Assignment Sample on Business project
Introduction
A business project is a sort of work that involves planning all of the activities, equipment, and labour required to accomplish the goals. The purpose of business project in an organisation is to efficiently complete the goals of the organization by allocating all available resources, including personnel, time, and planning ahead (Frederico, 2021). There are variety of challenges with every firm faces which may be internal and external. All the challenges need to be analysed by the firm effectively for making strategies and ways to remain competitive
in the worldwide market and to earn more revenue in future (Yazici, 2020).
This report includes various challenges which TESCO is currently facing in the international market. TESCO facing one of the biggest challenges which is intense competition which are currently existing in the external environment due to covid-19 or availability of cheap substitutes. The organisation also has trouble managing its supply chain as a result of weather-related destruction, transportation issues, and supply reliability. Increase in carbon
emissions which are produced during the production processes and other harmful chemicals used in the production or a huge amount of waste generation in the factories results in sustainable issues which are being faced by this firm recently.
This report will include all the current challenges and the problems which the organisation is facing. Furthermore, all the internal and external stakeholders are being identified with the level impact they have in the company. The current challenges will be evaluated and analysed deeply with the help of theories and models. Lastly, recommendations are being made for solving these current challenges in the company Tesco.
Challenges and problems
Brief overview
Tesco is a large, internationally recognized supermarket store with headquarters in Welwyn Garden City, England. In the year 2021, there are 4673 locations. There are 354744 employees currently working from various different regions. Tesco has expanded into industries including the selling of books, electronics, furniture, toys, apparel, and other goods (Catalão, 2022). In the year 2021 the firm is facing various challenges which high competition, sustainable issues, bad employees relation especially due to Covid-19.
Challenges and pro
blemsTESCO is currently facing a number of issues or challenges which are reducing its efficiency and revenue in the worldwide market. The key issues Tesco is facing in recent years are as
follows:

Figure 1 : Competitors of TESCO
(Source: Brignall, 2018)
High competition
Tesco is facing intense competition from other retail companies as well as from online retailers like Amazon. Increasing technology and innovation as result in creation of huge number of substitute products in the worldwide market and have decreased the demand for its product (Han et. al. 2022). The company must lower its pricing in order to remain competitive in the marketplace, which raises a new problem. By doing so, the company reduces its total margin or profit while also raising its manufacturing costs. TESCO is facing the problem of a complete monopoly in the market using a huge number of retail stores selling the same products at the same prices (Chen, 2022). Due to Covid-19, there is an intense shift from offline to online shopping which has also doubled the competition for
Tesco because customers have a wide range of options available online to buy the same products.
Supply chain management
The other difficulty this firm is now dealing with is that it depends on a complicated worldwide supply chain to get its products to market, and that supply chain is affected by problems with weather, transportation, and supply reliability. Due to the impact of Covid-19 .the cost of transportation and suppliers has increased, which has led to an unstable economic climate. Sustainability
The usage of non-renewable energy sources, significant food waste, and carbon emissions
generated during production procedures are the other current issues this firm is dealing with.
Numerous goods rely on the usage of dangerous chemicals, and switching to renewable
energy sources is quite expensive. Some of its branches are breaking the sustainability
requirement by creating a significant quantity of food waste (Kollias et. al. 2022). The issue
of corporate social responsibility, which must be adhered to in order to achieve long-term and
sustainable goals, is one that this organization is now dealing with.
Employees relations
This firms or many of its areas or factories are not following the policy of the Rights of the
employee protection act (Utama et. al. 2122). Some of its industries are not following a
healthy work culture environment and the labours are suffering from poor working conditions
and are paid less which is against the rule of corporate social responsibility (Dugan, 2022).
The employees are not getting fair pay and treatment in some of its industries.
All these challenges are current and will have to be reduced for overall long-term growth
high competition will lead to decrease in the profits of the firm, inefficiency in supply chain
will increase the cost or expenses of the firm, harming of the environment will lead to
decrease in the satisfaction of the customers or society for achieving long term goals and the
problem of unfair practices followed within the firm will lead to decrease in productivity and
performances which has to be reduced for increasing future competitive advantages.
