Assignment Sample on Critical Analysis of NPP Occupational Therapy Case Study
Introduction
The case study is based on NPP occupational therapy. In the case study, there is a discussion of the communication between Karl Welborn from NPP Occupational Therapy Limited, who is a consultant occupational therapist, and Susan Barnes from Coventry University. The activity of collaboration between Chartered Management Institute (CMI) and Coventry University is discussed here. Karl Welborn says that the CMI company provides rehabilitation services to patients who are suffering from brain injuries, dysfunctions, and other neurological diseases. The facility that this company provides occupational therapy, language and speech therapy, psychology and physiotherapy, etc. The collaborative activity of these two companies is highlighted here based on employee hiring.
1.2 Leadership
Transformational leadership theory
For this situation study, Karl Wellborn of NPP Occupational Therapy Limited displays components of the leadership hypothesis through the activities and ways to deal with driving his association.
Vision and Inspiration
Creative leaders have a reasonable vision of the future and rouse their groups to pursue that vision. Karl’s vision was to give innovative and patient-driven rehabilitation administrations (Derwin 2021). He strived to rock the boat and proposition better consideration. His obligation to make the most optimized plan of attack occupational therapy program and recovery colleagues’ pathway mirrors his visionary leadership.
Motivation and Support
Karl’s leadership style centers around persuading and supporting his group. He talked about how he energizes transparent correspondence, making his representatives feel esteemed and heard. By putting resources into staff improvement and coaching, he exhibits his obligation to their development and achievement. His methodology enables workers to take responsibility for their jobs.
Adaptability and Decision-Making
Creative leaders should adjust to changing conditions and settle on informed choices. Karl confronted the test of exploring the Coronavirus pandemic, which required speedy decision-making absent a lot of earlier data. He showed versatility and adaptability by making tough choices, for example, putting staff on leave of absence and carrying out security conventions.
Innovative Thinking
Karl’s eagerness to challenge customary practices and present innovative arrangements lines up with the Creative leadership attribute of cultivating inventiveness. He established organizations like Recovery Help and Discourse and Language Therapy to address neglected needs in his field (Zanini et al.2021). This innovative thinking benefits the two patients and the association.
Developing Future Leaders
Karl’s obligation to tutoring and instructing is indispensable to Creative leadership. He gives chances to staff to develop expertly, similar to his most optimized plan of attack occupational therapy program. By coaching people and advancing a reasonable professional pathway, he guarantees the improvement of future leaders inside the association.
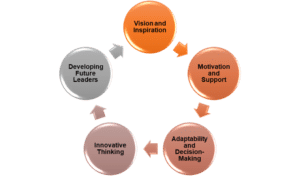
Figure 1: Transformational leadership theory
Collaborative leadership theory
Collaborative leadership is an administration style that emphasizes participation, teamwork, and shared decision-making among people inside an association.
Teamwork and Collaboration
Karl highlights the significance of teamwork and collaboration inside his association. He has numerous organizations under his holding, and he teams up with chiefs from various fields like discourse and language therapy, brain research, and physiotherapy. This cooperative approach permits them to cooperate, share experiences, and go with aggregate choices.
Vision and Innovation
Cooperative leaders frequently have a reasonable vision for their associations. Karl’s vision is in his calling and offers the most ideal types of assistance to clients. He supports innovation and creativity, permitting his group to track down better approaches to getting things done and working on patient consideration.
Mentorship and Development
Karl has a tutoring job in his association. He tutors a staff part in the most optimized plan of attack occupational therapy program and is engaged with instructing and preparing people to become master occupational specialists (Shinn et al.2021). This mentorship and obligation to staff development add to a cooperative learning climate.
Adaptability and Resolution
Karl shows adaptability and decisiveness, particularly in light of difficulties like the Coronavirus pandemic. He specifies that they needed to settle on hard decisions rapidly, even without complete data. Cooperative leaders are frequently adaptable and prepared to pursue informed choices under tension.
