LD7160 Assignment Sample – Managing Programmes and Projects 2022
Introduction
Fukushima is a nuclear power station in Japan. It was developed with the motive to supply electricity to the nation. However, the Tsunami made water contaminated by radioactive materials. The cleaning up disaster was funded by BBSRC and NERC. Recently, by obtaining the idea and technology, which the UK has been applying to remove impurities from the environment by using bacteria that produce minerals namely, hydroxyapatite that captures radioactive components from the environment is on the way (Drmkc.jrc.ec.europa.eu, 2021).
In the comparative application of these bacteria, it is found to be more effective than any other measures. In 2011, on 11 March, Tsunami occurred with a magnitude of 9 and caused damage to the station. Major challenges were faced by Tepco who is an electricity company used to manage this site. Tepco was used to decontaminate the seawater adjacent to harbour at any water before releasing into the environment.
The disaster made the power station ruined at large. Tsunami stopped the power supply and damaged three cooling reactors. It happened that four reactors were totally damaged. The first measure was taken to prevent radioactive materials from being wasted. No deaths were found due to damage to the power station but for preventive measures 10,000 individuals were evacuated for safety. In addition, 19,500 individuals were found to be killed due to the Tsunami.
As Tepco has close contact with the power station. It can be understood that the power station disaster had a great impact on the economy, environment and politically (Drmkc.jrc.ec.europa.eu, 2021). Technology hampered four cooling reactors of the power plant. Environmental leakage of contaminated water took place. In addition, three employees died in the power station. Official suit of the power plant was announced in December.
It is estimated that despite being a developed country, the infrastructure and facility is lacking to initiate the flow of development in the current era. Fukushima is a well known example of disaster in Japan (Bachev, 2021). The disaster not only led to several issues such leakage of contamination water, fire, explosion and many more but also detrimental to society.
Thus, an effort is made to highlight the situation of recent measures in Japan in terms of the Fukushima clean-up disaster. The conducted study will be discussing the scope and scale inhibited in destruction and impact of disaster in surroundings locally and worldwide. A critical discussion will be made on huge international issues associated to Nuclear power plant decommissioning and its related infrastructure.
The project was undertaken with the objective of controlling and handling such complex situations. In the discussion, analysis is made on cleaning up the locations and radioactive material waste management. A deep analysis is made on how Tepco is involved in this scenario (Drmkc.jrc.ec.europa.eu, 2021). TEPCO programmes and measures have been shown in this study.
Detailed Analysis of the Management of the Project
The Fukushima accident was the second-worst nuclear accident that has been caused in the history of nuclear power generation. However, TEPCO officials have significantly reported that tsunami waves were generated by the mainshock of the Japan earthquake that has significantly damaged the backup generators at the Fukushima Daiichi plant.
On the other hand, money three reactors that were operating were further successfully shut down (Pub.iaea.org. 2021). Additionally, the loss of power has caused the cooling system to fail within the first few days of the disaster.
It can be assumed that the project could have been managed significantly so that it could overcome the consequences of the disaster that has taken place. The project manager with the organizational skill, analytical mind as well as with their interpersonal abilities must be considered to achieve the project progress.
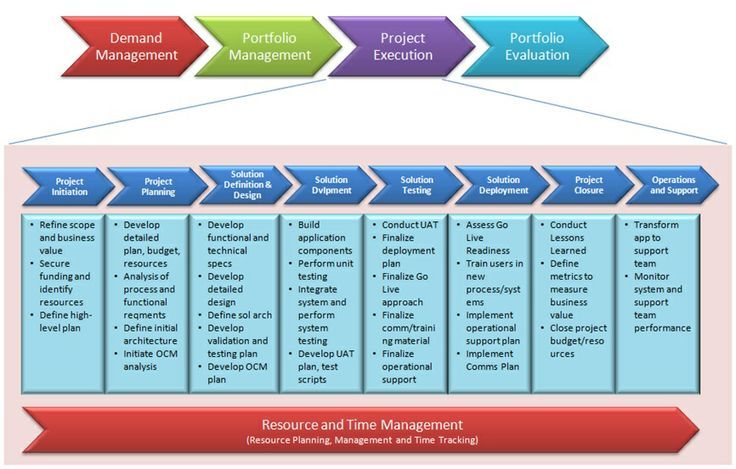
PMBOK that stands for Project Management Body of Knowledge is the entire process collection and the significant practices that are accepted as a standard within the project management industry (Bachev, 2021). Therefore, Fukushima must have initiated such practices through its different sections in order to achieve specific needs as well as to prevent any project failure that is witnessed in this situation.
