Assignment Sample BU7412 International Business
The UK is one of the vast Trading fields with highly appreciated international business strategies that can be applied to neighboring countries such as the United States Germany, France, the Netherland, and so on. In the first half of the year 2020, the UK government has set up its business with these countries by exporting and importing various goods. These countries accounted for nearly 40% of the total trade in the UK. This clear discussion will reflect the trade relationship between the UK and the neighboring countries. The internal business relationship also mentioned collecting information about current national and international trading strategies of the UK.
2. Critical analysis of Trade in the UK
Trade refers to the concept of selling and buying of services and goods, trade can occur between two parties within an economy. International trade refers to the expansion of markets for services as well as goods across borders. International trade results in the rise of competition and hikes in competitive prices, which allows the customer to avail of cheaper products.
It is observed that half of the UK economy is dependent on trade with other countries. As per calculations, 44 percent of the exports in the UK go to countries in the European Union. It has been observed that in the year 2016 about 47 percent of the imports came from countries outside the European Union, thus it is necessary to maintain proper trade relations with EU countries as well as other countries to develop the economy of the UK.
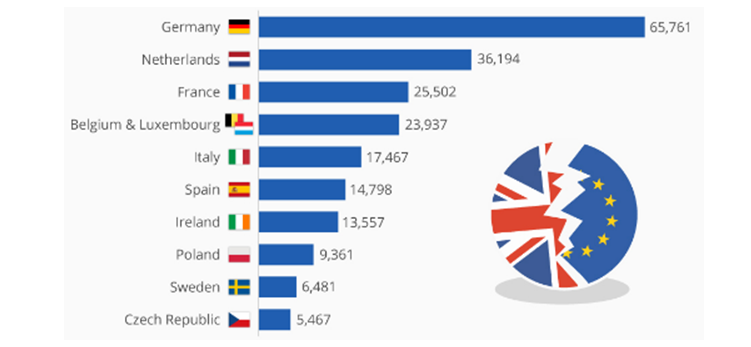
Figure 1: Trade Relations between UK and EU nations
(Source: Wto.org 2020)
The United Kingdom faces a few challenges in trade with its neighboring countries due to political, social, and legal factors. The destiny of the UK economy and the economy of European countries is largely connected; the UK faces some challenges while trading with these nations these challenges are as follows:
- High unemployment in France: The high rate of unemployment in France adversely affects the trade with the UK, France ranks fourth in the unemployment rates among all European countries. The rate of unemployment was 5.8 percent in 2019; this has affected the economy of the country severely (Economist.com 2020).http://BU7412 International Business The low productivity in the nation affects the openness of trade with the UK and hence lowers the rate of exports and imports between the nations. As per the views of Geppert & Matten (2006),http://BU7412 International Business rapid globalization acts as a threat to employment and increases inequalities.The exit of the UK from the EU has heavily affected the trading possibilities with France. The relocation of workers due to the high rates of unemployment has disrupted the stability of exports and imports between the nations. The lack of high productivity firms in France has also affected the rates of unemployment and resulted in lower trade between the nations (Economist.com 2020).http://BU7412 International Business
- Brexit: The British took an exit from the EU and this resulted in rising challenges in the UK trade. The constraints on the immigration laws can affect the labor force of the UK and in turn affect the trade within the nation. This exit resulted in the UK not being a part of the customs union; the country formed a trade agreement that enabled the nation to zero tariffs and quotas on traders’ goods and services (Economist.com 2020). http://BU7412 International BusinessThis put a big strain on the relations of the UK with Northern Ireland, the regulatory and customs border between the two nations have affected the trade between them. The free movement of traded goods and services in the UK and other EU nations has stopped due to Brexit and this has largely affected the rates of exports and imports between the UK and Northern Ireland.
The need to open up a local subsidiary for continuing business has also adversely affected the trade between nations. As per the views of Pankaj (2003), http://BU7412 International Business taxation of various EU businesses has also resulted in lowering the trade between the UK and its neighboring countries. The UK government has to negotiate new agreements of trade with countries outside the EU; this is also a challenge to trade in the UK (Economist.com 2020).http://BU7412 International Business
2.2 Barriers to Trade
The United Kingdom faces very few barriers in trade; the country has no significant investment barriers as well as faces no restrictions on repatriation of profits and capital transfer. Trade includes both exporting and importing goods and services. Considering Brexit the trade costs can rise between the UK and the EU.
