ECO501 Economics for Managers Assignment Sample
Here’s the best sample of ECO501 Economics for Managers Assignment, written by the expert.
Globalization and Factors contributed to rapid globalization of the world
Globalization is the increased interaction between people and companies across the world. This trend of increasing interaction has made much advancement in different sectors like manufacturing, automotive, agriculture, and service sectors. With the increased level of interactions between different nations, the developed countries have gained economic, social and cultural progress but at the same time, it also conflicts with the development pace of many sectors.
Globalization process involves goods, services, technology and capital resources and leads to improvement in various areas and also, concerns with the multiple economic networks, cultural and political interchange (Bridges, 2002). The economic globalization comprises globalization of finance, technology, market, production, institutions, labor, and corporations.
The globalization of world economy has improved the living standards of citizens but there are significant concerns in developed countries like Australia. The increased globalization has affected the survival of industries, especially manufacturing and motor vehicle industry. The recent boom of globalization has largely supported the developed countries by integrating the world through easy market entry, trade barriers reduction, increased foreign direct investment etc. (Overland, 2016).
Globalization is also considered as the theory of comparative advantage for many countries that can export their competitive products to the less efficient countries. Conversely, the latter country can also export the goods that are produced in efficient manner to the former country that might be deficient with those goods or the capability to produce those goods.
The underlying assumption in this concept is that all countries are not good in production of all goods and through globalization; they gain benefits by trading with each other. Furthermore, there is a wage differential in different countries because of different available resources and it leads to trade within the countries(Rosling, 2013).
Globalization also means that the trading countries follow the procedures and rules of World Trade Organization to oversee the terms and conditions of trade between the countries. The trading countries agree to the policies of trade and other non-discriminatory policies when they trade with each other.
With the emergence of globalization, the economic growth is leading to lowered consumer prices in the developed countries and also changed the balance between developed and developing countries.
It also affects the culture of both the countries and mainly, the developed countries are also facing issues of loss of cross border jobs and diminishing industries. There are many factors that have contributed to the rapid globalization of the world economy in recent years. Some of the factors are listed below.
- Technological change – Rapid changes in technology has cut the cost of transmitting communication and information and it is also referred as “death of distance” (O’rourke and Williamson, 2002). It is one of the key factors behind trade of knowledge based products with the utilization of web technology.
- Economies of scale – It is also believed that there is a rapid increase in the minimum scale of efficiency related to specific industries. The rising minimum efficiency scale increases, the domestic market is regarded as s a small scale for satisfaction of selling goods in that set of industries. And rest, the emerging countries have different transnational corporations.
- Different tax systems – The tax systems are adjusted broadly for attracting the foreign direct investment in many countries and desire to gain business benefits through favorable factors of production and lowered unit labor costs(Martell, 2010). There is also an issue of tax competition in many countries and they intend to bid and win available projects of foreign investment.
- Lack of protectionism – There are different forms of non-tariff protection like foreign exchange controls, import licensing that are gradually dismantled. The borders have been open and led to the fallen import tariff levels. In recent years, the non-tariff barriers like import quotas have been struggling to achieve economic growth in response to the current account deficits and persistent trade in the countries.
- Growth of Multinational and Transnational companies – To achieve profit and revenues, the global brands have involved in the global business and invested mainly to expand on international level (Overland, 2016). It is especially the case of businesses that have their house brands and have the potential to gain success on global scale. These companies intend to prove their success in growing countries as they are fueled by large number of middle class consumers.
Idea of Globalization in the Australian economy
The economic reforms have underpinned the economic growth in Australia. However, there are many costs to Australian in the long term because retreating from globalization is not the solution to the economic problems. The sense of engagement and open orientation with Asia can ensure the prosperity of the country.
The globalization in Australia is supported even after the negative effects on many industries like manufacturing, automotive etc. The recent financial crisis has served as a wake-up call to the Australian economy and encourages the attitude of Australian invincibility. There are a lot of financial linkages of Australians with rest of the world and these linkages are very crucial for the prosperity of Australian economy.
