AC0778 Public Health Assignment Sample
Module Code And Title : AC0778 Public Health Assignment Sample
Introduction
Background
In India, more than 67% of health specialists have adopted different types of healthcare tasks, including patient safety, patient involvement, direct commissioning, and technology datasets. On the other hand, more than 78% of health staff in the UK has adopted distinctive categories of healthcare tasks, including administration of health programmes, arrangement of funding agreements and assurance of proper treatment of patients (Ahmed and Memish, 2019). During the time of the COVID-19 pandemic, the medical government provided permission to health staff of the UK to pursue the healthcare tasks of dentistry and pharmacy.
On the other hand, the healthcare government of India has urged healthcare employees to pursue tasks and activities of both the physical therapy and occupational therapy of patients in order to take care of both the mental and physical health of patients. Duties linked with healthcare management tasks have shown to be beneficial for patients with health-related difficulties, such as cognitive impairment and physical handicapping.
This chapter provides background information for this research by presenting a problem statement pertaining to the healthcare management responsibilities in India and the United Kingdom during the COVID-19 pandemic crisis. Furthermore, this chapter provides an overview of the research’s aims and objectives by comparing and contrasting healthcare jobs in the United Kingdom and India, as well as other countries.
Problem Statement
The main problems of healthcare tasks adopted by health staff workers of both India and the UK include the rise of medical information explosion, slow diffusion of medical knowledge and burden of preventive medical errors among staff. In the UK, more than 67% of patients are facing crucial issues related to medical tasks, including nursing shortage and physician shortage (Correia, 2021). On the contrary, almost 89% of Indian patients are facing problems related to service quality, service integration and sustainable pharmaceutical pricing.
Aims and Objectives
Aim
The main aim of this research proposal is to compare healthcare management activities of both the UK and India during the time of COVID-19 pandemic.
Objectives
The main objectives of this research are provided below:
- To investigate different healthcare management activities in the UK and India
- To illustrate the disadvantages of the COVID-19 pandemic in healthcare sectors
- To provide recommendations to increase performance efficiency of healthcare staff in the UK and India
Research Questions
The main question of this research is provided below:
- How did India and UK manage the fundamental task linked to healthcare management during and past the pandemic of COVID-19?
- What are the disadvantages faced by healthcare management system of India and UK?
- What plausible recommendations can be suggested to improve efficiency among healthcare staff members to counter COVID-19 infection in UK and India?
Research Rationale
What is the issue?
The main issues of this research are the lack of medical assistance and the absence of proper nursing care in healthcare sectors of both the UK and India. This issue will increase the number of COVID cases in different places in India and the UK. In order to present the healthcare management system deployed by UK and India, the proper management of covid death rates and infection rates by healthcare system will be able to point out the intricacies faced by health care system of these two countries (Yang,2022).
Why is it an issue?
The absence of medical assistance is the major issue as it downgrades the self-confidence of healthcare staff working in these particular companies in two distinctive companies. The lack of interaction among workers is also a big issue in healthcare sectors in India and the UK during COVID-19 pandemic (Kulkarni and Anantharama, 2020).
Why is it an issue now?
In current times, the lack of transparency among healthcare workers during a pandemic is a major issue through which doctors cannot assure the safety of patients. This will also cause major problems for employees in healthcare corporations.
What does the research shed light on?
This research mainly sheds light on the comparison of healthcare management activities of both the UK and India during the time of COVID-19 pandemic.
Research Limitation
The main limitation of this research is the absence of qualitative datasets related to the information of healthcare tasks adopted by doctors during the time of COVID-19 pandemic in two different countries named India and the UK. Meanwhile, the other limitation is the absence of cultural interaction between healthcare members during COVID-19 pandemic time.