Purpose
The purpose of this report is to reduce all the current challenges which the TESCO is facing
such as the high competition problem with has to be reduce for increasing the competitive
advantage of the firm to earn more profit, supply chain management issues by creating a
strong supply chain management and creating a good relationship with the suppliers for
reducing the overall cost increasing the overall profit. The main purpose of TESCO needs to
reduce sustainability issues by using renewable sources of energy and increasing its employee
relations by following fair remuneration and other policies. All these problems are evaluated and analysed and various strategies and models will be used for solving all these current
challenges in this report.
Questions for evaluating the report
These are the questions that help in evaluating the current report.
What are the challenges and problems which are currently impacting TESCO?
How will these problems be addressed and ways in which TESCO can increase its
competitive advantage in the worldwide market?
Impact of Research on Stakeholders
Stakeholders are those who are interested in, have a stake in, or are interested in the firm’s
decision-making process based on their ownership interest in the company. They are the
primary individuals in charge of making various decisions that would aid in the expansion of
the business (Serravalle et. al. 2019). The present difficulties this firm, TESCO, is
experiencing have an influence on a number of internal and external stakeholders. All these
stakeholders are being analysed and their needs and interest have to be evaluated, the
stakeholder of TESCO is as follows:
Internal stakeholders
Shareholders: They are the key person or important shareholders of Tesco and bear
or all the losses faced by the firm in which the major shareholders are Norges Bank,
BlackRock, Inc., Fidelity International, and Schroders plc (Merrill, 2019). Current
issues faced by the company will automatically leads to decrease in their profits and
returns.
Employees: The employees who are the internal stakeholder responsible for
developing companies’ products and their satisfaction and needs must be fulfilled by
the company because they have a huge interest in the company’s affairs (Sangwa,
2021). They are the manager, executive, and lower-level staff and the challenges of
low wages and poor working condition is impacting employees and will lead to high
absenteeism and turnover.
External stakeholders
Competitors: Tesco is facing a huge competition form the companies like
Sainsbury’s, Morrisons, ASDA, Aldi. They are the main competitors and giving tough competition to the company due same products with similar prices being produced by
them (M RAHMAN, 2019).
Consumers: The main stakeholder is the customers who are using and buying Tesco
products and services (Lehtinen, 2020). Every week, Tesco satisfies the requirements
of millions of customers, who also serve as the company’s primary revenue source
since meeting their needs is essential to maintaining Tesco’s competitive edge and
fostering the long-term expansion of the business. owing to the same items being sold
for less money owing to increasing competition, the firm is losing consumers, and
customer satisfaction is declining as a result of recent sustainability problems.
Government: Tesco is required to abide by a number of laws and rules in the nation
or country where it conducts business. The business must adhere scrupulously to all
laws and norms, including those governing taxes, export and import restrictions, and
monetary policies that have an impact on Tesco’s external environment.
Suppliers: The suppliers who are supplying different types of raw materials to this company. Tesco has a huge number of suppliers and producers in the worldwide
market with reasonable prices but the current issues of supply chain management faced by this firm create difficulty for the company to satisfy every stakeholder.
Local communities: Tesco operates in many local communities and has a great
impact on their economies and social fabric. Local communities are the society or group of people in a common location and their needs have to be satisfied otherwise they may come out in protest.
NGOs and advocacy groups: These groups have a stake in Tesco’s operations mainly in areas regarding issues which are sustainability, fair trade, and animal welfare. This company’s sustainability issues and use of chemicals in their products created
difficulty in satisfying this stakeholder.
Stakeholder mapping matrix
Stakeholder matrix helps in or used as a tool in management of project for knowing the importance of each stakeholder and deciding the best strategy. Each internal and external stakeholder is affected due to these current challenges depending upon the level of power and interest they have in the company.
