BU7001 Management Research Project Assignment
TO ANALYZE THE ADVANTAGES AND CHALLENGES OF RELATIONSHIP MARKETING WITHIN THE RETAIL INDUSTRY – CASE OF EURO GARAGES UK
1.10 Structure of the Research
Chapter 1:
The first chapter deals with the provision of an introduction to the topic. Here, the researcher was noted to provide an overview of the topic of research. Not only this, a background to the company of Euro Garages, the UK was provided along with an evaluation of recent literature to provide a bird’s eye view of the problem. Along with this, the researcher was seen to frame the research problem and the research aim, objectives and questions based on which the research was conducted. Moreover, a rationale was provided to justify the choice of topic studies in the research work.
Chapter 2:
The second chapter provides the reader with an analysed view of the reviewed literature. Here, the researcher collected literary sources from books, journals and some reports and newspaper articles to evaluate the same and show the relevance to the topic. Moreover, the researcher was seen to provide a concept to relationship marketing along with the pros and cons related to the same. The researcher further identified and highlighted the gap in the literature and explained the conceptual model of the research.
Chapter 3:
The researcher explained the methodological approach involved in conducting the research work in this chapter. The researcher was first seen to provide a succinct view of the research paradigm involved along with the justification of the choice of research philosophy, research design and research approach chosen to conduct the thesis. Further, the researcher was seen to outline a research plan and state the type of research conducted along with the population targeted to do the research. Moreover, the sampling technique involved and the tool of the survey questionnaire was described in this chapter. The researcher further provided an insight into the ethical considerations involved in the research study.
Chapter 4:
This chapter dealt with the statement of findings and the analysis of research regarding the topic. Here, the researcher provided the results of the survey and discussed the application of the research methodology. Moreover, the results derived from the data collected via the survey was analysed in the chapter.
Chapter 5:
The researcher has provided a brief summarization of the research findings in this chapter. Moreover, the researcher gave an analysis of all the findings derived from the past literature along with the results derived from the survey. This brief analysis was used to derive a conclusion and link the same to the research questions and objectives framed in chapter 1 by the researcher.
Chapter 6:
The researcher has provided an altogether separately section to provide the recommendations of the research. The research began the chapter by identifying the limitations of the research study followed by the provision of SMART recommendations in the chapter.
It can be summarised that application of door-to-door marketing in Euro Garages, the UK and the low net profit margin of the company along with the rise of relationship marketing through online portals has increased the need for relationship marketing in the company. The researcher was seen to frame the research questions by dividing the primary research questions and the secondary research questions separately. Moreover, the structure and rationale of the research were explained in the chapter.
2.2 Concept of Relationship marketing
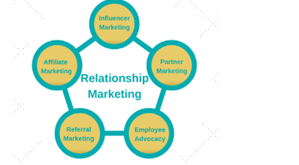
Relationship marketing is an important part of customer relationship management (CRM), which emphasizes a long term customer engagement and maintenance of customer loyalty. According to Wang, Wang & Liu (2016), relationship marketing does not focus on short terms business goals such as customer acquisition and increasing amount of sales volume. Moreover, the concept of CRM deals with a combined formation of sales practices, strategies and technological implementation within work process. As stated by Elbeltagi & Agag (2016), goal of CRM practice is to provide better customer service along with assistance to customer retention and these are helpful to increase sales growth. Similarly, aim or relationship marketing is to construct a strong, emotional customer connection with an existing business process. As demonstrated by Gummerus, von Koskull & Kowalkowski (2017), concept of relationship marketing can be better understood by illustrating three theories, such as commitment trust theory, traditional function/risk theory and innovation theory. Concept of relationship marketing is dependent of five components such as influencer marketing, partner marketing, employee advocacy, referral marketing and affiliate marketing [Refer to Appendix 1].A detailed discussion about these three theories is provided below:
