KF7031 Wireless Networks and Security Assignment Sample
802.11 WLAN data throughput and security overheads
Abstract
These projects mainly focus on the objective to analyze the wireless LAN 802.11 data throughput rate, security concerns and the other overheads that are included due to the security protocol that is applied. At present use of WLAN is increasing and it use can be commonly seen in colleges, organization and even in public places and residential area. The vulnerabilities in the network has also been increasing due to the increased and are various attacks are raised against these network and the main aim of these attacks are the data thefts. To protect the data from the vulnerabilities and to identify various threats necessary countermeasures to the various security challenges and issues. There are numerous protocols that are available to protect the data and provide security it depends upon the performance of the WLAN. The main challenge for the organization is to reduce the throughput delay and to reduce the overhead cost calculation that was incurred to protect the data. Some of the common IEEE standards in 802.11 family used for the development of WLAN of an organization are 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11ac, 802.11g, 802.11n etc. 802.11a is the IEEE standard protocol that provide security standard for WEP the performance, its throughput and the overhead involved is analyzed in this paper. The analysis is done using both the theoretical and implementation methods. For calculating the overhead the MAC and PHY layer overheads should also be included with varying data rate. Execution of the process should be carefully implemented while including the MAC frame which consists of PHY/MAC. The evaluation of the protocol should is done using various the data rate 5 Mbps and 11 Mbps. While calculating the throughput delay the overhead of UDP and TCP should be included. For the implementation of the protocol there are various networking tools that are available using which the transmission of packets can be analyzed.
Keywords: IEEE 802.1l, WEP protocol, MAC layer , PHY layer, Throughput, Security overhead
Introduction
The various security related vulnerabilities that affect the performance of the network and to prevent the vulnerability security measures are taken to protect the data. Calculation of the throughput overhead of 802.11b is analyzed in this paper. The analysis is done based on the various security issues that affect the overall throughput of the WLAN using 802.11b is done using the theoretical model and with an experimental model(Suroto, 2018). The theoretical model of the throughput is done based on the information collected using the IPERF and JPERF using the same data used for theoretical calculation the practical analysis is done. The most commonly used protocol in the wired network are Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) and WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) is the security protocol which is implemented to control the vulnerabilities in the WEP. Integrity check is included using the temporal key integrity protocol (TKIP) is used with the RC4 encryption for WPA (Jinji Zhang, 2020). The computational overhead should be included in the encryption and decryption algorithm (Ademola, 2018). To authenticate the messages that are passed a control message will be used along with the cryptographic overhead with the security protocol. There are various security protocols that are used in various layers in the network they are WEP, WPA2, IPSec, SSL, RADIUS etc to prevent the attacks.
Theoretical Frame work for Throughput(Ademola, 2018)
The throughput of a network is calculated based on the data that is passed through the network during a particular time frame. The amount of data transmitted may vary depending up on the transmission rate of the network. The throughput of a network TP can be calculated using the formula
TP=I /Tl(Px) – Tf (Px)
Here I denote the total volume of information that is being transferred between the sender and the receiver in the network. Tl(Px) denote the last packet and Tf (Px) denote the first packet while sending the information during the unit of time using the security protocol (Px)(Poonam Jindal, 2016). The response time of the network RT is said to be the total time that is required by the network to transfer the data stream from the source machine to the destination machine including the time taken to establish the connection and the security negotiation.
Experimental setup
The PC setup used for this analysis is shown in the below diagram. The OS used is a Linux and the servers and client are also Linux based. Here a single server is used to server both the clients (Alejandro Martinez, 2020). Based on the quality of the network the IPERF bandwidth is measured. The impact of the security is determined using the 802.11b WEP security protocol.
.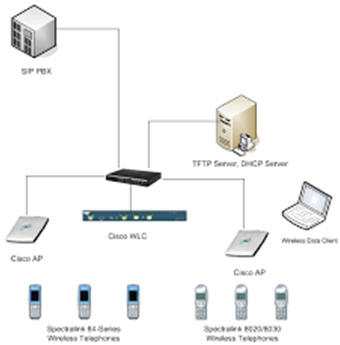
Using the above setup information is collected for comparison purpose. This network is executed five times using a bi-directional traffic which is executed with and without the security protocol WEP and the amount of data transmitted in the network is measured in Mbps and the average amount of data transferred is taken for the calculation in this paper. The table given below show the UDP and TCP value collected from the network setup with and without security protocol
| . Protocol | Item | No Security protocol | WEP security protocol |
| 802.11b | Average TCP | 4.41 | 3.79 |
| Average UDP | 9.28 | 9.21 |
There are four fields in the PHY header. The fields are listed below
- Signal
- Service
- Light
- CRC
The size of the PHY header is 48 bits
To calculate the MAC layer process and to predict the header type Wireshark packet analyzer is used
Wireshark packet analyzer is used for the calculation of the MAC layer process and predicting the header type
The overall throughput of the MAC layer with a payload of 1450 bytes is
Depending upon the various problems in the network and the metrics the performance may varies. A sample testbed is created to test and analyze the speed of the network using 802.11b which is integrated with direct sequence spread spectrum process
Simulation Result
From the simulation the throughput of the network using IEEE 802.11b protocol with and without security is compared and the result shows that performance with security is high when compared with the performance without security. The performance of the network throughput of 802.11b with average TCP and Average UDP of the information collected is shown in the below image.
