BSS058-6 Strategy and the Global Competitive Environment Assignment Sample
Module code and Title: BSS058-6 Strategy and the Global Competitive Environment Assignment Sample
Introduction
Every investor must assess their particular field of interest by identifying typical grounds of profitability in the future. For this purpose, appropriate analysis of the external environment should be done. This will help to identify potential challenges and opportunities that can be availed in the business process. Moreover, the separate dimensions can be studied to appropriate typical strategies.
This assignment is sorted to determine effective value proposition for a company to develop effective knowledge of their scope in the external market. Finance industry is sorted to explain this phenomenon and elaborate different facts. In this process, few scenarios will be identified and discussed to understand potential measures that must be taken to propose an effective strategy for increasing the scope of profitability. The finance sector of UK has been chosen as a potential source of investment for gaining meaningful value from customers.
They are identified as the main store of revenue for the proposed company. For this purpose, application of few strategic tools like Ansoff Matrix, target group segmentation, and Porter’s generic strategies will help to develop an efficient value proposition in this industry. A business model canvas shall also be prepared for concluding proposition.
Market Segmentation
A business should identify which section of the market is most likely to draw efficient cash flow for them during each year. It is supposed to divide their promotional strategies to cater towards different segments of that available market. Market segmentation could be classified into 4 types- demographic, behavioural, geographic, and psychographic. For this purpose, taste and preference of existing customers should be learnt.
This will help to develop an effective business plan. Growth in multiple sectors have considerably increased the need for financial services. It has been derived that small and medium sized enterprises grew by 61% since 2000 (Gov.uk, 2022). It can be understood that growth in diverse industries have fuelled the need for financing through the country. It has led to an exorbitant demand for both fintech and financial utilities. However, the customers are quite large in number.
They have typical alternatives available for each type of service. This gives them sufficient scope for bargaining with the firms. Any change in preference shall affect firms by substantial margins. Such segmentation could be arrived by proposing typical target groups according to the selected scenario of “end-to-end digitisation” of financial services. Ansoff matrix will help to accommodate specific plans for succeeding in this industry.
Identification of Potential Segmentation
Target Groups
Target groups are selective individuals who are usually spotted as potential clients of a business. As stated by Sanderson et al. (2018), financial services are mostly comprehended by people above 18 years of age. They are invested into different banking operations and financial solution for managing different types of funds. In case of this proposed business, such target groups are sorted to be people ageing from 21-55 years.
It has been known that such age group is most actively using financial services for accommodating their regular scope of operations. Moreover, digitisation is most commonly used by them to meet their different needs. It includes both men and women who pursue different careers but require financial assistance during each month. Having such a broad group of customers are likely to help them meet increased revenue during each period. People aged between 21 and 35 are more likely to acquire active services from such company. However, rest of the customer group shall integrate more focus upon investment related options suggested by such financial entities.