The Great East Japan Earthquake occurred in March 2011. It was due to the sudden release of energy at the interface where it was further seen that the Pacific tectonic plate is forced it is way under the North American tectonic plate. Thus, it has shaken the structure of the plant, its system as well as its components (Yamaguchi et al. 2017).
The recorded waves of the tsunami have exceeded the assumptions of hazards that were developed while the plant was significantly designed. The project was mainly constructed on the seismic hazards as well as tsunami waves, which was designed on the basic historical seismic records. Therefore, the project lacked to record any tectonic geological criteria, whereas there was also no re-evaluation on such criteria. However, Fukushima Prefecture is not considered to be the significant one by Japanese scientists.
It has further highlighted the vulnerabilities of Fukushima Daiichi to the nuclear power plant, as the project seems to have failed in reassessing the external hazards in a systematic as well as comprehensive manner.
The incident that had taken place in Fukushima Nuclear Power Station was caused due to the loss of reactor core cooling function as well as the loss of Alternate Current and the Direct Current. The challenges were being faced by Japanese electricity company TEPCO who were able to manage the site. It has further included decontamination of seawater into the adjacent harbour (Tepco.co.jp. 2021).
Additionally, to manage the crisis, the research has been conducted with the help of an interdisciplinary team belonging to the University of Birmingham as well as the collaborators who belong to the Japanese Atomic Energy Agency.
Furthermore, the reactor has been proved to be robust seismically, whereas it was vulnerable to tsunami. However, due to the lack of project management, the infrastructure was not maintained significantly.
The three different units were unable to maintain any reactor cooling as well as water circulation functioning. On the other hand, the electrical switchgear was not working appropriately (Oecd-nea.org, 2021). However, the military personnel and firefighters significantly supported TEPCO employees.
However, the implementation as well as the arrangements to ensure the worker’s protection against any radiation exposure, has been severely affected by the mismanagement at the site. In order to protect the emergency worker, a wider range of impromptu measures must be considered (Yamaguchi et al. 2017).
In order to manage the infrastructural issues by the project management team, a significant emergency worker must be designed along with providing them with adequate training at the border to protect them at the time of emergency (Bachev, 2021).
Furthermore, TEPCO has also developed a probabilistic safety assessment that did not consider any internal flooding or even fires as well as assumptions in respect to the operator’s actions were mostly optimistic.
Furthermore, the accident management guidance in respect to Fukushima Daiichi NPP has significantly compromised with relevant documentation that can be used by the operators that also includes emergency operating procedures as well as the server accident management guidelines.
Technical understanding is the most important aspect of project management that seems to be lacking by the project managers. On the other hand, it is further the basis of measures that must be considered in order to improve the safety of the power plant station (Ayoub et al. 2021).
The Fukushima Daiichi were mainly decommissioned; thus, the project would have required a more relevant understanding of the relevant specifics of the accident in respect to the accident progress that can efficiently manage the scientific knowledge base.
The failure of the project was mainly due to reason of miscommunication among the project management team as it is seen that Fukushima has provided its operators with less indication in respect to the actual plant condition. Therefore, the reason for the loss of the instrumentation as well as the control system has affected in preventing the severe accident or even failed to mitigate the consequences (Bachev, 2021).
Therefore the control system must be defined according to the design of the power plant as well as including spent fuel pool. Thus the management team must have ensured that the systems are protected so that they can be used whenever required. Therefore, the management must have endured the appropriate process management tool to enhance its strategies that further allow control of any vital project management.
Critical Evaluation of the Management of the Project
It is undeniable that project management is important for the success of aims and objectives. It is assumed that Tsunami is common in Japan, thus, it becomes necessary for the country to undertake a project to fight with such uncertainties. For managing the project or undertaking the Fukushima clean up disaster, project management is necessary if again the Tsunami occurs measures would be taken (Tepco.co.jp, 2021).
