Introduction
Active implementation of emerging technologies is highly helpful and supportive from a corporate perspective to ensure subsequent improvement of their existing products and offerings. With reference to this concern, the focus of this present assignment is kept on providing a review of the emerging business technologies in the operations of a UK supermarket retailer Sainsbury’s. The organisation is already observed to depend on some sort of advanced technologies like AI and ML. This assignment critically evaluates the innovative technologies of Sainsbury’s along with proposing them regarding the usage of emerging technology on their scale on demand to improve resilience. Lastly, possible future consequences of cyber risk are also identified with the inclusion of technology advancement in Sainsbury’s.
Task 1: Review of Emerging Business Technologies
1.1 Background
Sainsbury’s is a British retail organisation present in the UK, which was started in 1869. This organisation offers a wide range of grocery products, with 16% market share in the UK. It has almost 800 convenience stores and 600 supermarkets in the UK for providing services to customers (Sainsbury’s, 2024). The competing pricing and value-based pricing strategies are followed in this organisation for attracting the customers across the nation. The great quality and delicious availability of fresh foods and a wide range of grocery items with brands such as Argos, Nectar, and Habitat are involved in the organisation (Sainsbury’s, 2024). There are almost 152K employees working in the organisation.
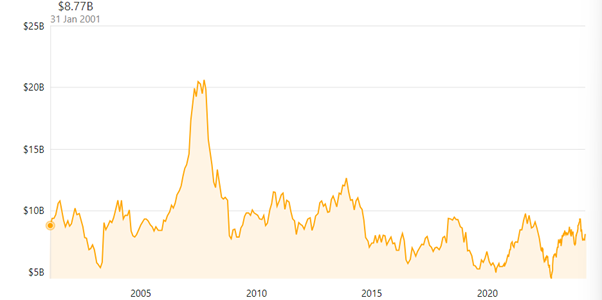
Figure 1: Market Capitalisation of Sainsbury’s
(Source: Companies Market Cap, 2024)
Along with the offline marketplace, Sainsbury has established its business in the online market space for maintaining innovations and developments in the company. Online operations have involved quick delivery of the products by 1 Hour across 10Kms in front of the stores (Sainsbury’s, 2024). Moreover, pick up services are also provided to customers who are providing online orders. These both online and file operations of the organisation have managed a market capitalisation of $8.08 Billion and have become 1914th most valuable company across the world (Companies Market Cap, 2024). Hence, its operations in both marketplace and market space have assisted to manage its operations successfully.
1.2 Evaluation of key innovative technologies that are transforming the organisation
Sainsbury’s operating in the UK market has focused on different business strategies to maintain the innovation of technologies in the company. This company has focused on digital transformation operations for optimising its services and quick responses to the market needs. Moreover, Sainsbury has invested $892.5 million in 2023 for maintaining information and communication technologies (ICT) development (Global Data, 2023). This shows that the organisation has involved ICT to make it a smart organisation with full application of innovative technologies. Even, the organisation is using different emerging technologies such as big data, cloud technologies, IoT and alternative reality for maintaining the operations of the company (Global Data, 2023). These technologies are helping Sainsbury to manage the introduction of SmartShop stores in London, where the till-free and check-out free shopping offers are being provided.
Moreover, the organisation has focused on a 100% loyalty program towards their consumers by maintaining the security of their data properly. The use of POS payment methods and other online methods are managed through self-serve houses that are protected with proper firewall in maintaining the safety of the customer’s data (TTEC, 2023). Additionally, the usage of unified data and analytics (D&A) with big data technology has assisted in storing the data properly. It has also used cloud technologies such as MicroStrategy Cloud, which is connected to Snowflake and AWS for managing the D&A mission of the organisation (Micro Strategy, 2023). Hence, applications of these technologies are helping in collecting and storing the consumer data in the organisation.
Task 2: Make Use of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies in the current scenario seem to be playing a pivotal role in enhancing business operations and creating a competitive edge in the market. According to Tan et al. (2022), emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), along with Machine Learning (ML), the Internet of Things (IoT) and Augmented Reality (AR) help in increasing organisational resiliency and assist in successful operations in the market. In the section above, it can be observed that Sainsbury’s has been operating with several innovative solutions within the market of the UK and other areas. This created a competitive edge for the company and helped to satisfy customers in the market. However, the stated emerging technologies can be implemented within the domain of Sainsbury’s in different ways to improve resiliency, enhance organisational scale on demand, minimise infrastructure investment alongside deploy effective solutions in a secured way.