Ansoff Matrix
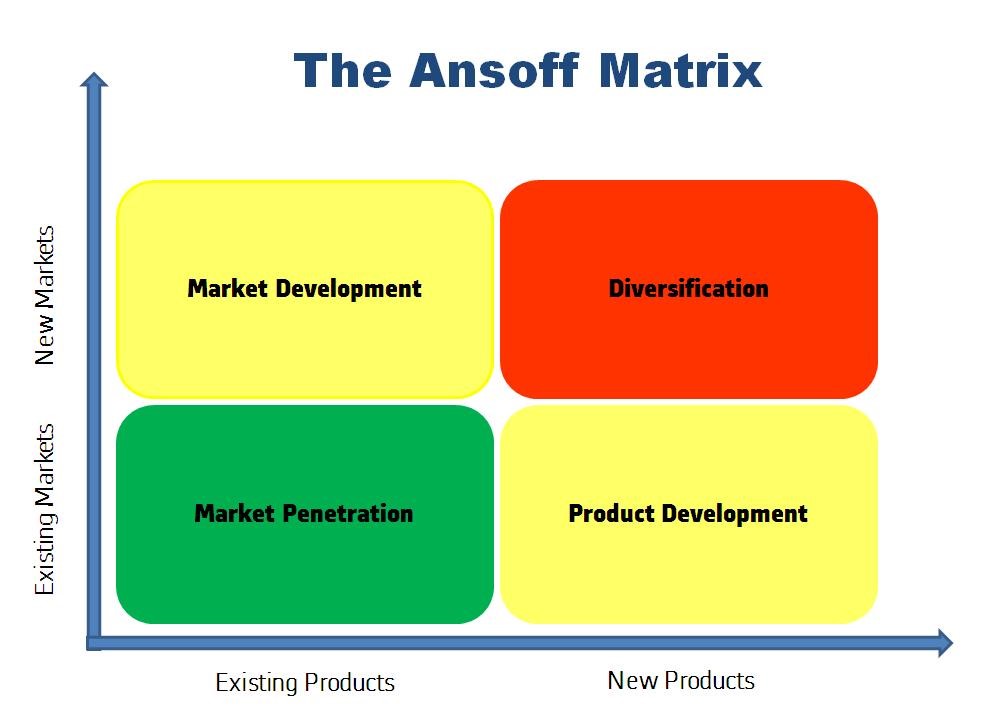 Figure 1: Ansoff Matrix (Source: Kurniawan et al., 2020)
Figure 1: Ansoff Matrix (Source: Kurniawan et al., 2020)
Ansoff matrix is an effective displacement of strategic disposition for understanding the approach of growing revenues. Such revenue can be managed by 4 different strategies (Kurniawan et al., 2020). It particularly stresses upon existing and new markets and products. In case of this business, market is existent with existing set of products. This recommends market penetration by the new firm by establishing a new business.
It implies that company has to floor different assets for penetrating in the market. New avenues of business proposition will be managed by them by accelerating growth though catering to selected clients during the business process. This business process will require to integrate sufficient scope for new firms to introduce similar operations like existing firms. However, technology will play a differential role to suggest adequate services to their clients. The new company will be able to enjoy a readymade customer base by such adoption of business plan.
Essential Factors of the Finance Industry
There are typical factors which contribute greatly to the finance industry of UK. such factors must be comprehended by any company which seeks to integrate their focus in this line of business. These factors have been identified as operational efficiency, risk management, and trust. Flexibility in operations management is supposed to reap most benefits for a company in this sector by maximising value for their customers.
It can be said that the company should employ sufficient resources for identifying particular institutions that can suggest maximum profitability for their clients. These software and personnel should be able to minimise their cost of capital effectively (Shad et al., 2019). This will help them pool more clients while appropriating business to their existing ones. Panel of employees working for a client must be able to manufacture effective finance for them through detailed exploration of potential sources.
Investment opportunities should be adequately determined for increasing returns and profitability. Similarly, identification of risk is another important task for companies involved in this industry. They should employ effective resources for recognising external calamities that can affect any business. According to Bergmann et al. (2020), appropriate budgeting could help them derive such apprehensions.
This will help them justify effective measures for their clients to control potential losses or damage. It is also regarded as a qualitative insurance for such clients. This industry is directly trading with consumer’s monetary content. Fair reporting and detailed description of different transactions shall help them create value for customers (Prodanova et al., 2019). It is very important for these companies to magnify their skills through competent management of client’s information. They should be able to prevent any leakage of sensitive data. This will help them fuel trust in their clients.
Strategic positioning
Strategic positioning highlights company’s comparative position within its industry matter of performance. It reflects choice of value a venture make about kind of value it will create and how it will be different from its rivals (Cuypers et al. 2020). Strategic positioning of the company operating in UK finance industries discussed through porter’s generic strategy.
Porter’s generic strategy
Porter’s generic strategy helps in analysing strategic positioning of an organisation in an industry. It highlights four genetic strategies “cost leadership”, “differentiation”, “cost focus”, and “differentiation focus” (Islami et al. 2020).
