Customers (or traditional business owners) satisfaction on the benefits of FinTech during COVID-19 lockdown
Section 1: Introduction:
The government’s reaction to the epidemic was swift, resulting in both possibilities and problems for the spread of financial inclusion in society. According to the World Bank, people and companies that have access to inexpensive, efficient financial goods and services that fit their needs (transactions, payments, savings, credit, and insurance) are better positioned to manage their operations in a responsible and sustainable manner (Raza Rabbani,2021).
The percentage of individuals who have a bank account or who use a mobile money service in a certain nation may be used to determine how financially integrated a country is.
I Account ownership, on the other hand, is just the beginning of a lengthy and drawn-out process. Whenever individuals have access to a financial institution, their capacity to save money and pay for basics like rent and energy bills is at its highest. This is true as long as they have access to a financial institution. There has been an increase in the amount of options to make financial services more widely available as a consequence of the COVID-19 epidemic and the ease with which financial transactions may be completed through mobile devices, made possible by digital finance.
Section 2: Literature Review:
It is the primary objective of this research to examine the influence of COVID-19 on consumer digital financial inclusion, and it evaluates both the potential advantages and the potential downsides of this legislative framework. The need to call attention to the multiple digital money channels that are becoming accessible, and that are making it possible to gain more involvement, is crucial in resolving the COVID-19 problem. As part of this, newly constructed accounts will be able to accept digital payments during COVID-19, and newly formed accounts will also be able to utilise newly formed accounts for other digital financial services during the same time period. In addition, the World Bank’s Global Findex database, which has information on digital merchant payments in Latin America, Europe, and Central Asia, will be enhanced in 2020 to incorporate additional information on digital merchant payments from throughout the world. During the course of its continuing reporting, Microfinance Opportunities will give updated information on an increase in the number of digital wage payments issued to workers of the Bangladeshi garment manufacturing sector.
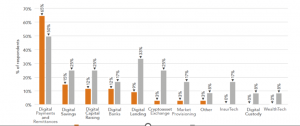
The fact that gaps in financial access make it more difficult for disadvantaged and marginalised communities to recover from influenza epidemics has been well acknowledged for some years. The usage of digital financial goods and services has expanded dramatically as a result of COVID-19; nevertheless, not all communities or customers have been able to embrace new technology at the same rate as other areas or customers. For consumers to take use of digital financial goods and services, they must have access to a mobile phone and an internet connection, as well as digital skills, which include the ability to operate mobile apps and online applications, among other things. The accessibility of these services is disproportionately low, with women, rural residents, and low-income individuals disproportionately underrepresented among those who do have access to these resources in the United States. As a result, they are more likely than other groups to be without access to and comprehension of digital technology and talents, resulting in them being at a competitive disadvantage. According to another study, women in low- and middle-income nations are 20 percent less likely than their male counterparts to own a smart phone or to use their mobile devices to access the internet than men in the same countries, according to the findings. It makes no difference whether or not women have access to information and communication technology. Women in Mexico and China, according to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), account for almost one out of every three mobile phone owners who do not have internet access due to a lack of digital skills, compared to just 15 percent of males in the same countries. According to the survey, a number of problems, including a lack of ID ownership and inadequate product design, have been highlighted as contributing to women’s restricted access to digital financial services. GSM Association estimates that there are 600 million rural inhabitants who do not have access to a mobile telephone network, which is a significant number. vi In addition to the availability of a digital connection (such as a mobile phone or data plan), factors such as a low demand for and investment in digital skill training have an influence on a person’s capacity to acquire new digital abilities. It is possible that insecure employment and high opportunity costs may make it harder for low-income customers to learn new digital capabilities. In order to keep up with the times, low-income customers may find it difficult to master new digital skills due to high opportunity costs and financial volatility (Abed,2021).
In order to execute digital transfers, governments used a variety of methods, which were all different from one another. Individuals who made deposits into their existing accounts as well as those who made deposits into brand-new accounts were among those who attended. This has resulted in the most common sorts of accounts in emerging markets differing from one another in terms of functionality based on where you lived when you opened them. Mobile money technology was found to be more widely used in Sub-Saharan Africa, which is known as the “mobile money capital of the world,” than in other parts of the world, according to a World Bank report; standard bank accounts, on the other hand, were found to be more widely used by governments in countries in South Asia and Latin America, according to the same study (Gentilini and others 2021).