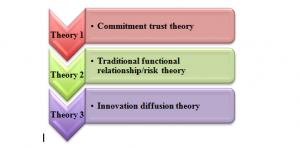
Figure 2.2.1: Concept of relation making: Three major theories
(Source: Created by researcher)
- Commitment trust theory
Commitment trust theory of relationship marketing is based on two fundamental factors, such as trust and commitment. In words of Verma, Sharma & Sheth (2016), this theory propagates the concept to meet demands of customers and by this process; a business body can increase its sales volume. This statement has been supported by Santacreu (2015), and this supporting statement states that a business always tries to win the trust of consumers and based on these trust factor, consumers tries to fulfil own needs. It is also to be mentioned that, in these process needs of both the parties that are consumers and business body meets own desired objectives. Moreover, in the view of Zhang et al. (2015), lack of engagement or commitment of business body towards its business or its consumers may lead to a misbalance in the functional relationship between concerned business and its consumers. Thus, it focuses on building long term relationship with customers rather forms a short time brand-oriented patronage between the same two. A brief discussion of the two major components of this theory is provided here:
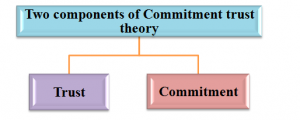
Figure 2.2.2: Two major components of Commitment trust theory
(Source: Created by researcher)
| TRUST | COMMITMENT |
| · Defined by confidence of both parties
· No party is allowed to harm the other through its activities · A business develop trust by fulfilling its promises towards customers · It is of two types, such as cognitive or performance trust and personality or effective trust. |
· Defines a long term desire for maintaining a valuable partnership, here, the partnership is between customer and business body.
· It demands continuous positive progress of provided services and product quality · An organization must be careful to keep its customers satisfied with its services and products. |
Table 1: Two major components of Commitment trust theory
(Source: Created by researcher)
Thus, based on the above discussion, it can be stated that maintenance of both trust and commitment is important to achieve business success by increasing sales volume and this can only be achieved from customer satisfaction attainment. Biemans (2018) has demonstrated the nature of consumers in UK and as per this study, customers of this country always favours to buy from those retailers who are continuing a better customer relationship and doing its business with a very little or no risk. It is also observed in concerned study that, various economic challenges have caused a loss of customer volume for some retailing organization of the concerned country. In this context, the latest economical factor of this country, BREXIT can be taken into consideration. Though various large retailing agencies are using modern relationship marketing management concepts within its work process, BREXIT implementation lowered the sales volume for this country in the financial year 2019 (Telegraph.co.uk, 2019).
- Traditional functional relationship/risk theory
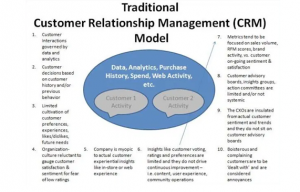
This theory comprises that customer relationship can be governed by analytical data received from consumers based on own experience. As stated by Kirby-Hawkins, Birkin & Clarke (2019), customer decision is generally dependent on customer history and product quality and thus, it always demands a better quality of goods and services. In the opinion of Izogo, Jayawardhena & Adegbola (2018), preference level, experience and future needs that are related to customer are always in a limited territory. An organization which is reluctant to fulfil these factors must face some problems related to customer satisfaction and sentiment and these may provide that organization with a lower rank of rating or an unfavourable rating. It is also true for UK retail companies which are focusing on some specified matrices such as sales volume and brand activity [Refer to Appendix 2]. It is also to be mentioned that, to receive positive impacts form business activities, managing authority of a business body must focus on ongoing satisfaction level and sentiment of customers. The concept of traditional functional relationship or risk theory also speaks for some specified algorithm to increase product and service quality and this can also be observed in the retail sector of UK (Telegraph.co.uk, 2019). Moreover, it is also to be noted that, each department of a business has to face various risk factors and to solve them in respective but suitable approach. Thus, retailed industry of concerned country can focus on both risk management and customer relationship maintenance theory to achieve better business success.