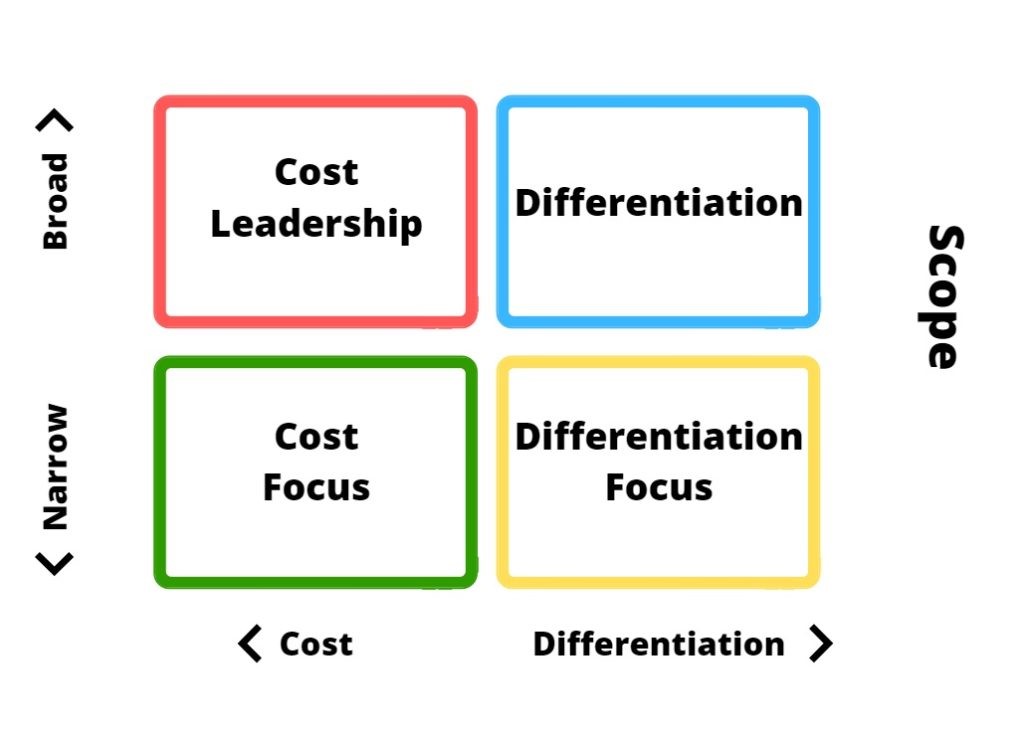 Figure 2: Porter’s generic strategy (Source: Islami et al. 2020)
Figure 2: Porter’s generic strategy (Source: Islami et al. 2020)
As per this model, cost leadership strategy states that focusing on cost leadership can given competitive edge to companies. The company can reduce costs for increasing profits and increase market share by charging lower prices. As per differentiation strategy, competitive edge can be achieved by companies by good research & development and working upon innovation.
While operating in finance industry, effective use of FinTech solutions can be helpful for differentiating offerings than rivals. As per cost focus strategy, companies focusing on particular niche market can understand market dynamics for fulfilling unique needs of customers. As a result, competitive edge can be obtained by the companies. Under differentiation focus strategy, companies aims to utilise effective sales and marketing techniques for making their unique product visible in market and gaining benefits from the differentiated products.
Considering all these strategies, it can be said that using differentiation strategy will be helpful for company in UK finance industry. UK finance industry is highly competitive and making organisations are operating therein. Thus, using differentiation strategy will help the company in delivering unique offerings to customers and making itself visible in the market.
Use of porter’s generic strategy for positioning
Use of porter’s generic model has been made for determining strategic positioning of the company in UK finance industry. This strategy has been used gaining brief understanding about cost leadership, differentiation and focus which has aided decision making about position of the company in finance market (Liyanage and Weerasinghe, 2018). As a result, the company was able to assess type of strategy it should use for gaining strong position in the market.