Patient-Centered Approach
Cooperative initiative frequently spins around a common obligation to serve the well-being of clients or patients. Karl’s emphasis on working on patient results and giving care mirrors this patient-centered approach.
Trust and Empowerment
Karl trusts his colleagues and enables them to deal with their own journals and be imaginative in their jobs (Khalil et al.2023). This trust encourages a feeling of pride and obligation among staff, making them more useful and committed.
1.3 Health and well-being
The organization, NPP Occupational Therapy Limited, driven by Karl Welborn, has exhibited a versatile way to deal with well-being and well-being despite challenges, especially during the Coronavirus pandemic. The organization principally centers around providing restoration services for clients with brain injuries and neurological infections. Here, we basically dissect their ongoing way of dealing with well-being and well-being.
Adaptability during the Pandemic
The organization’s reaction to the pandemic exhibits its obligation to wellbeing and well-being. They explored the uncertainties of Coronavirus, implementing strict wellbeing measures, such as PPE and risk evaluations, to guarantee the security of staff and clients (Zilcha-Mano et al.2020). This adaptability lines up with the theory of hierarchical flexibility, where the capacity to answer to unexpected difficulties is significant for maintaining well-being.
Focus on Staff Development
Karl underlines the significance of staff improvement, demonstrating a pledge to their well-being. This approach relates to the idea of a learning association, where continuous learning and development add to worker well-being. Encouraging reliability and input cultivates a positive working environment culture that benefits the two representatives and clients.
Innovation in Service Delivery
The formation of a most optimized plan of attack occupational therapy program and the Recovery Help initiative epitomizes innovation in service delivery. By recognizing the requirement for talented medical services experts and offering organized vocation pathways, they add to the well-being of the two workers and clients (Pliskin et al.2021). This approach resonates with contemporary medical services models that highlight patient-focused care and representative strengthening.
Holistic Well-Being
The organization’s holistic methodology, covering occupational therapy, physiotherapy, brain research, and discourse and language therapy, lines up with the biopsychosocial model of wellbeing. By addressing physical, mental, and social parts of well-being, they mean to give exhaustive consideration to clients, promoting general well-being.
Collaboration and Multi-Disciplinary Teams (MDTs)
The collaboration on customary MDT meetings and collaboration with different medical care experts indicates a consciousness of the significance of a holistic way to deal with well-being. The MDT approach, in view of proof-based practice, can upgrade the nature of care and, the well-being of clients.
NPP Occupational Therapy Limited’s way of dealing with well-being and well-being is described by adaptability, worker improvement, innovation, a holistic standpoint, and collaboration. These systems line up with contemporary medical care models and best practices, eventually contributing to the well-being of the two workers and clients (Cotigă et al.2021). Be that as it may, ongoing assessment and transformation will be urgent to guarantee the continued progress of these initiatives, particularly in the quickly evolving medical care landscape.
1.4 Diversity
Diversity and inclusion in the working environment are significant for cultivating a positive and useful climate.
Policy and Commitment
Effective D&I drives start with a reasonable and very much imparted commitment from top leadership. Associations frequently lay approaches and presentations that show their dedication to diversity and inclusion.
Training and Education
Organizations put resources into diversity training projects to teach employees about the significance of diversity, predispositions, and inclusive ways of behaving. These projects intend to make mindfulness and advance social capability among staff.
Recruitment and Hiring
Associations endeavor to make different candidate pools and lessen predispositions in hiring processes (Gupta et al.2021). They might execute blind recruitment methods, put forth diversity objectives, or work together with various ability channels.
Inclusive Culture
It is crucial for manufacturing an inclusive culture. This includes advancing equality, setting out opportunities for employee resource groups (ERGs), and cultivating a feeling of having a place for all employees, no matter what their experiences.
Metrics and Data Analysis
Numerous associations track diversity metrics to survey progress and recognize regions for development. These metrics can incorporate orientation, race, nationality, and more. Data analysis assists associations with pursuing informed choices and putting forth significant objectives.