- Innovation diffusion theory
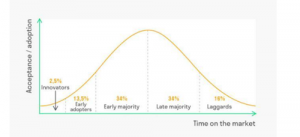
Innovation diffusion state that each product possesses a certain life of utilization and it depends upon the degree of usage that is a wear-tear approach. As demonstrated by Bozic & Kuppelwieser (2019), this theory also has a connection with market value and it can examine the rate of spreading of a market with a market place. This is useful to represent life cycle of a new product by considering five phases that is it divides customers into these phases. As established by Izogo, Jayawardhena & Adegbola (2018), these phases are innovators, early adopters; early majority, late majority, and laggards [Refer to Appendix 3]. It is the most vastly used marketing relationship theory in the entire world and this is providing good results to its applicators. As per research studies, most of the retail industries in UK are implementing this approach in own marketing process (Telegraph.co.uk, 2019). The following table is mentioned here to perform a brief discussion on these five phases:
| FACTORS | DISCUSSION |
| Innovators | Innovators are those who are responsible to bring some new products in market (Siliang, 2018). Various retail industry of UK is in this phase whenever any new product or services are being launched by these authorities. In this phase, a very low amount of consumers take a risk to buy these products or services and in the opinion of Partington (2019), these customers are defined as trendsetters. |
| Early adopters | This term represents those customers who are willing to invest in a new product or services and it is to be noted that, in this case, these are some scopes of risk. As commented by Kirby-Hawkins, Birkin & Clarke (2019), early adopters are larger in number as compared to innovators and mouth advertisers is a term that signifies the role of these group of customers in marketing process. |
| Early majority | This group of consumers is in favor of trends though taking risk is not favored in this case. In this context, opinion given by Biemans (2018) can be taken under consideration. As per this opinion, a larger number of individual exists in this group and are responsible to make a huge hike in the demand level of new product or services. UK retail industry is also an observer of this phase and a larger demand for newly innovated goods are noticed in this respect. |
| Late majority | In this phase, those individuals exist who are willing to buy a product when its demand level is at moderate level. As opined by Partington (2019), individuals of this stage at first ensure that the buying option is not a bad only then continues buying actions. |
| Laggards | Individuals those runs behind the popular present trend unconsciously or consciously come in this phase. In the opinion of Siliang (2018), in this phase product price lowered and those who have been waiting for this, perform buying activity in this phase. |
Table 2: Five phases of innovation diffusion theory of relationship marketing approach
(Source: Created by researcher)
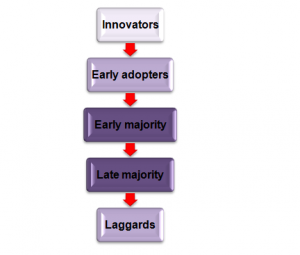
Figure 2.2.3: Five phases of innovation diffusion theory of relationship marketing approach
(Source: Created by researcher)
A rising aptitude of e-commerce in the retail sector is allowing UK retail industries to implement this theory within own business process. As per Bozic & Kuppelwieser (2019), implementation of this theory has allowed incorporating drastic changes in UK retail industry. As a result of this mortar and brick stores are also now able to perform both offline and online selling and marketing practices. Implementation of modern and advanced technological operations is also beneficial to attain a competitive advantage over other organization and to build a better relationship with consumers.
A researcher cannot investigate any issue without implementing any systematic approach when doing research work. This lack of systematic implementation of research work through a proper methodology often results in the researcher to face confusion in doing the research work. The chapter highlights the method applied by the researcher to conduct the research study. This was done for the application of the proper type of research to carry out a quantitative study to use the numerical data collected to support the research findings, thereby describing the advantages and disadvantages of relationship marketing in the UK retail industry, especially with reference to the firm of Euro Garages, the UK.