Potential strategic option
In a contemporary business environment, finance is important. Undoubtedly, finance is important in lives of individuals, organisations, and economy. Global economy and society are being transformed by strong forces of change. The financial services sector is at a turning moment in its development as a new “human-centred economy” takes shape. Potential strategic options of UK financial market are discussed as under:
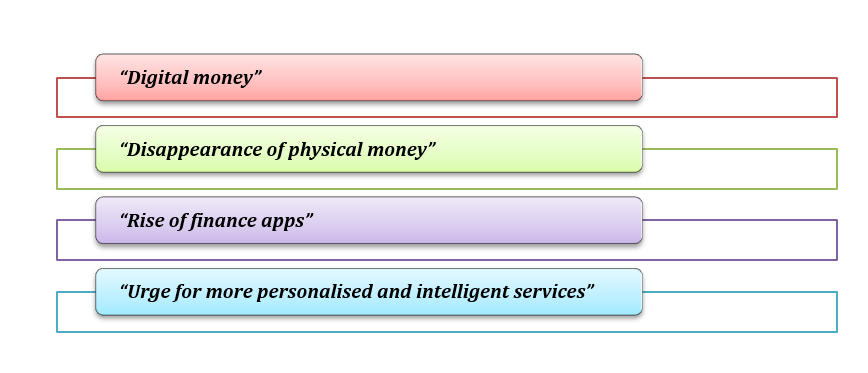 Figure 3: Potential strategic option (Source: Influenced by Forbes, 2022)
Figure 3: Potential strategic option (Source: Influenced by Forbes, 2022)
Market Development through “Digital money”
The exchange of money has become entirely digital. Through smartphone apps or by having phone scanned in a store, an individual may now pay for goods and services with the touch of a screen. As per Berentsen and Schär (2018), digital money is type of money that only exists electronically and simply facilitates transfer or payment of money online. It includes the use of credit cards, smartphones, online banking, online applications, and cryptocurrency platforms.
This trend was accelerated through the Covid-19 pandemic as individuals and ventures became reluctant in handling physical money. For instance, a facial recognition payment service called “Smile to Pay” allows users in China to make payments simply by grinning. Thus, contactless payment has surged. It has been expected that the financial marketplace will be more fluid and interdependent by 2030 (Deloitte, 2022). In short, trust of people in traditional forms of payment is transforming into digital payment and giving rise to digitalisation.
Product Development through “Disappearance of physical money”
Connection of individuals all over the world with money is forever changing due to money’s digitization, and eventually, physical money may cease to exist. If that seems unlikely, it can be estimated that more than 600 different currencies have vanished in past 30 years, and more may either vanish entirely or be supplanted by digital currencies (Forbes, 2022).
It would also impact major currencies. For instance, “European Central Bank” is already considering introducing a “digital euro”. Another subsequence of digitalisation of financial services is personal data of users becoming increasingly intertwined with money. For instance, payment for particular goods or services can be taken based on a particular identity. This helps in receipt and payment of money in less time but carries an enormous risk of identity fraud and data security.
Innovation through “Rise of finance apps”
The new wave of digital money is facilitated by mobile payment applications “digital wallets”. It can be assessed as app-based services that allow users to pay for things and transfer money to others. Many of these services are offered by digital-native start-ups and tech giants instead of transitional banking institutions.
These applications are powered by AI capabilities and data of consumers and provide threats to traditional banks and financial institutions. For instance, payments processed by Venmo, which is owned by PayPal, totalled $159 billion in 2020, up 59% from last year (Forbes, 2022). All of these aspects indicate the increasing trend of the banking system in the future with the introduction of digitalisation.
Concentric Diversification through “Urge for more personalised and intelligent services”
A huge stream of data is being created by the digitalisation of money on what customers do with their funds. It helps financial institutions in gaining helpful insight into the spendings of consumers. It also helps in analysing responses of consumers on other relevant financial products and services in future. For instance, Metro Bank which is an independent bank in UK uses an intelligence tool named “Insights”.
It helps in analysing consumers spending patterns and makes predictions about whether customers are likely to exceed their credit limit before next pay check or whether an expected expense can push them. Such types of personalisation and tailor-made services are expected to increase in future. It has been found that consumer intelligence is the most important predictor of profitability and revenue growth (Pwc, 2022). Thus, contemporary financial institutions would be more likely to provide more personalised services to customers through the use of technology in future.
