GLOBAL STRATEGY AND SUSTAINABILITY ASSIGNMENT SAMPLE 2023
Introduction
Globalization provides many opportunities for companies to enhance their capacities and achieve the desired position in the different markets. Globalization helps countries exchange information, technology and business for growth in various sectors (Kowalska et. al. 2020).
Through globalization, organizations can avail of raw material at the lowest cost and reduction in their operating cost. It also helps the organization to expand in new markets and reach new customers. For availing these benefits, in today’s scenario, organizations are required to formulate global strategies.
The present report is based upon the American Electrical Vehicle company, Tesla. The company mainly manufactures energy storage batteries, solar panels and electric cars.
The present report is aimed to analyze the company’s internal environment and external environment along with its global strategies for working. Further, the report also analyzes the company’s CSR and Sustainability strategies. In the last, the report provides some recommendations for the development of growth of the company.
Task 1:
Internal and External Environment
External environment factors are beyond the control of the organizations, and these impacts can be mitigated only through effective strategies (Moritz et. al. 2015). Tesla has also formulated several strategies regarding this: Porter’s five forces analysis, PESTEL analysis, Competitor’s analysis, and economic trends.
Analysis of Porter’s five forces model
Tesla uses this model to primarily analyse the impact of external forces on its corporate strategies. This model helps the organization allocate the bargaining power of its suppliers and buyers, availability of a substitute in the industry, its strengths among competitors and analysis of its position in the industry among competitors.
- Bargaining power of Suppliers (Low): Due to the fewer opportunities of direct product selling to the manufacturers and availability of fewer opportunities regarding the forward integration, the suppliers of the respective industry have very low bargaining power.
- Bargaining power of Buyers (Moderate): In the current period, various competitors in the industry are providing different benefits to the buyers, but Tesla is unique in its way and provides updated and innovative products to the buyers to retain them, and the switching cost is also very low (Stamatović al.2020). So the overall forces of buyers are moderate.
- The Threat of Substitute products (Moderate): The threat of substitute products is at a moderate level for the respective company in the industry as because of its continuous updating in its products and innovation, customers are more attracted toward the company other than its substitute, but now company’s like BMW, Volkswagen are also investing in this area and trying to compete with the company strongly.
- Rivalry among Industry (Strong): In the automobile industry, several giant companies are operating, such as Volkswagen, Chevrolet etc., which makes the industry highly competitive. Although, Tesla s able to secure its position at the top with the help of its innovation and high-level integration of its strategies.
- The threat of new entrants (Low): Entering such a well-established market requires a vast investment and well-developed infrastructure, which is not that easy for ordinary companies. Moreover, the Tesla company has a very strong customer base and a strong brand image that is not easily shakable, but the company still has a keen eye for this area.
PESTEL Analysis of Tesla
PSTEL analysis enables the company to analyse the impact of various factors related to government, environment, technology, and many more. Further, it explains how the company is coping with these factors successfully.
Political Factors: Due to the issues of pollution and global warming governments of several countries are imposing new strict rules and regulations for the companies and providing a few relaxations in Taxes and rebates to the companies who are contributing in this area (Namugenyi et. al. 2019).
Tesla has the upper hand in this as it produces environmentally friendly cars. The Cars of respective Company is using renewable energy. So the company can expand in various countries easily and grab the tax benefits also.
Economic Factors: The particular factor is concerned with the company’s profitability and growth. Economic growth, consumer income, inflation, exchange rate, and interest rate greatly impact organizations. Tesla is manufacturing the luxury product line in its cars but offers them at very affordable prices for all the income groups in the society (Indartono and Wibowo, 2017).
The company’s products required low fuel and low maintenance. Also, they provided innovative updated technological gadgets in its cars, which are comparatively budget-friendly and able to attract customers.
Social Factors: Social factors are concerned with consumers’ behaviour, demands, and societal norms. The respective company always makes sure that their products meet the customer’s standards and preferences. Tesla always tries to provide its customers with a delightful experience. With the proper strategies and timely market analysis Tesla is now playing successfully.
