BUS66001 Group Assignment Sample 2022
1. Introduction
Coca-Cola is a leading soft drinks producer globally and functions in over 200 countries. It sells non-alcoholic beverages of more than 400 brands and is an extremely valuable brand globally. It has provided licence and ownership to various brands that involve light and diet beverages, juice and drinks, water, coffees, teas, energy drinks and sports.
Coca-Cola possesses ownership interest in several canning and bottling operations. Furthermore, Coca-Cola vends finished beverage items providing Coca-Cola trademarks in over 200 countries (Coca-cola.co.uk, 2021). In December 2006 Coca-Cola functioned by eight fragments that involved South and East Asia, Pacific Rim, Africa, Latin America, European Union, North America, Middle East and Eurasia. Therefore, this report analyses case study of Coca-Cola based on competitive strategies and prevalent issues experienced by this company.
2. Literature review
2.1 Globalisation in soft drink industry
Coca-Cola Company has begun its network in soft drinks industry in 1920, now at this point is time, this company operating nearly 500 brands in over 200 countries. On a global scale, Coca-Cola company has applied a simple formula in order to provide an effective moment of refreshment.
Globalisation has impacted these soft drinks company in a modern corporation manner (Blackwood, 2020, p.103). Globalisation has led Coca-Cola Company to increase market competition associated with a price reduction for customers, to grip on worldwide market, and to gain a competitive advantage.
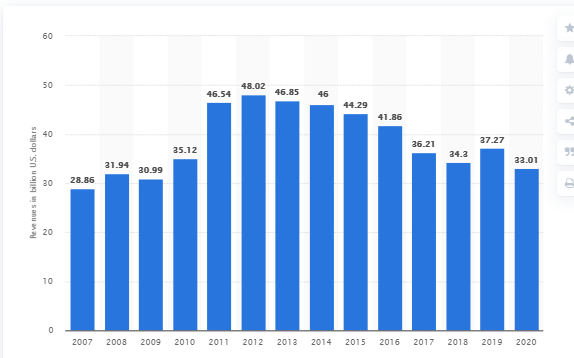
Figure 1: worldwide revenue of Coca-Cola Company
(Source: statista.com, 2021)
Above figure confirming net operating worldwide revenue of Coca-Cola company from 2007 to 2020. This shows that, in recent time net operating worldwide revenue of Coca-Cola is around $33.1 billion (US dollars). As this company is a marketer, retailer, and produces of non-alcoholic beverages, this is well known for Soft Drink Company.
Its net revenue has been increased from $28.86 billion in 2007 to a high range of $48.2 billion in 2012. In recent time this company owns more than 500 brands worldwide as soft drink beverages. At this current situation, Coca-Cola is most valuable and most recognisable brand in all over the world.
3. Methods
As per the view of future growth, Coca-Cola Company is trying to implement such panning or method which can be effective for their future growth strategy. This company needs to focus on optimising brand portfolio which can help their organisation to continue their divers of beverages for future. This ensures an effective emerge from any kind of crisis in the future.
Therefore, this company is focusing on network building in order to reach out to every customer all over the world through different supply chains. According to their plan, they want to build their bard using human instructs.

Future 2: planning in order to improve marketing efficiency and effectiveness
(Source: coca-colacompany.com, 2021)
The above figures confirm that, Coca-Cola Company wants to get their best potential customer base through an effective plan. In this technological era, at this recent time, 4.48 billion people are using social media in order to purchase their products. For effective marketing efficiency this company wants to use this Media tic platform as their supply chain platform and theft can ensure their potential growth in future.
4. Business Strategic Background
Business strategy of Coca-Cola involved straddling this company in various sectors of soft drink businesses. In 2004 in global trade, Coca-Cola led the way in value and volume by incorporating juices of vegetables and fruits, carbonates, and ready for drinking coffee segments. Moreover, it is a second leading company in Asian speciality and functional drinks.
Furthermore, it holds number three position in the list of bottled water companies (Coca-colacompany.com, 2021). Moreover, based on concentrates Coca-Cola holds second position in volume and has ranked third globally based on value aspects. With respect to ready for drinking tea, Coca-Cola has occupied first position in terms of values and has received third position in terms of volume.