Structure of dissertation
| Chapters | Summary |
| Chapter 1: Introduction | In this chapter, aims and objectives along with research rationale have been provided in order to compare healthcare activities in India and the UK. |
| Chapter 2: Literature Review | This chapter will provide details of existing information through the assistance of scholarly articles, journals, newspapers and online websites. |
| Chapter 3: Research Methodology | This chapter will provide information about the strategy and scope required to conduct secondary collection of data. |
| Chapter 4: Findings and Analysis | In this chapter, findings of information related to healthcare tasks in the form of graphs and charts in a very reliable and interrogated manner. |
| Chapter 5: Discussions | In this chapter, themes have been created related to different categories of healthcare activities adopted by employee hospitals in the UK and India. |
| Chapter 6: Conclusions and Recommendations | This chapter will provide a summary and recommendations based on this research. |
Empirical research
Introduction
The idea of literature review with an empirical approach is mainly defined as writings of overview based on selected topics through the assistance of scholarly articles, newspapers and online websites as a part of evidence in relation to identified topic. This chapter will provide information related to healthcare management works among the healthcare staff of India and the United Kingdom under the timeframe of COVID-19 pandemic. In the end, a proper gap in this literature will also be provided along with the description of the conceptual framework.
Conceptual framework
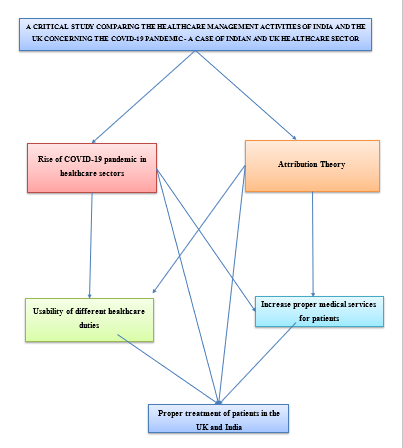 Figure 2.1: Conceptual Framework (Source: Author)
Figure 2.1: Conceptual Framework (Source: Author)
Importance of healthcare management activities
According to Migliori et al. (2020), the main importance of healthcare management activities is to ensure operations of entire health sections in order to maintain them in a seamless manner. The idea of healthcare management is essential in furnishing reliable and practical services to customers with the attribution of healthcare facility systems.
As argued by Prabhakaran et al. (2018), the main function of healthcare management is to implement organisational goals and targets. The other function is to properly supervise medical staff by recruiting new trainers for different segments of healthcare facilities in the near future. In the end, healthcare management duties also help in the development of schedules for employees in order to fulfil their duties at different intervals of time.
Healthcare management of India
According to Ravindra and Mor (2019), mixed-healthcare systems have been used by doctors of different healthcare sectors in India. Moreover, the mixed-healthcare sector in India has provided private healthcare services to patients in order to cure diseases of patients in a very comfortable and authentic manner. As argued by Semrau et al. (2018), more than 56% of patients in India are suffering from the disease of COVID-19 pandemic in the countries of India and the UK. The healthcare segments in India are not too good and not too bad depending on the way of treatment of expert and renowned doctors in a significantly optimised and interrogated manner.
Healthcare management of UK
According to Yang et al. (2020), healthcare management in the UK is following through with the Health and Service Act of 1946 with better treatment and curing of patients from the disease of COVID-19 pandemic. As argued by Ravindra and Mor (2019), the UK government has firmly led to the inclusion of the Health and Social Care Act of 2012 in order to decrease inequalities among patients between England and local, national corporations in a very renowned and authorised manner. In the UK, more than 67% of medical sokets have used the procedure of primary administrative healthcare systems in a very optimised and interrogated manner.
Theoretical apprehensions
Attribution Theory
According to Ahmed and Memish (2019), the idea of attribution theory is mainly used in healthcare management that will help to furnish access to the success or failures of different healthcare systematic programs in a very functional manner. As argued by Correia (2021), the usability of attribution theory has helped to concern ordinary people in order to utilize the interrogation of behavioural effects of patients in order to recover from COVID-19 pandemic in a much authorised manner. By using this theory, different perspectives of healthcare tasks will be improved among healthcare workers in both India and the UK in order to accurately manage their financial and economic benefits in the future.
Gap identified in empirical research
The main gap in this literature is that it does not provide any mitigation techniques for different kinds of healthcare issues that occurred during the time period of COVID-19 pandemic. Additionally, the literature also does not provide any solution related to the commencement of precautions of COVID-19 in both the UK and India.