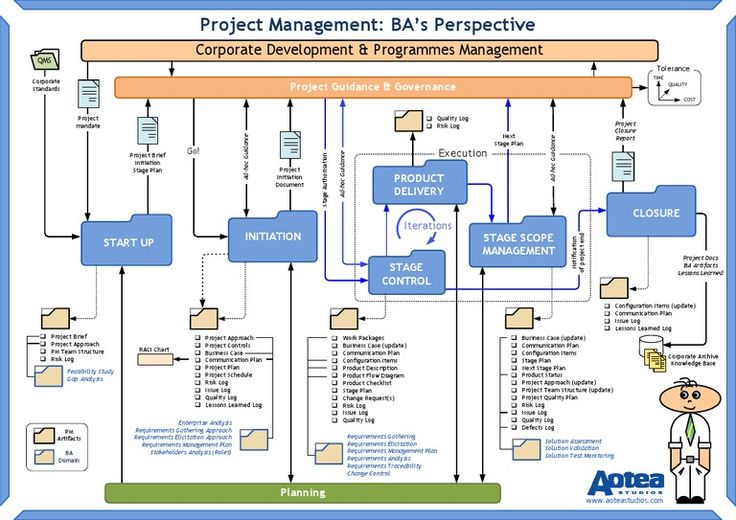
For managing the project the role of project manager is very crucial, he is held with strong responsibilities. In addition, time is important to be handled and make the accomplishment of the project on time. For managing the disaster, TEPCO had categorised the project into 5 stages
Project initiation
It is determined as the first stage in project management where aspects such as feasibility, value and probability of accomplishing the project is determined. Manager is the potential responsible for performing and discharging its responsibilities; here it decides what is needed and what must be done to achieve the objective (Tepco.co.jp, 2021).
For initiation, the project manager has determined two aspects of the activity: firstly, the Tsunami and considering measures for preventing damages occur in power plants.
Project planning
Project manager in this step plans the activities, which will be taken for the project. He engages the all team members and divides all the work accordingly. The project manager Shinichiro Kengaku was able to decide and took necessary action for this project. He was held to collect resources and all the material for project management (Tepco.co.jp, 2021).
Project execution
In this stage, the project manager led to execute the planning made for the project. This is the third stage of project management. Under Tepco management it is concerned with the arranging essential deliverables for fulfilling the customers (Tepco.co.jp, 2021). It is estimated that due to the occurrence of the Tsunami many sites get disrupted. It is engaged in making the project so effective that natural disasters have less impact on the environment.
Project monitoring
Under Tepco management, it is important for this company to have proper monitoring over the project. It undertakes resources and labour are well placed and organised. In addition it foresees the team members’ engagement (World-nuclear-news.org, 2021).
For making project management effective it has taken necessary strategies. It brought agility and activity for the team members to act faster in achieving the goal. In addition, the management had actively reviewed the engagement and team work deliverables with the passage of time and tok necessary action by keeping regular track on the work performed.
Project closing
This is the last stage where all actions are delivered and expect for profit to be received. Under Tepco management, this is made by accepting and executing work done and expecting loyalty from the environment (Tepco.co.jp, 2021). It is undeniable that Tepco has managed doing programmes and measures by suggesting tools to be implemented on the site.
Project cost management
This is the crucial stage where the management system holds. It is undeniable that the cost decides whether the project will be initiated or not. The government had increased the cost estimation for cleaning up disaster by around $75.7 billion from the real price tag of $202.5 billion.
Tepco has indicated that it will take around 3-4 decades of efficient management, government measures and execution. It had undertaken the observation that technology is comparatively very ancient for safety measures (Tepco.co.jp, 2021). It indicated the importance of flood management systems to be designed in such a way that it will avoid issues such as Tsunami.
Integration and change management
Integration is an important part of project management as changes are made according to planning. Management in cleaning up the disaster is important for this project. 30% of electricity is supplied from the nuclear power plant. The government has shut the supply of nuclear power until Fukushima is recovered.
The main motive of the project is to resolve all the damages made to the reactor of Fukushima and make it ready to supply (Tepco.co.jp, 2021). The integration of the resources and funding is developed that will be put in the process of recovery. Moreover, risk associated with the project will be removed by undertaking change management approaches.
Leadership and team development
Leadership is important for the project to be effective. Leadership is responsible for strong team building and accomplishment of projects. The Tepco, who had undertaken the responsibilities for cleaning up the disaster is of great importance. It is important for the Tepco management under the leadership of Shinichiro Kengaku, the company is well developed and managed by cold shut off of the site and remote-controlled robots to the site so that uranium melted fuel can be found to stop the disaster (Tepco.co.jp, 2021).
