PS4S16 Managing Projects and Programmes
Introduction:
Project management, commonly abbreviated as PM, is an important part of present-day activities. Various research studies along with Project Management Institute (PMI) have defined project management as a combination of different attributes. Schwalbe (2009) in his book defined (pg. 8) defined project management as the application of knowledge, skills, and techniques that help complete project activities that meet the requirements of the project (Schwalbe, 2009). Rose (2013) in the book on guide for project management body of knowledge (PMBOK) 5th edition mentioned that project manager is not only responsible for striving to meet the scope and cost but they also have to make an effort for meeting stakeholder expectations (Rose, 2013). An overview of the project management framework is presented in figure 1. Figure 1 highlights the key elements and process groups involved in project management. Overall, it can be mentioned that the IT projects must be delivered on time with higher quality (Karaman, and Kurt, 2015). Keeping in view this reason, organizations and project managers should utilize proper project management methodologies so that the projects can succeed within specified time and necessary constraints involved (Chin, Spowage, and Yap, 2012). Chin, Spowage, and Yap (2012) highlighted that methodologies can be classified into two different categories including project management methodologies and application development methodologies (Chin, Spowage, and Yap, 2012). However, as a part of this project, the focus is laid on project management methodologies.
With time, various PM methodologies have developed; however, according to the study by Chin and Spowage (2010), PM methodologies should have best practices, standards as well as guidelines. In the present time, modern PM methodologies are high in demand as they offer more interactivity and effectiveness (Chin and Spowage, 2010). Moreover, with technological development in the present time, traditional PM methods might lead to a strategic mismatch. Hence, in this research paper, the reason behind the use of modern PM methodologies will be assessed in detail. However, a major focus will be laid on agile methods. Agile project management methodology is a modern methodology that is preferred in planning and monitoring in 2021. The reason behind its use will be assessed in this report in detail.

Figure 1: Project Management Framework (Schwalbe, 2009)
Agile PM as an example of modern, responsive, and holistic P3M methodology:
The agile project methodology is utilized in various present-day projects. Carneiro, Silva, and Alencar (2018) in the research study highlighted that agile project management methodologies are characterized using the features of simplicity, flexibility, and dynamic approach that help in easy response and promote team integration. An evident role is played by agile methodology in organizing present-day projects in an effective manner (Carneiro, Silva, and Alencar, 2018). Agile project management is widely used in present years so that challenges posed by traditional, front-end planning are well-handled. Even though numerous authors have helped in pointing out major advantages of agile methods, numerous studies highlight the likelihood of project success linked with the utilization of agile methods (Serrador, and Pinto, 2015). Agile methods were mainly used for software development and are still predominant in the IT industry; however, it is now getting more popular in non-IT projects as well (Hayat et. al, 2019). Findings of the study by Serrador, and Pinto (2015) highlight that agile methods have a positive impact on various dimensions of project success. Moreover, the rapid growth of the agile PM method is observed in large-size organizations (Jovanović et. al, 2017). Agile PM methodologies assist the organizations in the search, acquisition as well as retrieval of knowledge that is important for high-quality services and products (Cegarra-Navarro, Soto-Acosta, and Wensley, 2016). Modern-day time is dependent on continuous growth, hence, agility helps the organization to characterize according to the continuous growth while helping to learn and adapt based on customer expectations and demands (Denning, 2011; Denning, 2016a, p. 13-14).
