BE275 Global Supply Chain and Operations Management
Introduction
In the traditional 3.0 industrialisation, the concept of innovation was not focused to a great extent. The influence of Industry 4.0 implementation on different aspects of business practices enables the inclusion of technological changes and digital transformation that further makes the whole manufacturing process more fluent.
In this study, the discussion will be made on the impact that Industry 4.0 has brought on business practices through the inclusion of modern tech support. Moreover, the report will specifically address the influence of Industry 4.0 in the supply chain, organisations operational structure, operations management and people associated with a company or entity.
Main body
Influence of Industry 4.0 on supply chain
Industry 4.0 focuses on how a management team of an organization manages its key function rapidly. The use of industry 4.0 enabled tools is utilized to increase supply chain management performance significantly by enabling a comprehensive approach towards increased logistic activities, information exchange and clarity (Hofmann et al. 2019).
There are a number of positive impacts to the industry 4.0 to the supply chain of an organization in which increased clarity and accuracy are two major benefits organizations have been experiencing. Thousands of vendors operate within a company’s warehouse in a global market and in such circumstances, complete transparency and major asset monitoring are critical.
Whereas, any weaknesses in operational risk management might result in supply chain interruptions, loose revenue stream and excessive expenses (Luthra Mangla, 2018). Efficient and effective supply chain technologies include a “supply chain network” which integrates data among manufacturers, service providers, and other sources, assuring increased agility.
Firms are able to react more effectively to problems in real-time and minimize risk. Whereas, industry 4.0 primarily influences supply chain in a positive way that enables the improvement of warehouse management (Luthra Mangla, 2018).
The digital revolution has the potential to greatly enhance warehouse management skills, particularly in terms of supply chain inventories and shipping (Pfohl, Yahsi & Kurnaz, 2015). As a result, the improved sensor services enable the organizations to track the product and calculate the timing of its arrival.
The RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology helps in locating the exact and accurate location of the package, even though the exact position of the product can be inside a truck during the shipment process. Hence, this level of precision allows the management to give employees destination-based guidance, which saves a lot of time; thus, reducing the number of hours spent on each shipment (Pfohl, Yahsi & Kurnaz, 2015). Companies get the opportunities to avoid risks like insufficient supply or non-compliance by using surveillance technologies provided by industry 4.0.
Modern machine learning techniques, on the other hand, analyse data to forecast demand effectively for a certain commodity rather than presenting a single prediction estimate, analysts report statistical properties of the expected demand quantity. This further allows organisations to analyse both the supply chain’s positive possibilities along with its adverse dangers and prepare correspondingly (Manavalan & Jayakrishna, 2019).
As a result, predicting mistakes have been cut by nearly half attributable to the application of predictive analytics technologies. Estimating resource utilisation more precisely and allows organisations to manage their inventories effectively that results in cost savings. Garay-Rondero et al. (2020) stated that the informative data can be sufficiently exchanged between the vendors, manufacturers, and customers with a highly developed computerised software system that manages the supply chain of the organization.
It starts to break down barriers and turns preparation into a gradual system because it is a shared interface (Manavalan & Jayakrishna, 2019). Indeed, it helps in the development of support and trust, as well as cooperative recommendation changes, particularly in non-competitive connections. Participants can collaborate on supply chain-related initiatives that would save revenue while also sharing best practices and learning from one another.
On the other hand, a proper networked infrastructure also reduces production time by improving communication, since manufacturers may issue timely alerts, improving investment risk management of an organization (Hofmann et al. 2019).
Hence, it can be stated that monetary choices are incorporated with consumption and production management in this kind of restricted design, costs may be altered based on predicted consumption, inventory level, and replacement capabilities. This increases income while also optimizing inventories. However, Hahn (2020) highlighted that Industry 4.0’s influence on the digital supply chain is not restricted to increased efficiency and production.