Summary
Hence, it is concluded that the chapter has provided authentic and reliable information connected to healthcare management works among the healthcare staff of India and the United Kingdom under the timeframe of COVID-19 pandemic. In the end, this literature has also provided an authentic space in this literature in order to investigate more about healthcare duties done by the medical staff of both the UK and India during the pandemic of COVID-19 disease.
Empirical data collection
Introduction
The data collection is a part of research methodology where the researcher will adhere to a particular mode of strategy and analysis technique to draw out plausible findings. The researcher will select interpretivism philosophy, exploratory design, secondary data collection, inductive strategy. It has proposed and justified the use of thematic analysis that could have the possibility to highlight various themes extracted from secondary resources.
Data collection strategy
In light of the Covid 19 epidemic, this study compares health care management practises in the UK and India. This study’s researcher will do secondary research using theme analysis to gather data on the chosen subject. Both India and the United Kingdom, as stated by Aburayya et al. (2020), aim at reducing the effect of Covid 19 on the health care industry.
This research will also provide light on how the health care industries in both the UK and India are using distinct strategic approaches. Both nations’ health-care systems will benefit from a comparison of their superior management practises, which will be conducted to better appreciate their efficacy (Pang et al. 2020). This research also aims to gather and analyse data on the involvement of the governments of India and UK in supporting the health care businesses to raise public awareness of global pandemic scenario. (Maida et al. 2020).
Data collection scope
The selection of secondary sources will prove to be beneficial for the concerned topic to highlight strategies formulated and implemented by UK and India. In addition to this, it will also discuss the result with the respect of education provided by the health care sector in both India and the UK in order to develop the immune system of the people and safety measures needed to be followed by them for preventing themselves from Covid 19 deadly virus.
This research study will also gather information on the number of people in the age group from 1 to above 40 years who received their Covid vaccination in order to fight against the global pandemic situation (Rajhans et al. 2020). They will also provide informative and relevant images in order to present their discussion and maintain the reliability of the research work.
Data analysis
The requirement of conducting an analysis of collected data will be progressed with the help of thematic analysis. Since secondary source of data will be extracted from various websites, articles and online PDFs, individual themes will help the research to highlight crucial findings from acquired data. Thematic analysis will result in construction of themes that would allow this research to present both sets of management procedure regarding healthcare system.
It would also be a useful technique to identify the claims made by UK and Indian government regarding their response rate on COVID-19 pandemic. These claims will be collected in the form of secondary data where individual themes will explore the death and infection rates managed by the overhaul of healthcare management structure after the spread of COVID-19 in these two nations.
Research Philosophy
The impact of a worldwide widespread on Indian and UK healthcare management activities has been explored utilizing the Interpretivism research philosophy. According to Turyahikayo (2021), The research will be able to convince gigantic sums of fabric to be inspected, and interpretivism considers thought was valuable for bigger thought for the inquiry.
The interpretivism thinking, on the other hand, was related to thoughts utilized to clarify circumstances and physical occasions in arrange to supply healthcare knowledge. Positivism examine thinking was excluded from this ponder since it may not give a total understanding of the revelations, which may cause issues within the future.
Research Design
The researcher will utilize an exploratory research design to distinguish the foremost critical and imperative components of healthcare management activities in India and the United Kingdom in respect of the pandemic. According to Casula et al. (2021), another reason to select an exploratory research technique for this issue is that, when compared to other examination methodologies, such as a realistic request arrange, the exploratory examination procedure will provide exact data on the examination study.
The deductive inquire about technique, on the other hand, will be illegal from this idea since the clear ask strategy as often as possible falls flat to supply the researcher with strong see findings. That will be why the researcher will choose an exploratory research strategy instead of a clear investigation strategy. In this case, the issue will require a wide extend of capacities, which can be obtained if the agent utilizes an exploratory strategy instead of a visual strategy, because it will empower the agent to accumulate information more totally and precisely on healthcare administration in India and the United Kingdom.