According to research done on agile project management methodology, this approach is accompanied by short delivery iterations with continuous learning (Sauser, Reilly, and Shenhar, 2009). At the start of the project, the project team is involved in streamlining planning along with requirement definition and design solutions. After this process is complete, the project team entails more planning and other project completion phrases in the next iterations. An overview of agile project management methodology is presented in Figure 2. In comparison to the traditional project management methods, the agile approach offers an immediate modification based on the recent review and modifications of project requirements in each iteration. Further, research highlights that agile methodology is a “feature-driven approach”, hence, it can help concentrate on the requirements of the project based on value as well as market share (Dybå, and Dingsøyr, 2015). Hence, the involvement of the customer in the scope is crucial as customer engagement ensures the agile project team is not investing too much effort in costly features. Based on this, agile project management methodology emphasizes “collaborative development” so that management results are derived from it and a continuous improvement is observed. Agile methodology is well-suited in the modern time as this methodology is highly interactive where team members, as well as stakeholders, are actively collaborating to help understand the project domain and develop priority functionality accordingly (Sauser, Reilly, and Shenhar, 2009).
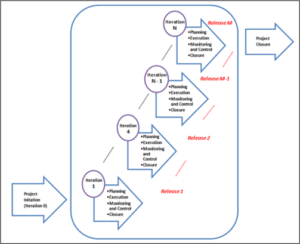
Figure 2: Agile Project Management Method (APM) Process (Sauser, Reilly, and Shenhar, 2009)
Project management of 2021 is a rapidly growing industry where the principal standard for managing IT projects is constantly changing. Even though the agile project management method came into existence a decade ago, however, this method offers greater flexibility and collaboration while facilitating different sectors (Franková, Drahošová, and Balco, 2016). Moreover, the research study highlights that concept of agility in the software development field addresses the volatile nature of software projects while addressing early project requirements. Modern methods are effective for present-day project management as methods like agile development are self-contained in each interaction where all requirements span over design, implementation, and testing (Ciric et. al, 2018). At the end of each iteration, the release is provided where all software components are entertained, the customer then provides the feedback and helps refine the requirements accordingly (Franková, Drahošová, and Balco, 2016). Agile software development is driven by the principle of “value-driven delivery” to help satisfy customers along with providing continuous delivery for software product features. Additionally, one of the major features of agile management is the ability of the method to fulfill change requirements. Project management 2021 is all about change, hence, the agile methodology doesn’t oppose the change as it exploits customers a competitive advantage (Chin, Spowage, and Yap, 2012). According to research done, agile project management (APM) is greatly influenced by updated methods such as Scrum (Dybå, Dingsøyr, and Moe, 2014). The scrum process is mainly driven with the help of iterations named “sprints”. Scrum development is carried with the help of the self-directing and organizing team involved in the project. As a part of scrum practice, the team is given authority on developing a plan that helps plan in achieving the goal in each iteration. Before each sprint, the team selects backlog items that are needed to be developed and tested as a part of the sprint (Schwalbe, 2009). In the present-day business world, business needs are changing and derived from different aspects. Moreover, current business processes are complex and interrelated with various communities involved. These challenges faced by business organizations require a flexible and adaptable approach so that the product and service are delivered faster (Špundak, 2014). Adaptability towards change is not well-provided by the traditional method. However, according to the Project Management Institute PMI), almost 80% of the software-related development is accomplished using the agile method as this method leads to modern managerial skills development along with providing flexibility, speed, and predictability (Rose, 2013).