Companies utilizing interactive technology supply chain activities are significantly more efficient than their competitors because of the advancement of supply chain visibility systems for each and every part of the production, sourcing, transportation, storage, and fulfilment (Garay-Rondero et al. 2020). Distribution network modernization solutions provide businesses with an advantage over their competitors, allowing them to better serve consumers, develop strong business partnerships, and generate new income streams.
Influence of Industry 4.0 on operations management in a company
The introduction of challenges and opportunities for operating management is assisted by the information technology. Management could now retrieve, manage, and appraised enormous amounts of information received from several and therefore, both internal as well as external processes, due to the new technological emergence (Faroukhi et al. 2020). Despite the fact that such cloud computing could be extremely beneficial to organisational structure.
All forms of company are responsible for creating and delivering things or providing services to customers and operations as a significant role. The practice of coordinating various procedures and their accompanying resources is known as operations management. As a result, operations are a critical component for businesses to maintain a competitive edge and development.
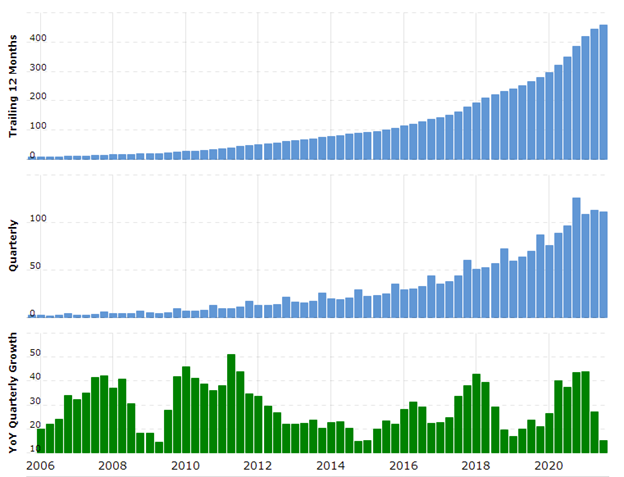
Figure 1: Growth of robots in business operations
(Source: Mordor Intelligence, 2021)
The operational management has an interacting element, controlling the overarching strategy that dictates the organisation’s direction, which has an influence on all other operational actions. Developing an operations strategy, identifying performance expectations, making customer experience design and innovation judgments, and controlling the range of the business are all examples of direction (Garay-Rondero et al. 2020).
The business, specifically consumers and rivals, has a significant impact on these strategic choices, which rapidly changes. In this relation, businesses are establishing a plan that allows them to respond faster to the market, adjust their strategies quickly, and transform their operations quickly.
In context of Industry 4.0 it is critical to investigate the possibilities of operational management in detecting the most appropriate strategic development for corporations. It is certainly essential in the contemporary market settings to have rapid and adaptable operation adjustments due to the rapidly evolving market requirements and opponents’ influence (Hofmann et al. 2019).
The process of identifying the material existence, structure, as well as commodities, accountable for producing goods and services, is known as the transformational design phase.
Design process, layout specification, innovation and workforce selection are all part of the design. All of these tasks are specified by the organization’s strategic goals, which include the sort of operation and desired aim, and often comprises conformational changes and considerable spending.
As a result, modifications in the structure of practices and activities because of market developments are delayed and often unachievable (Hutsaliuk et al. 2020). Therefore, having an adaptable, flexible, and decentralised process of transition, along with the capability to test innovations erstwhile to deployment, are offering organisations with a competitive advantage. Industry 4.0 features may have important impact as it encourages decentralisation and backs up with flexible solutions.