In 2004, this company reclassified specific sectors from North American functioning segment to corporate functioning segment (Coca-cola.co.uk, 2021). Moreover, in 2007 Coca-Cola restricted its North American trade to reflect this company’s strategic focus, generating three latest units of business for its beverages and sodas.
These business units involved still beverages, emerging brands and sparkling beverages and these further illustrated Coca-Cola’s emphasis on North-American marketplace, in which it experienced stiff competition from its rival PepsiCo Inc. Furthermore, in 2007 Coca-Cola acquired various fuse beverage brands that involves Refresh, Vitalize, Slenderize line and Tea for an unascertained price (Businessinsider.in, 2021).
Moreover, realignment and restructuring of Coca-Cola in present years have diminished this company’s substantial flexibility on carbonates, irrespective of these factors accounting for 83% of world-wide volume.
5. Business strategic issue
Strategic issues experienced by Coca-Cola Company involve decrease in sales in carbonated soft drink segment. Moreover, another prevalent issue includes present wellness and health trends ranging over beverage industry. A major issue experienced by Coca-Cola involves enhanced competition obtained from PepsiCo Inc.
5.1 Risks identified in soft drink industry in current time
Health and wellness issues: Regular consumption of soft drinks can impact on human health. Due to its phosphoric and carbonic acid, Coca-Cola has a pH of 2.6 which basically resembles natural gastric acid and it is important for fibber digestion. A survey regarding food safety confirmed that carbon dioxide bubbles and sodium bicarbonate and, in this beverage, might enhance dissolving effect. Its regular intake can effete on wreak havoc of taste buds.
Lack of innovation: effective innovation of this company can introduce with new product. And effective innovation can be able to respond with agility according to the demands of customers. This company has neglect product innovation badly since last few years.
Due to this reason, PepsiCo has taken that marketplace and its quality adapted by the customer instead of Coca-Cola. Due to this negligence of Coca-Cola Company, PepsiCo has overtaken the market value of this company for first time in 122 years (Opiate, 2020, p.107).
Changes in beverage business: In recent time, customers do preference such healthy foods. 93% of adults and one in five children are suffering from overweight issues. Due to this reason, consumers became more conscious about their healthy diet. Increasing consumer awareness leaves a negative impact on the soft drink industry worldwide.
Therefore, Coca-Cola company is facing an environmental business issue in their path of success. And these threaten and increasing awareness, decreasing the demand of soft drinks beverages (Demartini et al., 2018, p.3540)
Increased competition: in recent time, soft drinks beverages segments have a wide range of competition worldwide marketplace (Le et al., 2017, p.35). Coca-Cola soft drink beverages compete with many major international beverage companies with its numerous firms’ range.
PepsiCo, Nestle, Cadbury Schweppes, Kraft Food, Group Donne, and many more companies are on the competition level of Coca-Cola beverage companies.
Competition in industry
Coca-Cola experiences significant competition from its rivals in soft drink industry that involves Cadbury Schweppes and PepsiCo. Although Coca-Cola possesses four among top five companies of soft drink industry that involves Diet Coke, Coca-Cola, Sprite and Fanta, it further experienced a lower sales rate in 2006 as compared to PepsiCo. Furthermore, PepsiCo and Coca-Cola have spent an enormous fraction of money on promotion and advertising and have generated effective brand loyalty (Coca-cola.co.uk, 2021).
Moreover, PepsiCo possesses superior sales as compared to PepsiCo in global market. Furthermore, PepsiCo dominated North America in 2006 with its 22-billion-dollar sales, although Coca-Cola possessed only 7-billion-dollar sales in which maximum segment was from overseas.
Thus, PepsiCo. is a significant competitor of Coca-Cola and these brands have been competing for over a century in same sector and holds a leading position in beverage industry. Moreover, another competitive pressure for Coca-Cola involves “Brand name Loyalty”.
Based on reports of “Brand Keys Customer Loyalty Leaders Survey” this brand possesses superior customer loyalty in various industries. However, Diet Coke holds 47th position and Diet Pepsi holds 18th position in terms of possessing a majority of loyal customers for its brands (Jones and Comfort, 2018, p.34).
