BE267 International Business Environment Coursework
1. Introduction
In the books of World Trade Organization (WTO), GATT is The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade constructed mostly for the international transaction, that deals with mostly different market objectives. Additionally, the objectives may include tariff revisions, access to different key terms of the nations that influence the market, improve or decrease subsidies and modify the existing subsidy rate. It also offers to negotiate refined trade deals that disturb or create severe interference with two countries that have been trade allies which will be described in this essay.
2. Guiding principles of GATT and importance of them in post war world
2.1 Guiding principles of GATT in organizational design
GATT is based in Geneva, and it has been created with the objective of providing transparent and negotiable transactions that may let nations engage in trade without much thinking of the problems that used to block trades, mainly in the periods prior to the formation of GATT. In GATT, International Conferences are held mostly, that are called Rounds and these Rounds serve to research the different high tax rates and import duties that prevent smooth trade.
GATT has two principles to address, and those are by far one of those most devised principles that have been subjected to the real life world trade theme, where the different kinds of trade arrears have been thought of. The underlying principles have been structured in such a way that it becomes one of those successful models that reduces the efficacy of the barriers, erasing most of the import related problems.
Most countries face the problem of a high tariff situation, because a large tariff discourages international trade and subsequently causes the countries to move forwards with their bargaining on a systematic order of business.
Although the tariff rates have been revised and aligned with the current market situation, such tariff costs have become the topic to address in GATT conferences for a few years. The primary objective was not only to ensure a smooth trade pattern being developed within two countries, however also the creation of a systematic underlying factor that lets the international transaction run without much market interference.
The two most addressed principles of GATT has always been to provide the two nations that are involved in trade a trade without the discrimination which is also called The Principle of Nondiscrimination and Principle of Reciprocity .
Reciprocity serves as the practice of negotiating with a country, as if one country decides and offers to reduce the tariff and tax related barriers to trade, the other country does the same by reciprocating that same business manner, by reducing its own trade barriers.
This reciprocity mostly lies with the fact that the tariff related barriers are taken care of, by the tariff barriers getting minimized and reduced. In addition to this, reciprocity has been the outlining factor to address the tariff related issue, similarly the Nondiscrmination also takes return to provide nations a positive outcome in the part of trade exchange.
The Principle of Nondiscrimination states that if a country lowers its tariff and other domestic prices to facilitate the exchange of its commodities with a country, they have to offer such similar treatment of reducing the tariff and optimize the trade import tax to all to either countries as well (Crowley, 2003). If one tries to understand the matter closely, one will find that the Nondiscrimination holds the principle of reciprocity equally in it too, that serves two countries in trade.
2.2 Importance of the guiding principles to prevent tariff war of 1930 occurrence in the post war world
The Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act of 1930 has been one of the most negative impacts on the crop production of the United States where the increment of the rate of import duty to protect the American farmers neutralizes their competition from the outer shells of the different markets.
However, this thing retailed and created more problems later, as tew competition that has been surging all the while to reduce the competition got back as a bad omen, raising the Tariff rate to a high level and increasing the crop price. Many great Economists still argue on the fact that this Smoot Hawley Act was responsible for the tariff war that occurred in 1930 and also was the cause of the beginning of the Great Depression (Baldwin, 2016).
Trade generally suffered because of the increment of the tariff rate, and international trade considerably suffered due to this single phenomenon. The outing principles of GATT has been lying in the light of reciprocity and Nondiscrimination, that has been the beneficial factor for the trade engagement of both the country involved in trade. GATT usually amends the surging tariff rates by neutralizing the rate of appreciation.
The principle of Nondiscrimination facilitates a non partial approach towards trade that involves increasing the efficiency of the world trade system. GATT has made reciprocation the principle due to a good reason that the import tariff serves as a good amount of tax that discourages free trade. The principle of Reciprocal Tariff Reductions or Reciprocity that has been proven as one of the major good for even large countries, as without reciprocity there is a high increase in the price of imports, which prevents firms from entering foreign markets (Gulotty, 2020).
This allocation of resources in free trade is quite powerful when it comes to two countries both ready to reduce their own import tax and balance the market efficiency. The competitive firms that accelerate toward a larger market share, the lower share of tariff ensures free trade occurring between each other. In addition to this principle, the principle of Nondiscrimination offers to reduce the convolution of the nations trade engagement.
Nondiscriminaion includes the scene of Reciprocity, although it has the benefit to both large and small countries for optimum allocation of resources and getting the major macroeconomic countries to manage their high end costs from purchasing the low cost inputs. The declining of tariff rate is essential for free trade to flourish, as with an increase in tariff, both the productivity and the output suffer to a good extrent (Furceri et al., 2018).
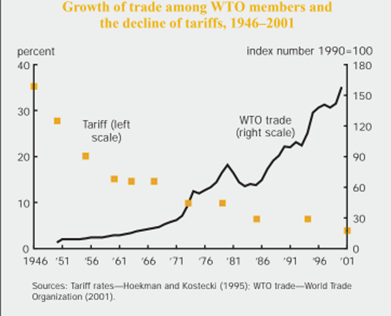
Figure 1 : Growth of trade among WTO members and decline of tariffs
(Source: Furceri et al., 2018)
3. Less success of WTO than GATT in world openness
3.1 Critical examination of successful GATT over WTO in ensuring world openness
The GATT institutional design has been in terms with the solving of different issues that lie to solve the tariff related problems of the nations. Although GATT itself holds such principles that might not hold the negotiations towards the countries in a smooth manner, therefore, reciprocity remains a central theme in the history of international trade (Schott, 2019). There were different tariff bindings that had lied in the plane, which were earlier might not be resolved due to this only reason and thus have been unsuccessful.