As per the views of Pankaj (2003),http://BU7412 International Business this will result in the rise of new tariffs and non-tariff barriers to trade; these include border controls, the difference in regulations in safety, and standards of Products. The few barriers that the UK faces while trading with France and Germany are as follows:
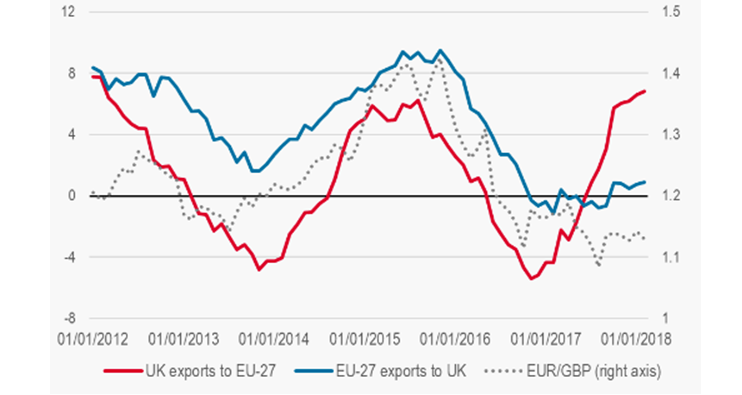
Figure 2: Export rates in the UK
(Source: Gemconsortium.org 2020)
- Tax on Imports: Brexit has affected the trade of the UK heavily in recent times; tariffs on the prices of imported goods will raise the price of goods. As per the views of Vaara, Tienari & Laurila (2006),http://BU7412 International Business the rise of the price of goods will in turn lower the rates of import affecting the economy. The rise in trade costs will hamper the trade relations between the UK and the EU nations such as Germany and France. According to Maguire & Hardy (2006),http://BU7412 International Business the rising rates of tax on imports will lower the possibility of trade between nations. The rising taxation on imports will result in the low availability of goods in the UK market and affect the economy. The consumers in the UK market will be highly affected by this rising rate. The government subsidy to industries within the UK after Brexit has also affected trade within the market.
- The difference in Regulations: The difference between regulations and policies for product standards and safety measures is another major barrier to trade. As per the views of Maguire & Hardy (2006), trade regulations and policies can affect the rates of export and import of a nation. The UK after Brexit has to make new policies and amend previous policies for maintaining trade relations with EU nations.
The change of safety protocols can result in the delay of transactions between the two nations; this will affect the export and import rates by increasing cost and time. As per the views of Vaara, Tienari & Laurila (2006) decisions made by the trade policy affect the various economic sectors within the nation. Prioritizing the trade agreements can help the nation to improve its rates of import and export. The financial sector is a major economic sector in the UK; Brexit has helped UK businesses to use the passporting rights to provide financial services to other countries in the EU (Economist.com 2020). Losing these rights can also act as a barrier to the export of the UK
2.3 Competition in Trade
Trade competition refers to the ability of an organization, industry, country, or state to export more than its imports. As per the views of Vaara, Tienari & Laurila (2006), http://BU7412 International Business competition in trade plays a significant role for business sectors across the nation. Competition in trade can have both positive and negative impacts on the business.
The competitiveness in trade reduces the price of the product which enhances the demand for the product. Additionally, BREXIT has negatively affected the business of the country, it has enhanced quotas and taxes on the product. It has enhanced the price of the product. Besides that, an increment in the price of the product has reduced the demand for the product. It has negatively affected the growth of net export and import of the UK.
The increment in the price of the product is accounted as a disadvantage for the country, which contributed a vital role in reducing the trade volume of the country. As per the views of Vaara, Tienari & Laurila (2006),http://BU7412 International Business the augmentation of price reduces competitiveness and affects the business of the nation. Apart from that, Brexit has affected the economy of the UK negatively which has reduced the GDP of the country (Worldbank.org 2020). As a result, the production of the nation has decreased and has affected the supply of the nation negatively. Therefore, it has reduced competition in the nation.
Numerous restrictions on businesses due to Brexit have also lowered the competition in the UK market; this has disrupted the local monopolies and resulted in lower exports and imports across the country. In international trade, the main competition rises between companies across nations. As per the views of Pankaj (2003), http://BU7412 International Business countries compete in international trade to gain influence and power. Moving away from the EU has affected the international trading capacity of the UK; this is a result of the different regulations of products, border control, and customs policies (Worldbank.org 2020). http://BU7412 International Business Sourcing from suppliers has been made difficult due to the changed policies and has affected the trade competition in the market.