High power and high interest
Customers
High power and low interest
Government
Employees
Shareholders
Low power and low interest
Competitors
Local community
Low power and high interest
Suppliers
NGO
Tesco has to take care of the interest of stakeholder in first quadrant due to they have high influence and interest within the organisation. The company also need to follow and provide all the details to the Government whereas the other two quadrant need less attention but these stakeholders are provided with enough information to make them feel involved and satisfied. Evaluation and analysis of secondary data
The primary goal of this research is to examine and assess the present difficulties or issues that Tesco is experiencing, as well as all the current Tesco circumstances that may have an effect on the company’s future operations, particularly its competitive advantage. Tesco’s internal strengths, possibilities, and problems for addressing all of the present challenges are discussed and analysed in the secondary data.
SWOT analysis
Swot analysis helps to identify all the internal strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats which the company has (Teoli et. al. 2019). This helps in preparing strategies for the future for increasing the competitive advantage of the firm. Tesco is a British international firm that has various internal threats and opportunities which are discussed as follows:
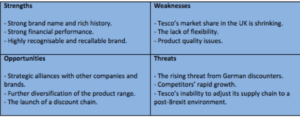
Figure 2 : SWOT analysis of Tesco
(Source: Tesco SWOT Analysis, 2019)
Strength
Tesco has a big advantage and it is the most recognised &
trusted retail brand in the UK and in the worldwide market (Rosnizam et. al. 2020).
After Covid-19 Tesco has established successful online
platforms for increasing its competitive advantage in the digital world.
TESCO is providing wide range of products and
services which includes grocery, electronics, clothing, financial services and more
with high-quality products and services.
The organisation has 6800 stores and millions of customers spread worldwide and the company has a large loyal customer base.
Weaknesses
Tesco has recently been dealing with a number of issues, which is weakening its
organisational structure. Tesco’s reliance on the UK market is limiting the development of its income. Tesco has received a lot of criticism in recent years because of its suppliers’ and workers’ unethical behaviour. In recent years, this company’s earnings decreased as a result of rising competition, shifting consumer tastes and preferences, and sustainability concerns.
Opportunities
This firm has the chance to eliminate all of its weaknesses and existing difficulties, and it has the ability to grow into new markets, especially in Asia and Africa. This business has the ability to attract new clients through its online offerings. Offering a wider range of goods and services will open up new options for this business (Jelassi et. al. 2020). Lastly, this business is a result of increased environmental concerns and the desire for sustainable products and practices. To boost its competitive edge, Tesco must create sustainable goods using sustainable practices.
Threats
The major threat to this company’s ability to increase sales in the fierce competition it faces from other shops and other online retailers like Amazon. Customer spending is decreased by economic uncertainty, particularly in the UK as a result of COVID-19. Tesco’s sales and profitability are impacted by shifting customer behaviours, such as a preference for online shopping and a need for sustainable products. Tesco’s operations are impacted by a number of government political and regulatory policies, including employment laws and environmental
rules.
It has been evaluated with the above data, Tesco can reduce all of its existing obstacles and increase its competitive advantage by using SWOT analysis to identify all of its strengths, opportunities, threats, and weaknesses. Tesco can then use these insights to replace all of its flaws and threats with strengths and take advantage of all of its opportunities. Tesco needs to seize every opportunity, such as expanding its online selection in order to draw in more people, product diversification, market development, producing more sustainably sourced goods and services in order to lessen the problem of sustainability and intense competition.
Value chain framework
An excellent framework for analysing all internal processes, including primary and
downstream business activities, is value chain analysis (Kano et. al. 2020). By dividing all of Tesco’s activities into main and secondary activities, and then identifying and studying each activity to find areas where value can be created or costs can be decreased, is a great technique for analysing all of the internal challenges Tesco is experiencing.
Primary activities in Tesco’s value chain
Inbound logistics: In Tesco’s inbound process, products are sourced from suppliers and managed throughout the shipping process to the shops. Tesco tracks and project future product demand using data analytics (Monte, 2021). Tesco has a number of distribution centres and warehouses in the UK that manage the supply chain and keep products that are received from suppliers before they are dispersed to customers.
Some of the challenges
Challenges: Tesco faces in this area include managing supplier relationships due to Covid-19 the cost of suppliers has increased and the cost of transportation has
increased which is also another challenge in its supply chain management.