Accountability and Leadership
D&I drives serious areas of strength for requirement and accountability. Selecting diversity officials or groups can assist with driving these efforts forward.
Feedback and Surveys
Organizations frequently assemble criticism from employees through overviews or center groups to understand their encounters and insights connected with diversity and inclusion (Gavron et al.2021). This information can direct further upgrades.
External Engagement
Drawing in with external associations and drives connected with diversity can assist associations with remaining informed about accepted procedures and access resources for development.
Legal Compliance
Consistency against separation regulations and guidelines is key. Associations should guarantee they meet legitimate prerequisites with respect to a potential open door and non-separation.
Task 2: Recommendation
Slide 1: Title
Slide 2: List of recommendation
- Foster Inclusive Leadership
- Implement a Diversity and Inclusion Task Force
- Introduce Flexible Work Arrangements
Slide 3: Justification of Foster Inclusive Leadership
- Inclusive leadership is essential for driving cultural change inside the organization.
- It establishes a clear vibe for the whole organization.
- It emphasizes that the aspects are strategies.
- Leaders epitomize the values of health, well-being, and diversity.
SN: Inclusive leadership is essential for driving cultural change inside the organization. At the point when leaders epitomize the values of health, well-being, and diversity, workers are bound to stick to this same pattern. It establishes a clear vibe for the whole organization, emphasizing that these aspects are strategies as well as integral to the company’s personality and achievement. Giving leadership training programs that emphasize diversity and inclusion, and appointing leaders with the abilities expected to create a different and inclusive workplace is essential. Inclusive leadership is essential in fostering a diverse and equitable work environment (Nickel et al.2021). It advances innovation and creativity by drawing upon many viewpoints and encounters. At the point when leaders value and include diverse voices, they tap into a wealth of one-of-a-kind ideas and arrangements that can move organizational achievement. Inclusive leadership raises representative confidence levels and engagement. At the point when individuals feel appreciated, regarded, and included, they are bound to be motivated and focused on their work. This enhances efficiency as well as lessens income rates, ultimately saving the organization time and assets.
(Source: https://www.qualtrics.com)
Slide 4: Diversity and Inclusivity
- Leaders need to focus on their own health and well-being.
- Leaders need to showcase the fundamental part of the organizational culture.
- This can be achieved by taking regular breaks.
- Encouraging open and transparent communication is essential.
- Leaders need to engage in regular conversations with workers.
SN: Leaders need to focus on their own health and well-being, showcasing that it is a fundamental part of the organizational culture. This can be achieved by taking regular breaks, maintaining a work-life balance, and participating in health and well-being initiatives (Grubbs et al.2020). Encouraging open and transparent communication about diversity and wellbeing issues is essential. Leaders need to engage in regular conversations with workers, showing empathy and ambition to address concerns. To advance diversity and inclusivity, the organization needs to think about the accompanying recommendation. Inclusive leadership aligns with societal values and expectations. In an increasingly diverse world, organizations that champion inclusivity are seen decidedly by clients, partners, and stakeholders. This can translate into an upper hand and a more grounded brand reputation. Inclusive leadership is a strategic, moral, and practical need in the advanced workplace, offering various advantages ranging from innovation and engagement to social obligation and enhanced reputation.
(Source: https://www.inclusiveleadership.com)
Slide 5: Justification of Implement a Diversity and Inclusion Task Force
- Directing regular diversity audits to recognize areas that require improvement.
- Creating and implementing diversity and inclusion training programs for all representatives.
- Observing and writing about progress in achieving diversity goals.
- Discrimination and bias can bring about exorbitant cases.
SN: A different and inclusive task force brings a large number of points of view and ideas, fostering innovation and better direction. By creating a dedicated task force, the organization demonstrates a guarantee of diversity and guarantees that initiatives are reliably and successfully executed. Directing regular diversity audits to recognize areas that require improvement. Creating and implementing diversity and inclusion training programs for all representatives. Observing and writing about progress in achieving diversity goals. Diversity and inclusion are essential for business development and innovation (Lyubomirsky et al.2022). A different workforce unites individuals from various backgrounds, encounters, and viewpoints. This diversity of thought and approach can lead to more creative critical thinking and a broader range of ideas.