Therefore, complete KSF determined for competitive rivalry involves global presence, brand image and size. It also experiences other strategic issues that involve enhanced conflicts with bottlers, deficiency of food safety, innovation, and compliances based on statutory regulations. Therefore, strategic issues experienced by Coca-Cola are illustrated through “Porter’s Five Force” model.
Potential new entrants in industry
Potential new entrants in this industry are comparatively low and do not provide a powerful competition in carbonated beverage industry. PepsiCo and Coca-Cola dominate this industry with their expertise distribution channels and powerful brand name.
Moreover, this industry is a completely saturated industry and chances of fresh growth of companies is less (Investors.coca-colacompany.com). Thus, these aspects fabricate complexity for new and unknown entrants for initiating to compete against persisting companies in this business. Furthermore, another major barrier faced by new entrants involves high cost of trucks, warehouses, economic scale and labourers (Mansour et al., 2019, p.1).
Therefore, new entrants would not be able to compete in terms of costs lacking economic scale. Thus, this market saturation and requirements of high capital renders extreme difficulty for companies to perforate this industry.
Power of suppliers
Suppliers involved in Coca-Cola are bottling secondary packaging providers and equipment manufacturers. Moreover, Coca-Cola does not perform any sort of bottling although this company possesses more than 36% of Coca-Cola endeavours. However, rest of Coca-Cola is observed to be a publicly merchandising company and it is a leading bottler globally.
As Coca-Cola possesses majority of bottlers thus, it is perceived to be a specific supplier that does not possess bargaining power (Coca-cola.co.uk, 2021). Moreover, concerns have been raised regarding simmering tensions among Coca-Cola Enterprises which is an enhanced strong and independent bottler and Coca-Cola.
Furthermore, Coca-Cola Enterprises handles more than 80% of market in US and also in sections of Europe. Thus, Coca-Cola is launching its latest products at a notable rate. Therefore, distributional and operational complexity based on launching of latest products is influencing bottler’s bottom line. Thus, conflict with bottlers is a significant threat for Coca-Cola.
Power of Customers
Customers of major soft drink companies and Coca-Cola are significantly discount stores, restaurants and large grocers. Thus, soft drink organisations dispense beverages to shops in order to resale to its potential customers. Therefore, power of customer in terms of bargaining is strong and evident.
Large discount stores and grocers purchase enormous volumes of soft drinks, this permits them to purchase these items at lower rates (Logan, 2020, p.21). However, restaurants possess less power for bargaining as they mostly do not provide order in enormous volumes.
Moreover, as there is an amplification in quantity of customers not intaking soft drinks would in-turn increase power for bargaining of buyers (Coca-cola.co.uk, 2021). Furthermore, consumers of soft drinks are shifting their consumption of regular carbonated drinks to bottled water, low-calorie carbonates, juices, sport drinks and teas. Thus, Coca-Cola is required to adapt with behaviour of its consumers for improvement in this industry.
Threat of Alternatives
Alternatives of Coca-Cola involve sport drinks, bottled water, tea and coffee. In present scenario, sports drinks and bottled water are exceedingly popular based on trends of healthy food intake and health consciousness among customers. Thus, this trend is encapsulated in beverage consumption standards as ageing baby breakers.
Additionally, tea and coffee are competitive alternatives as they contain caffeine. Moreover, soft drinks are effortlessly altered with coffee due to availability of special blends of coffee in market. Furthermore, surging quantity of Starbucks stores has provided various flavours for appealing in several consumer markets. These factors make threat of alternative products an extremely strong governing factor.
5.2 Strategies to mitigate current risks in soft drinks industry
In order to improve and mitigate current risks in soft drinks industry, the Coca-Cola Company needs to implement effective strategies which can bring them success in a worldwide marketplace. In order to improve health and wellness threats of Coca-Cola beverages, the company needs to implement such healthy foods into their menu.
That can support to health-conscious matter and can attract to such consumers as well. Many surveys have revealed that more than 35% of people are health-conscious at this recent time. Due to this reason, Coca-Cola needs o to prevent such health conditions by implementing healthy foods. Therefore, in order to take the market position solely, Coca-Cola Company needs to focus on innovating new products.