Technological Factors: Tesla is well known for its innovation and technology. Tesla is one of the top companies in the car manufacturing industry. Tesla provides its customer’s cars that are properly equipped with the updated and latest gadgets, redefined sustainability,
fuel-efficient, and online mobile system, which successfully attracts the customers (ökdeniz et. al. 2019). Technology is the biggest advantage of Tesla in the industry to survive and gain Advantage. Tesla has vast opportunities in this area and can sustain its sustainability more strongly.
Ecological factors: In recent scenarios, ecological factors have been the main concern of several countries governments. And for curing these issues, they are continuously formulating the rules and regulations and different laws regarding these issues.
Tesla Company is already manufacturing eco-friendly products and using renewable energy sources for its work. Thus they consume very low petrol and diesel. With the help of the company’s these features, the company’s growth in this series is very bright. Tesla can follow all the rules and laws designed by the government very easily; therefore, they can design their expansion strategy more flexibly.
Legal factors: Legal factors covers all the issues related to laws and legal standards like safety and health, advertisement standards, equal opportunities and consumer rights. Currently, the respective company is operating in several countries around the globe. It has a good reputation with a growth rate which signifies that Tesla can follow the proper laws and regulations of the host countries properly.
From the above PESTEL analysis, it can be concluded that external environment factors favour the respective company (Hernández and Garcia, 2018). Further, this also shows that organizations strategies and policies are in proper alignment with external influencing factors, which provides great opportunities for Tesla to grow in new markets and attract more potential customers.
Analysis of Internal Environment
The internal environment analysis enables a company to properly identify its strengths, weaknesses, threats, and available opportunities in the market (Mo and Wang, 2021). Moreover, it helps the company develop its strategies with proper consideration and effectively.
VRIO analysis
| Competency | Value | Rare | Imitable | Organized | Implications |
| Brand Image of Tesla | YES | YES | NO | YES | Provides a strong competitive advantage |
| Acquisition of Raw Material | YES | YES | YES | YES | Provides competitive Advantage |
| Pricing Strategy of the Tesla | YES | NO | Straightforwardly imitable by competitors in the industry | Yes, the company has a specific pricing analysis engine. | Temporary Advantage |
| Human Resource Management of the company | YES | NO | YES | YES | Competitive Advantage |
| Financial Base of the Company | YES | NO | These opportunities are always available for rivals in the market. | Tesla has a strong financial base which is helpful in the company’s sustainability (Matthews et. al. 2020). | Provides temporary Advantages |
| Marketing strategy of the company | Yes | No | Yes | various marketing competencies, which helps in utilizing lots of different areas of growth | Temporary Advantage |
| Logistics and Distribution channel | Yes | No | Imitable but a very costly affair and required a good relationship with supply chain members. | Yes | Competitive Advantage |
Valuable Resources: All those resources are helpful for the organization to stay protected from the potential threats and Risks in the industry (Guangul and Chala, 2019). In reference to a cited company, its logistics and distribution network, brand image, and Marketing network are valuable resources.
Rare Resources: These resources are acquired by very few competitors in the market compared to the organization, for a respective company, its technologically and innovative products list in this segment.
Imitable Resources: Those resources imitable by the competitors, such as Tesla Company’s HR policies and pricing strategies.
Value Chain Analysis
| Primary Activities (Tesla Company) | Support Activities (Tesla Company) |
| Ø Operations: Currently, Tesla has operations in more than 438 countries with more than 100 service centers.
Ø Sales and Marketing: Tesla mainly sells its products through online marketing and social media advertisements, making it different. Ø Logistic (inbound): As the company has a worldwide operation, it is very convenient for distributing the products also. |
Ø Procurement: Through the big supplier chain, the company can procure its raw material effectively.