In execution, most time and cash are normally spent on execution, during which plans are executed and done to make and pass on the best thing. In conventional undertaking the board (TPM), the undertaking bundle goes through execution of the totally portrayed plans through the engineering cycle pack; there is all around no cover among getting sorted out and execution aside from if a gigantic defect or hazard was seen or occurred during project execution (Shaughnessy, 2018). In APM, project execution is done reliably and a few accentuations and movements. The get-together several accentuations, each with its illustration of course of action, execution, seeing/control, and end. Each finished emphasis examination and results feed into the getting sorted out of the going with and future task accentuations (Denning, 2017). In APM, the rule gadgets for seeing and control are utilized at the cycle level during each time Scrum get-togethers and run survey parties near the culmination of every complement or run (Denning, 2016). The bit by bit Scrum is a short party to investigate any issues the social occasion is resisting. Taking out obstacles impeding associates from playing out their run endeavors is one of the central commitments of the Scrum Master (Hoda, and Murugesan, 2016). Systematically Scrums is held each day to plan and bestow work for the day and raise any perils, issues, or deterrents. Close to the completion of each cycle or run, the Scrum Master drives the run presentation review meeting with the Product Owner execution (Shaughnessy, 2018). The assignment bunch reviews with the Product Owner (customer) what it has wrapped up during the run; after the review, the thing aggregation is revived ward on the latest information and business needs inciting the accompanying accentuation/run cycle. Further, the light blueprint is perhaps the primary noticing and control artifacts used in APM execution (Shaughnessy, 2018). Figure 2 displays the headway in the current run by reflecting the amount of lingering story concentrates reliably. This is considered by APM to highlight the number of hours remaining to complete a customer story rather than the number of hours recently spent (Carneiro, Silva, and Alencar, 2018). In agile, a couple of tasks might be added and dropped from the thing or run scope as the nuances of customer stories become all the more clear (Hidalgo, and Morell, 2019). Despite the refinement of the thing develop, the gathering speed is noticed and changed stood out from the authentic gathering execution during the performed emphases. As the number of completed emphases increases, the accuracy in learning the gathering speed increases; thus the time and cost to complete the endeavor become all the more clear and more careful (Hidalgo, and Morell, 2019).
Change the executives in the APM see, on the other hand, is standard and worked with. Not at all like the wide and fundamentally depicted endeavor scope in TPM, APM bases on portraying colossal levels yet attracted extension as client stories that are needed to be passed on with the depicted venture discharge plan (Karlesky, and Vander Voord, 2008). During the inception season of an undertaking, the Product Owner produces client stories for the whole task, in any case makes abominable supporting documentation for those client stories held for the premier emphasis (Karaman, and Kurt, 2015). During the fundamental emphasis, the Product Owner produces positive documentation for client stories to be chipped away at in the subsequent cycle, etc. Therefore, if the increase changes, the contributed time on the degree is irrelevant and little change is required. Additionally, APM desires to cost, time and quality are fixed, and no one yet extension can change (Carneiro, Silva, and Alencar, 2018). In APM, the undertaking bundle makes arrangements to complete a fixed date for a specific expense, yet for a flexible degree. Accordingly, the endeavor bundle in APM rotates around chipping away at critical need project things and prerequisites that offer the most business respect. Precisely when a development change or another part is to be added to the undertaking’s certificate, it ought to be traded with a thing with a similar number of story focuses. This strategy is intriguing contrasted with the TPM approach where new highlights (scope) are added to the downside of cost and development date. In format, the distinction among APM and TPM concerning degree change the board comes from TPM’s feature on fixing the expansion, as it is the center need to fix a task’s assets, cost, and course of events (Carneiro, Silva, and Alencar, 2018). Abnormally, APM considers the worth of the undertaking that impacts the increase to be variable while project assets (time and individuals) are fixed. Maybe than TPM, the spot of deft is to have a little degree, quick development at a high rate (Paterek, 2017), with a more basic feature on correspondence instead of participation or plan (Weinstein, 2009). Furthermore, APM brings a particularly extraordinary arrangement of feature into reformist significance of degree and need, particularly in conditions when the client is experiencing issues articulating necessities. This is guaranteed as deft cycles outfit change for client’s key position and stresses steady consideration concerning the specific importance and collaboration improvement (Carneiro, Silva, and Alencar, 2018). Nimble social occasions address this test through vigorous and reformist accentuation between getting sorted out, execution, control, and transport.