Research Strategy
This study on healthcare administration exercises in India and the United Kingdom will utilize an Inductive research strategy. According to Burkhardt and Schoenfeld (2021), this will be due to the inductive method, which allows the investigator to uncover significant actualities and information without having to depend on one-sided information.
In this think about, the deductive ask into the approach will be dodged since it regularly falls flat to supply uniqueness when gathering information from different sources. The examiner will not utilize a consistent approach in this ponder issue since doing so would constrain their capacity to assess the sum of originality. This, as well, misfires to supply information in genuine time. (Semrau, 2019)
Research Method
Finding imaginative ways to display authentic substance may be troublesome, indeed, for prepared scholars. According to McGill et al. (2021), the Qualitative research procedure will allow for the collection of honest-to-goodness concerns from particular groups. These concerns will, at that point be changed over into information, which can be used to construct a pivotal fabric highlighting the impact of and around the healthcare administration operations in India and the UK in connection to the widespread that will be delivered.
Following the completion of this strategy, the examiner procures the benefits of a more upgraded and positive respect proposal. In the study, substances will be sought out instead of watched. In a couple of ways, subjective inquire about contrasts from conventional research. This approach dodges the propensity that happens when respondents look to reply to questions in a way that satisfies the examiner.
Empirical Approach
Research based on empirical evidence is significantly more in depth than observational research since it goes beyond what can be observed. Observations are only considered observations when they are accompanied by other information; otherwise, they are not considered observations. Researchers that do experimental study are defined by their willingness and capacity to publicly operationalize their findings using testable research questions, a feature that is shared by all scientists.
Natural environment observations made in a well-conducted study serve as the basis for research questions and hypotheses, which are subsequently evaluated in a laboratory setting. It is possible to document results in either a quantitative or qualitative manner, depending on how the observer intends to interpret the data and how it was gathered.
It will be necessary to develop a unique set of procedures for each location, environment, and study objective. While qualitative strategies are beneficial in a number of social science fields, quantitative approaches are beneficial in medical and physics difficulties. In many circumstances, qualitative techniques are better than quantitative approaches.
It is the endeavour of making observations and then responding to explicitly stated inquiries by accepting or rejecting a hypothesis that is at the heart of every empirical inquiry that experimental research is centred on.
Strategy
An empirical approach of asking and testing questions might be viewed as a more systematic methodology for asking and testing questions than a quantitative method. A valid strategy of learning is regarded anything that falls into the area of the metaphysical or abstract. This includes hypothesis, opinion, reasonable argument, and anything else that falls into this category. But when it comes to empiricism, it is predicated on the observations made by our senses in the “actual world,” as opposed to the “virtual world.”
When used in this context, the terms “experimentation,” “observation,” and “observational data” are all instances of what the term “empirical” signifies. To be considered as part of the scientific process, ethical proof must be observable with the five senses and must be observable with the five senses.
Instead than relying simply on reasoning or logic in order to get knowledge, empiricism emphasizes the acquisition of information via human experience and observation rather than through reasoning or logic alone (in other words, by rationality). Scientific hypotheses are described as hypotheses that can be tested by observation and experimentation, respectively, according to the scientific paradigm. To put it another way, controlled experiments are used to put information into practice.
Depending on the context, empirical data may be gathered by testing and observation in either a quantitative or qualitative format.
Experimentation is carried out for a number of different reasons.
Approach
Research based on empirical evidence is significantly more in depth than observational research since it goes beyond what can be observed. Observations are only considered observations when they are accompanied by other information; otherwise, they are not considered observations. Researchers that do experimental study are defined by their willingness and capacity to publicly operationalize their findings using testable research questions, a feature that is shared by all scientists.
Natural environment observations made in a well-conducted study serve as the basis for research questions and hypotheses, which are subsequently evaluated in a laboratory setting. It is possible to document results in either a quantitative or qualitative manner, depending on how the observer intends to interpret the data and how it was gathered.
It will be necessary to develop a unique set of procedures for each location, environment, and study objective. While qualitative strategies are beneficial in a number of social science fields, quantitative approaches are beneficial in medical and physics difficulties. In many circumstances, qualitative techniques are better than quantitative approaches.
