CA and SRI Assignment Sample
Introduction
Agriculture affects every individual on the earth. Agriculture is responsible for the food we eat, the coffee we drink, the ethanol that drives our vehicles, the grass seen on the golf course, and the plant fibres that make up our apparel. Agronomy is a technology that takes a comprehensive and complete perspective of agriculture. Consider the significance of agronomy in our everyday life. Agronomy is an agricultural subfield. It contains a comprehensive list of techniques for cereal plant growth. These plants include maize, wheat, sorghum, rice, pulse plants, and oilseeds. Due to the fact that cereal plants are the primary source of food for humans worldwide, agronomy is a study concerned with the process of plant growth and the essential circumstances for plant production. This exercise teaches agronomists how to use vitamins effectively to guarantee the crop’s development is optimal. Agronomists must have a comprehensive awareness of the soil’s features and their interaction with the growing crop. It takes into account the kind of fertilizer’s or vitamins required by a crop and the time of their administration. Additionally, agronomy describes the effects of environmental elements and meteorological conditions on the crop at different developmental phases. It displays a variety of key techniques for managing fungus, insects, weeds, and a variety of crop varieties.
Conservation agriculture
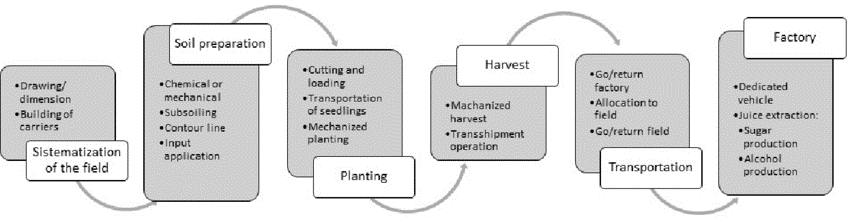
Due to the unfavorable and diversified external pressures of growth and climate change, conventional agriculture in rainy uplands has lost its productivity. A shift toward more sustainable cropping structures, such as conservation agriculture manufacturing structures, may assist maintain soil quality while increasing crop output and the farmer’s net financial benefit. Reduced tillage, intercropping, and cowl planting tactics developed specifically for maize-based completely made buildings were examined in highland Odisha, India, during a three-year period in these studies. The research examined crop output, device productivity, and profitability using a maize equal yield and dominance evaluation. The results indicated that maize grain production was not substantially different over time or between CAPS treatments, even when cowpea yield was included as an extra yield source in intercropping systems. This, in turn, must contribute to agricultural production’s long-term intensification in order to fulfil family income and food needs.
METHODS
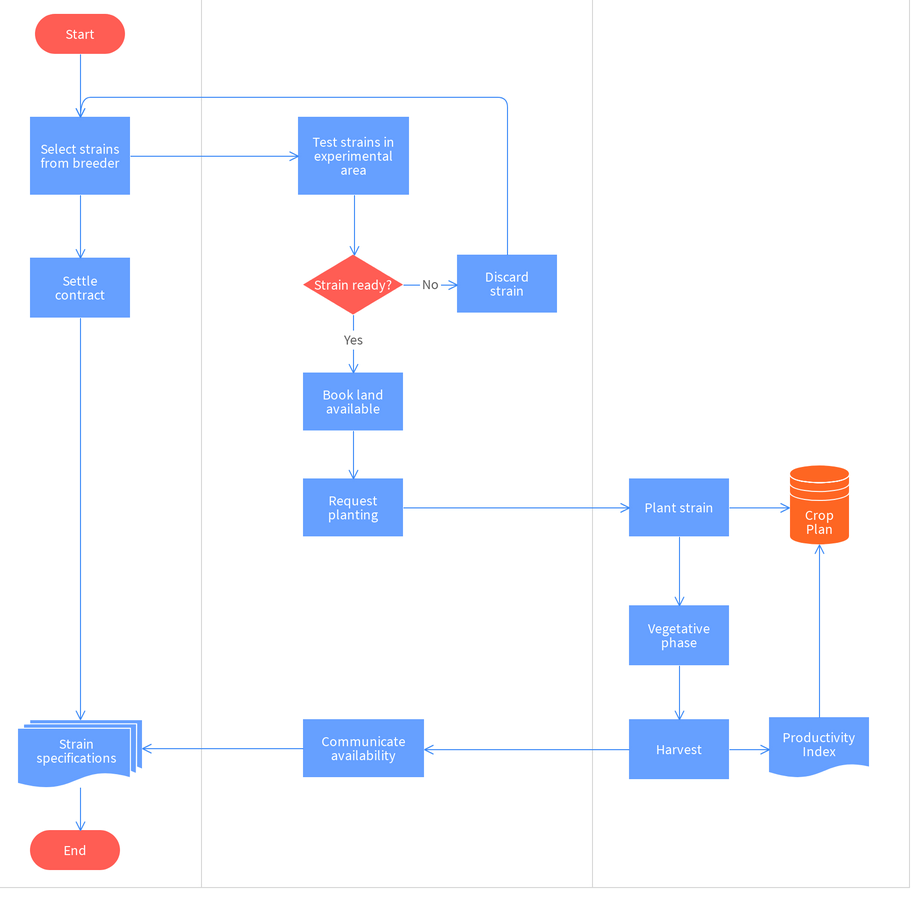
The soil of the examiner web website online is specially evolved from collegial of the examiner website online is maize at some point of the wet season (mid June–September) observed via way of means of mustard as a post-rain season crop during October to January (Devendran,2019).
Impact of Conservation Agriculture
