HI6005 Management and Organisations in a Global Environment Assignment Sample
Here’s the best sample of HI6005 Management and Organisations in a Global Environment Assignment, written by the expert.
Introduction
Globalisation is a common term in today’s society that indicates the cross cultural activities, mixing up with others and witnessing others’ cultures. This assignment discusses on the globalization from different aspects as well. It includes different theories and the weekly activities have been narrated here.
Week 1 –
Q1. Would workers in Australia, America or Europe accept the Taylorism in this form today?
According to me, Taylorism will not be accepted in this form by the workers in Australia, America or Europe because their process of scientific management involves less efficient employees. The concept and the study of Taylorism are demeaning to the employees who have less knowledge regarding the work.
Q2. Consider the design of scripts for use in Call Centre’s, can you see Taylorism in that? Explain.
Most of the time the scripts used in the Call Centers are pre-designed according to the customer’s response. The scripts have predetermined answers to the communication. Yes, there is Taylorism in the work processes of the Call Centers. The scripts determine that the employees of the Call Centre do not have the ready know-how knowledge of responding to the customer. The workers are not ready and proactive enough to face the customer’s query, which means they cannot provide effective response n time.
Q3. This clip is showing history from 100 years ago. Some would say that “the world has moved on” and these ideas are out of date. However could there be parts of the world today for which these ideas might be just what they need? Explain
There are ideas which are still being used around the world by different societies and organizations such as Mercedes, Audi, and Ford. These companies applied the concept of assembly line aligned with the scientific management of the workers by reducing the quantity of the individual work. This resulted in mass production under low cost. The production line was speeding up.
Week 2 –
Activity 1 –Thomas Friedman on globalization; 3 Eras of Globalisation; World is flat.
Q1. What would be some of the key drawbacks or risks of living in the flat world of globalisation 3.0 as Friedman describes it?
Friedman indicated two trends – adoption of increased collaborative business systems and the increased number of Indian and Chinese consumers in the global market. According to him, the Flat world is the platform without any barriers for the increasing demographics, no barriers in the communication process and here the collaborative business process is carried across the boundaries. But there disadvantages in living in this version of Globalisation 3.0 (Cerny and Prichard, 2017).
- Business ethics tend to decrease the independence of the business organization. Interdependence tends to cause friction between the business organizations
- Different people tend to think differently
- Globalisation business negatively impacts small institutions by initiating their own regulations and rules thus making them abide by the regulations for the services and product
Q2. Do you agree with Friedman’s iron rule of the flat world? Explain.
It can be agreed with Friedman that the word is flat and according to him “when the world is flat, whatever can be done will be done” which signifies that things can be progressed with one’s self-help or to get things done you will see to someone for the help. He also explains that business competition is no longer a competition between countries or between companies, thus indicating that the competition is levelling up. In his writing, he also says that there will be two types of countries heading, “High imagination enabling countries and low imagination enabling countries. He also signified the importance of the liberal arts subject such as, humanities, history, and literature that explain the history behind the rise of globalization (Krugman, 2017).
Q3. Is the level of globalisation uniform across the world? Explain.
Globalisation is different due to the difference present in the cultural values. Cultural value differs across nations, organization, regions etc. Giant conglomerates such as KFC, Hindustan Lever, Procter & Gamble are present everywhere but it does not allow the consumers to adopt the same cultural value. Cultural values create the perception about the product or service for the consumers to accept the product or services. Due to the difference in the cultural values, the companies enhance product quality so that their products can be successfully accepted (Giudici and Rolbina, 2018).
Activity 2: Pankaj Ghemawat on Globalization.
Q1. Has your view on globalisation changed after listening to Professor Ghemawat? Explain.
According to Professor Ghemawat, the world is not flat. He explains that we have failed to reach a satisfactory standard of integration. He wants others to compare the activities occurring domestically or across the borders and the activities occurring in cross-border as the total percentage. The differences are huge and orders or boundaries is a matter of great significance in this changing world (Zell, 2018). He provided the proof with examples saying that record of telephonic data, when identified and compared between imagining globalization vs. actual, showed the huge difference. The difference between the quantities of international phone records to the actual quantity was only 2%, the number is much less than what it was expected. The survey regarding the foreign direct investment and the immigrants of the first generation highlighted the optimistic viewpoint for the Ghemawat globalization.