It is the endeavour of making observations and then responding to explicitly stated inquiries by accepting or rejecting a hypothesis that is at the heart of every empirical inquiry that experimental research is centered on.
An empirical approach of asking and testing questions might be viewed as a more systematic methodology for asking and testing questions than a quantitative method. A valid strategy of learning is regarded anything that falls into the area of the metaphysical or abstract. This includes hypothesis, opinion, reasonable argument, and anything else that falls into this category. But when it comes to empiricism, it is predicated on the observations made by our senses in the “actual world,” as opposed to the “virtual world.”
Investigation
Experimental science in general and empiricism in particular are two disciplines of science that aim to accumulate a corpus of knowledge about the natural world via experimentation. Empiricism has created rules of behaviour in order to ensure that the outcomes of empirical testing are not tainted by outside influences. When it comes to scientific research, for example, scientists go to great measures to eliminate any preconceived assumptions, expectations, or views from the debate at hand, and to concentrate on just what can be objectively proven.
Scientists work to improve our knowledge of the world one tested idea at a time, and they rely on evidence-based research to do so. In empirical research, the features of falsifiability and repeatability are critical, which means that conclusions may be revised over time as new evidence comes to light.
Finally, empirical data leads to generalisations that may be refined and revised further depending on the questions we put to ourselves at the end of the day. For the investigation of a wide range of phenomena, researchers have employed a wide range of design strategies.
In science, there is a virtuous circle of work that must be maintained.
The importance of empirical inquiry should not be underestimated, yet learning about the world should not be limited to a single style of inquiry. When it comes to scientific study, students commonly confuse the phrases “empirical scientific approaches” with “science,” yet empiricism is merely one of the many instruments that scientists might use in their studies.
When qualitative and quantitative procedures are utilised in tandem, the data they produce is more complete since the approaches are integrated and the results are more accurate. The following are the steps involved in the scientific process, summarised in the following manner:
Observation
It is required to gather and organise empirical data in order to carry out observational research properly. Using the example of birds, a scientist may discover that certain birds of a given species do not migrate, whilst other birds of the same species do migrate. In addition, the scientist sees that the birds appear to grow in size throughout the years that they are on their journey. Aside from that, he is well aware of the physical difficulties that birds encounter on their migration treks.
Induction
Afterwards, through the process of induction, the hypothesis is developed further. When a claim is backed by a large number of supporting assumptions, a method known as hypothesis testing is utilised to assess whether or not the claim is supported. “Is having a sufficiently considerable body weight connected with deciding to migrate each year?” scientists might inquire based on findings from prior studies and current knowledge in the field of migratory bird study.
It is possible for him to just infer that it is rather than assume that it is. His method to testing his notion appears to be distinct from what we’ve learnt so far about him. An example of his method is to tag and weigh an entire flock of birds, after which he tracks their travels to determine whether or not they are migrating.
Deduction
It is deductive reasoning that is used to arrive at a certain conclusion, and it is dependent on logic and rationality to do this. It is possible to develop the underlying logic of an experiment by the use of deductive reasoning. The experiment conducted by a scientist proved that high bird weight is associated with migration. If this is the case, I would expect to see those birds that are heavier migrate, while those who are lighter remain in their current place. I suspect that if I don’t see larger birds moving more frequently than smaller birds, the relationship between bird weight and migration will not be established after all.
The first step in testing a hypothesis is to go back to the empirical processes and re-examine the hypothesis. This is called the validation stage. Following the completion of an experiment, analysis of the data, and formulation of a conclusion based on the findings, a scientist is faced with the challenge of making sense of it all. It is possible that statistical methods will be utilised to analyse and explain his findings when working in this environment. If he sees that practically every heavier bird migrates, he will have evidence to support his claim that weight and migration are related to one another.
Ethical Consideration
The authenticity of research information will be maintained throughout the progress of this empirical research. According to Crespi-Abril, and Rubilar (2021), data storage and use of collected information should not be manipulated to meet the required criteria for research. This study would ensure URL of secondary data such as journals; websites and online articles are provided to prove the empirical findings is conducted.
