BU L7 The Tourism and Hospitality Industries
Introduction
The hospitality and tourism sector is regarded as one of the main drivers of a substantial amount of financial resources globally and the sector has also created a significant number of employment opportunities for people everywhere. Therefore, the same might be considered as one of the most imperative business sectors and thus, the components prevalent within the same, the kind of stakeholders the industry has along with that the evaluation of how operations are conducted need to be assessed critically. The report will attempt to address all the aspects that drive the tourism and hospitality sector by taking the case of Marriott and scrutinising how the company derives value to obtain a more in-depth analysis of the given industry.
Organisation background
Marriott International or popularly known as Mariott is a hotel chain that mainly operates within the tourism and hospitality industry the company has almost 30 different brands under their name such as the JW Marriott group, the Ritz-Carlton, the W hotel chain, Fairfield by Mariott and more. The hotel chain might be regarded as one of the biggest groups working in a similar industry and their revenue which was approximately 2.3 billion dollars in 2021, further justifies the claims (Marriott International, inc. 2022). In their annual report, it was further established that the sudden emergence of the pandemic might not disrupt the business of the brand as they employed approximately 92,000 rooms globally in 2021 when the epidemic was at its peak (Marriott International, inc. 2022). On the other hand, the company has hired over 120,000 employees in various properties of the corporation and overall they are known to manage approximately 205,000 associates (Marriott International, inc. 2022).
Reason for doing this task
The task is being conducted to provide an in-depth evaluation and analysis concerning how the tourism and hospitality industry bounced back from the horrifying impacts they have suffered during the pandemic and how the implementation of technology and innovation might help to achieve that. The entire task has been based upon the tourism system of Leiper and the same has provided more flexibility in completing the task quite successfully the theoretical framework has further provided more information regarding the tourism eco-system and the kinds of components present in them. Therefore, it has been predicted that by doing this the entire ecosystem of the tourism and hospitality industry will be more easily comprehensible.
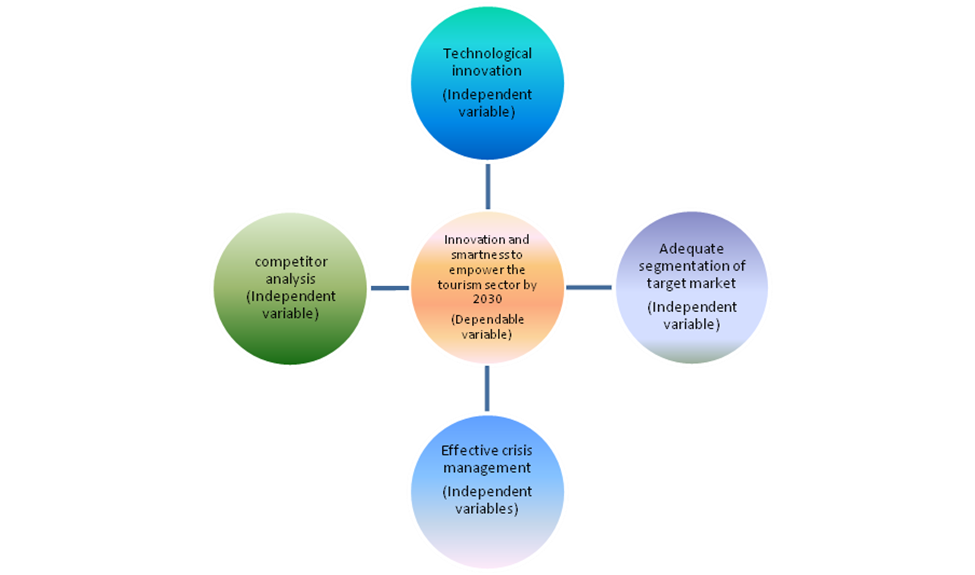
Figure 1: Conceptual framework
(Source: Self-Created)
Exploiting the technologies and smartness with the innovations
It has become a significantly known fact that the emergence of the pandemic has brought on different business sectors and it is safe to say that the tourism and hospitality industry has not been spared from the same (Xiang et al. 2015). Therefore, it has become significantly imperative that a thorough change-management process is implemented within the same and the most effective way to do that might be through the means of technology. The 4th industrial revolution has helped to bring significant advancement within the landscape of technology and the same could also be implemented within the said industry to derive and retain customers during such trying times. Research has stated that corporations might further utilise the aspect of the internet to its full potential for recruiting employees from the same and thereby, blurring the domestic and global boundaries (Ladkin and Buhalis 2016).