Section 3: Research Method
During COVID-19, both the commercial and governmental sectors began the transition to electronic payments and financial transactions, with the private sector demonstrating the most leadership in this area. Although economic activity has slowed, the number of mobile money accounts has increased at a rate double that predicted for 2020, with 1.2 billion accounts projected by the end of the year. viii According to Visa, the international credit card industry, more than 13 million customers made their first ever online transaction in the first quarter of 2020, the firm said. (Bary\s2020). As a consequence of the virus’s spread throughout the continent, PayPal reported a “tremendous boom” in online sales, while Nigerian mobile money company Paga reported a 200 percent increase in quarterly clients, as well as a 200 percent increase in merchants on its network.
Design of questionnaire
- It is claimed by the business that data from Orange, another mobile money provider, reveals that payments to international merchants have increased by 55% this year. Do you agree with this statement?
- It is an abbreviation for the phrase “hamburger” (Berger, 2020). It was Latin America that had the greatest increase in e-commerce growth, according to the World Economic Forum, with sales jumping by 37 percent in only the previous year alone, according to the World Bank. DO you think this statement is reliable ?
- It wasn’t until the sixteenth month of the epidemic’s first year of existence that money that had been transferred back from outside was unaffected by the disease. Do you agree with this statement ?
Methods
A large number of individuals in low-income countries were afraid that their capacity to transmit money overseas would be hampered when COVID-19 entered into force in January 2018. East Asia and the Pacific, Central Asia, and Sub-Saharan Africa are among the locations where remittances from government sources have declined in recent years. East Asia and the Pacific are two of the world’s most populated areas, with a combined population of more than a billion people, making them the world’s most populous regions. East Asia and the Pacific are also two of the world’s most populous regions (driven by Nigeria).
Validity and reliability
According to World Bank forecasts for the year 2020, official remittances to poor countries would have decreased by an average of 1.6 percent per year on average by the year 2020. There is one critical caveat to remember: it is possible that official remittance flow estimates were exaggerated as individuals began to migrate from cash to digital remittances, and from informal to formal remittances, as a result of the pandemic lockdowns and travel restrictions, which made it more difficult to transport cash in person. Remittances via mobile money channels climbed by 65 percent in 2020x, according to the GSM Association; these advancements seemed to have played a crucial role in maintaining financial flow during the epidemic (World Bank 2021).
Section 4: Data Analysis
This will be further developed as part of the next Global Findex upgrade, which is slated to be released in early 2022 and will allow for more documentation and quantification of digital accounts and payments (Chen2021).
To name a few of the subjects being discussed at the conference, digital finance is being explored for its possible use in COVID-19 assistance and other government payments, as well as the transition to digital remittances and digital wage payments, among other things (Purba,2021).
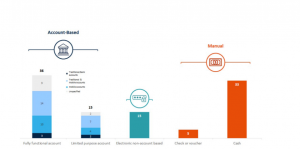
According to a research done by financial authorities in 2020, digital financial services, particularly those connected to payments, are on the rise and will continue to develop. During COVID-19, the Globe Bank and the Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance (CCAF)xi conducted a survey of financial regulators in 114 countries across the world to get a better understanding of market trends. The results of the study were presented during the conference. It was at this occasion that the researchers revealed the results of their study findings. According to the researchers, the data will be made public in the middle of 2020 at the earliest. Several months after reporting a 66 percent growth in online payment volume, the Federal Reserve announces a 24 percent increase in digital banking, savings (22 percent), and loans (14 percent) (14 percent ). With substantial margins in every single one of these sectors, emerging markets outperformed established markets across the board, and this was true across the board across all industries.
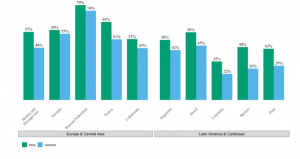
At the moment, there is a scarcity of information available on the effect of COVID-19 on digital financial inclusion in the developing world. Following the conclusion of COVID-19, a number of countries have reacted by adopting new programmes and laws, and these efforts have already yielded significant insights and early information on the success of the policies that have been implemented so far (Liu,2022).