Outbound logistics: Transporting items from warehouses or stores to clients is a part of outbound logistics. Tesco offers home delivery services in addition to its online buying and delivery platforms (Krishnan et. al. 2023).
Challenges:
Tesco is dealing with issues including managing delivery schedules,
maintaining product quality throughout transportation, and dealing with the issue of lowering delivery costs in order to increase revenues.
Operations:
Tesco has over 4600 stores and operates all over the world. It offers a range of physical shop types, including metro, express, and extra. Some of its stores are open every day of the week, 24 hours a day. Tesco operations also encompass a variety of tasks, such as managing inventories, displaying products, and managing stores and their inventory.
Challenges:
Assuring product quality and availability, controlling inventory levels
across all shops, and upholding a consistent customer experience are the problems this organisation has in this sector.
Marketing and sales:
Company Tesco employ a wide range of conventional and
digital marketing tactics, as well as data analytics, to entice consumers and establish trusting bonds with them. In 2020, it will have made significant advertising
investments in the UK.
Challenges:
Several of its prior advertisements drew criticism for providing
inaccurate and deceptive information. Other difficulties that this business is dealing with include client preference changes, competition from other merchants, and the expense of advertising initiatives.
Service:
Tesco offers a range of services, including after-sales support through
managing returns, exchanges, and consumer complaints. By assisting consumers in finding items or addressing their issues, the business also offers assistance to its clients. Secondary activities in Tesco’s value chain
Procurement: The procurement department at Tesco is responsible for finding the correct suppliers who are willing to supply at the lowest rates, as well as suppliers that can assist save costs and add value to the items by offering various packaging options.
Challenges:
After COVID-19, the supplier’s demand grew, and the firm is currently
having trouble managing supplier relationships as a result of pricing negotiations and
keeping low costs with the suppliers.
Technology: Self-checkout devices are only one of the many technologies Tesco
utilises. The retailer also uses data analytics to examine or predict consumer demand
(Alexander, 2020). The Tesco shop in London was the first cashless establishment,
and it is now equipped with cameras and other technology to operate as an
autonomous supermarket and boost its competitiveness.
Challenges: The expense of technology investment, the loss or security of consumer
data, and fast technological development are the areas or issues the organization is
experiencing.
Human Resources:
Tesco employs almost 360 000 people and provides flexible
employment opportunities as well as a variety of programmes and support services for its staff (Mohanty, 2022).
Challenges: Due to poor working conditions in certain of its stores and a rise in
employee turnover brought on by the payment of fewer benefits and compensations, this firm is now experiencing difficulties with employee relations.
Infrastructure: Tesco’s infrastructure consists of planning, financing, general administration. Tesco is listed on the London Stock Exchange so that it may sell its shares and raise money to run its business. It also manages all of its tangible assets, including its shops, cars, and storage facilities.
Challenges: Some of the difficulties it has in this area are the expense of sustaining these assets and the environmental effects of its activities, which are causing problems with sustainability.
It has been evaluated that relationships with international suppliers can be formed in order to negotiate prices, and that all delivery cost issues can be resolved by implementing new technology within the company in order to improve product quality and effectively manage all inventory levels. Tesco uses aggressive advertising and promotion strategies to assist
address the marketing and sales issues. In order to increase product quality and efficiently manage all inventory levels, it has been found that partnerships with foreign suppliers may be built in order to negotiate prices. Additionally, all delivery cost difficulties can be fixed by deploying new technology inside the business. Tesco employs strong marketing and sales
methods to help deal with the problems (Ajibola, 2020).
Porter’s five forces analysis
The five components of Porter’s five forces analysis are used to determine the company’s
competitive advantage. This model aids in determining the business environment in light of
external factors that impact the competitive advantage of the organization (Juliana et. al.
2019). Tesco’s present difficulty is dealing with fierce competition, and this tool helps to
analyze the elements that are impacting it. There are various factors which affect its comparative advantage which are as follows.