Digital payment- One of the most effective ways that technology could mitigate the problems that the tourism and hospitality industry is facing, which is to bring more guests during unprecedented times is the integration of cashless payment methods. That will further enable the individuals to effectively discard the fear of getting contaminated and practise social distancing to be safe from the pandemic (Wisniewski et al. 2021)
Robot butlers- Instead of sending humans to serve guests in their rooms and conduct several tasks such as cleaning and laundry, the hotels could bring in robots that could also perform similar tasks and that would further help the corporations to make the organisation digitised or smart during the pinnacle of the pandemic (Kim et al. 2021).
Temperature checking with Artificial Intelligence (AI) – The system of temperature checking might also enable them to evaluate individuals who have relative body temperatures. That way they would get to analyse people who might carry the virus with them and in that context, the hotel authority might take some additional actions that will further ensure the safety of the guests. Apart from such technologies the corporations might also take leverage of Information Technology of social media platforms as the concept of marketing has been highly impacted by these platforms and to sustain amid intense competition they need to utilise the same (Buhalis and Mamalakis 2015).
An analysis of the target market
The analysis of the target market of Marriott will be based on the effective STP model which is also known as segmentation, targeting and positioning.
Segmentation- The Company has segmented its market among mostly the rich population and people who are profoundly fond of getting luxury accommodations and tend to have a significantly opulent lifestyle. No specific area has been selected for targeting the consumers as the hotel chain is global; however, they have meticulously built all their properties amid the city centre, near any attractive location such as the beach or close to the airports.
Targeting- The corporation fundamentally targets people who are within the age group of 25-65 and have a relatively high to moderate income as people without a significantly high-paying job might fail to afford the luxury services provided by the hotel group.
Positioning- The brand positions itself as one of the most luxurious, premium-quality service providers in the market and they mainly target people belonging to the upper class of society.
An analysis of the key players in the market
Even though they are one of the most well-known hotel chains in the world, Marriott also has some of the toughest competitors in the market. The competitors of Marriott include the Radisson group of hotels, The Four Seasons LTD., the BWH hotel group, Hyatt hotels and more.
External environment and crisis management and resilience that Marriott attracts
Porter’s 5 forces
New entrants threat in the industry
Marriott is a well-established and leading in the tourism and hospitality industry that deals with accommodation in the company, however, according to Porter’s 5 forces the new entrant’s threat in the industry has been seen to be low. Any new entrant in the business of hospitality and tourism requires a good amount of investment in the process of advertisement and infrastructure. It has been much more difficult for any new entrant to arrange this capital to compete for equity in the company again after the Covid-19 impact which has made the operators switch work from home facility.
Threat of substitutes
The threat of existing substitutes for Marriott has been recorded as high as it is the biggest five stars of the recent world hence the switching of work form, and home has made the other tourism and hospitality industry steps in the major loss such as Marriott. Thereafter it has taken the shares of Marriott in the limited experience in the advantageous and luxury platform. Moreover, it has been seen that the familiarity of Marriott among the targeted and preferred customers as the external stakeholder has been brewing by days with the unstoppable quality and standard without the haunt of new alternatives. The organisation carries on building good relations among the staff and the customers that attract more regularly even after the wide swipe of the pandemic (Stoyanova-Bozhkova et al. 2020).
Power of customers
The power of customers in Marriott has been seen to be moderate as the place of the customers is divided into two parts where the dividend is the travelling on vacation in the luxury hotels and the divisor is the business personnel who are always in need of such luxury facilities. The switching cost has been seen to be high as the preference of the customers as the external stakeholder is seen to be fixed in Marriott where it will be low if the action starts reciprocating the external environment. The decision-making process of the hotels in the tourism and hospitality industry has been seen to develop as the necessity of care, with knowledge of the destination language and limited negotiating scope has made the customer have to be stored in the perspective of the company and its profit (Rubio-Escuderos et al. 2021).