Overall competition is at an immaculate high. Development is advancing at an extraordinary speed. Affiliations ought to pass on additional with fewer resources (Carneiro, Silva, and Alencar, 2018). Regardless of the way that there is no ideal response for a project the board and accomplishment, pioneers and directors are going to deft endeavor the leaders as a basic response for help this test. The growing strain to pass on quality things in a dynamic and rapidly changing overall market obliged specialists to make APM ways of thinking (Carneiro, Silva, and Alencar, 2018). Ordinary endeavor methods of reasoning are seen as the wellspring of custom in the project the board and have been deprived for a long time; their accomplishment in explicit undertakings is highlighted by various scientists (Jovanović et. al, 2017). In any case, for complex endeavors, especially IT and programming ones, ordinary procedures can be for the most part deficient as essentials are tricky and capricious. APM has emerged with its significantly iterative and consistent cycle, where adventure gathering and accomplices viably participate to grasp the region, recognize what ought to be developed, and center on handiness (Jovanović et. al, 2017). As opposed to TPM, the place of swift is to have a little degree and speedy transport at a high rate. APM highlights correspondence instead of cycles or plans. APM yields phenomenal advantages; its advantages come from different parts, key of which is broadened usefulness and quality. Usefulness results from its smoothed out nature, versatility to change, supportive nature, and spotlight on benefits in the business local area (Jovanović et. al, 2017). Tries that have utilized APM were on various events more viable than those utilizing TPM in cost and quality; what’s more, APM projects had on various events more significant advantage from experience (Sauser, Reilly, and Shenhar, 2009). Likewise, APM has approved itself as an accommodating system to control high-hazard, time-delicate inventive work projects by virtue of its lightweight cycles that lead to fit dynamic and efficiency (Sauser, Reilly, and Shenhar, 2009). The standard client affiliation and early idea testing accomplish results that are fast and delicate to business regions. These outcomes, as such, increment client devotion, which further develops client trust, upkeep, and responsibility, and converts into monetary advantages like further developed game plans, profit, and ordinary benefit.
Conclusion:
To conclude, Project management, regularly truncated as PM, is a significant piece of present-day exercises. Different exploration concentrates alongside Project Management Institute (PMI) have characterized project management as a mix of various properties. Schwalbe (2009) in his book characterized (pg. 8) characterized project management as the utilization of information, abilities, and methods that help total project exercises that meet the prerequisites of the undertaking (Schwalbe, 2009). Rose (2013) in the book on the control for a project management assemblage of information (PMBOK) fifth release referenced that project administrators aren’t just answerable for endeavoring to meet the degree and cost however they likewise need to put forth an attempt for meeting partner assumptions (Rose, 2013). It tends to be referenced that the IT ventures need to be followed through on schedule with better caliber (Karaman, and Kurt, 2015). Keeping in see this explanation, associations and undertaking administrators ought to use legitimate venture management strategies so the projects can prevail inside determined time and important imperatives included (Chin, Spowage, and Yap, 2012). Jaw, Spowage, and Yap (2012) featured that strategies can be characterized into two distinct classes including project management procedures and application advancement techniques (Chin, Spowage, and Yap, 2012). Nonetheless, as a piece of this undertaking, the attention is laid on project management systems. With time, different PM philosophies have grown; in any case, as per the examination by Chin and Spowage (2010) PM strategies ought to have best practices, principles just as rules. Right now, present-day PM approaches are highly sought after as they offer greater intuitiveness and viability (Chin and Spowage, 2010). Also, with innovative advancement in the present time, conventional PM techniques may prompt a strategic mismatch. Consequently, in this exploration paper, the explanation for the utilization of present-day PM strategies was evaluated in detail. Be that as it may, a significant spotlight will be laid on light-footed strategies. The agile project management approach is an advanced strategy that is liked in arranging and observing in 2021. The explanation for its utilization was evaluated in this report in detail.
References
Carneiro, L.B., Silva, A.C.C. and Alencar, L.H., 2018, December. Scrum Agile Project Management Methodology Application for Workflow Management: A Case Study. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IEEM) (pp. 938-942). IEEE.
Cegarra-Navarro, J.G., Soto-Acosta, P. and Wensley, A.K., 2016. Structured knowledge processes and firm performance: The role of organizational agility. Journal of Business Research, 69(5), pp.1544-1549.