Increases in human populations and the rising demanding situations of weather alternate suggest that the world`s agricultural structures will want to supply extra meals in an surroundings this is more and more variable and in which the best of our herbal aid base is declining. Farmers require to get admission to quite a number gear and sources to permit them to become aware of if the concepts of CA are in all likelihood to steer be suitable for his or her state of affairs and well-designed, domestically tailored structures to efficiently triumph over the agronomic, social and monetary demanding situations that may be related to its use. Crop diversification” is the exercise of cultivating multiple species in a given agricultural area, with the shape of crop rotation and association (Bandara,2019). The diversification in cultivated species will increase the variation ability of agricultural structures to weather alternate via way of means of enhancing soil fertility and structure, soil water preserving ability and water and vitamins distribution via the soil profile, supporting to save you pests and diseases, and growing yield stability. Indeed, the assorted cropping structures are extra solid and resilient than monoculture structures. Crop diversification promises quite a number surroundings services, contributes to enhance crop productiveness and resilience of farming structures and decreases GHG emissions from agricultural activities (Kaweesa,2019). “Permanent soil natural cowl” with crop residues and/or cowl vegetation (e.g. legumes, cereals, or different vegetation planted among the primary vegetation, usually for the gain of the soil in place of the crop yield) permits weather alternate variation via way of means of decreasing soil erosion and degradation which may be exacerbated via way of means of the effect of severe climate events (e.g. severe precipitations, droughts and intervals of soil saturation, severe heat, robust wind events) and enhancing the stableness of the conservation agriculture gadget. Indeed, cowl vegetation enhance soil homes (fertility and best), assist to control soil erosion, keep soil moisture, keep away from compaction of the soil, include pest and diseases (Perera,2019).
According to the International Water Management Institute, it was based on a project titled Groundwater Governance in the Indo-Gangetic and Yellow River Basins in Asia, which was primarily designed to build the capacity of senior and mid-career water managers in Asia, specifically in countries such as India, Nepal, Bangladesh, Pakistan, and China, according to the International Water Management Institute As a consequence of the initiative, researchers were able to get a more comprehensive knowledge of groundwater from a range of perspectives, including physical, socioeconomic, governance, and policy considerations. They were able to figure out how groundwater may be used in an economic and environmentally friendly way.