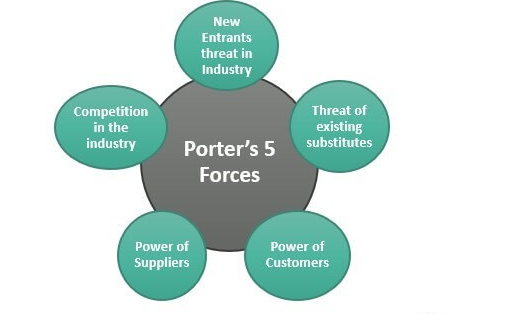
Figure 2: Porter’s 5 forces
(Source: Rubio-Escuderos et al. 2021)
Power of suppliers
The power of suppliers in Marriott as external stakeholders has been seen to be low as the suppliers involve maintenance, infrastructure, and food which have been shown by the company to be much heedful. The dealing of Marriott with its suppliers is well maintained as it back poses the value of the brand again maintaining the long-term relationship with a cautious look which has made the company in the reading list. The time when it comes to a new involvement in the hotel carries with its many dimensions and processes before the finalising of the item. Suppliers have the value of being the biggest client of the company with excellent options that deal with the appliances that reduce the supplier’s power of the hotel.
Competition the industry
Competitors of Marriott in the industry may be determined to be high involves the Hyatt, Hilton, Four Seasons hotels and resorts, Carlsen and many more as the hotels serve the same values and advantages in the tourism and hospitality industry. They offer the customers as a part of external stakeholders by distributing offers and heavy discounts that will encounter more customers as the external stakeholder on the basis. Marriott is heading the competition in terms of building pipelines and hotel rooms with more than 4,00,000 rooms. By maintaining the structure of the industry in developing the strategy and the technology which will stop more tourists from visiting the place regularly is the foremost work of communication and technology information in the industry in external environments (Qi et al. 2008).
Elements of Resilience and crisis management
There are four elements of crisis management and resilience which are listed below:-
Identifying team roles and responsibilities
In this process, the management team of Marriott deals with managing the emergency by detecting and monitoring the process in resilience and assessing the impact of the crisis that activates the response and command towards it. The management team of Marriott implements contingency plans and measures that are implemented in the emergency period by communicating important information with all staff and stakeholders. The management team of Marriott makes sure that the available resources are available on the company’s funds so that the disruption in the process may not favour (Pizam et al. 2022).
The formal incident assessment process and team
The management team of Marriott shape the elements of crisis management by maintaining accountability which will include making the point on the individual responsible for the process. The manner the individuals indulge in the responsibility will help in the reduction of the elements in the crisis management in Marriott which will detect the overall crisis and will mitigate it accordingly in crisis management and resilience (Paraskevas et al. 2011).
Incident Action Planning (IAP) skills
The Incident Action Planning (IAP) skills centralised and managed the team for the incident that will support the plans of the Marriott management team in the action taken at the time of ensuring the objective which will deliver the synchronised operation. The objectives of the pains are delivered by the Marriott management team in the retention of the employees and delivering the services that had been choked at the time of Covid-19 in crisis management and resilience.
Communication of effective crisis management team
The strategy that has been set for the management of crisis management and resilience has been reputedly made based on the connection of the communication among the teammates in Marriott. Thus Marriott has faced useful feedback on the outcome of the discussion that deals with understanding the demands and desires of the audience (Page et al. 2017).
An analysis of the economic, health, socio-cultural and environmental impacts of Covid-19 on the tourism and hospitality industry
Economic impacts
The outbreak of Covid-19 has been impacting the tourism and hospitality industry which has made the sector weakened by creating a major loss in finances, reduction has been seen in the demands of the customers as the external stakeholder. Due to the negative impact of Covid-19 the rate of unemployment in accommodation has been to increase with 1,32,000 in 2020 whereas it was seen to 1,88,500 in 2019 (refer to appendix 1). The total contribution in tourism and travel has been to drop down to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) worldwide from 2019 to 2020 as it was $4,775 billion in 2020 whereas it was $9,630 billion in 2019 (Statista. 2022).
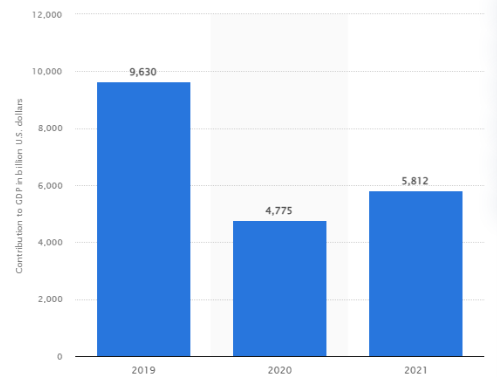
Figure 3: Economic impacts
(Source: Statista. 2022)
Health impacts
The impact of Health due to Covid-19 on the tourism and hospitality industry has been drastically deteriorating as the employees at that time were most affected by the negativity of Covid-19. The year 2020 has seen mass death in many sectors similarly in the tourism and hospitality industry the employees as the internal stakeholder saw the deadliest year at the time of pore vaccination. The employees had to compromise with the health benefits that were deteriorating the condition of the situation hence notice was taken by the organisation in terms of taking precautions (O’Regan et al. 2021).