Ø HRM policies: Tesla is a company of principals and follows the HR policies with great care. It believes that employees are its primary stakeholder in the company’s sustainability. Ø Technology: The cited Company is well known around the globe for its sound technology and innovation in products (Alghalith, 2018), which requires heavy investment, but Tesla can invest such an amount. |
SWOT analysis
| Strength:
Ø Strong Brand image Ø Partnership with big companies like NRGSTREAM, Southeast APDA and many more. Ø The unique and different way of establishing the Business model |
Weakness:
Ø Hefty Investment Ø Globally Low expansion Ø Succession Strategy Ø Customers are still reluctant to fully trust electric vehicles. |
| Opportunity:
Ø Proper marketing for improving electric vehicle demand with the association of environment-friendly features Ø Developing countries market for expansion (Gudz, 2015) Ø The company can achieve autonomous Driving excellence |
Threat:
Ø Limited infrastructure that supports electric vehicle manufacturing Ø Entry of new players Ø New renewable energy sources development like solar energy vehicles. |
Task 2:
Strategy in the global environment:
The term “global strategy” refers to a strategy that considers a variety of business elements such as the product, the manufacturing site, the market, the competition, and the suppliers.
It involves a product analysis based on international and domestic standards (Kaletnik and Lutkovska, 2020). To maintain its growth and achieve a competitive advantage to protect its hard-won position in the global automobile industry, Tesla Inc. is a private company that produces electric vehicles. Some worldwide plans were also developed, including:
- A wholly-owned subsidiary: Tesla puts its customers’ pleasure and desires first at all times. This technique aids the organization in understanding its customers’ perspectives and developing innovations and technologies in response to the customers’ desire to skim off the top layer of new prospective consumers in the industry(Giacobbe al. 2016).
- Exporting: Tesla sells its products worldwide to suit the needs of its consumers.
- Strategic Partnership: To extend its business abroad, Tesla believes in a collaborative method (Sarvaiya al.2018).
- An engineering firm in Germany: Panasonic is a global corporation that is now one of Tesla’s most prominent suppliers and Asia’s second-most valued technology business.
- Joint ventures: Tesla is active in several nations, including America, China, and others, through joint ventures.
Tesla’s Global Strategy’s goal:
Every firm has a specific motivation for developing a new strategy, and for Tesla, the most important one was to expand globally. They also seek to boost their profit margins and expand their consumer base globally (Bilbeisi and Kesse, 2017). Expansion on a global scale gives the organization a new chance to expand into new areas and capture previously untapped prospective clients in developing nations. The corporation may also obtain them at cheap costs from other countries in terms of resources.
Tesla’s Recommendation:
- Tesla may also extend their company in established nations, providing them with a well-developed market, as well as the advantages of economic and political stability, as well as the necessary technical advancement (Du and Li, 2021)
- Companies may target developing-country markets since they have a lot of room to expand and pay whatever the corporation wants.
- Market penetration, market diversification, market development, and market expansion are all development and growth techniques the organization might use. These methods will aid the company’s global expansion, and a market diversification plan will assist them in attracting new customers (Saxena and Vibhandik, 2021).
- Tesla may also strengthen their customer satisfaction process to make it more consumer-friendly, which will allow them to build more inventive and technologically advanced goods based on the needs of its customers.
- The corporation may launch a new division aimed at budget-conscious customers in their automotive product range. To date, the business has only released high-end vehicles with cutting-edge technology and cutting-edge features. They are still out of reach for the majority of market customers.
Task 3:
Benefits and risks are associated with vertical and horizontal integration schemes. These integration plans are also dependent on the corporate level strategy of the particular firm, which can be summarised as follows:
Vertical Integration:
Vertical integration refers to acquiring other firms inside one’s supply chain to strengthen the company and save costs. Instead of outsourcing the production process, this integration brings it in-house. Backward integration occurs when a corporation buys a company that gives raw materials to the enterprise (Jewell et. al. 2019). In the case of Tesla, they are well-versed in their supply chain, and they primarily engage in vertical integration and produce novel goods within their organization. Tesla has recently merged vertical chains like battery manufacturing, electric motor manufacturing, and a sophisticated central control system. The corporation mainly uses this method to boost profits and lower manufacturing costs.
Horizontal integration:
Horizontal integration strategy refers to a process in which a firm buys a competing company to access its market, grow its client base, and boost profitability. In the case of Tesla, vertical integration is emphasized to support the company’s sourcing (Pérez-Lara et. al. 2020).
Corporate strategy suggestion (Tesla Inc.)