They need to implement a diver of product lines in terms of introducing a new product in marketplace. That basically increases the profit of the company and allows them to grow; therefore, it can lead to Coca-Cola Company in value creation (Coacher et al., 2017, 9.564).
Therefore, Coca-Cola company is most trusted brand for a longer period of time, at this time, this company is facing such regulate and safety issues regarding their beverages.in order to mitigate this issue, this company needs it implement such quality systems into their products.
As 1.3 billion of Coca-Cola products are used regularly throughout the world, this company needs to address such regulatory and food safety issues as early as possible. Coca-Cola has had a long competitive history from its original time. At this time Coca-Cola has place its soft drink market share about 42% in order to make this above 60% this company needs to implement more healthy foods and juice (Faradisty et al., 2019, p.153).
6. Critical analysis of organisational structure
Coca-Cola re-fabricated its geographical functioning segments and have provided a different naming to these aspects. Therefore, North America that used to include “The Minute Maid Company”, presently incorporates Puerto Rico from Europe, Latin America, and Eurasia transformed their names to Middle East, Europe and Eurasia.
Furthermore, Middle East and Africa, excluding reclassified segments of Middle East, transformed their naming to Africa. In 1923, during initial days of Coca-Cola, Fanta became a primary soft drink irrespective of Coca-Cola, which was marketed by this company. Moreover, in this year Coca-Cola company also expanded towards concentrates and fruit juices with acquisition of “The Minute Maid Company”.
This incorporates frozen drinks and citrus concentrates including Hi-C and “The Minute Maid Company” to its sprouting portfolio. Thus, in initial segment of 2001, “Asia Pacific” was renamed as Asia. Furthermore, in year 2002, Egypt was rechannelled from Eurasia, Middle East and Europe to Africa. Coca-Cola in 2004 rechannelled a specific segment of North American functioning segment to corporate functioning segment.
However, in 2007 Coca-Cola restructured its business in North America by generating three latest units for business for its beverages and sodas and have reflected its strategic emphasis (Arab, 2018, p.7). In 2005, Coca-Cola along with its supplementary “Coca-Cola Hellenic Bottling Company” settled in proceedings on its deal with “Multon Juice Company” of Russia.
Multon Company possessed local Nico, Dobry and Rich brands and has been a market convener in Russian vegetables and fruit category by possessing 22.9% volume of shares. Moreover, “Coca-Cola Hellenic Bottling Company” sells, distributes and produces non-alcoholic beverages and functions in overall ten regions.
Furthermore, Coca-Cola Ltd. provides marketing, advertising and research leadership and also quality assurance assistance to bottling plants. In 2007, this company acquired various brands of “Fuze Beverage” that involves Refresh, Vitalize, Slenderize lines and Tea at an unrevealed cost. Therefore, realignment and restructuring of Coca-Cola in current years have diminished due to massive dependency on carbonates.
7. Portraying organisational data facts and figures
Financial analysis can be done for Coca-Cola companies that can show the income and in-flow of money in the firm for last few decades. Financial ratios that have been derived from financial statements are used for appraising a company’s financial status in market.
Income statement of Coca-Cola
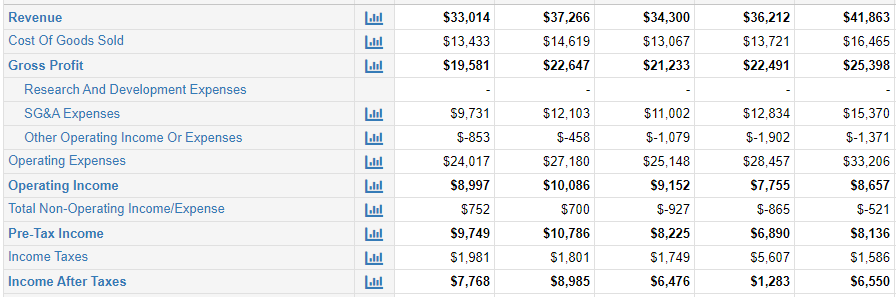
Figure 3: Income statement of Coca-Cola
(Source: Macrotrends.net, 2021)
The above income statement shows that the company tends to develop and aims at fostering growth for long-term. Coca-Cola has been successful to achieve a revenue amount of 33 billion US dollars in financial year 2020. Although it is a fact that this figure shows a decline from last year 2019. In 2019 their revenue was 37 billion US dollars thus it has depreciated by 11% than 2019.