Threat of new entrant:
Tesco does not face a significant threat from new competitors since doing business in this sector demands a significant commitment of time, money, and resources, making it impossible for a startup to compete with an established market leader like (Tesco Moura, 2021). Entry into the retail sector is difficult due to factors including brand awareness, scale economies, and distribution channel access. Tesco has no need to worry about being threatened by new competitors and can improve its competitive edge because these new enterprises are not a threat.
Threats of substitutes:
For Tesco, the threat of alternatives is moderate. The products sold by Tesco, such as groceries, petrol, clothing and electronics, have a large number of substitutes because a variety of retail industries produce the same goods and sell them at the same prices everywhere, posing a threat to Tesco’s ability to increase its profits and competitive advantage. Customers find it challenging to switch to alternative merchants due to Tesco’s wide range of products and strong or well-known brand (Monte, 2021).
Challenge:
Contrarily, Tesco is presently under intense competition from rivals like
Aldi, Sainsbury’s, and Amazon who provide the same goods at comparable costs and with comparable features, posing a threat of product substitution.
Bargaining power of customers: Another factor that existed prior to COVID-19 is the bargaining power of the consumer, which is low in Tesco’s case because it offers customers products for basic needs that maximize economies of scale and have prices that hardly vary between retail establishments (Zhang, 2020). Today’s increased competition and number of rivals in the retail sector
gives consumers more negotiating leverage because they have more options and canquickly move to a different shop if they are dissatisfied with Tesco’s costs or selection. Due to a rise in consumer bargaining power, this is causing the current difficulty of intense competition for this business.
Bargaining power of suppliers:
Tesco has little negotiating leverage with suppliers since
there are so many different producers and suppliers to choose from, and switching suppliers is not a difficult process for retail outlets like Tesco (Yawson, 2022).
Challenge:
Following Covid-19 and the current difficulty organisation is having
managing its supply chain, there has been a rise in the prices suppliers charge to
supply goods due to an increase in the cost of raw materials, which has made it more difficult for Tesco to negotiate prices and boost its profits in order to gain a longer- term competitive advantage.
Competitive rivalry: Due to fierce competition from several retail businesses including Sainsbury’s, Walmart, ASDA, Aldi. Tesco is under tremendous competition. providing fierce competition because they have developed robust logistical and supply systems, and they provide almost identical goods at nearly the same costs (Seong-Young, 2019).
Challenge:
Tesco faces stiff competition from these businesses in order to generate
high income since they all employ aggressive marketing and advertising campaigns or
cutting-edge technologies to improve their operations and competitive advantage.
It has been evaluated from the competitive analysis of Tesco that it has no need to worry about the new entrance in the market due to difficulty in the entry of this sector but on the other hand TESCO faces challenges like threats of substitution in which Tesco need to
produce product in a way so that it has less substitutes available in the market. Consumers’ negotiating power may be a hurdle for businesses, so they need to invest more in advertising and concentrate on diversifying their product lines to draw in more consumers. Creating partnerships with overseas suppliers will aid in lowering suppliers’ negotiating strength.
Recommendation and conclusion
Recommendations
From the above study, it has been analysed the current issues faced by the company Tesco.
This firm is facing various challenges and problems which are high competition,
sustainability issues, supply chain management problems, and employee relations problems.
models or theories with deep details and information helps in finding all the pros and cons of the problems, areas which are lacking such as all the primary and secondary activity information and competition in the external market. This information helps in identifying the key issues which are causing this problem. Tesco mainly faces the issue of high competition due to increasing technology and various online retailers are giving it tough competition. TESCO due to the increasing cost of
transportation, raw materials, and supplier’s costs has created supply chain management issues. Some of its stores are not providing fair wages and treatment to its employees and the use of non-renewable sources causes sustainability challenges. There are various recommendations through which this company can reduce all these current challenges such
as:
Improving working conditions of employees
Tesco must adhere to fair pay practises and foster a healthy work environment for its employees in order to maintain its competitiveness in the outside market. To do this, it must adopt a diversity and inclusion policy that values the participation of all groups of individuals from all cultural backgrounds (He et. al. 2019). The company must provide various compensation and other benefits by following the theory of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs in which all the basic to higher-level needs are satisfied based on employees’ performances
(Kang, 2019). This will help in creating a positive working relationship and improve the
employee’s relation to work hard and increase productivity.