Under the leadership of Shinichiro Kengaku, the company had integrated and installed the emergency generator into the site. Under this, they were able to manage the damage that occurred in the place. Moreover, Tepco was able to restore the automated cooling system within damaged reactors and manage everything on time for six months.
Communication
Having a well defined team in Tepco, it has led the communication flow smoother by adopting all forms of communication mode. Tepco decided to unveil each and every part of issues to all individuals in the department so that measures could be taken. It took out the venture of having a communication channel set such as horizontal and vertical form of communication. It is undeniable how the earthquake has cut the line of power supply in Japan (Tepco.co.jp, 2021).
It led to the emergence of the emergency generator to be used in times of needs. The power failure had disabled the pumps which used to be circulating cooling water. As the reactor negatively works when overheated, it starts to melt and a fire explosion takes place. It has damaged the three floors of the building. It is evident that the four reactors were severely damaged.
It is estimated that Tepco employees remained on site to stabilize the power plant and began with clean up.
In 2011, the major challenges which the Tepco faced was that the filtering system exceeded its target; it was touched to 90%. It was the first time the system became intolerant.85,000 tons were found to be decontaminated and around 10,000 tons of radioactive material were left to be treated (Tepco.co.jp, 2021).
The nuclear waste product generated through filters was already used upto 70%. At that time Tepco, intelligently figured out the way of cooling the reactor to avoid the damages done by Tsunami. Tepco had decided to prevent heat damage by injecting cooling waters to the reactors. Fukushima had many seawater piping trenches and Tepco tried to remove the accumulated water from those trenches.
It is found that a major part of Northern Japan is recovering from the Tsunami disaster and there is no doubt that Fukushima is just at the initial stage of its process. The project is taken for recovery and cleaning up are estimated to be time consuming and costly. It would need effective management and government support.
As per the Toshiba reactor maker, it has stated that decommissioning of the damaged occurred in Fukushima will take 10 years for cleaning up. However, it is more than that. Different agencies have estimated different costs in recovering the damages (Tepco.co.jp, 2021). Prime minister estimated a cost of 1 yen trillion. In 2016, the cost for recovery was estimated by the Ministry of Economy and Ministry of Trade and Industry to be the cost of 21.5 trillion Yen. The cost is unbearable and needs many sources to be funded.
The Lesson Learned conception, initiation and management of the project
In 2011, the Fukushima disaster was caused due to the mismanagement of the Tokyo Electric Power company (TEPCO). Below is a detailed analysis of the commissioning of nuclear power plants, destruction of infrastructure, cleanup of the location and radioactive waste management.
Due to the nuclear accident in the power plant of Fukushima, a tsunami had taken place. It disabled the power supply of that area, and nuclear power plants became obsolete (Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, 2021). All three units of the nuclear power plant became inactive within a few hours. Daini and Daichi, both of the two units, were highly affected by the tsunami.
Decommissioning of power plants means inactive power plant after completion of tenure of the power plant when the time given in the license is over. Before the earthquake, TEPCO authorities were so confident about the nuclear plants that they thought such a tsunami could not affect the power plant.
Such an assumption was not verified by the government or other authorities, and the Japanese government was not prepared for the fatal accident. Later, it was seen that the design in the plant structure of TEPCO was wrong. From the Fukushima accident, it can be said that when any authority is going to start a nuclear power plant, it needs to focus on the design first (HOLLNAGEL and FUJITA, 2021).
Then, it needs to be verified by the higher authority rather than self-verification. Due to pressure in the plant, area hydrogen explodes a lot which causes infrastructural damages. Besides, the equipment of the plants became obsolete, and many personnel were injured due to the eruption of toxic gases. Citizens within a radius of 25 km were evacuated from the power plant area.
However, the Fukushima Daini plant was not damaged in 2011, and TEPCO has announced plans to decommission the plant in 2018. TEPCO has submitted the report of decommissioning to the Nuclear Regulation Authority. It will take almost forty-four years to decommission the plant.
According to Tepco, authorities are concerned about radioactive waste (Federal Office for Radiation Protection, 2021). The NRA has approved of the decommissioning process and added that they would pay attention to the safety of the common people and workers.
The design of the nuclear power plant was ineffective, which was developed by TEPCO. Due to the hydrogen explosion, all the three plants became inactive, and equipment was damaged. The electricity supply was damaged, and many people died due to short-circuit. Many buildings were flooded with water.