However, they had been successful to achieve an 8% increase in revenue than 2017. This shortcoming of revenue is due to economic depression which is caused by spread of covid-19. Their mobility of business was limited for 2020 significantly.
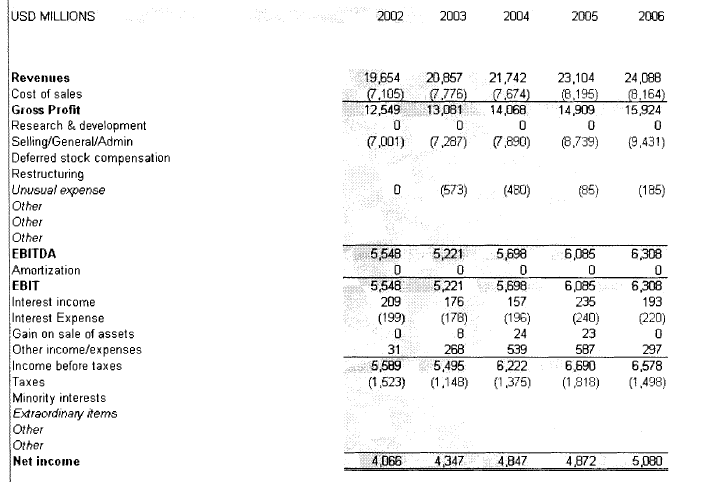
Figure 4: Income statement of Coca-Cola from 2002-2006
(Source: Tien, 2019)
The above figure shows Coca-Cola’s financial data from 2002 to 2006. This figure shows that in previous years this company fostered constant growth. They have been able to grow their revenue from $19 million to $24 million. It is also a notable fact that they had focussed to reduce their cost of production.
Through reducing this cost, they have been able to achieve a higher income or return on investment. Their cost of production slashed from 36% to 33% (Tien et al., 2019, p.57).
Discussion of balance-sheet
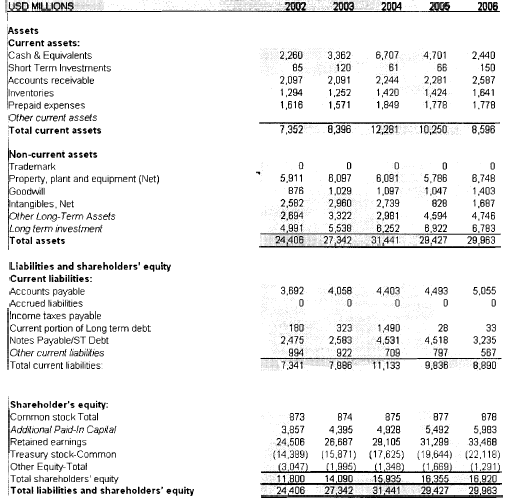
Figure 5: Balance sheet of Coca-Cola
(Source: Macrotrends.net, 2021)
The above figure shows the balance sheet of Coca-Cola Company in 2002-2006. This figure shows that the debt percentage decreased by 0.96 in last financial years, yet it is mentioned that this percentage is rightfully aligned with norms of soft-drinks industry.
It additionally shows that liquid assets that are available for Coca-Cola is not sufficient for deeming their short-term financial obligations. Yet, it is mentionable that the operating profits are more than sufficient. The long-term debt increased from $154 million to $1314 million in 2006. Yet their revenue status hoses that they have been sufficiently successful in growing their income.
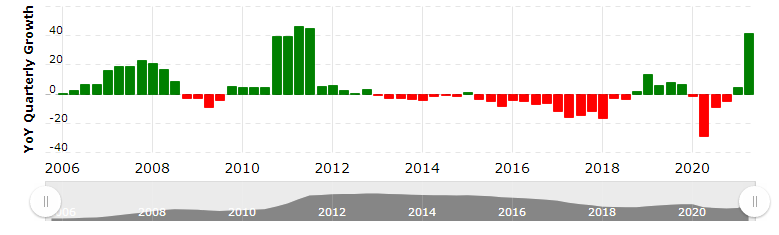
Figure 6: Revenue growth of coca-cola
(Source: Macrotrends.net, 2021)
8. Case study findings and analysis
Coca-Cola has long reigned supreme in the carbonated soft drink market. These two girls have created significant brand loyalty and made it very difficult for new rivals to enter the sector and take away market share by investing large sums of money on advertising and promotion.