As per the views of Pankaj (2003),http://BU7412 International Business this change of trading policies has resulted in lower collaborations across national borders, which affected the competition in trading. The loss of free trade within the EU has also resulted in deteriorating rates of export and import. As per the views of Pankaj (2003),http://BU7412 International Business this has lowered the market competition of trade in the UK and affected the economy.
The nation has shown a high amount of trade deficit in the primary years of Brexit after that the efficiency of production of the nation has allowed them to maintain its export and import value of the nation. For example, in the year 2019, the trade deficit has narrowed by 14.9billion and it has created a positive impact on the GDP of the country (Worldbank.org 2020).http://BU7412 International Business
3. Evaluation of Mitigating steps and initiatives
The UK government has taken so many initiative steps and strategies to develop its business compatibility with neighboring countries such as Germany, France, and so on. As per the relation of Harreld et al. (2007), http://BU7412 International Business the national companies can also take these facilities of open trade strategies in the UK. The international company who wants to see their business in the UK has to pay minimum taxes to the UK government. The UK cannot produce some necessary things to import from the neighboring countries.
These are “crude oil”, “refined petroleum”, “Packet medicaments”, and computers”. Germany is the most important trading partner of the UK as for its high capacity for technology and electrical production. As per the opinion of Baker & Wurgler (2007), the Netherlands, France, and Belgium are also rich in medicine, perfume, luxury cars, and so on.
The following two points are introduced to provide a clear discussion about the business strategies taken by the UK government used during the trade with neighboring countries and existing companies inside the country.
3.1. Initiatives
Business strategies are divided into two parts internal strategies and external strategies. The internal business plan or strategies are applied for the companies founded and owned in the UK but the external strategies are for the countries that have the potential to trade with the UK by exporting and importing the necessary goods Douglas & Wind, (1987).http://BU7412 International Business The Government of the UK has taken some steps to develop international and national trading:
Investment: The UK government has recently organized business conferences with the business department of the neighboring countries and other global countries. As per the opinion of Barney (1991),http://BU7412 International Business the Government of other countries shows their interest in setting business collaboration after analyzing the demand. Foreign companies are influenced by the UK government to invest in the UK after analyzing the business infrastructure and facilities.
The UK government is trying to collaborate with those companies of neighboring countries for reducing the high demand for petroleum, cars, electronics, and medicines. As per the opinion of Brown & Eisenhardt, (1997),http://BU7412 International Business in the budget, the UK government had spent £270 million between the year 2009 to 2010 and this analysis has proved the strong and effective initiatives for incrementing the business with the neighboring countries as “Belgium”, “Denmark”, “France”, “Germany”, “The Netherlands”, and “Norway”.
Figure 1: Initiatives
(Source: Bbc.com 2020)
Laws: The two main neighboring countries with which the UK has been executing its export and import business are Germany and France. The trading relationship between these two countries can be called a love-hate relationship by the massive support of laws powered by the two countries.
The political background of Germany and the UK had gone through a long way of difficulties and that is why the trading relationship is affected. As per the opinion of D’Aveni et al. (2010), http://BU7412 International Business the UK government has shown its interest to trade with Germany in 2016 and announced to export nearly £75.1 billion and export £49.1 billion. As per the statistics, the laws of these two countries are so helpful for international trade that the UK is the Fourth largest business partner of Germany.
The other most important country is France, which exports “machinery”, “Boilers” and “nuclear Reactors”. The Railways and Tramways are also exported by the UK to France for B. As per the opinion of Ft.com (2020), http://BU7412 International BusinessFrance is the fourth largest business partner of the UK after the Netherlands because the trade relationship of this country is always an example for the other neighboring countries of the UK.
Communication: Business communication means the agreement to import or exports the necessary things of two or more countries. Business communication reflects the transport facilities given by the government of two countries for business purposes. The transport system of Germany and The UK is very high and appropriate for national and international business.
High-recommended business communication is maintained in the friendly trading relationship between these two countries. According to Douglas & Wind, (1987), Germany imported food and drink from The UK worth £1.5 billion and that has proved the economical and supportive contribution of Germany to the UK. German companies such as “Volkswagen Group”, and “And BMW” are popular car manufacturing and selling companies in the UK. According to Bbc.com (2020),http://BU7412 International Business the strong population of France (64.7 million) has a supportive effect on the trading relationship with the UK.