2.1 Augmented Reality (AR)
AR is the implementation of virtual data which is being produced within a computer environment into a real-world scenario. It is being integrated in a way so that audiences or customers can be able to perceive with their sense organs. However, Lavoye et al. (2021) stated that AR is highly important as it helps in the reduction of production, design, and maintenance costs. It is also highly significant to resolve an issue faster and in a more efficient manner. Looking into the operations of Sainsbury’s, the company has been observed to be implementing AR for the purpose of bringing editorial adverts and content to life (The Drum, 2022). This helps the company to ensure proper interactions with customers in the market. Apart from that Sainsbury’s has also been observed to be involved with AR usage at the time of shopping digitally. For instance, customers can measure toy size through AR features available within Sainsbury’s application (Sainsbury’s, 2022).
However, to increase resiliency within the organisation, Sainsbury’s can also implement AR within its physical store. Like the notion of digital application, physical stores of Sainsbury’s can also implement a magic mirror technology that will help customers measure the size of clothing and select the colour of their choice. It will provide high resiliency in terms of shopping experiences of customers and the organisation can also scale on demand within the market. Most importantly, using AR facilities within physical stores will also minimise the infrastructure investment in terms of hiring store managers or employees to assist customers in their shopping journey. Henceforth, it will also deploy solutions in terms of fitting, exchange and others further ensuring proper experience of shopping.
2.2 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI, on the other hand, indicates a computer system which is highly capable of executing complex tasks which cannot be executed by humans. It is highly important as it supports proper reasoning, solutions to different issues and making decisions in a fast way that could benefit the overall organisation (Oosthuizen et al. 2021). Nonetheless, the significance of AI lies in the reduction of errors alongside automation that increases organisational efficiency. Sainsbury’s, in the current scenario, seems to be using AI to optimise orders within stores, increase efficiencies and improve the areas of forecasting (BlueYonder, 2022). Besides, Sainsbury’s is also focused on using AI to identify customers based on their previous shopping experiences (Barry, 2024). To ensure proper implementation of AI within Sainsbury’s, the company can also indulge in automated inventory management. In this respect, Sainsbury’s can implement AI within its inventory management areas for the purpose of effective and automated management of inventory which reduces infrastructure investment followed by an increase in organisational resilience.
2.3 Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT is another emerging technology that mainly indicates collective networks in terms of different connected devices alongside technology that aims at facilitating communication between clouds and devices (Kaur et al. 2022). This technology is highly effective as it increases productivity and helps organisations to adapt to different business models. Apart from that, it also provides the facility to work with technological advancement and lighten the work pressure through the instances of automation. Most importantly, it also enhances customer experience and ensures data-driven decisions within a domain. However, Sainsbury’s in the current scenario seems to be using different IoT technologies to ensure technology development within the domain. For instance, the company operates with a 100% LED system while it also includes a system of Wi-Fi along with scan-and-go technology, online applications and many others that help them to connect with customers effectively (Novel Energy, 2022). However, to focus on organisational resilience, Sainsbury’s can implement wearable devices for customers of offline shopping that will consist of sensors. This technology will assist customers to be directed towards the required parts within a store and will also help customers select the right fit for them.
2.4 Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning, on the other hand, is highly connected towards AI. However, it is the study alongside the development of a statistical algorithm that helps organisations learn from different information and generate potential outcomes (Kumar et al. 2021). ML is highly important as it deals with data-driven recommendations that ensure continuous improvement within a domain. Looking at the scenario of Sainsbury’s, the company has been observed to be using ML for the purpose of improving focus of demand and sales within the market followed by optimisation of store orders and increasing the notion of sustainability (BlueYonder, 2022). However, the magic mirror recommended for Sainsbury’s in terms of implementing AI technology can also be used in terms of machine learning in a customised way. For instance, the magic mirror previously recommended for Sainsbury’s could also implement the feature of data-driven recommendation. As a result of this, customers will not only get the right fit for them but can also get numerous recommendations regarding the product they should try to look more beautiful.
Task 3: Planning for the Future
The consequences of cybersecurity risk factors are explicitly associated with the preference of emerging technologies in the corporate field. The inclusion of technologies and features in the form of artificial intelligence and machine learning as well as big data analytics and others usually impose the threat of data security and privacy. The toxic consequences of data privacy related risk factors are also considered as a topmost ongoing trend of cybersecurity. As an example, the reference of recent statistics can be considered, which reflected the growth of data breaches by 72% in between the time from 2021 to 2023 (John and Swanston, 2024). Along with this, growing evidence of cybersecurity attacks and threats are also reported among the businesses, which raised subsequent questions about data security. Along with this, the generic consequences of data breach are also extending the threat of cybersecurity in recent times. The conceptualisation of data breaches and security risks are eventually extending additional expenses for the corporate entities. For evidence, the emergence of average data breach related incidents reflected an additional cost of around USD 4.45 million across global businesses (John and Swanston, 2024).