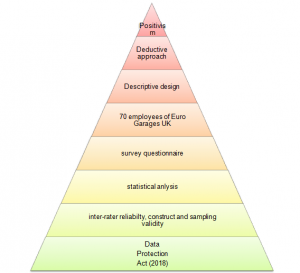
Figure 3.1: Research Plan
(Source: As influenced by Walliman, 2017; created by the researcher)
According to the above figure, the researcher will implement the use of an epistemological branch of research philosophy to implement positivist research philosophy when doing the researcher. The researcher further planned to apply deductive research approach and descriptive research design to conduct the research on a group of customers and employees of Euro Garages the UK. The application this sample was planned to derive relevant data for describing the merits and challenges involved in the use of relationship marketing so that this may be considered by Euro Garages the UK when applying social media in marketing practices to increase sales and profits of the company. The researcher also planned to implement a survey questionnaire to collect quantitative data and do statistical analysis to analyse the results.
The research work of Quilan et al. (2019) highlighted that the three philosophies of positivism, interpretivism and realism come under the branch of epistemological branch of research philosophy. The research philosophy of interpretivism involves the segregation of various elements in the thesis, which is then interpreted based on the identified themes of the research topic (Bell, Bryman & Harley, 2018). On the other hand, realism philosophy of research involves the use of realistic data leaving no scope of bias in the research work (Quinlan et al. 2019). However, Saunders et al (2015) highlighted that positivist research philosophy is the branch of research philosophy in which the researcher applies the use of numerical and factual data to justify the conclusion derived in the research study.
3.2.1.1 Justification of Research Philosophy
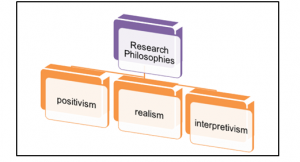
Figure 3.3: Types of Research philosophies
(Source: As influenced by Easterby-Smith, Thorpe & Jackson, 2015, p.48)
As seen from the above figure, a researcher can apply positivism, realism or even interpretivism research philosophy when conducting a research study. As per the view of Easterby-Smith, Thorpe & Jackson (2015), interpretivism research philosophy applies the use of various elements and themes which is the basis of interpretation of each element of data. However, every individual can interpret data in a different manner. Moreover, realism involves the use of realistic data. However, it is not possible to gain realistic data of a company so easily leading to the rejection of these two research philosophies in the research.
According to the research of Jackson (2015), exploratory research design delves into the various questions framed and seeks to explore each and every facet of the research study. This research design helps to find the extent of the prevalence of variables and identify problems as well as the influence of the same on an industry of company. The explanatory research design is also known as the causal research design. As understood from the term itself, it seeks to explain the cause-effect relationship between two or more variables in a research study. Descriptive research design is used to describe all the aspects in research such as that of advantages and disadvantages regarding a topic.
3.2.2.1 Justification of Research Design
The researcher has framed the research questions based on the research topic – advantages and cons of relationship marketing. Since the researcher has not explored the research issue to identify problems nor has he showed any cause-effect relationship, leading to rejection of exploratory and explanatory research designs. Moreover, the researcher has only investigated the pros and cons of relationship marketing in this topic, justifying the choice of descriptive research design for the research study.
As per the research of Saunders et al (2015), inductive research approach involves a bottom to top approach. The application of such as a research design results in the researcher to use the research findings to derive a concept, resulting in innovation and formation of new concept through the research study. On the other hand, deductive research approach involves a top to bottom approach in research. This results in the researcher to use various past literature to derive a concept, based on which research questions or hypothesis is framed. Moreover, the findings of the study are used to test the framed hypothesis, leading to the formation of a conclusion regarding the issues investigated in the research study.
3.2.3.1 Justification of Research Approach
The researcher has framed the research questions for the topic and gained an understanding of the issue by reviewing various past literary sources to derive a concept of the topic. Moreover, a survey was conducted, and data collected were statistically analysed and linked with the research objectives and questions. This resulted in a deduction of the conclusion from the findings, and no such new concept was formed. Hence, the deductive approach was found to be more suitable for the research study.