Analysis of potential strategic option for the company
Nowadays, financial markets all over the world are transforming due to use of technology and digital solutions. It is not only changing the normal financial system but also taste and preferences of consumers about financial services. Below is the analysis of potential strategic options on the financial industry:
 Figure 4: Analysis of potential strategic option (Source: Influenced by Deloitte, 2022)
Figure 4: Analysis of potential strategic option (Source: Influenced by Deloitte, 2022)
“Customers will become more sophisticated”
With increased facilities and services offered by financial institutions to customers, consumers will become more sophisticated in the future. This will pose some pressure on the financial market for delivering value-creating services to customers. With the evolution of technology, consumers’ wants and needs are evolving while new financial platforms are allowing them to serve their own needs.
As opined by Islam et al. (2020), treating customers as stakeholders and delivering services as per the expectations will put the firm in a better position for retaining existing customers and attracting new ones. It will help in the transformation of the overall financial industry.
“Unprecedentedly fluid and interdependent financial market”
New trends in financial market led to continued emergence of new disruptors like fintech, players from other industries, digital giants, and other new entrants. These new entrants to the financial market have distinct beliefs and strengths as well as weaknesses (Zhang-Zhang et al. 2020). Innovative business models and alliances will be developed by these entrants to survive efficiently in this market. An unprecedentedly fluid and interdependent financial market will be developed in the future.
“Rise of risk factor”
With increase in technological advancement and digitalisation, the use of customer data has been raised for providing financial services to customers. Financial institutions all over the world are using personal data of customers for offering them relevant financial services and modifying their offerings (Frost et al. 2019). However, this gives rise to risk of unprotected data, hacking and improper utilisation of customer personal data. In the coming future, when the use of technology will be at its peak, such threats will increase further.
“Improved quantity and quality of data sources”
Nowadays, financial institutions all over the world aim to provide good quality financial services to customers. The ability of these ventures to meet customer expectations depends on their access to and understanding of these ever-growing data flows, which are now the possibly changing factor in production (Kumar and Nayyar, 2020). To remain competitive, incumbents in the financial market will need to rethink their data policies, finding a delicate balance between sharing data with allies and upholding strict control over confidential information.
“Establishment alliance ecosystems”
Companies that develop alliance ecosystems early will gain major advantages in changing the financial market. To integrate financial services into other customer-focused enterprises, firms have the chance to create a “financial layer” in the software platform (Deloitte, 2022). Non-financial businesses can then incorporate that layer into their product offerings to provide financial services to their customers and create new businesses based on it. As a result, they would be able to survive in changing financial market in the future.
“Unique opportunity to address major societal issues and make new markets”
With the evolution of financial market, financial services firms have a rare chance to solve large societal problems and open up new markets without suffering a sizable loss in growth or profitability. By proactively re-establishing trust and transforming corporations could have been in a position to have an impact on practically every sector of the economy (Duan et al. 2021). As a result, better financial services could be provided to customers in future.
Discussion of potential strategic option for the company
Potential strategic option highlight possible events that can occur in the UK financial market and can affect performance of the company. Potential strategic option that can be occurred in UK financial market are discussed as under:
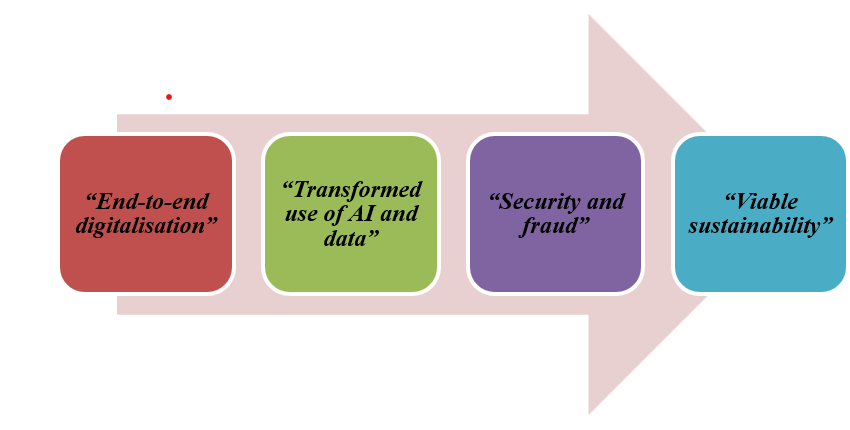 Figure 5: Potential strategic options for the company (Source: Influenced by Naudé, 2021)
Figure 5: Potential strategic options for the company (Source: Influenced by Naudé, 2021)
“End-to-end digitalisation”
With increased use of technology and innovation in UK financial markets, organisations will start embracing extreme digitisation for reshaping operations and driving innovation. To win the race of all things digital, financial institutions can adopt new ways of exploiting exponential technology like hybrid cloud, AI, and automation (Naudé, 2021). As big data has become immensely crucial for financial industry it can allow organisations to improve financial services and maintain stable revenue schemes by delivering personalised recommendations to clients.
