies/global/global-consumer-spending [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Tien, N.H., (2019). Comparative Analysis of Multidomestic Strategy of P&G and Unilever Corporation. International journal of foreign trade and international business, 1(1), pp.5-8.
Unilever, (2022). Unilever simplifies organisation. [Online]. Available at: https://www.unilever.com/news/press-and-media/press-releases/2022/unilever-simplifies-organisation/ [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Unilever, (2023). 1900 – 1950 – Joining forces, Unilever comes to life. [Online]. Available at: https://www.unilever.com/our-company/our-history-and-archives/1900-1950/#:~:text=On%202%20September%201929%2C%20Margarine,decide%20on%20an%20amalgamation%20instead. [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Unilever, (2023). Advertising and marketing. [Online]. Available at: https://www.unilever.com/planet-and-society/responsible-business/advertising-and-marketing/ [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Unilever, (2023). Business integrity [Online]. Available at: https://www.unilever.com/planet-and-society/responsible-business/business-integrity/ [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Unilever, (2023). Safe and sustainable by design. [Online]. Available at: https://www.unilever.com/planet-and-society/safety-and-environment/safe-and-sustainable-by-design/ [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Unilever, (2023). We are Unilever. [Online]. Available at: https://www.unilever.com/our-company/#:~:text=We%20are%20Unilever,company%20with%20a%20global%20purpose. [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Unilever, (2023). We are Unilever. [Online]. Available at: https://www.unilever.com/our-company/ [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Unsilver, (2023). Our approach. [Online]. Available at: https://www.unilever.com/our-company/our-approach/ [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Unsilver, (2023). Our brands. [Online]. Available at: https://www.unilever.com/brands/ [Accessed 16 March 2023]
Unnamalai, T. and Gopinath, R., (2020). Brand preferences and level of satisfaction in consuming noodles among working women in Tiruchirapalli district. International Journal of Management, 11(11), pp.2909-2917.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