Socio-cultural impacts
During the times of Covid-19, the world has faced major heartbreak in every sector however the socio-cultural impact on tourism has been seen as a shift from quality to quality which was traditionally measured in the statistics of highlighting the visitor number. The citizens have boosted the participation of the community in domestic tourism which has made the local culture offer strategic social and economic importance. Cultural tourism has been seen to enhance entrepreneurship and innovation with access to the market and the choice of the people (Mistilis et al. 2014).
Environmental impacts
There have been many restrictions that have grown the bottom line of the long and short term of the implication with the harsh reality faced by the world in Coivid-19 which stopped mobility and has documented the challenges. There were many restrictions in the tourism and hospitality industry at the time of Covid-19 which has taken the breath of the public on the international platform. There have been restrictions such as stopping domestic and international flights in the country, and the stay-backs of the customers and team members in the hotels have made the days and the nights bitter.
Methods of innovation and smartness that may support the recovery resistance to tourism
Sustainable approach
The creation of a smart approach towards the recovery and resilience of tourism with innovation and smartness is necessary for the long-term development that has made the destination smarter by the day. The use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) the Meta-driven methods that make the correct decision have enhanced the process of the Internet of Things (IoT) and have assured innovation. The innovation in tourism has the deeper segmentation that strengthens nature and ecology and has ensured the approach for the recovery of resistance to tourism (Ladkin et a. 2016).
Estimating the damage
There is a lot of data that determines the intensity of the damage of the pandemic and the crisis caused by it the destination caused by the damage will be mitigated with the usage of smart innovation and support that tourism has reliance. The estimate however shows the improvement that has the building capability that the business needs to return from the original basis. Digital usage is implemented in a proper manner that helps in the fast work with low issues in the world of tourism and hospitality industry.
Digitalised tourism
Digitalisation in tourism helps in the growth of mass tourism which accelerates the base of the faculty which has the allocated destination for the recovery and considers the manner of smartness. The implementation of digitalisation in almost every sector of the organisation has made the usage of the system better and easy access with the maintenance of the pattern with smartness, and sophistication that may support the recovery of resistance of tourism with the innovation in tourism and hospitality industry (Kichuk et al. 2019).
Future of the organisation in new realities in the global market
Working as a team
The need of settling down with harmonised tourism should be the main agenda that will conceptualise the manner of tourism over the past few years which will encourage and determine the resilience of the sector. The consecutive years of the pandemic have seen the drastic dimensions which are needed to be reconstructed by 2030 that will empower the global tourism and hospitality industry with innovation and smartness (Fan et al. 2019).
Planet and people
The initiative by the UNWTO on the best tourism villages has been launched from 44 villages to 32 countries that will enhance the skills which will be recognised in the upcoming years till 2030. The need to maintain the balance between the planet and people is necessary for tourism and the saving of the resources and the sanctuary is needed as it will attract tourism in different ways.
Mainstreaming tourism
Mainland tourism will be more concentrated with the help of recovery plans in the actions that will determine the social and economic base of hospitality and tourism till 2030 with the innovations. The need of recognising the pattern is compulsory which will make the planning which will ensure the recovery plans with innovation.
Conclusion
From the above discussion, it may be concluded that the company Marriott has been reluctantly showing the effective manners that bring the tourism and the hospitality industry straightway. The usage of Porter’s 5 forces has determined the range of the company in making success in the tourism industry with effective strategies and choices where there have been identified many competitors. There are targeted customers who enjoy and prefer the company for many reasons which also state the ability of the company to scrutinise the value and concepts in the development.
References
Buhalis, D. and Mamalakis, E., 2015. Social media return on investment and performance evaluation in the hotel industry context. In Information and communication technologies in Tourism 2015 (pp. 241-253). Springer, Cham.
Fan, D.X., Buhalis, D. and Lin, B., 2019. Tourists’ online and face-to-face social contact and destination immersion. e-Review of Tourism Research, 16(2-3), pp.224-233.
Kichuk, A., Brown, L. and Ladkin, A., 2019. Talent pool exclusion: the hotel employee perspective. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management.