The presentation of URL will also help in determining whether the research is conducted with properly conducted study or manipulated findings. Moreover, the collected data would be subjected to Data Protection Act, (2018) and university guidelines on academic misconduct. It will result in properly conducted research where collected data is stored in secured platform without jeopardising the valuable findings extracted for analysis and discussion in later aspects of research.
However, research ethics would not be considered appropriate unless the reference links are cited along with the presentation of statistical or qualitative findings regarding healthcare management in UK and India. The need to make a comparative discussion on healthcare system structured in UK and India to counter the situational crisis from COVID-19 pandemic can also be done through findings extracted from government portals. This would not only help in meeting the requirement of empirical research but also result in evidence based solution without putting concerns on ethical foundation of this research.
Limitation
The first limitation that will be faced by the researcher while collecting secondary data related to the topic is the language issue because some of the journal articles which contain relevant information on the topic are published by using a different language rather than the English language.
Another restriction that will be encountered by the researcher is the publication years and incomplete text. In addition to this, some of the journal articles will contain more than five years old information related to the topic, and incomplete information will be provided related to the selected topic. Along with that, some of the authors will also restrict their work due to which researcher needed to purchase them before accessing them.
Summary
In conclusion, it can be stated that in respect of the pandemic the healthcare management activities in India and the UK the research methods which will be utilised, would make a good impact for the study and the future up-gradation for further research.
Reflection on my role
While doing this study, the knowledge and challenges I have gained and faced have been discussed by using different factors of the Gibbs reflective model, which has been mentioned in the following.
Description
When I have started working on this research, I have gained different knowledge regarding the initiatives taken by the UK and India’s health care industry in order to manage and decrease the impact of Covid 19 on human health. I have also learned that the health care sectors of both countries are raising awareness among the people with full support from the government regarding this deadly disease and the precautions needed to be taken by them. Apart from that, I have also received appropriate support from my professor by seeking feedback from them regarding the improvement required in my work quality in a positive manner.
Feelings
Earlier, when I have started working on this research proposal, I was nervous about whether I will be able to maintain the quality of my work or not. However, when I have received positive feedback from my professor in relation to the topic, approval has increased my support me to identify my weak as well as strong skills, which are creating challenges and benefit for me to complete my work within the given time.
Evaluation
Through this research study, my strong skills which have been highlighted while gathering information related to the selected topic. In this context, I have identified that my time management skill, as well as decision-making and problem-solving skills, are strong skills that have supported me to maintain the quality of my work. On the other hand, my weak skills are communication skills as well as research skills and analysis skills, which have created challenges for me to gather and analyse the data related to the selected topic. I will also face challenges in preparing the final report and submitting my research work within time.
Analysis
It is important for me to work on my weak skills in order to achieve a successful outcome from my future research work. I have developed an appropriate action plan for developing my identified weak skills to reach a logical conclusion from my selected research topic. Apart from that, I will be able to collect authentic information from relevant websites related to the topic in order to analyse those data. Working on my identified weak skill will help me to gain successful career growth by doing proper research work in an effective manner.
Conclusion
Thus, it can be concluded that this research study has supported me to learn new things related to the initiatives taken by the health care sectors in both UK and India and compare their effectiveness for providing protection to the people during covid situations. It has also encouraged me to gather information on the number of people who received their covid vaccination dosage in both UK and India and compare their ratio for understanding which country is more concerned about the safety of their citizen during this global pandemic situation.
Action Plan
| Skills | Description | Time |
| Communication | It is important for me to develop my communication skill as it will help me to communicate with my professor and seek suggestions while collecting secondary information related to my topic. | 2 months |
| Research | It will also help me to gather relevant and authentic information for the selected research topic from different sources. | 3 months |
| Analysis | It will support me to analyse all the collected data from the topic and understand the actual issue in order to reach a logic-based conclusion. | 4 months |
Table 1: Action plan
References
Burkhardt, H. and Schoenfeld, A., (2021). Not just “implementation”: the synergy of research and practice in an engineering research approach to educational design and development. ZDM–Mathematics Education, 53(5), pp.991-1005.