While taking the reference of Sainsbury’s, the organisation is proposed to depend on proactive implementation of augmented reality-oriented solutions in the form of innovation. Due to this reason, the organisation may also experience the negative threats of data theft or breach (Kaspersky, 2024). This aspect is needed to be considered by the management of Sainsbury’s as an integral part of creating a secured and safe database to support flexible progress with emerging technologies. Along with this, the retail industry is also experiencing creasing cyberattacks with data privacy related issues due to increasing digital transactions and others. For instance, 24% of the cyberattacks usually target the retailers due to having varying levels of security, which make them exposed to the cyber criminals (Fortinet, 2024). As a result of this, the trust level of the consumers is also declining as 62% of the retail consumers in reset times disclosed a lack of confidence level from their perspective regarding the security of their data (Fortinet, 2024).
Another 25% of the global consumers confidently stated the risk of poor data safety practices with the retailers (Fortinet, 2024). This aspect may emerge as a significant threat for Sainsbury’s with reference to secure their governance and control strategy with active digitization over the company wide data and information concept. To address this risk, Sainsbury’s will have to look for abiding by the guidelines of the General Data Protection Regulations (GDPR) along with focusing on the empowerment of security solutions within their business data and information strategy.
Another most significant cybersecurity trend in recent times reflects the consideration and rise of ransomware (Kaspersky, 2024). The prime reason behind the emergence of this risk factor reflects accelerated digitisation across the corporate environment with the integration of remote working and others. These aspects have created new targets for ransomware. However, this also imposes serious risks with the possibilities of stealing confidential information and data from the database of an organisation. The attribute of encryption would also make it difficult to be accessed after being hit by ransomware. Sainsbury’s, in this case, imposes the chances of being negatively affected due to ransomware attack.
With reference to recent statistics, more than two thirds of the retail corporate entities with 68% reported the experience of high ransomware attacks during 2022 (Mahendru, 2023). This evidence reflects the negative implications of ransomware attacks in the retail sector. Sainsbury’s may be negatively impacted because of this threat with a negative influence on their brand recognition due to risking valuable consumer as well as financial information and data. Apart from that, approximately 26% of the retail organisations, during the previous year, also reported a complete disruption of their operations due to the emergence of ransomware attacks before the conceptualisation of data encryption (Future CIO, 2024).
Sainsbury’s also includes the chances of service disruption, which is a major concern of cyber security for them with reference to the digitisation of their enterprise-wide information and control strategy. However, the overall measure of ransomware attacks is subsequently coming down as compared to the datasets from 2021 to 2024. During 2021, 34% retailers reported the occurrence of ransomware attacks, which has come down to 20% during 2022 (Future CIO, 2024). Based on this evidence, some sort of improvements can be highlighted within the measure of data security and solution due to which the retailers are being able to reduce the evidence of ransomware attacks in recent times. Among different types of cybersecurity attacks and risk factors reported within the retail sector, ransomware has taken a share of 13.04% (Fortinet, 2024).
With reference to the mentioned factual evidence, Sainsbury’s need to improve their existing data security solutions with a substantial focus on the prevention of cybersecurity attacks as mentioned.
Conclusion
The overall report has presented a wider overview regarding the negative consequences of the cybersecurity risk factors with reference to the implementation of emerging business technologies in the operations of Sainsbury’s. While operating with technological soundness, Sainsbury’s is proposed to consider augmented reality-oriented solutions across their physical store along with AI for inventory management and others. The risk factors like data security and privacy as well as ransomware attacks are highly signified as the most important cyber security trend in recent times, which are likely to be addressed by the organisation through the extension of data security solutions.