Theoretical throughput value that was calculated using the formula was plotted in a graph which was shown in the below image. In the graph x axis is used to denote the payload on the network and the y axis is used to denote the data rate variation. There is a delay in the throughput when the payload is increased.
Discussion
Various combinations of protocols and different scenario are used to evaluate the protocol. The nodes in the network are created virtually. The performance of the WEP is taken by varying the size of the nodes. From the experiment we have identified that 802.11b provide a good security for the data against the various vulnerabilities which was created in the network and handled by 802.11b protocol (Saurabh Malgaonkar, 2017). But the overhead involved in implementing the 802.11b protocol which is included in the MAC layer and PHY layer is also included along with security overhead. A comparison of result is done before and after implementing the encryption protocol. The variation in the performance is having a huge variation. When the encrypted data is passed through the network it is difficult for the attackers to attack the encrypted data and the security protocol prevents the attacks.
Throughput of the network is calculated theoretical based on the time taken in sending and receiving the data from the sender to the receiver during a particular period of time. When compared with the PHY layer and MAC layer the data transferred through the MAC layer is high and the overhead of the MAC is calculated including the MAC frame overhead. The test is performed in congested and uncongested network traffic (A. Aneja, 2016).
Based on the analysis done on 802.11b theoretical and practical performance we can identify that there will be an increase in the rate of data transfer will affect the throughput. The delay in sending the packet through the network is due to the various vulnerabilities which can be overcome by implementing the MAC frame fragmentation (Hatm Alkadeki, 2015). The MAC protocol and the PHY protocol analysis is used to identify the relationship between the delay in the packet transmission rate and the throughput of the network. This is due to the increased overhead and the transmission of data vary when the security protocol is implemented due to which the overhead involved in the packet transmission is also increased.
Conclusion
The data transfer rate that is used to conduct this experiment on 802.11b WLAN network performance is based on 11 Mbps. The WEP protocol is used for the communicating between the client and the server. For security of the information being transferred WEP protocol is used. The implementation of the security protocol at MAC and PHY layer is included in the calculation of the overhead which provide a increased overhead of data transmission when compared with the overhead without security protocol. The transmission of bit rate will not affect the delay due to the encryption and decryption process involved in the data. The experiment done using the 802.11b protocol shows that it manages the various vulnerabilities that are created in the network. WEP protocol can be used to enhance the security level of the data but it will reduce the performance of the network.
Bibliography
- Aneja, G., 2016. A Study of Security Issues RElated with Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi). International Journal of Computer Science Trends and Technology .
Ademola, O., 2018. Imact of Wireless Security protocols on data throughput. Computing information systems, development infromatics & allied research journal, pp. 1-12.
Ademola, O. E., 2018. Impat of Wireless Security Protocols on Data Throughput. Computing, Information systems, development informatics & allied reserch journal, pp. 1-12.
Alejandro Martinez, E. C. J. R., 2020. Analysis of Low Cost Communication Technologies for V2I Applications. Applied Sciences, pp. 1-18.
Hatm Alkadeki, X. W. a. M. O., 2015. IMPROVING PERFORMANCE OF IEEE 802.11 BY A DYNAMIC CONTROL BACKOFF ALGORITHM UNDER. International Journal of Wireless & Mobile Networks (IJWMN), https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1601/1601.00122.pdf, p. 9.
Jinji Zhang, X. W. L. W. P. S., 2020. Experimental Study and Theoretical Verification of Explosion-Proof Performance of Insulated Glass. Shock and Vibration, pp. 1-6.
Poonam Jindal, B. S., 2016. Experimental Study to Analyze the Security Performance. Wireless pers communication.
Saurabh Malgaonkar, R. P. A. R. A. S., 2017. Research on Wi-Fi Security Protocols. International Journal of Computer Applications.
Suroto, 2018. WLAN Security: Threats and Countermeasures. International Journal on Informatics Visualization.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