The government of France organizes the International trade fair and the UK is the main guest as an international export-import partner. The business communication between these two countries is so strong that France has reached the third largest ‘e-commerce market” after the UK and Germany.
As per the opinion of Mintzberg (1990), more than 40 million shoppers are engaged in the online business market for making strong business communication not only with the UK but also all over the world.
3.2. Measures
International trading strategies can be measured by evaluating the nature of trade and supply chain management. The determination of two countries’ trade value is based on the “balance of trade” with the potential of subtracting the value of imports and export. The trading relationship between the UK and Germany or The UK and France is based on a friendly cooperative business relationship.
The overall development of any country depends on the balance of its export and import business. According to Eisenhardt & Martin (2000), http://BU7412 International Business “trade surplus” is identified if a country like the UK can be successful in selling products more than buying. On the other hand, if the country buys its products more than the amount of selling then it is called the “Trade Deficit”.
The business coordination between the UK and Germany has provided a major increment in the trade economy of these two countries. The trade volume of a nation can be measured through the net export and import of the nation. As per the opinion of Mintzberg (1990), http://BU7412 International Business the year 2015, Brexit has negatively affected the economy of the country; the exit from the EU has reduced the trade volume of the country as a whole. This in turn has created a negative impact on the total imports and export.
The implementation of quotas and tariffs has enhanced the total amount of tax in the nation. It has enhanced the price of the product, which has reduced the total trade volume of the country. Besides that, it is measured through the balance of payment. As per the opinion of Harreld et al. (2007), http://BU7412 International Business balance of payments is described as the value of exports – the value of imports = balance of trade.
A negative value of the balance of trade describes a trade deficit in the nation. Additionally, the Brexit situation in the nation has resulted in a reduction in the value of the balance of trade.
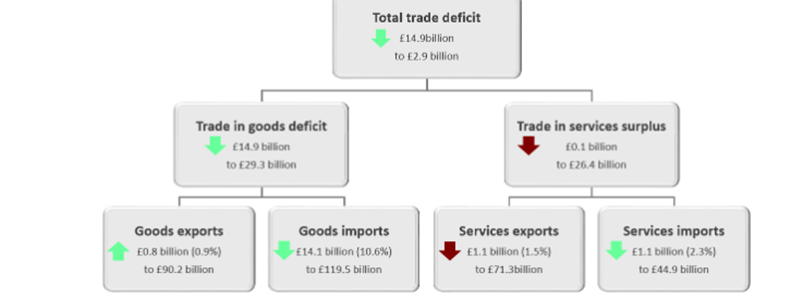
Figure 2: Measures
(Source- Levitt, 1993)
The above figure has shown that the UK faced a trade deficit in the year 2019. The goods export of the nation has increased compared to Goods imports in the nation. The export has increased by 0.96% and the import has decreased by 10.6% (Ft.com, 2020). http://BU7412 International Business
4. Conclusion
The UK is one of the largest trading markets in the World for a friendly-business relationship with neighboring countries like Germany and France. The critical analysis of the national and international trading capacity in the UK is executed in this business report.
The internal and external business environment is supportive of the neighboring countries to set up an export or import business with the UK. Some challenges are identified during the business communication with Germany and France. The trade bearers are mentioned to build up strong business strategies for the neighboring countries.
A massive competition between the native companies and companies from France and Germany is identified and this is elaborately mentioned in this business report. This analysis of business relationships can help to plan strong future business strategies for these three countries. The Government of the UK, Germany, and France has taken so many initiative steps to develop the volume of business between them.
The trade measurement is done after analyzing current export and import business executed within the UK and two other countries like Germany and France. Most importantly, this detailed analysis of trade relations has provided an overall conception of European trading tradition.