Although new competitors attempted to expand on the market, both companies responded by lowering prices, causing new entrants to limit their expansion plans. Initially, the company concentrated on the cola section of the market (Goodluck, 2020, p.765). Cola signed an exclusive global agreement with Royal Crown (RC) Cola for its cola concentrate.
In the United States, RC Cola is a small player. RC Cola’s products were known for their exceptional quality, but they were never able to effectively compete with Coke. They entered into an agreement with Lablow, a Canadian supermarket retailer, to furnish the retailer with its own, exclusive brand of cola. The Loblaw private label brand, dubbed “President’s Choice,” was inexpensive, became highly popular, and snatched market share from both Coke.
Despite this attractive value offer, few merchants were prepared to sell private-label colas for fear of offending Coca-Cola and Pepsi, whose products were a key source of grocery store traffic. Cott’s breakthrough came when the company agreed to provide Wal-Mart with a private-label cola called “Sam’s Choice.”
Cott found WaLMart to be the ideal distribution channel. Wal-Mart was making inroads into the supermarket sector, and customers went there to seek inexpensive costs, not to buy branded goods (Chiu, 2019, p.9). Cott’s sales rose in tandem with Wal-supermarket Mart’s division. Cott quickly introduced other varieties to its menu, such as lemon-lime soda, which was a hit with customers as a competition to 7up and sprite.
In 2006, Coca-Cola increased its revenue by about 4%. In the same year, it surpassed the US$24 billion mark. Outside of the firm’s native US market, the company produced 73 percent of sales. Brand expansions and an ever-expanding distribution network have been the primary drivers of recent development. Coca-volume Cola’s growth has been hampered by a global standstill in carbonates (Serôdio, 2018, p.1594).
In 2006, volume increase in terms of cases was just 2%, and the important North American and European, Eurasia, and Middle Eastern markets remained flat. Some investors’ perceptions of the company’s future financial growth prospects have been influenced by the slowdown in carbonates.
In 2005, the Canadian soft drinks industry earned $6.1 billion in revenue, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.5 percent over the previous five years (2001-2005). During the same time period, market consumption volume grew by 0.5 percent, reaching 5402.7 million.
In 2005, litres were consumed. In 1972, Canadians consumed an average of 55.1 litres of soft drinks, and during the next three decades, consumption increased by an average of 2% each year. Increased availability of soft drinks, as well as the development of diet and flavoured soft drinks, fuelled this extraordinary rise. Canadians drank 107 litres of soft drink per year in 2005.
(Statistics Canada, 2007) (Serodio, 2020, p.2647). Carbonate’s sales were the most profitable for the Canadian soft drinks industry in 2005, earning $2.9 billion in revenue, or 47.8% of the market’s total value. Juice sales accounted for $1.25 billion in revenue, or 20.5 percent of the market’s total value. The market will reach a value of $7 billion by the end of 2010 if it continues to perform at current rate.
By the end of 2010, the market volume is expected to reach 5513 million litres. Even though Canada provides just 4.5 percent of the value of the American soft drinks industry, the US creates 79.4 percent of the market’s value. Concentrate producers, bottlers, retail outlets, and suppliers were all engaged in the manufacturing and distribution of soft drinks (Datamonitor, 2006).
Three economic metrics may be used to analyse the soft drink industry: market size, growth rate, and total profitability. The size of this industry’s market has changed throughout time. Non-alcoholic beverage consumption is dominated by soft drinks with a market share of 46,8 percent. According to Data monitor (2005), in 2004 the overall market value of soft drinks was $307.2 billion, with a market value estimate of $367.9 billion by 2009.
In addition, the number of soft drinks sold in 2004 was 325,367.2 million litres, according to Nielsen (Maani, 2019, p.74). Although the soft drink business is profitable and has significant profit potential, it faces several challenges in capturing market share. Recent criticism of the growth rate has been made owing to the saturation of the soft drink market.