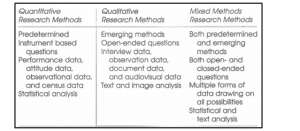
The works of Cresswell & Cresswell (2017) highlighted that the type of research is often based on the design of data collection involved in a research study. As highlighted by McCusker & Gunaydin (2015), quantitative researcher involves the collection of numerical data which can be measured by the researcher for further analysis, whereas a qualitative data is one which does results in the researcher to gain in-depth knowledge into the research issue. A mixture of these methods results in the application of mixed research study. Since the researcher has used survey questionnaire to conduct a statistical analysis of the results, quantitative type of research was deemed as more suitable for the research (Refer to Appendix 4 and Appendix 5).
Bell, E., Bryman, A., & Harley, B. (2018). Business research methods. 5th Ed., Oxford: Oxford university press. Retrieved from: https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=J9J2DwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=business+research+philosophy&ots=GLfBde5OCM&sig=eHCcAwfoVlYQf2K9Q3LXOxq27VM#v=onepage&q=business%20research%20philosophy&f=false [Retrieved on 29 August 2019].
Biemans, W. (2018). Managing innovation within networks. Abingdon: Routledge. Retrieved from: https://content.taylorfrancis.com/books/download?dac=C2017-0-60954-7&isbn=9781351330442&format=googlePreviewPdf [Retrieved on 21 August 2019].
Bozic, B., & Kuppelwieser, V. G. (2019). Customer trust recovery: An alternative explanation. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 49, 208-218. Retrieved from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S096969891830941X [Retrieved on 21 August 2019].
Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2017). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. 2nd Ed., London: Sage publications. Retrieved from: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/73b7/18e508fa943dfb22a9cb5fb17f888239ad0e.pdf [Retrieved on 29 August 2019].
Easterby-Smith, M., Thorpe, R., & Jackson, P. R. (2015). Management and business research. 5th Ed., London: Sage. Retrieved from: https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=SfwaCAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=business+research+philosophy&ots=x1EIu2FpIs&sig=TP9BzvlnWboymS1AhW-wF5Qsz7M#v=onepage&q=business%20research%20philosophy&f=false [Retrieved on 29 August 2019].
Elbeltagi, I., & Agag, G. (2016). E-retailing ethics and its impact on customer satisfaction and repurchase intention: a cultural and commitment-trust theory perspective. Internet Research, 26(1), 288-310. < http://irep.ntu.ac.uk/id/eprint/33170/1/10695_Agag.pdf>
Gummerus, J., von Koskull, C., & Kowalkowski, C. (2017). Guest editorial: relationship marketing–past, present and future. Journal of Services Marketing, 31(1), 1-5. < http://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1151468/FULLTEXT02>
Hair Jr, J. F., Wolfinbarger, M., Money, A. H., Samouel, P., & Page, M. J. (2015). Essentials of business research methods. 2nd Ed., Abingdon: Routledge. Retrieved from: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/9781315704562 [Retrieved on 29 August 2019].
Izogo, E. E., Jayawardhena, C., & Adegbola, E. A. (2018). Creating particularized trust in e-retailers through experiential value and generalized trust. Journal of Strategic Marketing, 1-23. Retrieved from: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ernest_Izogo/publication/325630123_Creating_particularized_trust_in_e-retailers_through_experiential_value_and_generalized_trust/links/5b1e11b9aca272021cf583ef/Creating-particularized-trust-in-e-retailers-through-experiential-value-and-generalized-trust.pdf [Retrieved on 21 August 2019].
Jackson, S. L. (2015). Research methods and statistics: A critical thinking approach. 5th Ed., Boston: Cengage Learning. Retrieved from: https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=rTZ-BAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR4&dq=research+approach&ots=c1jvFL4Bcw&sig=JzFi8JKZXh4_wmS7XP6geAZXTFE#v=onepage&q=research%20approach&f=false [Retrieved on 29 August 2019].