Week: 4: Activity: 2:
Q1. In what ways do you think innovative culture is related to (agile) organizational structure?
An organization is termed as agile that has a multi-dimensional strategy in the competitive business environment. The organization should be capable to make custom products during short run production, able to meet instant demand need in the same line of the production. An agile organization should be able to do so all these things in short duration and in low cost without hampering the quality standards of the product (Jonas et al. 2018). The production might be located in any international location extern or internal within the source of an organization. Knowledge source is the important apex group that commands, controls and manages the communication process of the organization. The system acts as the backbone of the organization making it capable to face the competitive forces of the global market.
Innovative culture leads to the transformation of a business organization from one form to another and it requires senior management’s leadership direction and the organization should be capable of innovating new business standards and creative ideas that will help the organization to thrive the competitive scenario.
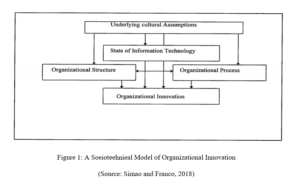
Organisational culture is dependent on the values that have been followed by the organization for a long time. Employees perform the task that has been allocated to them depending upon their specialized knowledge and ability to complete the task. Culture manifests an organization’s visions and mission statements which are the philosophy of an organization.
Innovation culture in an agile organization relates to the following:
- Achieving flexibility in the value chain related decisions in the organization.
- Information Technology boosts the flexibility in the organization’s activity.
- Inter corporate connections are mandatory to maintain and control the hold of itself within the electronic boundaries of commerce.
- The requirement of professionals with specialized knowledge is the organization promotes efficiency in the work process.
- Creative communication between systems, corporate entities, and systems enhance the competitiveness of the business organization.
Innovative ideas and decisions lead to better creating of strategy that will help the agile organizations to react proactively with different competitive global market forces (Zell, 2018). This will further help the organizational employees to work productively, efficiently and effectively maintaining all the organizational standards, thus maintaining the organizational values. Open system culture and flexibility will interconnect both the inter and intra technology of the agile organization thus creating an innovative organization.
There are several ways to initiate innovative culture within an organization:
- Organised and efficient teamwork in relation to the innovative ideas in the multi-dimensional organized company.
- Teamwork is necessary for achieving success. Communication feedback among the departmental employees must lead to decision making.
- Reducing the cultural differences to achieve outstanding performance in the activities of the organization.
Organisations adding innovative technology must have equally skilled professionals to process it flexibly across the organization’s pyramid.
Proper application of the above steps will help the company to gain an optimistic result. Moreover, an organization needs to be innovative to thrive in the global market forces (Simao and Franco, 2018).
Conclusion
Globalization is necessary for the large business conglomerates to survive in this era of innovation and disruptive technology. It comes with its drawbacks too. It is quite difficult to describe the uniformity of the globalization across the nations. Organizations need to reposition themselves with the changing innovation and technology. It demands its employees stay updated with all the skilled knowledge necessary for the organizations to make strategic decisions. An agile organization tends to capitalize on its past activities so that it can place successfully for achieving long-term objective or goals.
It is mandatory to maintain the healthy relationship between the organized structure and the innovative cultural practices for globalizing the business. The capacity of the business organization lies in the way how they implement the innovative technologies aligned with the organizational goals and objectives.
References
Cerny, P.G. and Prichard, A., 2017. The new anarchy: Globalisation and fragmentation in world politics. Journal of international political theory, 13(3), pp.378-394.
Jonas, J.M., Boha, J., Sörhammar, D. and Moeslein, K.M., 2018. Stakeholder engagement in intra-and inter-organizational innovation: Exploring antecedents of engagement in service ecosystems. Journal of Service Management.
Krugman, P., 2017. Crises: The price of globalisation?. In Economics of Globalisation (pp. 31-50). Routledge.
Simao, L. and Franco, M., 2018. Understanding the Influence of R&D Collaboration on Organizational Innovation: Empirical Evidences. International Journal of Applied Behavioral Economics (IJABE), 7(3), pp.54-73.
Zell, D., 2018. Changing by design: Organizational innovation at Hewlett-Packard. Cornell University Press.
_______________________________________________________________________________
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