Diversification and product development
The company Tesco to remain competitive in the outside market need to diversify its operation into different areas with new or existing products in the new market to attract a huge number of customers (Abdullaeva et. al. 2021). To remain competitive TESCO needs to develop its products by reducing its overall cost with the help of advanced technology and innovation. The competition which this company is facing can also be reduced by various marketing efforts such as more advertisements on social platforms and giving more emphasis
on online product offerings (Rosnizam et. al. 2020). Internationalization or tapping into a new market will also increase its revenue.
Adoption of advanced technology Tesco can enhance its supply chain management by implementing various technologies like
blockchain, automation, and artificial intelligence (AI), which will automatically help in lowering the cost of transportation and improving the efficiency of its supply chain operation (Zolas et. al. 2021). It will also help in forecasting demand and effectively securing all customer data, which helps in reducing all waste. This technology will also strengthen relationships with suppliers since it enables tight cooperation with all of the company’s global
suppliers, enhancing communication, teamwork, and risk management (Santoso et. al. 2022). Tripple bottom line approach
Tesco should use a triple bottom line approach for reducing the issue organisation facing currently. This approach focuses on the Three P’s which are people, planet and profit. Tesco should earn high profits by protecting the planet or environment and people with its sustainable production and manufacturing processes (Zia et. al. 2019). The company has to fulfil all the social responsibility to protect society by using renewable sources and methods for producing the products. The company should use eco-friendly practices and methods such
as reducing the wastage of food and reducing carbon emissions. The demand for sustainable products has increased after covid-19 which Tesco needs to fulfil. This company can also collaborate with stakeholders, NGOs and Government agencies for promoting sustainability.
Situational leadership
The effectiveness and productivity of the worker are determined by their performance. Tesco has to establish a strong leadership style in order to meet the needs and wants of its employees and promote an effective workplace culture owing to the unfavourable working conditions and bad employee relations in certain of its stores (Daniëls et. al. 2019). Through continuous feedback from the leaders to the workforce and the inclusion of them in different
decision-making processes, situational leadership will assist the company in empowering its people and boosting their morale. With this leadership, all employees are treated fairly, and a competitive team is built to boost revenue and fulfil long-term objectives.
In general, COVID-19 has presented Tesco with a number of difficulties that must be overcome by the business in order to realize long-term objectives. To stay competitive with the outside world, the company must implement a variety of policies and strategies, including building a strong team, utilizing sustainable practises, maintaining proper connections with suppliers through a variety of technologies, diversifying its areas of
operation, and creating distinctive products and services for new markets in order to boost revenue.
Conclusion
From the above report, it has been concluded that Tesco has been experiencing various types of current challenges and problems mainly due to pandemics and the unstable economy in the UK market. The current issues faced by Tesco are high competition due to increase technology and innovation and a huge number of substituted products available in the worldwide market, supply chain management issues due to an unstable economic climate and Covid-19, an increase in the number of food wastage, carbon emission generated during its
production process is creating sustainability issues, low wages and poor working conditions are being followed in some of its stores.
Furthermore, this report helps in analysing all these problems and proving areas which need improvement with the help of various theories and models. SWOT analysis is used for knowing all the internal strength, weaknesses, opportunities and threats for dealing with the challenge, value chain analysis is used for analysing all the primary and secondary activities
and the activities which are lacking and needs improvement, the Porter 5 forces model has been used in this report for determining all the external factors which are decreasing Tesco’s competitive advantage.
Lastly, the recommendations are developed in order to enhance the working circumstances for employees by implementing different policies and leadership philosophies following an analysis of all the internal and external elements that are causing these issues. The triple bottom line strategy should be advised to assist reduce the sustainability difficulties encountered by Tesco. The use of innovation and technology aids in decreasing supply chain concerns and enhancing profitability
References
Abdullaeva, M.N., Masharipov, M.N. and Allamuratova, M.S., (2021). DIVERSIFICATION
OF PRODUCTION AS A CONDITION FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF INDUSTRIAL
ENTERPRISES. Экономика и социум, (2-1 (81)), pp.5-10.