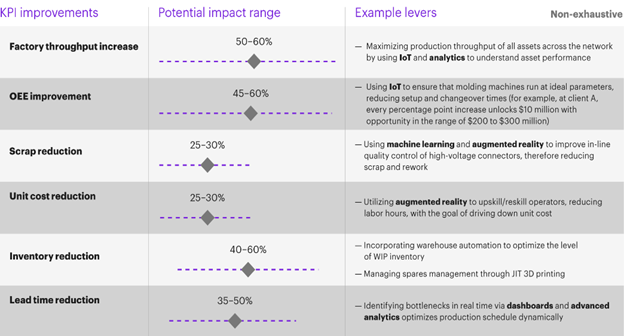
Figure 2: Factors accelerating Industry 4.0
(Source: Mehl, Faruki & Anderson, 2021)
Alongside, products and services are being generated and provided to buyers after operations and procedures have been designed. All actions in the supply chain management are planned and controlled to ensure the component’s performance (Hofmann et al. 2019). The business’ productivity is ensured through controlling capacity and optimising the supply chain’s response to change policies, as well as monitoring the impact among all supply chain actions on business profitability.
Furthermore, supplies are carried out using methods to properly manage costs. Methods and approaches that require the processing of information and data enhance the distribution activities. These data or information are frequently gathered throughout time and in various situations, in connection to the specific moment, and based on the research analysis.
This procedure may undermine the accuracy and consistency of the conclusions. As a result, through collection of actual data and incorporating it into the decision-making process, organisations have increased execution (Mahmoudi et al. 2021).
The responsibility of supply chain management does not conclude while product delivery. It is a continuous system with limited opportunity for growth and development. Due to the changing factors, such as consumer wants and competitors’ supplies, the loop of representing a viable product cannot consistently operate to the very same criteria (Zahedi et al. 2021).
As a result, businesses are developing into a dramatic and evolutionary improvement strategy that is backed by approaches such as quality assurance, mistake prevention, and product development. Performance improvement operations, like delivery activities, depend on reliable and up-to-date input variables.
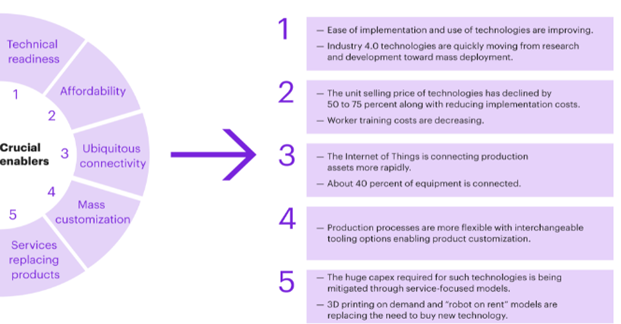
Figure 3: Industry 4.0 transforming the business operations
(Source: Mehl, Faruki & Anderson, 2021)
Influence of Industry 4.0 on organizations
Bulk manufacturing of products was on the rise with no innovation and motivation towards the employees for reaching for new ideas and ways. However, with the advent of 4.0 industrialisation, the organisations are extensively influenced by the new technologies such as digitalisation of various things, the internet of things, advancement of technologies and several others (Manavalan & Jayakrishna, 2019).
The main focus has shifted from bulk production to innovation in the products as the times are evolving and so are the demands of people. Therefore, in order to fulfil the shifting needs of the consumers, the organizations need to pace up with the time. With the indulgence of industry 4.0, the efficiency of the industries has increased to a great extent and along with that the productivity.
The main focus of industry 4.0 is to enable the organisation with more productivity in less time with fewer efforts with the assistance of new and advanced technologies (Yadav et al. 2020). The time of production can be greatly minimised and as the time can be saved, other things can be brought into focus.
Furthermore, 4.0 technologies allow the processes of business, line of products and departments to communicate smoothly regardless of their current locations, platform, time zone and others with the help of cloud-based systems and others. Moreover, industry 4.0 facilitates agility and flexibility.
For instance, scales of production can be monitored easily without spending much time and effort in the processes. Introduction of new products becomes easier with the saving time of existing jobs in the organizations. On the other hand, industry 4.0 can extensively influence the organisation into adopting new techniques aiming for better production with increasing concern on sustainability which can eventually trigger customers into making purchases which can, in turn, increase the profitability of the organization (Bai et al. 2020).
Manual processes can be eradicated to a great extent with the application of smart technologies which alternatively will help the companies to minimize errors and other such mistakes. On the other hand, the services to the customers will be greatly improved as the technologies will enable the companies with automated systems of payments, resolving of any issues and others.