As a result of years of hard work, the Institute has been able to conduct a significant amount of activity in India, first as a non-resident mission and then as a resident mission. After many years of hard effort, the Institute was finally established as a resident mission in the year 2000. IWMI made a variety of information and ideas accessible, based on the expertise and experience gained throughout its many years of work in India, as well as material obtained from research performed in a number of countries across the globe, available. There were lessons learned from other nations such as China, Mexico, and Africa in addition to those learned from the United States that were incorporated in the study’s conclusions. It was on the basis of this knowledge and skill, which was gained via a range of activities, that IWMI was able to grow and develop throughout the years.
There have been a number of efforts to improve water management in agriculture in India over the course of several years, but a number of efforts funded by the CGIAR Challenge Program on Water and Food (CPWF) and the IWMI-TATA Water Policy Research Program have been particularly effective in this regard. CPWF and the IWMI-TATA Water Policy Research Program are two such initiatives.
As a direct consequence of this work, the issue of groundwater consumption in India has been raised to the forefront of the national conversation on irrigation policy as a result of this endeavour. As a result, it assisted decision-makers in taking into account the long-term viability of groundwater management, imitating strategies employed by more mature groundwater economies, and implementing certain effective groundwater management policies, among other things.
Advantages of Conservation Agriculture
Conservation agriculture is aimed to conserve, enhance and make extra green use of herbal sources through included control of soil water and organic sources blended with outside inputIn coordination with different recognized true practices conservation agriculture is a base for intensified sustainable agricultural manufacturing. The yield degrees of CA structures are similar with or even better than the ones below traditional extensive tillage structures, this means that that CA does now no longer because yield consequences and on the identical time, it complies with the usually ordinary thoughts of sustainability (Egresi,2021). As an end result of the elevated machine range and the stimulation of organic procedures with the soil and above the floor in addition to because of decreased erosion and leaching, the usage of chemical fertilizer and pesticides, which include herbicides, is decreased with the lengthy term. Ground water sources are replenished thru higher water infiltration and decreased floor runoff. (Gunarathne,2019). Labor necessities are usually decreased via way of means of approximately 50%, which lets in farmers to store on time, gasoline and equipment costs. Fuel financial savings below conservation agriculture has been mentioned via way of means of the track of sixty five percentages in general. The increased adoption and unfold of conservation agriculture technology mainly conservation-tillage and residue retention on soil floor in rice and wheat primarily based totally cropping machine is attributed to collection of capacity advantages (Wickramaarachchi,2019).
Challenges in conservation agriculture
Conservation agriculture as an upcoming paradigm for elevating vegetation would require a progressive machine attitude to address diverse, bendy and context unique wishes of technology and their control. Conservation agriculture Research and Development, for this reason will name for numerous progressive capabilities to deal with the challenge. Some of those are:
- Understanding the machine – Conservation agriculture structures are a whole lot extra complicated than traditional structures. Site unique know-how has been the principle hassle to unfold of CA machine. Managing those structures successfully could be fairly traumatic in phrases of information of fundamental techniques and thing interactions, which decide the complete machine performance. For example, floor maintained crop residues act as mulch and consequently lessen soil water losses via evaporation and keep a mild soil temperature regime. However, on the equal time crop residues provide an effortlessly decomposable supply of natural depend and will harbor unwanted populations or regulate the machine ecology in a few different manners. No-tillage structures will have an effect on intensity of penetration and distribution of the basis machine which, in turn, will have an effect on water and nutrient uptake and mineral cycling. Thus the want is to understand conservation agriculture as a machine and increase control techniques (Priyadarshani,2019).
- Site specificity – Adapting techniques for conservation agriculture structures could be fairly web page unique, but gaining knowledge of throughout the web sites could be a effective manner in information why positive technology or practices are powerful in a fixed of conditions and now no longer powerful in every other set. This gaining knowledge of technique will boost up constructing a know-how base for sustainable useful resource control (Madushani,2019).