“Transformed use of AI and data”
Deploying factories and transforming the data environment can put data into action for accelerating transformation. It can help the company detect cases like money laundering, fraud, and collusion. As a result, effective management of financial services can take place and better services can be provided to clients. As per the scenario, organisations in the financial industry can collaborate AI and big data with financial services for providing standard quality financial services to customers and at the same time strengthen data security.
“Security and fraud”
In the future, security and fraud management could be enhanced in the financial market. It would include elimination of human mistakes as much as possible for preventing data breaches. organisations will work on maintaining up-to-date security systems and aim to prevent malware in systems. This scenario indicates staying one step ahead in new frontiers of cyber security as bad actors could become increasingly sophisticated.
“Viable sustainability”
To launch initiatives that meet market expectations, financial institutions were required to find viable sustainability models. This will include effective obedience to corporate ethical objectives, and regulatory requirements, and conducting an acceptable cost-benefit analysis. This will facilitate providing reliable and user-friendly financial services to customers.
Value proposition
Value proposition is the part of company’s overall marketing strategy that provides declaration of statement which introduces company’s brand to target customers. It tells consumes what the venture stands for, why it deserve their business and how it operates (Da Costa Fernandes et al. 2020). Value proposition of the company which is going to operate in UK’s financial market is analysed as under:
Business canvas model
It helps in analysing clear goal of an organisation or an industry. It includes 9 elements like “customer segments”, “value propositions”, “channels”, “customer relationships”, “revenue streams”, “key resources”, “key activities”, “key partnerships”, and “cost structure” (Sparviero, 2019). Business canvas model of a company for operating in UK finance industry is as under:
Value proposition canvas
Value proposition canvas sheds light on customers’ problem and producing offerings to solve them. It helps in ensuring all products and services are positioned arounds customers’ needs and values. Value proposition canvas for the finance company is as under:
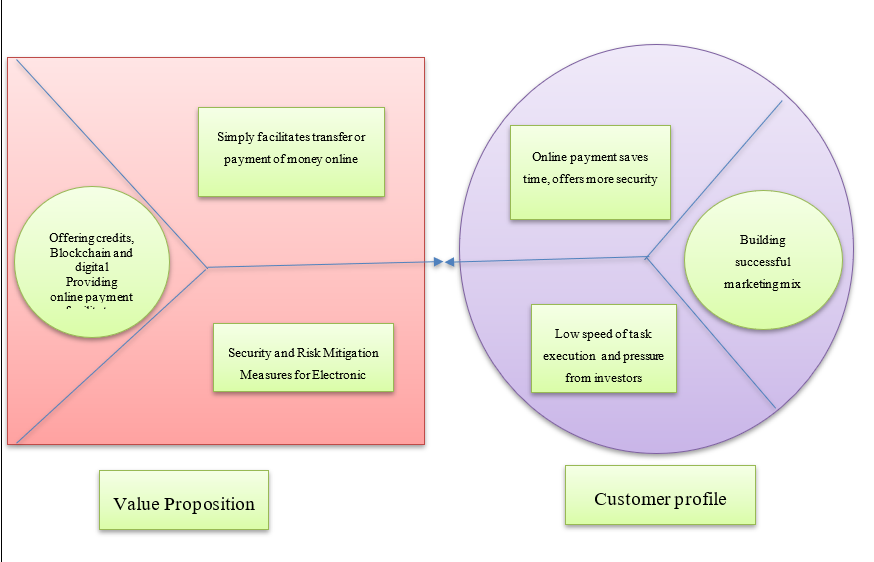 Figure 6: Value proposition canvas (Source: Created by author)
Figure 6: Value proposition canvas (Source: Created by author)
Recommendations
Recommendations related to future of the financial market has been discussed below in context of UK financial market:
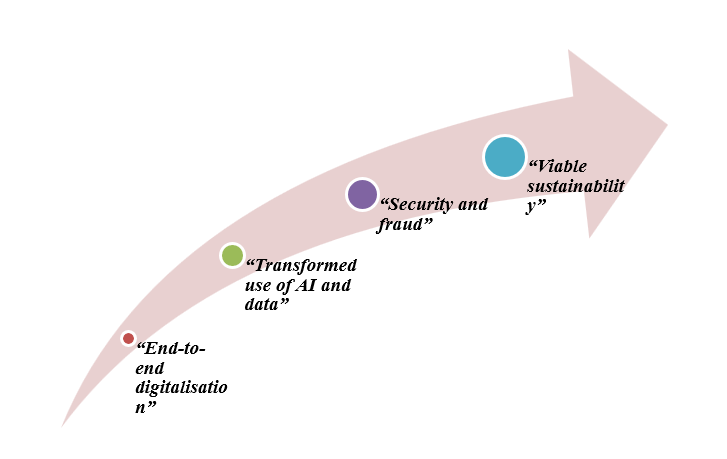 Figure 7: Potential recommendations for future of company in financial market (Source: Influenced by Dietzmann et al. 2020)
Figure 7: Potential recommendations for future of company in financial market (Source: Influenced by Dietzmann et al. 2020)
“End-to-end digitalisation”
Company in UK financial market should improve efficiency of financial services, to facilitate appropriate financial forecasts, and performance through end-to-end digitalisation (Dietzmann et al. 2020). Besides, it will provide a brief insight to the company who aim to offer value-creating financial services to customers.