With more automated systems, the complaint from the consumers in respect to the product qualities will also diminish as technologies will greatly decrease the error which in general were caused by humans. On the other hand, due to decreasing the amount of error, the cost can be controlled to a huge level by using smart technologies. Wastage of inventory can be controlled and along with that, the issues with shortage of inventories can also be mitigated through the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the technologies (Butler et al. 2021).
Moreover, through the use of AI, demands can also be forecasted for particular products in specific markets. Accordingly, the products can be manufactured and advertised into the market for better sales. Altogether, the advent of industry 4.0 has extensively influenced the organisation in several aspects with the acceleration of the profitability.
Along with the consideration of operational flexibility, an advanced market analytics approach under the lights of industry 4.0 technologies eventually provide adequate opportunities for growth for respective business organisations. Trstenjak et al. (2020) stated that it helps to prolifically understand current market trends and consumer preferences according to which organisational production offerings are conceptualized.
A profound step is also provided by respective businesses upon sustainability with the implications of industry 4.0. As an example, the context of a global renowned retailer Unilever can be considered that has been able to increase their business agility with the help of cloud-based big data analytics platform. Serving as one of the world’s largest consumer goods organisations, Unilever has highly benefited through the implications of industry 4.0 features that highlighted different consumer perceptions and purchasing behaviour along with industrial trends.
This aspect has been highly emphasized by the organisational Management for ensuring business growth over the wider consumer market. In order to highlight the evidence of this statement, Unilever global revenue generation can be notified that has maintained profound stability and growth throughout the previous decade. Despite experiencing the toxic impact of the covid-19 pandemic, Unilever was able to efficiently comply with the current market preferences through industry 4.0 implications that helped them to achieve 50.7 billion euros revenue (Statista, 2021).
Influence of Industry 4.0 on people in the company
With regards to the implications of the new industrial revolution under the lights of industry 4.0, different lucrative features can be reflected that is increasing its accountability across the wider business area. With the rapid consideration of business localisation and internationalisation, a respective workforce of the business entity is also being able to advance their existing skills and knowledge level that can be supportive to comply with the requirements of industry 4.0.
For example, increasing preference for advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and robotics, analytics and internet of things, big data and others can be noticed in the business fields (Müller, Buliga & Voigt, 2021).
The usage of technological advancement concerning the features of industry 4.0 has been improving the internal operational aspects of an organisation. It has been leading respective companies to ensure distinctive employee satisfaction by enlarging their dedication and knowledge level.
Stojanova, Lietavcova & Vrdoljak Raguž (2019) stated that it is also influencing the employees’ mindset with greater accountability in the professional field in terms of being familiar with advanced technological maintenance. In order to highlight real business evidence of this case, the context of Amazon can be considered. Serving as a renowned Global retailer, Amazon has paid attention to deploy advanced technologies like artificial intelligence in marketing, big data in supply chain, advanced analytics to understand consumer trends and current market preferences, and others (Tjahjono et al. 2017).
As a result of this, Amazon employees are eventually able to stabilize their skills growth with regards to handling industry 4.0 technologies in the workplace that eventually increased their satisfaction level. It can be supported by the evidence of an employee survey program undertaken in Amazon where 94% of employee satisfaction was recorded due to which they would like to recommend Amazon to their friends as a place to work (Del Rey, 2021).
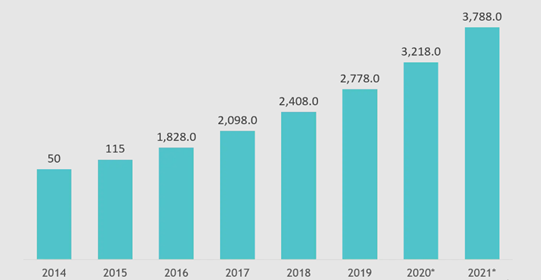
Figure 4: Amazon growth
(Source: Macro Trends, 2021)
It is eventually interrelated with reliable empowerment of organisational productivity in the competitive operational market. For example, it can be highlighted that Amazon experienced a 15.26% increase in their quarterly revenue ending on September 30, 2021 (Macro Trends, 2021).