Drawbacks from agronomic perspective
Soil fitness gets in particular robust interest in narratives surrounding Conservation Agriculture Indeed, the concept that soil, and soil lifestyles mainly, is beneath risk underpins most, if now no longer all, requires Conservation Agriculture. Nonetheless, the time period soil fitness is inherently problematic. Just like soil nice, soil fitness is a field concept, which calls for disaggregation to be significant. While it could be understood as something high quality to try for, underlying soil features want significant signs which may be measured and monitored over lengthy intervals of time. Moreover, agronomic practices which gain one element of soil fitness frequently have terrible results on different features consisting of nitrate leaching, number one manufacturing or GHG emissions, there’s generally now no longer one course in soil fitness, however a couple of trade-offs (Yuliani,2019).
(Source: Bandara,2018)
Many web sites and testimonials regarding Conservation Agriculture spotlight the significance of soil biodiversity, and mainly the macro- and micro-organisms which might be answerable for the organic biking of nutrients. Reports of declining soil biodiversity beneath in depth agriculture and the simplification of soil meals webs have caused huge alarm regarding soil fitness. For example, a latest document of an advisory frame to the Dutch authorities becomes entitled. While research simply screens variations in soil meals webs among cultivated fields, grasslands and herbal vegetation, the hyperlinks with soil characteristic are in large part mounted through correlation (Udeshani,2019).
Preconditions for smallholder farmers
There has been more and more fast adoption of CA structures at some stage in the beyond 20 years: there has been adoption of the structures previous to this, however adoption and advances have been slower than they had been in extra recent years. Statistics on regions of specific cultural practices are hard to attain and it’s miles probable that those figures masks very one of a kind machine practices, a number of which in reality may not classify as CA, including the ones regions wherein the land is tilled for one crop and the subsequent crop seeded with- out tillage. Most of the vicinity is on exceedingly big business farms the usage of heavy tractors and equipment, while exceedingly little is on smallholdings, specially the usage of guide or animal traction structures. There are, however, a few critical exceptions to this: in Brazil there is an expected 200,000 hectares of everlasting CA being practiced on There has been more and more fast adoption of CA structures at some stage in the beyond 20 years: there has been adoption of the structures previous to this, however adoption and advances have been slower than they had been in extra recent years. Locally built networks might also additionally guide the improvement and diffusion of CA know-how amongst smallholders. Networks also can offer get entry to assets for smallholder farmers considering the fact that a hit implementation of CA technology calls for farmers to growth the depth in their farming (Bandara,2019).
(Source: Bandara,2018)
System of Rice Intensification
Rice is the maximum critical crop worldwide. It is the staple meals for 50–60% of the worldwide populace and its call for maintain to grow. The records of agriculture are the records of intensification. Intensification follows success innovations. When this era is usually recommended for exercise with the farmers` fields, there might also additionally stand up a few holes among the scientists and farmers` effects. Especially in Bangladesh this hole has been discovered to be drastically high. In the SRI sub-challenge, to decrease this hole, farmers were added to the forefront. In this regard, resource-negative farmers had been focused for rice cultivation the use of SRI. The specific function of the sub-challenge is that the farmers, via organized farmers` area schools, are the implementers of the techniques beneath trial. The researchers` position is in particular that of facilitators in imparting them with the fundamental know-how on SRI techniques, tracking their area operations and control practices, and comparing the effects in their trials. It become innovation with the yields this is Green revolution with the mid sixties that catalyzed a change from the situations of meals scarcity to one in every of self-sufficiency and past making India with the process, a international chief with the wide variety of agricultural commodities.
(Source: Bandara,2018)
Methods
The System of Rice Intensification includes cultivating rice with as lots natural manure as possible, beginning with younger seedlings planted singly at wider spacing in a rectangular pattern; and with intermittent irrigation that continues the soil wet however now no longer inundated, and common inter cultivation with that actively As but no fashions had been evolved to offer a multidisciplinary expertise of rice manufacturing sustainability. To fill this hole we blended methodological processes from unique disciplines right into an unmarried version permitting the social, monetary and environmental metrics to be measured on the identical time. This lets in the identity of trade-offs and synergies among unique sustainability indicators. The version is primarily based totally on a streamlined Life Cycle Assessment and the International Reference Life Cycle Data System (ILCD) Handbook (European Commission, 2010). To this we fused Value Chain Analysis (VCA) and social measures.