There are certain reasons for which WTO might win over GATT, and that has to do with the existence of the non-discriminatory policies, which has attracted a strong criticism from different economist all and the globe. In the WTO curriculum operation, a country may not show favouritism towards a particular nation as it has to be impartial towards all the other countries as well.
On the other hand, in GATT, a country may offer to bargain into some exceptions whereby it may still provide the deal with only those countries that successfully have an advantage over the free market of the goods. The treatment of different foreign services and goods is treated with the same order by the policies of WTO, which changes to a different degree in GATT.
However, the principles of GATT have become more realistic and successfully have conveyed the applicability of the situation to a higher amount, only by having that the treatment of foreign goods and services are subjected to change in the international market depending on the tariff rates of the country. It may be said in a different tone that the policy of GATT has laid more on the grounds of bringing a change in the market of international business, being a successful policy investment. GATT has an advantage, that it contains a larger scope in the market of different services, and is not limited such as WTO.
WTO on some hand has been unsuccessful to maintain the line of different services and products, and the domestic tariffs do not stay constant in an uprising barometer of global inflation.
The intellectual property rights and services that have become too expensive on demand for an import, it is appreciative as how the WTO does not discriminate, yet the cost of tariff does not dissolve. The policies of GATT never have put severe restrictions to curtail trade, and thus it has never had good limitations on the offshoring of the production stages.
Offshore progression has been the regular thematic change in the firm’s changing way of globalization, furthermore, WTO has set restrictive trade policies that caused the successful exchange of goods and services. It always may not be taken as a good option especially where international trade is involved. The effective rate has reduced owing to the trade liberation policies that prevail, although the reduction in the taxes has been more attributed towards the change in globalization (Harvard University Press Blog. 2021).
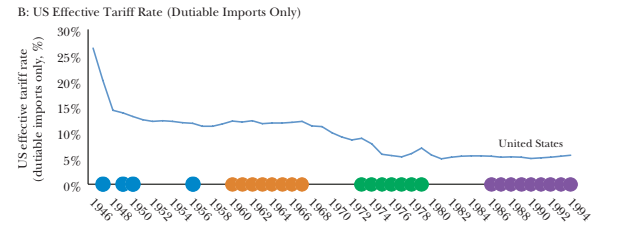
Figure 2: Effective tariff rate over years in US
(Source: Harvard University Press Blog. 2021)
The trade policy has been much changed by the introduction of GATT principles, and has provided the relative drive towards the growth of trade and has seen exponential increase in terms of the reducing costs of tariff. The different sections of GATT have given a successful contribution toward the growth of GDP all over different countries, and the elasticity of trade may be taken in to flatten. The new policy remedies that GATT has brought into that have made the successful entry of different new nations to enter international trade with competitive advantage.
The impartial approach toward market liberalization and bringing in the reduction in the tariff rates has influenced the foreign market for demand for different goods without the fear of investors to back off from the ground. The typical cycles of the boom and bust phases of the economic cycle has been the rotational factor of most economies, has remained much in taint of the hopeful and negative attitude of the global market (Ocampo, 2016).
The GATT system has integrated the trade system of stacking the diversities in trade with success in spite of being classical before the arrival of WTO. The policies of GATT, if discussed in the light of global market chain expansion, were successfully launched in the trade divisions of different countries.
The countries could think of constructing their own trade regulations that have room for exchange between two different countries, which has the layer of protectionism on different industrial policies (Rodrik, 2018). In addition to the boosting of trade where the share of a country in its import is quite small, the imposition of a large amount of tariff may cause a high price which has largely prevented the liberal policies of GATT.
The Bretton Woods Conference gave rise to the birth of GATT, where it has also created the International Monetary Fund and also the International Bank for reconstruction and development (Antonio, 2017). The Nondiscriminating tariff policy has been always indicative that the tariffs collected are being operated from lower end cost countries, where not only the tariffs are set almost the same for the different countries, moreover, also prevent the rotation of goods to let a rise in the import tax.
4. Conclusion
From the above discussion it may be concluded that, the rise of GATT much before the coming of WTO was necessary, as while the former dealt with only the goods and services, and did not provide statutory limitations over intellectual rights, the need for WTO was prescribed. However, the original motive of GATT remains intact to this day, as the core principles remain unchanged and almost unmodified.
5. References
Crowley, M.A., 2003. An introduction to the WTO and GATT. Economic Perspectives, 4(2003), pp.42-57.
Furceri, D., Hannan, S.A., Ostry, J.D. and Rose, A.K., 2018. Macroeconomic consequences of tariffs (No. w25402). National Bureau of Economic Research.
Baldwin, R., 2016. The World Trade Organization and the future of multilateralism. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 30(1), pp.95-116.
Gulotty, R., 2020. Chapter Six. The Design of Reciprocal Trade Agreements. In Narrowing the Channel (pp. 133-147). University of Chicago Press.
Schott, J.J., 2019. US Policies Toward the GATT: Past, Present, Prospective. In GATT and Conflict Management (pp. 23-45). Routledge.
Harvard University Press Blog. 2021. Harvard University Press Blog. [online] Available at: <https://harvardpress.typepad.com/hup_publicity/> [Accessed 15 December 2021].
Ocampo Gaviria, J.A., 2016. A brief history of the international monetary system since Bretton Woods (No. 2016/97). WIDER Working Paper.
Rodrik, D., 2018. Populism and the economics of globalization. Journal of international business policy, 1(1), pp.12-33.
Antonio Ocampo, J., 2017. Resetting the international monetary (non) system (p. 304). Oxford University Press.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