Reference List
Barry, A., (2024). The popular British supermarket is making it more difficult for shoplifters to strike. [Online]. Available at: https://www.gbnews.com/lifestyle/sainsburys-ai-security-alcohol [Accessed on 27 March 2024]
BlueYonder, (2022). Enabled by Blue Yonder, Sainsbury’s Leverages AI and ML for Supply Chain Optimization. [Online]. Available at: https://blueyonder.com/mx/es/knowledge-center/collateral/enabled-by-blue-yonder-sainsburys-leverages-ai-and-ml-for-supply-chain-optimization [Accessed on 27 March 2024]
Companies Market Cap, (2024). Market capitalization of Sainsbury’s (SBRY.L) [Online]. Available at: https://companiesmarketcap.com/sainsburys/marketcap/#google_vignette [Accessed on 25 March 2024]
Fortinet, (2024). Retail Cybersecurity Statistics Not To Be Ignored. [Online]. Available at: https://www.fortinet.com/solutions/industries/retail/retail-cybersecurity-statistics [Accessed on 25 March 2024]
Future CIO, (2024). Retail sector is unable to halt ransomware attacks, study finds. [Online]. Available at: https://futurecio.tech/retail-sector-is-unable-to-halt-ransomware-attacks-study-finds/#:~:text=Only%2026%25%20of%20retail%20organisations,%2C%20and%2028%25%20in%202022. [Accessed on 25 March 2024]
Global Data, (2023). J Sainsbury – Digital Transformation Strategies [Online]. Available at: https://www.globaldata.com/store/report/j-sainsbury-plc-enterprise-tech-analysis/#:~:text=Taking%20the%20initiative%2C%20a%20step,for%20payment%20confirmation%20before%20they [Accessed on 25 March 2024]
John, S. M. and Swanston, B., (2024). Cybersecurity Stats: Facts And Figures You Should Know. [Online]. Available at: https://www.forbes.com/advisor/education/it-and-tech/cybersecurity-statistics/#:~:text=As%20the%20globe%20becomes%20more,%25%2C%20surpassing%20the%20previous%20record. [Accessed on 25 March 2024]
Kaspersky, (2024). Top Ten Cybersecurity Trends. [Online]. Available at: https://www.kaspersky.com/resource-center/preemptive-safety/cyber-security-trends [Accessed on 25 March 2024]
Kaur, J., Santhoshkumar, N., Nomani, M.Z.M., Sharma, D.K., Maroor, J.P. and Dhiman, V., (2022). Impact of Internets of Things (IOT) in retail sector. Materials Today: Proceedings, 51, pp.26-30.
Kumar, M.R., Venkatesh, J. and Rahman, A.M.Z., (2021). Data mining and machine learning in retail business: developing efficiencies for better customer retention. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, pp.1-13.
Lavoye, V., Mero, J. and Tarkiainen, A., (2021). Consumer behavior with augmented reality in retail: a review and research agenda. The International Review of Retail, Distribution and Consumer Research, 31(3), pp.299-329.
Mahendru, P., (2023). The State of Ransomware in Retail 2023. [Online]. Available at: https://news.sophos.com/en-us/2023/07/05/the-state-of-ransomware-in-retail-2023/#:~:text=The%20proportion%20of%20retail%20organizations,70%25%20in%20last%20year’s%20report. [Accessed on 25 March 2024]
Micro Strategy, (2023). How Sainsbury’s Democratized Its Data to Empower Every Colleague. [Online]. Available at: https://www.microstrategy.com/customer-stories/sainsburys-data-and-analytics-case-study [Accessed on 25 March 2024]
Novel Energy, (2022). Sainsbury’s adds IoT capability in plan to go all-LED. [Online]. Available at: https://novelenergylighting.com/blog/sainsburys-adds-iot-capability-in-plan-to-go-all-led#:~:text=Sainsbury’s%20is%20to%20add%20Internet,supermarkets%20entirely%20by%20LED%20lighting. [Accessed on 27 March 2024]
Oosthuizen, K., Botha, E., Robertson, J. and Montecchi, M., (2021). Artificial intelligence in retail: The AI-enabled value chain. Australasian Marketing Journal, 29(3), pp.264-273.
Sainsbury’s, (2022). It’s AR-gos: Britain’s leading toy retailer first to launch LEGO® models in Augmented Reality. [Online]. Available at: https://www.about.sainsburys.co.uk/news/latest-news/2018/lego-augmented-reality#:~:text=Sainsbury%27s%20Group%20has%20a%20significant,of%20toys%20when%20shopping%20digitally [Accessed on 27 March 2024]
Sainsbury’s, (2024). About us. [Online]. Available at: https://www.about.sainsburys.co.uk/about-us [Accessed on 25 March 2024]
Sainsbury’s, (2024). Sainsbury’s. [Online]. Available at: https://www.sainsburys.co.uk/shop/gb/groceries/discoverhome/shopping-online [Accessed on 25 March 2024]
Tan, Y.C., Chandukala, S.R. and Reddy, S.K., (2022). Augmented reality in retail and its impact on sales. Journal of Marketing, 86(1), pp.48-66.
The Drum, (2022). Sainsbury’s magazine uses augmented reality to bring editorial content and adverts to life. [Online]. Available at: https://www.thedrum.com/news/2012/09/05/sainsburys-magazine-uses-augmented-reality-bring-editorial-content-and-adverts-life [Accessed on 27 March 2024]
TTEC, (2023). Sainsbury’s Serves Up Fresh Customer Data. [Online]. Available at: https://www.ttec.com/articles/sainsburys-serves-fresh-customer-data [Accessed on 25 March 2024]