Chin, C., Spowage, A. and Yap, E., 2012. Project management methodologies: a comparative analysis. Journal for the advancement of performance information and value, 4(1), pp.106-106.
Chin, C.M.M. and Spowage, A.C., 2010. Defining & classifying project management methodologies. PM World Today, 12(5), pp.1-9.
Ciric, D., Lalic, B., Gracanin, D., Palcic, I. and Zivlak, N., 2018, March. Agile project management in new product development and innovation processes: challenges and benefits beyond software domain. In 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Innovation and Entrepreneurship (TEMS-ISIE) (pp. 1-9). IEEE.
Denning, S., 2011. Successfully implementing radical management at Salesforce.com. Strategy & Leadership, 39(6), pp. 4-10.
Denning, S., 2016. Agile’s ten implementation challenges. Strategy & Leadership.
Denning, S., 2016. How to make the whole organization “Agile”. Strategy & Leadership.
Denning, S., 2017. Strategic agility: Using agile teams to explore opportunities for market-creating innovation. Strategy & Leadership.
Dybå, T. and Dingsøyr, T., 2015, May. Agile project management: From self-managing teams to large-scale development. In 2015 IEEE/ACM 37th IEEE International Conference on Software Engineering (Vol. 2, pp. 945-946). IEEE.
Dybå, T., Dingsøyr, T. and Moe, N.B., 2014. Agile project management. In Software project management in a changing world (pp. 277-300). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Franková, P., Drahošová, M. and Balco, P., 2016. Agile project management approach and its use in big data management. Procedia Computer Science, 83, pp.576-583.
Hayat, F., Rehman, A.U., Arif, K.S., Wahab, K. and Abbas, M., 2019, July. The influence of agile methodology (Scrum) on software project management. In 2019 20th IEEE/ACIS International Conference on Software Engineering, Artificial Intelligence, Networking, and Parallel/Distributed Computing (SNPD) (pp. 145-149). IEEE.
Hidalgo, E.S. and Morell, M.F., 2019. Co-designed strategic planning and agile project management in academia: case study of an action research group. Palgrave Communications, 5(1), pp.1-13.
Hoda, R. and Murugesan, L.K., 2016. Multi-level agile project management challenges: A self-organizing team perspective. Journal of Systems and Software, 117, pp.245-257.
Jovanović, M., Mas, A., Mesquida, A.L. and Lalić, B., 2017. Transition of organizational roles in Agile transformation process: A grounded theory approach. Journal of Systems and Software, 133, pp.174-194.
Karaman, E. and Kurt, M., 2015. Comparison of project management methodologies: prince 2 versus PMBOK for its projects. Int. Journal of Applied Sciences and Engineering Research, 4(4), pp.572-579.
Karlesky, M. and Vander Voord, M., 2008. Agile project management. ESC, 247(267), p.4.
Paterek, P., 2017. Agile transformation in project organization-issues, conditions and challenges.
Rose, K.H., 2013. A guide to the project management body of knowledge (PMBOK® Guide)—Fifth Edition. Project management journal, 3(44), pp.e1-e1.
Sauser, B.J., Reilly, R.R., and Shenhar, A.J. (2009). Why projects fail? How contingency theory can provide new insights—A comparative analysis of NASA’s Mars Climate Orbiter loss. International Journal of Project Management, 27, 665–679.
Schwalbe, K., 2009. Introduction to project management. Boston: Course Technology Cengage Learning.
Serrador, P. and Pinto, J.K., 2015. Does Agile work?—A quantitative analysis of agile project success. International Journal of Project Management, 33(5), pp.1040-1051.
Shaughnessy, H., 2018. Creating digital transformation: strategies and steps. Strategy & Leadership.
Špundak, M., 2014. Mixed agile/traditional project management methodology–reality or illusion?. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 119, pp.939-948.