Tea and coffee (11.8 percent) and bottled water (11.8 percent) are among the non-alcoholic beverage industries that are increasing (9.3 percent ). As rivals embrace new product lines, sports drinks and energy drinks are also projected to rise in popularity.
A differentiation strategy is used by Coca-Cola to compete in the global beverage industry and generate value for its customers and consumers. As Coca-mission Cola’s statement states: Aspirational Moments: To add value and make a difference through creating value. In order to maximise the potential of Trademark Coca-Cola and accelerate the expansion of key brands in each region, Coca-Cola will take advantage of rapid consumption possibilities to increase margins, customer recruitment and revenue.
Coffee, energy drinks, and sports drinks are all part of this profitable noncarbonated industry. Coca-Cola will first focus on tea, juice, soy, and improved hydration platforms when it enters this market (Wangwe, 2018, p.6544).
9. Suggested Solutions and Recommendations
- Coca-Cola Company needs to improve its distribution strategy which can ensure better supply chain management all over the world.
- In order to sustain in world market, Coca-Cola company have to ion improve their brand image, in such secretion they can use brands portfolio which helps in increasing drive system and frequency system.
- Coca-Cola Company has to focus on such an innovative strategy that can help them to bring relevant equipment or products to the world marketplace, therefore, they have to enhance their intelligence experimentation in order to introduce their brand in an effective way (Sing ram et al., 2020, p.2455).
- Coca-Cola Company needs to integrate with digital networks in order to advertise their products on a world platform; they have to create a value on digital strategy to reach out to more effective customers.
10. Conclusion
The Coca-Cola Company was unable to keep track of every rumour that circulated in every direction. It would be helpful if the official website of the Coca-Cola Company had a message board. There, members of the public may discuss their issues and provide solutions. The Coca-Cola Company, on the other hand, could demonstrate to the public its steps to deal with the situation. The public would then be aware of the facts and the eventual effects, rather than just being aware of the issues.
Reference List
Journals
Arab, N., 2018. Relationship between dimensions of Brand Equity and 4Ps of Marketing Mix-Place, Product, Promotion, & Price: Coca Cola-Consumer Based Qualitative Survey
Blackwood, R., 2020. Chestnut beer, Corsica-Cola, and wine bottles: The commodification of Corsican in the linguistic and semiotic landscapes of the island’s drinks industry. International Journal of the Sociology of Language, 2020(261), pp.103-118.
Chiu, H., Fischer, D. and Friedman, H., 2019. Board Diversity in Audit and Finance Committees: A Case Study of Coca-Cola. In Diversity within Diversity Management. Emerald Publishing Limited.
Colchero, M.A., Rivera-Dommarco, J., Popkin, B.M. and Ng, S.W., 2017. In Mexico, evidence of sustained consumer response two years after implementing a sugar-sweetened beverage tax. Health Affairs, 36(3), pp.564-571.
Demartini, M., Pinna, C., Aliakbarian, B., Tonelli, F. and Terzi, S., 2018. Soft drink supply chain sustainability: A case based approach to identify and explain best practices and key performance indicators. Sustainability, 10(10), p.3540.
Faradisty, A., Hariyani, E. and Wiguna, M., 2019. The effect of corporate social responsibility, profitability, independent commissioners, sales growth and capital intensity on tax avoidance. Journal of Contemporary Accounting, 1(3), pp.153-160.
Goodluck, S., 2020. The Impact of Automation on Employment in Manufacturing Industry: a case of Coca Cola company in Tanzania (Doctoral dissertation, Mzumbe University).
Jones, P. and Comfort, D., 2018. The Coca Cola Brand and Sustainability. Indonesian Journal of Applied Business and Economic Research, 1(1), pp.34-46.
Le, A., Jiang, J., Sandor, M., Stashick, M. and Zhang, L., 2017. Business Ethics: The Coca-Cola Company. Simon Fraser University Undergraduate Journal of Philosophy, 1(1), pp.35-45.
Logan, W., 2020. Economic Creativity and Business Wealth in United States and United Kingdom. Journal of Economics, 4(1), pp.21-30.