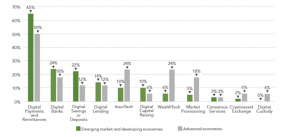
As a result of the adoption of COVID-19 by certain nations, in other circumstances, this may give an opportunity to speed the transition to a more widespread acceptance of digital alternatives to conventional financial services, which is now taking place. It has become more difficult to utilise digital technology in instances when cash is still necessary for basics like as food, gasoline, and other important transactions during the crisis, particularly after the closure of cash-in/cash-out facilities. This section of the website has a wealth of valuable information on a variety of topics, including peer-to-peer (P2P) payments, merchant payments, digital wage payments, and ecommerce. Women, the elderly, and people who live in rural regions are among the groups who need extra care as a consequence of their greater vulnerability to the virus. Women, the elderly, and people who live in rural areas are among the groups who require special attention. Individuals who reside in rural regions, women, the elderly, and people with disabilities are some of the categories that deserve particular consideration (Nathan,2022).
Section 5: Conclusion
Other decisions were made, such as increasing the total number of access points on the network, which would be accomplished over the course of many months. To make up for the time that had been wasted while G2P distribution was mostly reliant on cash-out stations, financial institutions made significant investments in expanding their agent network (as it was in Ecuador at the time). Following adjustments to qualifying conditions, current agents who had previously been denied the opportunity to offer cash out services by financial institutions would now be able to do so with greater ease as a consequence of these changes. RSPs and agents of such institutions were given permission to continue offering remittance services throughout the epidemic since they were seen to be major service providers in a number of different countries. RSPs, mobile money service providers, and their partners were declared “essential services” by the governments of both the transmitting and receiving nations, allowing the illness to spread. For the illness to spread, they must be available at all times, which means they must be accessible at all times. Countries such as the United Kingdom, Mexico, India, and the Philippines were among the first to allow remittance service providers to continue operating despite the fact that the vast majority of G20 countries (including Russia, Argentina, Switzerland, and Germany) have allowed them to do so even without explicitly declaring that they are an important service (as has been the case in the United States).
References
Abed, S.S., 2021. A literature review exploring the role of technology in business survival during the Covid-19 lockdowns. International Journal of Organizational Analysis.
Akdeniz, Ö.O., 2022. Utilization of Fintech Applications during the Covid-19 Pandemic. In Digital Transformation. IntechOpen.
Bhasin, N.K. and Gulati, K., 2021. Challenges of COVID-19 During 2020 and Opportunities for FinTech in 2021 for Digital Transformation of Business and Financial Institutions in India. In E-Collaboration Technologies and Strategies for Competitive Advantage Amid Challenging Times (pp. 282-299). IGI Global.
Chen, X., You, X. and Chang, V., 2021. FinTech and commercial banks’ performance in China: A leap forward or survival of the fittest?. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 166, p.120645.
Le, M.T., 2021. Examining factors that boost intention and loyalty to use Fintech post-COVID-19 lockdown as a new normal behavior. Heliyon, 7(8), p.e07821.
Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y. and Xiao, H., 2022. Small business owners’ Fintech credit in crises: Theory and evidence from farmers under the COVID-19. Pacific-Basin Finance Journal, 71, p.101692.
Modgil, S., Dwivedi, Y.K., Rana, N.P., Gupta, S. and Kamble, S., 2022. Has Covid-19 accelerated opportunities for digital entrepreneurship? An Indian perspective. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 175, p.121415.
Nathan, R.J., Setiawan, B. and Quynh, M.N., 2022. Fintech and financial health in Vietnam during the COVID-19 pandemic: In-depth descriptive analysis. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 15(3), p.125.
Purba, J., Samuel, S. and Budiono, S., 2021. Collaboration of digital payment usage decision in COVID-19 pandemic situation: Evidence from Indonesia. International Journal of Data and Network Science, 5(4), pp.557-568.
Raza Rabbani, M., Asad Mohd. Ali, M., Rahiman, H.U., Atif, M., Zulfikar, Z. and Naseem, Y., 2021. The response of Islamic financial service to the COVID-19 pandemic: The open social innovation of the financial system. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 7(1), p.85.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