The roads were damaged. It became a major problem for those who were trying to rescue the victims but could not reach them. The safety experts or the engineers were not aware of the safety of the common people and personnel of the power plant (World-nuclear.org. 2021).
The operating system was not running smoothly, and the authority was not giving attention to finding fault. Due to the huge damage to the infrastructure, many radioactive gases were released into the open air, and people were injured for that reason. Radiation levels in the whole area increased in the whole city.
The Fukushima accident was rated at the degree of 7 on the radiological event and international nuclear scale. Over 4-6 days, the continuous 940PBq (1-31) eq scale of radioactivity was noted to have disrupted around four Fukushima Daiichi reactors as a result (World-nuclear.org, 2021). This caused severe damage to the Tepco business as a result. Public health and the environment suffered a lot due to nuclear radiation.
According to the description studies, it is determined that the absence of preparation and poor communication were the main cause triggering the disaster. After the disaster of the tsunami, the incident turned into a nuclear accident at Japan’s Fukushima plant (World-nuclear.org, 2021). This was reported as the worst atomic crisis that took place in 25 years.
Massive damage to the people and overall infrastructure had occurred at that time. Evacuation and relocation have been done based on the safety of the people. It left an aftereffect on public health as well as on social and economic structure.
This causes a huge inclination on mortality rate. This also affects people mentally, psychologically and emotionally. A high rate of post-traumatic stress disorder has been noticed among the survivors (Federal Office for Radiation Protection, 2021). Due to the radiation, the risk of developing different kinds of cancer has increased among people.
No record of death has been mentioned, but more than 160 employees were completely affected due to the disaster. The health community of Japan works a lot to strengthen the public health facilities and make them suitable for the survivors. To minimize the risk, a specially trained specialist has worked on it to prevent further repetition.
The environmental implications were reported to be severely damaging the regions of Japan. The radiological conditions existing in Japan worsened. The radioactive fallout was reported over the land and sea by precipitation and wind (Federal Office for Radiation Protection, 2021). It is determined that the northwestern areas incurred a higher degree of contamination, mainly in the prefecture of Fukushima.
It is identified that the incurring hydrogen explosions caused by the tsunami and earthquake destroyed the reactor buildings at the Fukushima power plant. The foodstuffs were contaminated due to the radioactive materials that were mainly gathered on the leaves or directly over the agricultural products such as vegetables and fruits.
This way, the Fukushima accident contaminated the vegetable crops. This way, the accident created a lot of waste management issues (World-nuclear.org, 2021). The atmosphere was polluted, and water bodies were affected due to the radioactive materials.
Conclusion
Through the above discussion, it is evident that it is necessary to develop a significant model in order to cope up with the nuclear event. However, Fukushima is significantly affected by the tsunami due to the inappropriate project management team.
TEPCO’s intention was to ensure a systematic preparation in respect to smooth and regulatory review along with no reworking. Thus, it can provide safe work with no waste that would lead to a stable power supply. Hence, the counter measures to overcome such a situation in the future.
It is even necessary to ensure awareness in respect to the concerned parties. Hence, with effective management the consequences of natural disaster to turn out to be a manmade disaster can be overcome
The Fukushima accident or the Fukushima nuclear accident that took place in Japan has caused huge damage to the country. The occurrence of the tsunami created a big impact on the country from a different perspective. The increase of heat in the reactor’s core has made the fuel reactor 1,2 and 3 get overheated which leads to melting down and release of radiation. That created a
strong negative impact on the ground surface of the country. In March of 2011, three huge disasters took place together: tsunami, earthquake and Fukushima nuclear disaster. Few minutes back from the tsunami, they had no power supply available for people.
It can be concluded that the Tsunami had impacted the power supply of Japan. It affected the power station very badly. It had a large impact on the technological, environmental and many more. The conducted study has highlighted the measures and performance made by the Tepco. Firstly, it informed us that radioactive water had accumulated in unit 2 of the turbine building.
Later on the advice was given by the Nuclear Safety Commission to the Tepco to take all the measures to prevent the damages. It is undeniable that Tepco had announced roadmaps for the restoration of damages made by the Tsunami. The effective move of the Tepco was able to find the leakage pipeline where it was found that leakage could cause contamination of radioactive waste material to the seawater and it was sure to have the most polluted water.