Tesla is now mainly focused on vertical integration, and profiting from this won’t be easy. To prevent the disappointment, they experienced in the Chinese market, they must develop new techniques to capture the market more slowly (Hoelzlhammer, 2018). A might also prioritize a company’s development.
Task 4:
Carroll’s Pyramid:
Carroll’s pyramid model’s primary objective is to examine why and how a firm engages in corporate social responsibility. The mentioned pyramid of CSR forms to be a basic structure that formulates an argument stating the reason for which a business enterprise should come forward to accomplish their social obligations. The creator of the said pyramid emphasized on four basic responsibilities of the organization that is economic, legal, ethical, and discretionary or philanthropic responsibilities (Carroll, 2016). Thus, Carroll’s pyramid model is taken under consideration for analyzing Tesla’s Corporate Social Responsibility strategies:
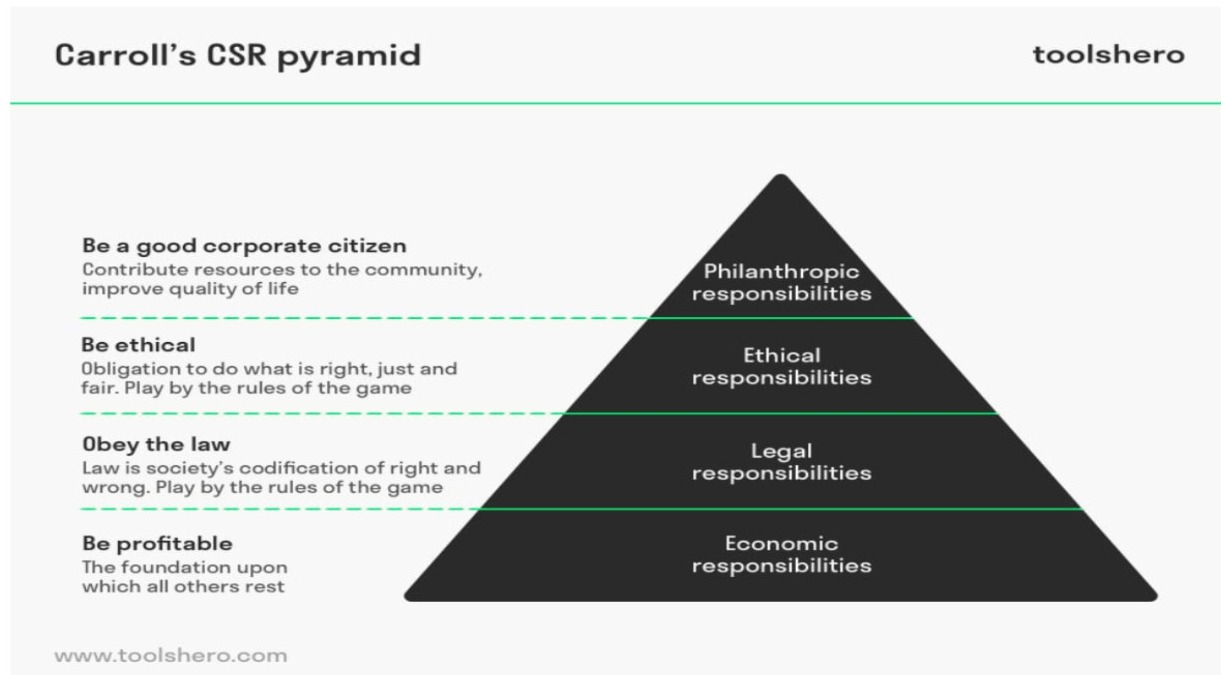
Figure 1: Carroll’s CSR Pyramid
(Source: Janse, 2020)
Philanthropic responsibility
Philanthropy is at the top of the pyramid, taking up the most delicate spaces.The stated firm is mainly dedicated to safeguarding the environment, as seen by the case study. As a result, they create their goods and earn revenues utilizing sustainable and environmentally friendly raw materials and energy sources to better the environment and community. They also set out to lower their carbon footprints and dangerous gas emissions in their plants.