In case, these linkages are taken for granted, there is a huge financial fragility and growing sentiments of protectionist in the country(Jones, 2010). There are three major considerations that provide that led to the mismanaged trade and business in the global world. First factor is related to the inability to improve the commonwealth fiscal position that has putted the credit rating to risk for the Australian economy.
The second factor is the fearful attitude of Australian economy towards the proposals of foreign investments that has led to the increased risks of ability to join the partnerships on region basis. And the third factor is the populist infatuation that has led to the profitability of domestic banks and put the robustness of institutions at high risk (Overland, 2016). The economy of Australia is also indicated in the below figure and it depicts the importance of import, export pressures on the economy.
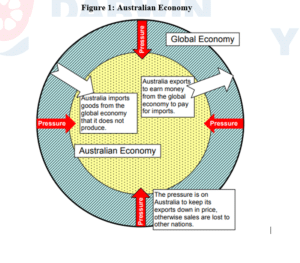
Globalization does not provide equal benefits to all and in context to Australia; it is related to the pressure of globalizations that need to be handled efficiently by the country. The main reason behind supporting the idea of globalization in Australian economy is the dependency of Australia on the global economy (Martell, 2016). Australia needs to export goods and commodities to other countries to earn more and pay for the imports from other countries.
It can be considered that the competencies of Australia like gold, coal, wheat should be exported so that the clothing, cars, televisions can be imported from other countries. The export level of Australia is dependent on the competitiveness of prices in the global market. The competitiveness of prices depends on different aspects of industrial relations like wages and salaries, efficiency of workplaces, overall cost of production etc.
So, it is important for Australia to remain competitive in the global economy and the government can put downward pressure on salaries and wages and upward pressure on the factors of productivity in their industrial relations policy(Ritzer, 2011). The failure to ensure the competitiveness in the global economy can result in unemployment, business failure and overall contraction of the economy. It can also lead to lowered lifestyle of people in Australia.
The technology advancements also continue to expand to promote increased globalization. The current scenario is also leading to the development of emerging countries like India and China. In these countries, workers are paid small fraction of amount paid to Australian workers. It makes these emerging countries very competitive in the global market. There are many goods and commodities that are made cheaply in these countries and that has major impact on the lost jobs and diminishing industries in Australia.
However, taking strong actions on the aspects of globalization can lead to prosperity of Australian economy in much better manner(Bridges, 2002). These actions include downward pressure on salaries and wages and upward the productivity pressure. The Australian economy need to follow this suit with the expanding global economy so as to reap benefits of world globalization.
The idea of globalization is supported because the Australian economy has the required capability and can reap benefits by increasing the export level and putting pressure on productivity matters. Many countries have experienced slow aggregate income growth in the recent years and there is a consensus that the reduced growth is shared equally with the gains accrued by wealthy citizens(Overland, 2016).
It is also considered that the majority of countries were disappointed with the economic outcomes of globalization but soon started to globalize at a faster pace. The crisis in Australia is a result of a retreat to nationalism and lack of trust of regulators and financial intermediaries other than their own country. Globalization has not caused lack of trust rather; there are many domestic policy failures in the countries that affected the position of countries in global world. Australia can be benefitted largely from the international orientation across the social, financial and economic dimensions.
Gain and loss from globalization in Australia and India with respect to manufacturing industry
The effects of globalization are not same for every country and industry. The freer trade, tariff cuts and easy foreign investment has increased the exposure to the globalization forces. It is indicated that the broad utilization of globalization has led to economic growth or loss of GDP. In case of Australia, the costs and benefits of globalization are as follows:
Benefits:
- Openness involves reduced tariffs and low protection due to globalization has forced the country to allocate resources in production areas that can provide comparative cost advantage. It had led to better efficiency and uplifted the economic growth(Jones, 2010).