Reference List
Baker, M., & Wurgler, J. (2007). Investor sentiment in the stock market. Journal of economic perspectives, 21(2), 129-152. Retrieved from https://pubs.aeaweb.org/doi/pdfplus/10.1257/jep.21.2.129 [Retrieved on 12 January 2021]
Barney, J. (1991). Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. Journal of Management, 17(1), 99-120. Retrieved from http://www.academia.edu/download/35036864/Journal_of_Management-1991-Barney-99-120.pdf [Retrieved on 12 January 2021]
Bbc.com (2020), Capitol riots: FBI warnings amid fears of more pro-Trump violence Retrieved from https://www.bbc.com/news/world-us-canada-55625707 [Accessed on 12 January 2021]
Brown, S. L., & Eisenhardt, K. M. (1997). The art of continuous change: Linking complexity theory and time-paced evolution in relentlessly shifting organizations. Administrative science quarterly, 1-34. Retrieved from http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.460.2424&rep=rep1&type=pdf [Retrieved on 12 January, 2021]
D’Aveni, R. A., Dagnino, G. B., & Smith, K. G. (2010). The age of temporary advantage. Strategic management journal, 31(13), 1371-1385. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Richard_Daveni/publication/229916347_The_age_of_temporary_advantage/links/59d93896aca272e60966d0c5/The-age-of-temporary-advantage.pdf [Retrieved on 12 january, 2021]
Douglas, S. P., & Wind, Y. (1987). The myth of globalization. Columbia Journal of world business, 22(4), 19-29. Retrieved from https://faculty.wharton.upenn.edu/wp-content/uploads/2012/04/8712_The_Myth_of_Globalization.pdf [Retrieved on 12 January, 2021]
Economist.com 2020 Retrieved from: http://www.economist.com
Eisenhardt, K. M., & Martin, J. A. (2000). Dynamic capabilities: what are they?. Strategic management journal, 21(10‐11), 1105-1121. Retrieved from https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/1097-0266%28200010/11%2921%3A10/11%3C1105%3A%3AAID-SMJ133%3E3.0.CO%3B2-E [Retrieved on 12 January, 2021]
Ft.com (2020), Democrats introduce impeachment article in effort to oust Trump Retrieved from https://www.ft.com/content/906a66c1-01e0-422e-92d2-ebdebf0b95b9 [Accessed on 12 January, 2021]
Gemconsortium.org 2020. THE WORLD’S FOREMOST STUDY OF ENTREPRENEURSHIP Retrieved from: http://www.gemconsortium.org
Geppert, M., & Matten, D. (2006) Institutional Influences on Manufacturing Organization in Multinational Corporations: The ‘Cherrypicking’ Approach, Organization Studies, 27 (4), pp. 491 Retrieved from: http://epubs.surrey.ac.uk/232496/3/Matten_%26_Geppert_in_OS_2006.pdf
Harreld, J. B., O’Reilly III, C. A., & Tushman, M. L. (2007). Dynamic capabilities at IBM: Driving strategy into action. California management review, 49(4), 21-43. Retrieved from https://www.martylow.org/s/DynamiccapabilitiesatIBM.pdf [Retrieved on 12 January, 2021]
Imf.org 2020 Retrieved from: http://www.imf.org
Levitt, T. (1993). The globalization of markets. Readings in international business: a decision approach, 249. Retrieved from http://www.academia.edu/download/32053268/T.Levitt.pdf [Retrieved on 12 January, 2021]
Maguire, S., & Hardy, C. (2006). The emergence of new global institutions: A discursive perspective. Organization studies, 27(1), 7-29. Retrieved from: https://minerva-access.unimelb.edu.au/bitstream/handle/11343/116074/18-maguire-hardy-IMO-30C-FINAL-2005-10-04.pdf?sequence=4&isAllowed=y
Mintzberg, H. (1990). The design school: reconsidering the basic premises of strategic management. Strategic management journal, 11(3), 171-195. Retrieved from https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/smj.4250110302 [Retrieved on 12january, 2021]
Pankaj, G. (2003) Semi-globalization and international business strategy, Journal of International Business Studies, 34 (2), pp. 138-152. Retrieved from: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.927.1793&rep=rep1&type=pdf
Vaara, E., Tienari, J., & Laurila, J. (2006). Pulp and paper fiction: On the discursive legitimation of global industrial restructuring. Organization studies, 27(6), 789-813. Retrieved from: https://helda.helsinki.fi/bitstream/handle/10227/400/OS,%20Vaara%20et%20al,%202007.pdf?sequence=3
Weforum.org 2020. Retrieved from: http://www.weforum.org
Worldbank.org 2020 Retrieved from: http://www.worldbank.org
Wto.org 2020 Retrieved from: www.wto.org
Know more about Uniquesubmission Services :-