Ethical responsibility
Doing the right thing, being fair in all situations, and avoiding damage are examples of the pyramid’s ethical layer.Transparent and appropriate legal processes are encouraged at Tesla, and the company is dedicated to upholding the industry’s ethical standards.Aside from that, its management actively involves its executives in the implementation and development of their plans and decision-making to ensure that they are reliable and loyal. According to the case study, the corporation also established and embraced an ethical corporate culture.
Legal responsibility:
The legal responsibility of the business to follow the law is the pyramid’s second level.Fair laws and legislation are being practised in Tesla, as evidenced by the case study. When a firm begins operations in a new nation, it pays close attention to the host country’s laws, rules, and regulations. It adheres to them to conduct business without interruption.According to the case study, the legal considerations that impact Tesla include equality and pay, as well as the safety and health of the company’s personnel.
Economic responsibility:
The bottom of the pyramid shows a company’s primary responsibility to make money.This component is concerned with an organization’s commitment to profit to ensure its long-term existence in the industry. As a result, according to the case study, Tesla began developing electric automobiles that made the most use of environmentally beneficial materials to maximize revenues from the idea. They also contribute to society’s economic progress by providing a variety of work possibilities, one of the company’s primary obligations.
Tesla’s ethical problems:
- Employee regulation:
- Workplace safety: Following then, a recorded a considerable number of injuries regularly (Beus al.2016). Tesla has received several accusations alleging discrimination and workplace harassment. According to one former employee, Tesla’s work climate is highly racist.
- Health Safety: Organizations’ primary focus in 2017 was safety and health. As a result, according to the case study, Tesla was unable to offer adequate working conditions for its employees, resulting in identifying health-related symptoms such as chest discomfort, irregular breathing, and fainting. It raises issues about the organization’s safety concerns among its personnel.
As a result, it is suggested that the firm examine its health and safety regulations and improve them. And put them in place with more zeal and staff assistance.
- False and misleading statements
Following the firm’s health and safety difficulties in 2017, the corporation was chastised for making false and deceptive statements about its three automobile models. Even though the factory audit resulted in a win for Tesla in 2019, the claims against them are dismissed. The litigation, however, significantly affected the company’s public image (Bruijl, 2018).
Recommendation:
Tesla has a unique suggestion method that has gotten the firm to where it is now. It’s one of the most well-known firms on the planet, and it’s doing well right now. In this scenario, it should maintain its accounting and financial accounts. Furthermore, the company must prevent incidents that harm its reputation and image in the marketplace.
Conclusion:
It can be inferred from the preceding study that an examination of a company’s internal and external environment is critical in developing global growth plans and identifying the company’s strengths, competencies, opportunities, and threats. Porter’s five forces analysis, value chain analysis, PESTEL analysis, and VRIO analysis may be used to create these strategies successfully. The study details and describes Tesla’s business strategy, worldwide environment plan, and CSR practices. There are also some suggestions for the company’s long-term growth and development.
References
Alghalith, N., (2018). Tesla: innovation with information technology. International Journal of Business Research and Information Technology, 5(1), pp.37-51.
Beus, J.M., McCord, M.A. and Zohar, D., (2016). Workplace safety: A review and research synthesis. Organizational psychology review, 6(4), pp.352-381.
Bilbeisi, K.M. and Kesse, M., (2017). Tesla: A successful entrepreneurship strategy. Morrow, GA: Clayton State University.
Bruijl, G.H.T., (2018). The relevance of Porter’s five forces in today’s innovative and changing business environment. Available at SSRN 3192207.
Carroll, A.B., (2016). Carroll’s pyramid of CSR: taking another look. International journal of corporate social responsibility, 1(1), pp.1-8.
Du, X. and Li, B., (2021), December. Analysis of Tesla’s Marketing Strategy in China. In 2021 3rd International Conference on Economic Management and Cultural Industry (ICEMCI 2021) (pp. 1679-1687). Atlantis Press.
Giacobbe, F., Matolcsy, Z. and Wakefield, J., (2016). An investigation of wholly‐owned foreign subsidiary control through transaction cost economics theory. Accounting & Finance, 56(4), pp.1041-1070.