“Transformed use of AI and data”
Company in UK financial market should effectively utilise AI and data analytics for digital transformation of financial services. As a result, errorless financial decisions could be made for offering good financial services and modifying existing financial services.
“Security and fraud”
Company in UK financial market should effectively deal with cybersecurity issues and maintain effective data protection. With effective use of AI and big data, unpatched vulnerabilities from the financial system can be mitigated and at the same time, chances of human errors could be reduced to a minimum.
“Viable sustainability”
Company in UK financial market should redefine traditional financial services and promote a system of digital currency and transactions. It is not only helpful for developing next-generation financial management systems but should also facilitates consumers’ experiences to gain competitive edge (Zaki, 2019).
Conclusion
Finance industry has been a growing sector in UK since past few years. Number of firms in this industry has grown effectively. It can be concluded that it is a responsible contributor to economic development in UK. There is a great scope for value creation through adequate analysis of external factors for the firm. Technological development in this country is currently at their peak.
The industry is enabling companies to exploit further resources to appropriate suitable scope for value creation. Porter’s generic model describe this industry as a potential source of competitive hub for a new entrant. Future trends suggest growing dependence on digital transactions due to increased demand for online payments. Fast and easy transactions are facilitated through these channels.
Moreover, businesses have issued their interest in fintech solutions since the past few years. Typical factors concerning this industry have been identified as trust, operational efficiency, and risk management. These factors are supposed to manufacture substantial support for client firms to increase their scope of profitability. Impact of each trend has also been described along with typical scenarios. New organisation in this industry has a potential scope of growth during following years due to the rising demand and improvement in technology.
Reference List
Berentsen, A. and Schär, F., (2018). The case for central bank electronic money and the non-case for central bank cryptocurrencies, 3(1), pp.8-13.
Bergmann, M., Brück, C., Knauer, T. and Schwering, A., (2020). Digitization of the budgeting process: determinants of the use of business analytics and its effect on satisfaction with the budgeting process. Journal of Management Control, 31(1), pp.25-54.
Cuypers, I.R., Ertug, G., Cantwell, J., Zaheer, A. and Kilduff, M., (2020). Making connections: Social networks in international business. Journal of International Business Studies, 51(5), pp.714-736.
Da Costa Fernandes, S., Pigosso, D.C., McAloone, T.C. and Rozenfeld, H., (2020). Towards product-service system oriented to circular economy: A systematic review of value proposition design approaches. Journal of Cleaner Production, 25(7), pp.120-127.