Moreover, stable and consistent revenue increase is also recorded from the perspective of Amazon over the last five years which signifies greater consideration of industry 4.0 technologies in the organisational productivity. The aforementioned figure has been eventually demonstrating the profound uplift of Amazon over the global market with successive deployment of industry 4.0 features (Macro Trends, 2021).
The consequences of the disruptive innovation theory can be considered in order to justify the extended preference of industry 4.0 technologies for advanced production and operational techniques implementation in business. The theoretical understanding predicts an innovative process through which a small organisation might be able to challenge an established business by entering at the market bottom and rapidly moving up the market (Christensen et al. 2018).
This process is conducted by targeting the ignored market segment of the incumbent and thereby providing seamless solutions to their mainstream consumers for positively influencing their purchasing intention in future. Similar consequences can be reflected from the perspective of Amazon. The organisation has paid attention to ensure prolific growth of workforce productivity by referring to the concept of industry 4.0 implications in their businesses.
Extended competitive advantage is eventually gained by the organisation in this case which also highlights explicit positive features of industry 4.0 technologies to firmly empower an organisational market presence. It can be supported with the evidence of Amazon where the company was able to obtain a brand value of USD 254.19 billion during 2021 ahead of the respective competitors like Google, Microsoft and others (Statista, 2021).
With regards to the aforementioned analysis and real business evidence of Amazon, prolific concerns of industry 4.0 technologies implementation can be recognised. In this case, the maintenance of a transverse relationship can be predicted between industry 4.0 technological implications in an organisation and their workforce flexibility and increased productivity. From this viewpoint, the involvement of industry 4.0 features can be recognised as a subsequent pathway to ensure organisational progress, flexibility and increasing operational efficiencies through a motivated workforce.
Conclusion
The overall report has provided a complete understanding to signify industry 4.0 technologies from a business perspective. The attributes of positively influencing supply chain features, operations management and others have increased its accountability for ensuring profound business growth in future.
The business operational transformation under the shape of industry 4.0 aspects have eventually influenced respective organisational workforce with the advancement of their skills and knowledge level. It has eventually increased their satisfaction and motivation which maintains a supportive relationship with the organisational productivity growth.
Concerning the real business evidence of Amazon and Unilever, positive implications of industry 4.0 can be noticed. However, the business Companies recommended extending research and development and events to efficiently deploy industry 4.0 features in their services.
Reference list
Bai, C., Dallasega, P., Orzes, G., & Sarkis, J. (2020). Industry 4.0 technologies assessment: A sustainability perspective. International journal of production economics, 229, 107776.
Butler, T., Espinoza-Limón, A., & Seppälä, S. (2021). Towards a capability assessment model for the comprehension and adoption of AI in organisations. Journal of AI, Robotics & Workplace Automation, 1(1), 18-33.
Christensen, C. M., McDonald, R., Altman, E. J., & Palmer, J. E. (2018). Disruptive innovation: An intellectual history and directions for future research. Journal of Management Studies, 55(7), 1043-1078.
Del Rey, J., (2021). Amazon employees say you should be skeptical of Jeff Bezos’s worker satisfaction stat [Online]. Retrieved on 5 December 2021 from <https://www.vox.com/recode/22407998/jeff-bezos-94-percent-amazon-workers-recommend-friend-stat-connections-program>
Faroukhi, A. Z., El Alaoui, I., Gahi, Y., & Amine, A. (2020). Big data monetization throughout Big Data Value Chain: a comprehensive review. Journal of Big Data, 7(1), 1-22.
Garay-Rondero, C.L., Martinez-Flores, J.L., Smith, N.R., Caballero Morales, S.O. & Aldrette-Malacara, A. (2020). Digital supply chain model in Industry 4.0, Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, 31(5), 887-933.