Ajibola, E.B., (2022). An investigation into talent management in the Irish retail sector: a
case of Tesco, Aldi and Super Valu (Doctoral dissertation, Dublin, National College of
Ireland).
Alexander, I.N., (2020). The influence of technological innovations on organization’s
competitive advantage: Case study on Irish food retail company (Tesco) (Doctoral
dissertation, Dublin, National College of Ireland).
Brignall, M. (2018), Tesco ‘planning’ discount chain to take on Aldi and Lidl, [online]
Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/business/2018/feb/11/tesco-planning-discount-
chain-to-take-on-aldi-and-lidl
Catalão, I.D.P., (2022). Equity research: Tesco PLC (Doctoral dissertation, Instituto Superior
de Economia e Gestão).
Chen, J.J., (2022). Tesco Plc. In International Cases of Corporate Governance (pp. 27-44).
Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
Daniëls, E., Hondeghem, A. and Dochy, F., (2019). A review on leadership and leadership
development in educational settings. Educational research review, 27, pp.110-125.
Dugan, E. (2022), Workers in Thailand who made F&F jeans for Tesco ‘trapped in effective
forced labour’, [online] Available at:
https://www.theguardian.com/business/2022/dec/18/workers-in-thailand-who-made-ff-jeans-
for-tesco-trapped-in-effective-forced-labour.
Frederico, G.F., (2021). Project Management for Supply Chains 4.0: A conceptual framework
proposal based on PMBOK methodology. Operations Management Research, 14(3-4),
pp.434-450.
Han, Z., Wood, S., Coe, N.M. and Alexander, A., (2022). The shifting foundations of
territorial embeddedness in food retailing: recent insights from China. The International
Review of Retail, Distribution and Consumer Research, pp.1-24 He, Z., Shao, H., Zhang, X., Cheng, J. and Yang, Y., (2019). Improved deep transfer auto-
encoder for fault diagnosis of gearbox under variable working conditions with small training
samples. Ieee Access, 7, pp.115368-115377.
Jelassi, T., Martínez-López, F.J., Jelassi, T. and Martínez-López, F.J., (2020). Internal
Analysis: e-Business Competencies as Sources of Strengths and Weaknesses. Strategies for e-
Business: Concepts and Cases on Value Creation and Digital Business Transformation,
pp.97-124.
John Dudovskiy, (2016), Tesco value chain analysis, [online] Available at: https://research-
methodology.net/tesco-value-chain-analysis/
Juliana, J.P.E. and Nyoman, Y.N., (2019). Factors influencing competitiveness of small and
medium industry of Bali: Porter’s five forces analysis. Russian Journal of Agricultural and
Socio-Economic Sciences, 89(5), pp.45-54.
Kang, S.K. and Kaplan, S., (2019). Working toward gender diversity and inclusion in
medicine: myths and solutions. The Lancet, 393(10171), pp.579-586.
Kano, L., Tsang, E.W. and Yeung, H.W.C., (2020). Global value chains: A review of the
multi-disciplinary literature. Journal of international business studies, 51, pp.577-622.
Kollias, S., Ye, X., Yu, M., Duan, W., Leontidis, G., Swainson, M. and Pearson, S., (2022).
AI-enabled Safe and Efficient Food Supply Chain.
Krishnan, A., De Marchi, V. and Ponte, S., (2023). Environmental upgrading and
downgrading in global value chains: A framework for analysis. Economic Geography, 99(1),
pp.25-50.
Lehtinen, J. and Aaltonen, K., (2020). Organizing external stakeholder engagement in inter-
organizational projects: Opening the black box. International Journal of Project
Management, 38(2), pp.85-98.