Kim, S.S., Kim, J., Badu-Baiden, F., Giroux, M. and Choi, Y., 2021. Preference for robot service or human service in hotels? Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 93, p.102795.
Ladkin, A. and Buhalis, D., 2016. Online and social media recruitment: Hospitality employer and prospective employee considerations. International journal of contemporary hospitality management.
Ladkin, A., Willis, C., Jain, J., Clayton, W. and Marouda, M., 2016. Business travellers’ connections to home: ICT s supporting work‐life balance. New Technology, Work and Employment, 31(3), pp.255-270.
Marriott International, inc. 2022. AnnualReports.com. Available at: https://www.annualreports.com/Company/marriott-international-inc (Accessed: October 31, 2022).
Mistilis, N., Buhalis, D. and Gretzel, U., 2014. Future destination marketing: the perspective of an Australian tourism stakeholder network. Journal of Travel Research, 53(6), pp.778-790.
O’Regan, M., Salazar, N.B., Choe, J. and Buhalis, D., 2021. Unpacking over-tourism as a discursive formation through interdiscursivity. Tourism Review.
Page, S.J., Hartwell, H., Johns, N., Fyall, A., Ladkin, A. and Hemingway, A., 2017. Case study: Wellness, tourism and small business development in a UK coastal resort: Public engagement in practice. Tourism Management, 60, pp.466-477.
Paraskevas, A., Katsogridakis, I., Law, R. and Buhalis, D., 2011. Search engine marketing: transforming search engines into hotel distribution channels. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 52(2), pp.200-208.
Pizam, A., Ozturk, A.B., Balderas-Cejudo, A., Buhalis, D., Fuchs, G., Hara, T., Meira, J., Revilla, R.G.M., Sethi, D., Shen, Y. and State, O., 2022. Factors affecting hotel managers’ intentions to adopt robotic technologies: A global study. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 102, p.103139.
Qi, S., Law, R. and Buhalis, D., 2008. Usability of Chinese destination management organization websites. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 25(2), pp.182-198.
Rubio-Escuderos, L., García-Andreu, H., Michopoulou, E. and Buhalis, D., 2021. Perspectives on experiences of tourists with disabilities: implications for their daily lives and the tourist industry. Tourism Recreation Research, pp.1-15.
Statista. (2022) Travel and tourism: Contribution to global GDP 2021, Statista. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/233223/travel-and-tourism–total-economic-contribution-worldwide/ (Accessed: October 31, 2022).
Stoyanova-Bozhkova, S., Paskova, T. and Buhalis, D., 2020. Emotional intelligence: a competitive advantage for tourism and hospitality managers. Tourism Recreation Research, pp.1-13.
Wisniewski, T.P., Polasik, M., Kotkowski, R. and Moro, A., 2021. Switching from cash to cashless payments during the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond. Available at SSRN 3794790.
Xiang, Z., Tussyadiah, I., & Buhalis, D. (2015). Smart destinations: Foundations, analytics, and applications. Journal of Destination Marketing and Management, 4(3), 143-144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdmm.2015.07.001.
Appendices
Appendix 1
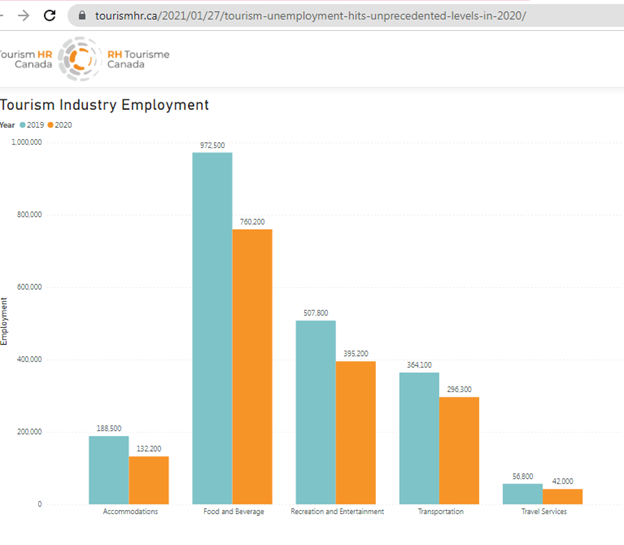
https://tourismhr.ca/2021/01/27/tourism-unemployment-hits-unprecedented-levels-in-2020/
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