Hahn, G. J. (2020). Industry 4.0: a supply chain innovation perspective. International Journal of Production Research, 58(5), 1425-1441.
Hofmann, E., Sternberg, H., Chen, H., Pflaum, A., & Prockl, G. (2019). Supply chain management and Industry 4.0: conducting research in the digital age. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 49(10), 945-955.
Hutsaliuk, O., Koval, V., Tsimoshynska, O., Koval, M., & Skyba, H. (2020). Risk Management of Forming Enterprises Integration Corporate Strategy. TEM Journal, 9(4), 1514.
Luthra, S. & Mangla, S. K. (2018). Evaluating challenges to Industry 4.0 initiatives for supply chain sustainability in emerging economies. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 117, 168-179.
Macro Trends, (2021). Amazon Revenue 2006-2021 | AMZN. [Online]. Retrieved on 5 December 2021 from <https://www.macrotrends.net/stocks/charts/AMZN/amazon/revenue>
Mahmoudi, A., Deng, X., Javed, S. A., & Yuan, J. (2021). Large-scale multiple criteria decision-making with missing values: project selection through TOPSIS-OPA. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 12(10), 9341-9362.
Manavalan, E., & Jayakrishna, K. (2019). A review of Internet of Things (IoT) embedded sustainable supply chain for industry 4.0 requirements. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 127, 925-953.
Mehl, D., Faruki A., and Anderson, N. (2021). A brave new world for manufacturing. [Online] Retrieved on 5 December from: <https://www.kearney.com/operations-performance-transformation/article/?/a/the-state-of-industry-4.0-article>
Mordor Intelligence, (2021). INDUSTRY 4.0 MARKET – GROWTH, TRENDS, COVID-19 IMPACT, AND FORECASTS (2021 – 2026). [Online] Retrieved on 5 December from: <https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/industry-4-0-market>
Müller, J. M., Buliga, O., & Voigt, K. I. (2021). The role of absorptive capacity and innovation strategy in the design of industry 4.0 business Models-A comparison between SMEs and large enterprises. European Management Journal, 39(3), 333-343.
Pfohl, H. C., Yahsi, B.,& Kurnaz, T. (2015). The impact of Industry 4.0 on the supply chain. In Innovations and Strategies for Logistics and Supply Chains: Technologies, Business Models and Risk Management. Proceedings of the Hamburg International Conference of Logistics (HICL), 20 (31-58). Berlin: epubli GmbH.
Statista, (2021). Most valuable brands worldwide in 2021 [Online]. Retrieved on 5 December 2021 from <https://www.statista.com/statistics/264875/brand-value-of-the-25-most-valuable-brands/>
Statista, (2021). Revenue of Unilever Group worldwide from 2007 to 2020. [Online]. Retrieved on 5 December 2021 from <https://www.statista.com/statistics/269190/global-revenue-of-the-unilever-group-since-2007/>
Stojanova, H., Lietavcova, B., & Vrdoljak Raguž, I. (2019). The dependence of unemployment of the senior workforce upon explanatory variables in the European Union in the context of Industry 4.0. Social Sciences, 8(1), 29.
Tjahjono, B., Esplugues, C., Ares, E., & Pelaez, G. (2017). What does industry 4.0 mean to supply chain? Procedia manufacturing, 13, 1175-1182.
Trstenjak, M., Opetuk, T., Cajner, H., & Tosanovic, N. (2020). Process planning in Industry 4.0—current state, potential and management of transformation. Sustainability, 12(15), 5878.
Yadav, G., Kumar, A., Luthra, S., Garza-Reyes, J. A., Kumar, V., & Batista, L. (2020). A framework to achieve sustainability in manufacturing organisations of developing economies using industry 4.0 technologies’ enablers. Computers in industry, 122, 103280.
Zahedi, A., Salehi-Amiri, A., Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M., & Diabat, A. (2021). Designing a closed-loop supply chain network considering multi-task sales agencies and multi-mode transportation. Soft Computing, 25(8), 6203-6235.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