M RAHMAN, (2019), Stakeholders of Tesco (An analysis of Tesco’s stakeholders), [online]
Available at: https://www.howandwhat.net/stakeholders-of-tesco-an-analysis-of-tescos- stakeholders/Merrill, G.J. and Merrill, G.J., (2019). How Sinful Is Your Shopping Basket? The Reporting
of Tesco in 2006, 2007 and 2008. The Political Content of British Economic, Business and Financial Journalism: A Deficit of Perspectives, pp.143-181.
Mohanty, J., (2022). Sustainable Marketing of Csr Through Employee Volunteering: The Tesco Experience. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 26(S2).
Monte, A., (2021). A study of value chain reconfiguration processes under Covid-19 pressures: the case of Tesco PLC in the United Kingdom.
Moura, M.B.L.D., (2021). Equity Research in Food & Retail Industry-TESCO PLC (Doctoral
dissertation, Instituto Superior de Economia e Gestão).
Richard S, (2020), Situational leadership model, [online] Available at:
Rosnizam, M.R.A.B., Kee, D.M.H., Akhir, M.E.H.B.M., Shahqira, M., Yusoff, M.A.H.B.M., Budiman, R.S. and Alajmi, A.M., (2020). Market opportunities and challenges: A case study of Tesco. Journal of the Community Development in Asia (JCDA), 3(2), pp.18-27. Sangwa, S., (2021). Research and Economics.
Santoso, R.W., Siagian, H., Tarigan, Z.J.H. and Jie, F., (2022). Assessing the benefit of adopting ERP technology and practicing green supply chain management toward operational
performance: An evidence from Indonesia. Sustainability, 14(9), p.4944.
Seong-Young, K., (2019). Competitive market embeddedness, diversity of the institutional
environment, and firm performance. Management international, 23, pp.183-196.
Serravalle, F., Ferraris, A., Vrontis, D., Thrassou, A. and Christofi, M., (2019). Augmented
reality in the tourism industry: A multi-stakeholder analysis of museums. Tourism
Management Perspectives, 32, p.100549.
Suleman (2019). Tesco PLC Expansion into Germany Using International Market Servicing
Strategy, [online] Available at: https://bohatala.com/tesco-plc-expansion-into-germany-using-
international-market-servicing-strategy/
Teoli, D., Sanvictores, T. and An, J., (2019). SWOT analysis.
Tesco SWOT Analysis, (2019). [online] Available at: https://15writers.com/sample-
reports/tesco-pestel-swot-porters-five-forces-value-chain/
24
Utama, A.G.S., Verma, M., Ng, J.Y., Kee, D.M.H., Nga, C.S., Izzati, N.N., Ng, Y.X. and
Khoiruwnia, F., (2022). A Research on Tesco’s Consumer Purchasing Behavior towards E-
Commerce during the Pandemic Period. International Journal of Accounting & Finance in
Asia Pasific (IJAFAP), 5(1), pp.53-63.
Vaidya, D. (2021), Triple Bottom Line (TBL) – Definition, Examples, Benefits, [online]
Available at: https://www.wallstreetmojo.com/triple-bottom-line/.
Yawson, D.E. and Yamoah, F.A., (2022). The TESCO Club Card Loyalty Programme: The
Gold Standard. In Contemporary Retail Marketing in Emerging Economies: The Case of
Ghana’s Supermarket Chains (pp. 77-87). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Yazici, H.J., (2020). An exploratory analysis of the project management and corporate
sustainability capabilities for organizational success. International journal of managing
projects in business.
Zhang, L. and Chung, D.J., (2020). Price bargaining and competition in online platforms: An
empirical analysis of the daily deal market. Marketing Science, 39(4), pp.687-706.
Zia, M.K., Pervaiz, S., Anwar, S. and Samad, W.A., (2019). Reviewing sustainability
interpretation of electrical discharge machining process using triple bottom line
approach. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green
Technology, 6, pp.931-945.
Zolas, N., Kroff, Z., Brynjolfsson, E., McElheran, K., Beede, D.N., Buffington, C.,
Goldschlag, N., Foster, L. and Dinlersoz, E., (2021). Advanced technologies adoption and
use by US firms: Evidence from the annual business survey (No. w28290). National Bureau
of Economic Research.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