- The force of lower tariffs has led to cost cutting of production and lifted the efficiency to compete and survive against imports. Many firms have also gained huge earnings with rising export sales.
- Lower tariffs have also led to the import of new equipment and use of updated and efficient technology in production areas. IT improves the competitiveness and GDP factors.
Costs:
- Lower tariffs have caused the exports to grow at very high rates, and the exported production has risen from 14 to 23 percent from 1984-85 to 2012-13.
- Foreign investment encourages and helps the business investment level in Australia but at the same time, it increases the competitiveness in the market for Australia(Hopkins, 2004).
- Deregulated labor market. The globalization has also made the wage system and labors competitive. And at the same time, the uncompetitive parts of economy like manufacturing industry have suffered in short and medium term because of structural unemployment resulting from global exposure and related policies.
On the contrary, there is an increased importance of globalization in Indian economy. After the globalization and industrial revolution, India has major contribution to the GDP of the world and dominates many sectors. The economy has managed to manage the faster economic growth rates as compared to other countries like Europe, United States and Australia.
For example, the Chinese economy has expanded with an average rate of 9 percent from last 3 years, India has expanded with an average rate of 5 percent and the average expansion rate of Australia is 3 percent(Overland, 2016). The faster growth in GDP led to the rapid rise in the disposable income of citizens, high living standards and better purchasing power(Ritzer, 2011).
The policy measures includes liberalization of managed trade that includes reduction in tariffs, acceptance of globalization benefits, openness to trade in global market, increased economic freedom, better lifestyle, spending on health and education, and privatization of government businesses.
In context to manufacturing industry, it is considered that wages are the largest input cost for the business. Considering the same, labor is very cheap in India and many countries have outsourced labor-intensive work to the country. It has ultimately increased the contribution of India to the GDP of whole world.
For example, the labor-intensive areas of manufacturing production are conducted in India as there are low hourly payments, whereas the labor costs in Australia, New Zealand, and France are very high. The hourly pay rates in India, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Mexico, and Indonesia are approximately US 0.25 to US 1.00 and the minimum wage rate of Australia, New Zealand, and France are approximately $16 per hour(Rosling, 2013).
However, the minimum wages in these countries have also reduced in last decades and causes the companies to review their locations. The investment from the richer countries is mobile and can be moved by setting up their factories in other countries, where labor is cheap as it will boost the profits of company. Despite this trend, there are many instances where the improved labor efficiency in high wage countries has attracted the industries by affecting their cost advantage.
Globalization helps in gaining the economies of scale and many other benefits but it need to be reaped efficiently by the countries. In case of India, the country has utilized their competitive advantage to gain benefits from other countries but in case of Australia, the fear of extensive import and exports have led to the losses of country. In addition, the manufacturing industry has faced many problems because it is a labor-intensive industry and have many negative factors associated with it.
References
Bridge, G., 2002. Grounding globalization: The prospects and perils of linking economic processes of globalization to environmental outcomes. Economic Geography, 78(3), pp.361-386.
Hopkins, A.G., 2011. Globalisation in world history. UK: Random House. Retrived from: https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=fzrmYjzq7XsC&oi=fnd&pg=PA1&dq=Hopkins,+A.G.,+2011.+Globalisation+in+world+history.+UK:+Random+House&ots=pmBaU_BU4g&sig=hhX5kKHfDG9yNd7aqxcTFnRxWuY#v=onepage&q&f=false
Jones, A., 2010. Globalization: key thinkers (Vol. 1). UK: Polity Press, John Wiley & Sons.
Martell, L., 2016. The sociology of globalization. UK: John Wiley & Sons.
Overland, I., 2016. Energy: The missing link in globalization. Energy Research & Social Science, 14, pp.122-130.
O’rourke, K.H. and Williamson, J.G., 2002. When did globalisation begin?. European Review of Economic History, 6(1), pp.23-50.
________________________________________________________________________________
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