Deloitte (2022). About potential trends on the Finance Industry. Available at: https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/pages/financial-services/articles/future-of-financial-services.html/[Accessed on 26th June 2022]
Dietzmann, C., Heines, R. and Alt, R., (2020). The convergence of distributed ledger technology and artificial intelligence: An end-to-end reference lending process for financial services. In Proceedings: Twenty-Eighth European Conference on Information Systems, 3(1), pp.7-21.
Duan, H., Li, J., Fan, S., Lin, Z., Wu, X. and Cai, W., (2021), October. Metaverse for social good: A university campus prototype. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, 3(2), pp. 153-161.
Forbes (2022). About potential trends on the Finance Industry. Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2022/03/25/the-4-biggest-future-trends-in-the-financial-sector/[Accessed on 25th June 2022]
Frost, J., Gambacorta, L., Huang, Y., Shin, H.S. and Zbinden, P., (2019). BigTech and the changing structure of financial intermediation. Economic Policy, 34(100), pp.761-799.
Gov.uk, (2022). About bargaining power of consumers. Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/businesspopulationestimates2021/businesspopulationestimatesfortheukandregions2021statisticalreleasehtml#:~:text=Figure%205%3A%20Non%2Demploying%20and,2000%20and%202017%20to%202021&text=Overall%20the%20number%20of%20SMEs,employing%20businesses%20grew%20by%2027%25 [Accessed on 27.6.2022]
Islam, R., Ahmed, S., Rahman, M. and Al Asheq, A., (2020). Determinants of service quality and its effect on customer satisfaction and loyalty: an empirical study of private banking sector. The TQM Journal, 4(2), pp.7-12.
Islami, X., Mustafa, N. and Topuzovska Latkovikj, M., (2020). Linking Porter’s generic strategies to firm performance. Future Business Journal, 6(1), pp.1-15.
Kumar, A. and Nayyar, A., (2020). si 3-Industry: A sustainable, intelligent, innovative, internet-of-things industry. In A roadmap to Industry 4.0: Smart production, sharp business and sustainable development, 4(3), pp. 1-21.
Kurniawan, D., Iswahyudin, M.D. and Suciati, T.R., (2020). SWOT Analysis and Ansoff Matrix in Creative Food Industry Business Development: A Study on Creative Food Business “Komala”. Open Access Indonesia Journal of Social Sciences, 3(2), pp.128-136.
Liyanage, A.S. and Weerasinghe, T.D., (2018). The effect of strategic flexibility on strategy-performance nexus: A conceptual model. Kelaniya Journal of Management, 7(1), pp.26-39.
Naudé, W., (2021). Artificial intelligence: neither Utopian nor apocalyptic impacts soon. Economics of Innovation and new technology, 30(1), pp.1-23.
Prodanova, N., Trofimova, L., Bashina, O., Kachkova, O., Ilienkova, N. and Polyanskaya, T., (2019). Approaches for obtaining audit evidence at fair value measurement. International Journal of Economics and Business Administration, 7(3), pp.279-292.
Pwc (2022). About potential trends on the Finance Industry. Available at: https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/industries/financial-services.html/[Accessed on 24th June 2022]
Sanderson, A., Mutandwa, L. and Le Roux, P., (2018). A review of determinants of financial inclusion. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 8(3), p.1.
Shad, M.K., Lai, F.W., Fatt, C.L., Klemeš, J.J. and Bokhari, A., (2019). Integrating sustainability reporting into enterprise risk management and its relationship with business performance: A conceptual framework. Journal of Cleaner production, 208, pp.415-425.
Sparviero, S., (2019). The case for a socially oriented business model canvas: The social enterprise model canvas. Journal of social entrepreneurship, 10(2), pp.232-251.
Zaki, M., (2019). Digital transformation: harnessing digital technologies for the next generation of services. Journal of Services Marketing, 4(1), pp.8-11.
Zhang-Zhang, Y., Rohlfer, S. and Rajasekera, J., (2020). An eco-systematic view of cross-sector fintech: The case of Alibaba and Tencent. Sustainability, 12(21), pp.89-97.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