The effect of growing SRI
Farmer poverty is regularly blamed on low farm gate prices. The minimal assist charge (MSP) has been in location for nearly 1/2 of a century, and is designed to offer help to farmers thru placing a ground to the rural marketplace charge post-harvest. The MSP is liable for more than a few unintentional results which includes growing an imbalance in deliver and call for of numerous vital products, for instance a shift from oils and pulses to wheat and rice and for many years its continuation has been debated. However, at gift it stays a vital mechanism for controlling the farm gate charge in lots of states. Table nine indicates that growing the farm-gate charge for rice with the aid of using 10% will increase the returns with the aid of using 38% and 15% for manage and SRI respectively. This is a dramatic growth for manage farmers, however from a decrease base. So interestingly, even as the farm gate charge is critical, its significance is marginal in comparison to the selection of rice cultivation methods.
Small holder farmers on SRI
Our farmers have valued indigenous knowledge about rice cultivation, which may be expanded to boost productivity and profitability, as well as contribute to a more sustainable rice manufacturing system. Rice specialists have developed cutting-edge technology for greatly improving rice yields; nevertheless, these technologies are strongly dependent on expensive cutting-edge inputs, as well as the use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides that have a negative impact on the soil and environment. Increased irrigation via the use of subterranean water will also have an adverse effect on the ecosystem. Typically, after verifying their study plots, professionals supply farmers with a new era. While it is often recommended to exercise in farmers’ fields during this time period, there may be some disparities between scientists’ and farmers’ results. This gap has been shown to be rather wide, especially in Bangladesh. Farmers were put to the forefront in order to address this deficit in the SRI sub-challenge. Through the adoption of SRI, resource-poor farmers were targeted for rice cultivation in this setting. The sub-challenge is unusual in that it requires farmers to execute the trial ideas via organised farmers’ local schools. The researchers serve mostly as facilitators, giving them with fundamental understanding of SRI methods, monitoring their area operations and control practises, and comparing the results of their studies. SRI was pioneered in Madagascar via direct farmer interaction.
Recommendations
However, taking into account the generation’s varied behaviours, especially in the context of sub-projects, the following suggestions may be made. Because they are based on a single manufacturing season, they are speculative estimations. Risks: The SRI approach may no longer be appropriate for widespread software deployment, since it needs adequate soil drainage and well-managed irrigation infrastructure to provide high-quality results. If soil development procedures such as the addition of natural organic matter and biomass and the selection of a suitable cropping sample are disregarded, SRI techniques will no longer provide the most efficient results. Weed control is another key aspect of a successful SRI farming operation. If weeding is not performed concurrently to control weeds and improve soil aeration, the SRI approach will not provide all of the advantages. Sustainability: The SRI method places a premium on accurate information regarding its standards and farmers’ ability to manage them properly. It requires farmers’ commitment and drive, as well as early monitoring by field-level extension specialists. Nongovernmental organisations (NGOs) may also play a critical role in extending SRI. Collaboration with non-governmental organisations is critical to the long-term viability of this unique form of rice cultivation. Scaling up: Large farmers that are more ready to take risks may be given with subsidies under the SRI agriculture programme, ultimately motivating smaller and poorer farmers. Additionally, substantial use of mass media is necessary to spread the SRI approach across the country.
Conclusions
Both CA and SRI have validated capacity to growth rice manufacturing and agriculture techniques at the quantity of adherence to its fundamental standards. More importantly, they goal to assist fit the environmental requirement of sustainable agriculture with the monetary desires of the farming community. I assume it’ll have a fantastic effect in maximum areas if this concept is time-honored and observed through. With the right control competencies that farmers are inclined to provide it a try. Even though the equipment producers may not be too enthusiastic promoters of CA, they sense much less system is needed and the want for tillage system might be reduced. A few different styles and fashions have emerged in current years, which give required avenue map for wider adoption.