A D&I task force can improve representative engagement and satisfaction. At the point when representatives perceive that their organization values diversity and inclusion, they are bound to feel a consistency of belonging and commitment. This leads to increased productivity and reduced income rates, ultimately saving recruitment and training costs. Besides, diverse and inclusive workplaces are bound to attract leading talent, giving the organization a competitive advantage in the talent market.
(Source: https://www.aihr.com)
Slide 6: D&I Task Force
- This decreases income rates.
- This decreases the associated expenses of enlistment and training.
- It also creates a positive workplace that attracts top talent.
- It can facilitate training programs, studios, and awareness campaigns.
SN: Cultivating diversity and inclusion further develops representative engagement and maintenance. At the point when representatives feel valued and included, they are bound to be satisfied with their work and focused on the company’s prosperity. This decreases income rates and the associated expenses of enlistment and training. It also creates a positive workplace that attracts top talent. A Diversity and Inclusion Task Force can act as a catalyst for cultural change inside the organization. It can facilitate training programs, studios, and awareness campaigns that challenge biases and advance comprehensive behavior. This cultural shift can lead to further developed teamwork, decreased clashes, and enhanced cooperation among representatives, all of which add to a more useful and pleasant workplace (Raimundo et al.2020). Implementing a Diversity and Inclusion Task Force is not simply a moral imperative but also a strategic business choice. It enhances innovation, moderates legal dangers, further develops worker engagement, and cultivates a more comprehensive culture. By putting resources into diversity and inclusion, organizations position themselves for long-term achievement, adaptability, and seriousness in today’s different and steadily advancing world.
(Source: https://arteducators-prod.s3.amazonaws.com)
Slide 7: Justification of Introduce Flexible Work Arrangements
- Flexible work arrangements allow employees to pick when and where they work best.
- This autonomy can lead to increased productivity.
- Introducing flexible work arrangements can benefit both employers and employees.
- Offering flexible work arrangements is a strong enlistment contraption.
SN: Flexible work arrangements enable representatives to all the more likely manage their work-life balance, decreasing pressure and advancing overall well-being. Access to mental health assets shows that the organization cares about the mental health of its representatives, creating a strong climate. Introducing flexible work arrangements is a strategic move that can benefit both employers and employees. Flexible work arrangements allow employees to pick when and where they work best. This autonomy can lead to increased productivity as individuals can align their work hours with their peak performance times, ultimately working on results and effectiveness. One of the main benefits of adaptability is further developed work-life balance. Employees can more readily shuffle their personal and professional obligations, lessening pressure and exhaustion. This leads to happier, more engaged, and healthier employees who are bound to stay with the company long-term. Offering flexible work arrangements is a strong enlistment contraption. Candidates frequently focus on companies that give such benefits (Rauch et al.2021). It helps in maintaining maximum talent and saving on enrollment and onboarding costs. Adaptability encourages a diverse workforce. It adjusts individuals with various requirements, like parents, guardians, or individuals with disabilities, allowing them to participate completely in the workforce.
(Souce: https://www.ringcentral.com)
Slide 8: Flexible Working Arrangements
- This advances inclusivity and a broader range of points of view inside the organization.
- Flexible work arrangements enable companies to tap into a global talent pool.
- Candidates frequently focus on companies that give such benefits.
- Employees can logically transition to remote work.