Kirby-Hawkins, E., Birkin, M., & Clarke, G. (2019). An investigation into the geography of corporate e-commerce sales in the UK grocery market. Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science, 46(6), 1148-1164. Retrieved from: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/126880/3/e-commercerevisions.pdf [Retrieved on 21 August 2019].
McCusker, K., & Gunaydin, S. (2015). Research using qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods and choice based on the research. Perfusion, 30(7), 537-542. Retrieved from: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.968.2338&rep=rep1&type=pdf [Retrieved on 29 August 2019].
Partington, R. (2019). UK retailers suffer weaker sales due to BREXIT uncertainty. [Online]. The Guardian. Retrieved from: https://www.theguardian.com/business/2019/mar/05/uk-retailers-suffer-weaker-sales-due-to-brexit-uncertainty [Retrieved on 21 August 2019].
Quinlan, C., Babin, B., Carr, J., & Griffin, M. (2019). Business research methods. 2nd Ed., Andover: South Western Cengage. Retrieved from: https://www.dora.dmu.ac.uk/handle/2086/16559 [Retrieved on 29 August 2019].
Santacreu, A. M. (2015). Innovation, diffusion, and trade: Theory and measurement. Journal of Monetary Economics, 75, 1-20. < https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/35311/1/MPRA_paper_35311.pdf>
Saunders, M. N., Lewis, P., Thornhill, A., & Bristow, A. (2015). Understanding research philosophy and approaches to theory development.In Research Methods for Business Students, Harlow: Pearson Education Retrieved from: http://oro.open.ac.uk/53393/ [Retrieved on 29 August 2019].
Siliang, C. (2018). Analysis on the Usage Intention of Mobile Payment. Retrieved from: https://lnu.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1318496/FULLTEXT01.pdf [Retrieved on 21 August 2019].
Telegraph.co.uk (2019). The future of retail. [Online]. The Telegraph. Retrieved from: https://www.telegraph.co.uk/business/tips-for-the-future/future-of-retail/ [Retrieved on 21 August 2019].
Verma, V., Sharma, D., & Sheth, J. (2016). Does relationship marketing matter in online retailing? A meta-analytic approach. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 44(2), 206-217. < https://www.jagsheth.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/Does-Relationship-Marketing-Matter.pdf>
Walliman, N. (2017). Research methods: The basics. 2nd Ed., Abingdon: Routledge. Retrieved from: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/9781315529011 [Retrieved on 29 August 2019].
Wang, W. T., Wang, Y. S., & Liu, E. R. (2016). The stickiness intention of group-buying websites: The integration of the commitment–trust theory and e-commerce success model. Information & Management, 53(5), 625-642. < https://daneshyari.com/article/preview/553705.pdf>
Zhang, X., Yu, P., Yan, J., & Spil, I. T. A. (2015). Using diffusion of innovation theory to understand the factors impacting patient acceptance and use of consumer e-health innovations: a case study in a primary care clinic. BMC health services research, 15(1), 71. Accessed from: https://bmchealthservres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12913-015-0726-2, Accessed on: 28th August, 2019
Appendix 1: Five components: Theory of relationship management
(Source: https://cdn-blog.cpcstrategy.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/18032332/EXHIBITION-21.png)
Appendix 2: Traditional customer relationship management
(Source: https://stevenjeffes.files.wordpress.com/2012/01/traditional_crm_model.jpg?w=630&h=461)
Appendix 3: Innovation diffusion theory
(Source: https://www.toolshero.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/diffusion-of-innovations-theory-model-toolshero-768×576.jpg)
(Source: As derived from Cresswell & Cresswell, 2017, p.13)
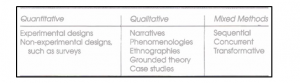
Appendix 5: Differences between Quantitative, Qualitative and Mixed Research
(Source: As derived from Cresswell & Cresswell, 2017, p.17)