Guangul, F.M. and Chala, G.T., (2019), January. Solar energy as a renewable energy source: SWOT analysis. In 2019 4th MEC international conference on big data and smart city (ICBDSC) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
Gudz, Y.F., (2015). FEATURES OF USING THE VRIO-ANALYSIS FOR ASSESS THE ECONOMIC POTENTIAL OF FOOD COMPANIES. The Genesis of Genius, 1(2), pp.55-59
Hernández, J.G.V. and Garcia, F.C., (2018). The link between a firm s internal characteristics and performance: GPTW & VRIO dimension analysis. Revista de Administração IMED, 8(2), pp.222-235.
Hoelzlhammer, A., 2018. A Strategic Audit of Tesla.
Indartono, S. and Wibowo, F.W., (2017). VRIO and THES based development of university competitive advantage model in formulating university strategic plan. International Information Institute (Tokyo). Information, 20(10A), pp.7275-7283.
Janse, B. (2020). Carroll’s CSR pyramid. [Online]. Accessed from: https://www.toolshero.com/strategy/carroll-csr-pyramid/. Accessed on: 13th January 2022.
Jewell, J.J., Rivas, J.A. and Mankin, J.A., (2019). Tesla: Is the Market Efficiently Pricing or Efficiently Excited?. Journal of Critical Incidents, pp.NA-NA.
Kaletnik, G. and Lutkovska, S., (2020). Innovative Environmental Strategy for Sustainable Development. European Journal of Sustainable Development, 9(2), pp.89-89.
Kowalska-Pyzalska, A., Kott, J. and Kott, M., (2020). Why Polish market of alternative fuel vehicles (AFVs) is the smallest in Europe? SWOT analysis of opportunities and threats. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 133, p.110076.
Matthews, T., Hirve, M., Pan, Y., Dang, D., Rawar, E. and Daim, T.U., (2020). Tesla Energy. In Innovation Management in the Intelligent World (pp. 233-249). Springer, Cham.
Mo, F. and Wang, Y., (2021). Risk and Opportunity Analysis of Tesla Motors Inc. Marketing Strategy and Business Ethics Study:–A Mini-Review. BCP Business & Management, 13, pp.440-449.
Moritz, M., Redlich, T., Krenz, P., Buxbaum-Conradi, S. and Wulfsberg, J.P., (2015), August. Tesla Motors, Inc.: Pioneer towards a new strategic approach in the automobile industry along the open-source movement?. In 2015 Portland International Conference on Management of Engineering and Technology (PICMET) (pp. 85-92). IEEE.
Namugenyi, C., Nimmagadda, S.L. and Reiners, T., (2019). Design a SWOT analysis model and its evaluation in diverse digital business ecosystem contexts. Procedia Computer Science, 159, pp.1145-1154.
ökdeniz, İ., Kartal, C. and Kömürcü, K., (2017). Strategic assessment based on 7S McKinsey model for a business by using analytic network process (ANP). International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 7(6), pp.2222-6990.
Pérez-Lara, M., Saucedo-Martínez, J.A., Marmolejo-Saucedo, J.A., Salais-Fierro, T.E. and Vasant, P., (2020). Vertical and horizontal integration systems in Industry 4.0. Wireless Networks, 26(7), pp.4767-4775.
Pillai, R.M. and Fazio, L.K., (2021). The effects of repeating false and misleading information on belief. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Cognitive Science, 12(6), p.e1573.
Sarvaiya, H., Eweje, G. and Arrowsmith, J., (2018). The roles of HRM in CSR: strategic partnership or operational support?. Journal of Business Ethics, 153(3), pp.825-837.
Saxena, N. and Vibhandik, S., (2021). Tesla’s Competitive Strategies and Emerging Markets Challenges. IUP Journal of Brand Management, 18(3).
Stamatović, M., Jovičić, A. and Parojčić, D., (2020). CUSTOMIZATION–INNOVATION WHEN OFF-THE-SHELF IS OUT OF THE QUESTION. Facta Universitatis, Series: Economics and Organization, pp.141-155.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