SN: This advances inclusivity and a broader range of points of view inside the organization. Flexible work arrangements can lead to cost savings for both employers and employees. Diminished driving costs office space prerequisites for employers, and savings on transportation and childcare for employees, can have a positive financial impact. In the midst of crises, for example, natural disasters or health crises, flexible work arrangements guarantee business continuity. Employees can logically transition to remote work, maintaining operations in any event, when the physical workplace is unavailable (Robinson et al.2021). Decreased driving and office space necessities can add to a company’s environmental sustainability goals. Fewer cars on the road and lower energy utilization in workplaces can decrease the organization’s carbon impression. Employees who have the opportunity to structure their work life are in many cases more satisfied and engaged in their roles. This can lead to higher morale, further developed teamwork, and a positive company culture. Flexible work arrangements enable companies to tap into a global talent pool. Geographic constraints are limited, allowing organizations to enlist the best talent, regardless of their location.
(Source: https://cdn.sketchbubble.com)
Slide 9: Summary
- These recommendations center on leadership.
- These recommendations center on diversity.
- These recommendations center on health and well-being.
SN: These recommendations center around leadership, diversity, and health and well-being to construct a culture that values these aspects inside the organization (Rush et al.2022). By implementing these recommendations, the case concentrates on how organizations can create a workplace where representatives feel valued, included, and upheld in their quest for health and well-being.
Task 3: Personal and Professional account
Leadership Skills
Leadership Skill 1- Adaptability
Karl recognizes the significance of adaptability in leadership. This skill involves the capacity to adjust and flourish in a quickly evolving climate, as proven by his swift response to the challenges posed by the worldwide pandemic in his medical services business. Adjusting to unforeseen circumstances and swiftly devising strategies for business progression permitted Karl’s organization to keep giving essential recovery services to weak clients, adding to their well-being and prosperity.
Leadership Skill 2- Innovation
Innovation is another key skill that Karl values. His willingness to investigate new, intelligent fixes has empowered him to foster momentous programs like the fast-track word-related treatment scheme and the Recovery Assist drive. These innovations conform to the CMI’s set of rules, especially the guidelines of “Empowering Innovation” and “Accomplishing Results” (Hays-Grudo et al.2021). By fostering a culture of innovation inside his association, Karl has worked on the nature of care as well as demonstrated a guarantee of continuous improvement and the advancement of his group’s prosperity.
Leadership Behaviours
Leadership Behavior 1- Coaching and Mentoring
Karl identifies coaching and mentoring as vital behavior for his leadership style. His experience as a competitor and his job in fostering a fast-track treatment scheme demonstrates his commitment to sustaining and directing rising professionals. This behavior resonates with the CMI governing set of rules and guidelines for Creating Self and Others (Ionescu et al.2021). By investing in the development of his colleagues, Karl ensures their personal and professional improvement as well as contributes to a positive work environment culture that prioritizes the well-being and prosperity of its staff.
Leadership Behavior 2- Trust and Empowerment
Karl places a strong emphasis on trust and empowerment in his leadership approach. He values the trust he instills in his group, giving them the opportunity to deal with their own diaries and be imaginative in their roles. By enabling his colleagues to take ownership of their work and decide, Karl enhances their work satisfaction and prosperity as well as sets a point of reference for moral and responsible leadership.
Use of CMI code
The professional and ethical behavior of the staff of CMI can be guided by the “CMI Code of Conduct”. The vision of the company can be reflected by the implementation of the CMI code. The best practices of the company and the best service from the employees of this company can be provided by the implementation of the CMI code.
Inclusion of Critical account
The key areas of leadership skills and leadership behavior can be included as critical accounts to implement the CMI code in the leadership practice. The leadership skills that have been considered here are adaptability and innovation of the leaders of the organization, which can facilitate the activity of the organization (Mancini et al.2023). The leadership behavior that the leaders have considered here is “coaching and monitoring” and “Trust and Empowerment”.
Ensuring critical account
Karl Welborn’s decision to foster adaptability and innovation as leadership skills and coaching and mentoring, alongside trust and empowerment as leadership behaviors, demonstrates his obligation to the CMI’s implicit set of rules and principles. These skills and behaviors not only add to the success of his association yet in addition assume a fundamental part in sustaining a culture of well-being and prosperity among his colleagues.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