References
Bandara, U.G.C., Diyabalanage, S., Hanke, C., van Geldern, R., Barth, J.A. and Chandrajith, R., 2018. Arsenic-rich shallow groundwater in sandy aquifer systems buffered by rising carbonate waters: a geochemical case study from Mannar Island, Sri Lanka. Science of the Total Environment, 633, pp.1352-1359.
Dunuwila, P., Rodrigo, V.H.L. and Goto, N., 2018. Sustainability of natural rubber processing can be improved: A case study with crepe rubber manufacturing in Sri Lanka. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 133, pp.417-427.
Egresi, I., Prakash, S.L., Maduraperruma, B., Withanage, A., Weerasingha, A., Dezsi, Ş. and Răcăşan, B.S., 2021. What Affects Support for Wetland Tourism? A Case Study from Sri Lanka. Sustainability, 13(16), p.8802.
Gunarathne, A.N., Kaluarachchilage, P.K.H. and Rajasooriya, S.M., 2020. Low-carbon consumer behaviour in climate-vulnerable developing countries: A case study of Sri Lanka. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 154, p.104592.
Kaweesa, S., Mkomwa, S. and Loiskandl, W., 2018. Adoption of conservation agriculture in Uganda: A case study of the Lango subregion. Sustainability, 10(10), p.3375.
Kumar, B., Singh, U.K. and Ojha, S.N., 2019. Evaluation of geochemical data of Yamuna River using WQI and multivariate statistical analyses: a case study. International Journal of River Basin Management, 17(2), pp.143-155.
Madushani, K.P.K., Amarasinghe, M.D., Ratnayake, R.M.C.S. and Dahanayaka, D.D.G.L., 2021. An ethnobotanical approach to control Typha angustifolia: A case study from Sri Lanka.
Paranage, K. and Yang, N., 2020. The existence of multiple hydro-mentalities and their implications for water governance: a case study from Sri Lanka. Water, 12(7), p.2043.
Perera, E.N.C., Jayawardana, D.T., Jayasinghe, P. and Ranagalage, M., 2019. Landslide vulnerability assessment based on entropy method: A case study from Kegalle district, Sri Lanka. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 5(4), pp.1635-1649.
Priyadarshani, K. and Senarath, S., 2021. Classroom Factors that Influence Self-esteem in Gifted Children: A Case Study in Sri Lanka.
Ranagalage, M., Wang, R., Gunarathna, M.H.J.P., Dissanayake, D.M.S.L.B., Murayama, Y. and Simwanda, M., 2019. Spatial forecasting of the landscape in rapidly urbanizing hill stations of South Asia: A case study of Nuwara Eliya, Sri Lanka (1996–2037). Remote Sensing, 11(15), p.1743.
Udeshani, W.A.C., Dissanayake, H.M.K.P., Gunatilake, S.K. and Chandrajith, R., 2020. Assessment of groundwater quality using water quality index (WQI): A case study of a hard rock terrain in Sri Lanka. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 11, p.100421.
Warnasuriya, T.W.S., Gunaalan, K. and Gunasekara, S.S., 2018. Google earth: A new resource for shoreline change estimation—Case study from Jaffna Peninsula, Sri Lanka. Marine Geodesy, 41(6), pp.546-580.
Wickramaarachchi, W.A.M.S. and Dandeniya, W.S., 2021. Cellulose Decomposition Potential of Soil as Affected by Vegetable Cultivation: A Case Study in Kegalle District, Sri Lanka. Tropical Agricultural Research, 33(1).
Yuliani, S. Y., Pajri Aprilio, Sri Lestari, and Yenie Syukriyah. “Decision Support System for Internship Using Multifactor Evaluation Process (MFEP) Method Case Study: Department Of Computer and Informatics Engineering Bandung State Polytechnic: https://doi. org/10.37178/ca-c. 23.1. 134Practical work is to apply the knowledge that has been gained during college in cases that exist in the institution or company that you want to go to. This research was conducted based on internship program that is held every year in Informatics Engineering, Bandung State Polytechnic ….” CENTRAL ASIA AND THE CAUCASUS 23, no. 1 (2022): 1329-1348.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