Casula, M., Rangarajan, N. and Shields, P., (2021). The potential of working hypotheses for deductive exploratory research. Quality & Quantity, 55(5), pp.1703-1725.
Correia, T., (2021). The precariousness of political management of the SARS‐CoV‐2 pandemic in the search for scientific answers: calling for prudence in public health emergencies. The International Journal of Health Planning and Management.
Crespi-Abril, A.C. and Rubilar, T., (2021). Moving forward in the ethical consideration of invertebrates in experimentation: Beyond the Three R’s Principle. Revista de Biología Tropical, 69(Suppl. 1), pp.346-357.
Finkelstein, S., Sharma, U. and Furlonger, B., (2021). The inclusive practices of classroom teachers: a scoping review and thematic analysis. International Journal of Inclusive Education, 25(6), pp.735-762.
Kulkarni, B.N. and Anantharama, V., (2020). Repercussions of COVID-19 pandemic on municipal solid waste management: Challenges and opportunities. Science of the Total Environment, 743, p.140693.
Maida, M., Sferrazza, S., Savarino, E., Ricciardiello, L., Repici, A., Morisco, F., Furnari, M., Fuccio, L., Morreale, G.C., Vitello, A. and Burra, P., (2020). Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on gastroenterology divisions in Italy: a national survey. Digestive and Liver Disease, 52(8), pp.808-815.
McGill, E., Er, V., Penney, T., Egan, M., White, M., Meier, P., Whitehead, M., Lock, K., de Cuevas, R.A., Smith, R. and Savona, N., (2021). Evaluation of public health interventions from a complex systems perspective: a research methods review. Social Science & Medicine, p.113697.
Migliori, G.B., Thong, P.M., Akkerman, O., Alffenaar, J.W., Álvarez-Navascués, F., Assao-Neino, M.M., Bernard, P.V., Biala, J.S., Blanc, F.X., Bogorodskaya, E.M. and Borisov, S., (2020). Worldwide effects of coronavirus disease pandemic on tuberculosis services, January–April 2020. Emerging infectious diseases, 26(11), p.2709.
Pang, K.H., Carrion, D.M., Rivas, J.G., Mantica, G., Mattigk, A., Pradere, B., Esperto, F. and European Society of Residents in Urology, (2020). The impact of COVID-19 on European health care and urology trainees. European urology, 78(1), pp.6.
Prabhakaran, D., Singh, K., Roth, G.A., Banerjee, A., Pagidipati, N.J. and Huffman, M.D., (2018). Cardiovascular diseases in India compared with the United States. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 72(1), pp.79-95.
Rajhans, V., Memon, U., Patil, V. and Goyal, A., (2020). Impact of COVID-19 on academic activities and way forward in Indian Optometry. Journal of Optometry, 13(4), pp.216-226.
Ravindra, K. and Mor, S., (2019). Distribution and health risk assessment of arsenic and selected heavy metals in Groundwater of Chandigarh, India. Environmental pollution, 250, pp.820-830.
Semrau, M., Alem, A., Abdulmalik, J., Docrat, S., Evans-Lacko, S., Gureje, O., Kigozi, F., Lempp, H., Lund, C., Petersen, I. and Shidhaye, R., (2018). Developing capacity-building activities for mental health system strengthening in low-and middle-income countries for service users and caregivers, service planners, and researchers. Epidemiology and psychiatric sciences, 27(1), pp.11-21.
Turyahikayo, E., (2021). Philosophical paradigms as the basis for knowledge management research and practice. Knowledge Management & E-Learning: An International Journal, 13(2), pp.209-224.
Yang, C., Sha, D., Liu, Q., Li, Y., Lan, H., Guan, W.W., Hu, T., Li, Z., Zhang, Z., Thompson, J.H. and Wang, Z., (2020). Taking the pulse of COVID-19: A spatiotemporal perspective. International journal of digital earth, 13(10), pp.1186-1211.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:


I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.com/sk/register?ref=T7KCZASX