Maani Hessari, N., Ruskin, G., McKEE, M.A.R.T.I.N. and Stuckler, D., 2019. Public meets private: conversations between Coca‐Cola and the CDC. The Milbank Quarterly, 97(1), pp.74-90.
Mansour, N., Ceschin, F., Harrison, D. and Long, Y., 2019. Mapping & classifying business models to replace single-use packaging in the food & beverage industry: A strategic design tool.
Opait, G., 2020. The Coca-Cola and Pepsi-Cola Businesses,„Fizzy Meeting” in the Management of the Pole Position. Economics and Applied Informatics, (1), pp.167-176.
Serodio, P., Ruskin, G., McKee, M. and Stuckler, D., 2020. Evaluating Coca-Cola’s attempts to influence public health ‘in their own words’: analysis of Coca-Cola emails with public health academics leading the Global Energy Balance Network. Public health nutrition, 23(14), pp.2647-2653.
Serôdio, P.M., McKee, M. and Stuckler, D., 2018. Coca-Cola–a model of transparency in research partnerships? A network analysis of Coca-Cola’s research funding (2008–2016). Public health nutrition, 21(9), pp.1594-1607.
Singaram, R., Ramasubramani, A., Mehta, A. and Arora, P., Coca Cola, 2020: A study on the marketing strategies for millenniums focusing on India. IJARD, ISSN, pp.2455-4030.
Tien, N.H., Vu, N.T. and Tien, N.V., 2019. The role of brand and brand management in creating business value case of coca-cola Vietnam. International Journal of Research in Marketing Management and Sales, pp.57-57.
Wangwe, N.C., 2018. The Effect of Brand Equity on Consumer Purchasing Intention in Fast Moving Consumer Goods: A Case Study of Coca Cola Kenya (Doctoral dissertation, United States International University-Africa).
Websites
Coca-colacompany.com, 2021, 2020 Business & Environmental, Social And Governance Report, Viewed on 21/07/2021 from <https://www.coca-colacompany.com/reports/business-environmental-social-governance-report-2020>
Coca-colacompany.com, 2021, About Coca-Cola Company, Viewed on 09/04/2021 from <https://www.coca-colacompany.com/>
Coca-colacompany.com, 2021, Future Growth Strategy Of Coca-Cola Company, Viewed on 15/01/2021 from <https://investors.coca-colacompany.com/strategy/growth-strategy>
Harbert.auburn.edu, 2021, Organisation Culture Of Coca-Cola Company, Viewed on 05/01/2021 from <https://harbert.auburn.edu/binaries/documents/center-for-ethical-organizational-cultures/cases/coca-cola.pdf>
Macrotrends.net, 2021, Market Revenue Of Coca-Cola Company, Viewed on 12/02/2021 from <https://www.macrotrends.net/stocks/charts/KO/cocacola/revenue>
Statista.com, 2021, Net Operating Revenues Of The Coca-Cola Company, Viewed on 05/02/2021 from <https://www.statista.com/statistics/233371/net-operating-revenues-of-the-coca-cola-company-worldwide/>
Investors.coca-colacompany.com, 2021, STRATEGY, Viewed on 21/07/2021<https://investors.coca-colacompany.com/strategy>
Businessinsider.in, 2021, 7 Brilliant Strategies Coca-Cola Used To Become One Of The World’s Most Recognizable Brands, Viewed on 21/07/2021<https://www.businessinsider.in/strategy/7-brilliant-strategies-coca-cola-used-to-become-one-of-the-worlds-most-recognizable-brands/articleshow/47649874.cms>
Coca-cola.co.uk, 2021, COMMUNITY, Viewed on 21/07/2021 <https://www.coca-cola.co.uk/community>
Coca-cola.co.uk, 2021, INGREDIENTS, Viewed on 21/07/2021 <https://www.coca-cola.co.uk/ingredients>
Coca-cola.co.uk, 2021, MARKETING, Viewed on 21/07/2021 <https://www.coca-cola.co.uk/marketing>
Coca-cola.co.uk, 2021, OUR BRANDS, Viewed on 21/07/2021 <https://www.coca-cola.co.uk/brands>
Coca-cola.co.uk, 2021, SUSTAINABILITY, Viewed on 21/07/2021 <https://www.coca-cola.co.uk/sustainability>
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