However, the move taken by Tapco stops more leakage of waste material to the site. Moreover, the government of Japan introduced a policy to prevent groundwater from flowing from the reactor building. The issue was resolved by taking instant measure. On contrary, it is found that recovery and clean up will be made upto 30 to 40 years.
References
Ayoub, A., Stankovski, A., Kröger, W. and Sornette, D., 2021. Precursors and startling lessons: Statistical analysis of 1250 events with safety significance from the civil nuclear sector. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, p.107820.
Bachev, H., 2021. Agri-food Implications of Fukushima Nuclear Accident-Lesson Learned for Risk Managment (No. 5793). EasyChair.
Drmkc.jrc.ec.europa.eu. 2021. [online] Available at: <https://drmkc.jrc.ec.europa.eu/portals/0/Knowledge/ScienceforDRM2020/Files/supercasestudy_02.pdf> [Accessed 26 August 2021].
Federal Office for Radiation Protection. 2021. Environmental impact of the Fukushima accident: Radiological situation in Japan. [online] Available at: <https://www.bfs.de/EN/topics/ion/accident-management/emergency/fukushima/environmental-consequences.html> [Accessed 26 August 2021].
HOLLNAGEL, E. and FUJITA, Y., 2021. THE FUKUSHIMA DISASTER – SYSTEMIC FAILURES AS THE LACK OF RESILIENCE.
Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. 2021. Summary. [online] Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK253923/> [Accessed 26 August 2021].
Oecd-nea.org. 2021. [online] Available at: <https://www.oecd-nea.org/upload/docs/application/pdf/2021-03/fukushima_10_years_on.pdf> [Accessed 26 August 2021].
Pub.iaea.org. 2021. [online] Available at: <https://www-pub.iaea.org/mtcd/publications/pdf/pub1710-reportbythedg-web.pdf> [Accessed 26 August 2021].
Tepco.co.jp. 2021. [online] Available at: <https://www.tepco.co.jp/en/press/corp-com/release/betu12_e/images/120620e0104.pdf> [Accessed 26 August 2021].
Tepco.co.jp. 2021. [online] Available at: <https://www.tepco.co.jp/en/hd/newsroom/press/archives/2021/pdf/210222e0101.pdf> [Accessed 26 August 2021].
Tepco.co.jp. 2021. [online] Available at: <https://www.tepco.co.jp/en/press/corp-com/release/betu12_e/images/120620e0104.pdf> [Accessed 26 August 2021].
Tepco.co.jp. 2021. Business Risk | TEPCO. [online] Available at: <https://www.tepco.co.jp/en/hd/about/ir/management/risk-e.html> [Accessed 26 August 2021].
Tepco.co.jp. 2021. Management Policies | TEPCO. [online] Available at: <https://www.tepco.co.jp/en/hd/about/ir/management/index-e.html> [Accessed 26 August 2021].
Tepco.co.jp. 2021. Our Responsibilities to Fukushima | TEPCO. [online] Available at: <https://www.tepco.co.jp/en/hd/responsibility/index-e.html> [Accessed 26 August 2021].
Tepco.co.jp. 2021. TEPCO : Challenges of TEPCO | Management Commitment. [online] Available at: <https://www.tepco.co.jp/en/challenge/csr/introduction/management-e.html> [Accessed 26 August 2021].
Tepco.co.jp. 2021. TEPCO : Corporate Information | Profile / Leadership. [online] Available at: <https://www.tepco.co.jp/en/corpinfo/overview/p-leader-e.html> [Accessed 26 August 2021].
Tepco.co.jp. 2021. TEPCO : Plan & Action. [online] Available at: <https://www.tepco.co.jp/en/decommision/planaction/index-e.html> [Accessed 26 August 2021].
World-nuclear.org. 2021. Fukushima Daiichi Accident – World Nuclear Association. [online] Available at: <https://www.world-nuclear.org/information-library/safety-and-security/safety-of-plants/fukushima-daiichi-accident.aspx> [Accessed 26 August 2021].
World-nuclear-news.org. 2021. Tepco announces restructuring – World Nuclear News. [online] Available at: <https://www.world-nuclear-news.org/C-Tepco-announces-restructuring-1908154.html> [Accessed 26 August 2021].
Yamaguchi, A., Jang, S., Hida, K., Yamanaka, Y. and Narumiya, Y., 2017. Risk assessment strategy for decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power station. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 49(2), pp.442-449.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

