Assignment Sample on Leading in Complex Health Systems
Introduction
A Health System Map
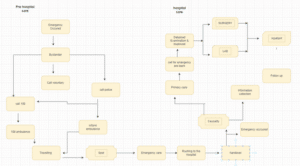
Figure1: Health System Map
(Influenced by Alanazi et al., 2021)
Commentary
The Health System Map displays the project’s execution strategy for decreasing missing medicine at an authorized hospital in Palakkad Kerala. The Health System map depicts the seamless coordination of pre-hospital and hospital care in order to provide comprehensive and efficient healthcare delivery. During the pre-hospital care phase, emergency medical services (EMS) and first responders provide immediate and life-saving assistance on-site or while transporting patients to medical facilities. Patients that arrive at hospitals are given specialized treatments, diagnostics, and medical attention by qualified healthcare personnel. The map emphasizes the crucial connections between these stages, stressing timely and accurate information transfer, simplified processes, and optimal resource allocation to improve patient outcomes and save lives. The objective of the endeavor is to create a reliable method for detecting medication-related disorders. SMART goals include identifying healthcare concerns, establishing a prescription reminder system, including tracking project progress (Oleribe et al., 2019). Team development involving specialists such as physicians, nurses, and occupational therapy professionals, as well as organizational management is part of the project. The importance of patients, health personnel, government, physicians, nurses, and pharmacies in the initiative’s success is highlighted via stakeholder analysis. The evaluation plan specifies project objectives, indicators, data-gathering techniques, and a project way out. The sustainable development strategy discusses prospective financing sources for guaranteeing the sustained viability of the project.
Critique: The Healthcare Systems Map gives a complete picture of the prescription drug adherence implementation strategy. It provides a well-organized strategy by outlining the major objectives, stakeholders, financing requirements, assessment methodologies, and long-term sustainability plan. The map, on the other hand, may benefit from having more explicit and verifiable indicators to measure development and achievement. Incorporating evaluations of risks and mitigation measures would also improve the plan’s thoroughness. The project might think about resolving possible issues with technology uptake, staff training, and particularly patient adherence to the medicine reminder system.
Annotated Bibliography
Greenhalgh, T. and Papoutsi, C., (2019). Spreading and scaling up innovation and improvement. Bmj, 365
The doctor is working in the surgery, and the nurse who oversees things in the hospital ward. There must be a policymaker within the boardroom who may easily lose sight of everyone the new technology, care routes and approaches to service that has the potential to improve the level of care, protection, and economic efficiency. Nonetheless, we acknowledge that regardless of whether there is compelling proof regarding their benefits, breakthroughs are rarely widely adopted. There are obvious reasons why disseminating an invention throughout an entire medical system is difficult. Any change requires effort and it generally means paying money, distracting personnel from their regular job, modifying strongly held culture or professional conventions, and taking hazards in different ways.
Crain, M.A., Bush, A.L., Hayanga, H., Boyle, A., Unger, M., Ellison, M. and Ellison, P., (2021). Healthcare leadership in the COVID-19 pandemic: from innovative preparation to evolutionary transformation. Journal of Healthcare Leadership, pp.199-207.
The goal of the present research was to examine the early construction, operation, and success of a COVID-19 executive team, as well as the change of healthcare facilities at West Virginia University’s Schools and Medical Center (WVUHS). The study looked at how Kotter’s leading transformation eight-stage model may help to comprehend the factors that influence efficient organizational transformation in the aftermath of the COVID-19 epidemic.
Executive Summary
The group management plan seeks to put in place a strong system to prevent skipped medicine events at a government-run medical Centre in Palakkad, Kerala. The fundamental goal of the work is to create a powerful system, which can detect and resolve concerns connected to missing medicine to improve patient welfare and security (Bryce et al., 2020). The proposed project adheres to SMART targets, which ensure that goals are clear, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound. The suggestion involves implementing a medication reminder system to help promote healthcare knowledge and enhance healthcare management to accomplish that goal. To promote effective teamwork and the treatment of patients, the project includes a multi-disciplinary group of doctors, nurses, occupational specialists, and management of organizational affairs. Patients, hospital employees, the government, physicians, nurses, along with pharmacists are among both outside and internal groups identified through stakeholder analysis. Proper interaction and synergy between the parties involved will be essential for the project’s success (Akinwale et al., 2020). The project’s finance requirements include personnel wages, training fees, equipment, servicing, and payments to medical providers. A comparison of costs and benefits and a health-benefit evaluation will be performed to assess the project’s economic viability and healthcare results.
PESTLE Analysis of the health management problem
The PESTLE analysis performed for the medical facility project within the state-owned hospital in Palakkad, Kerala, gives a complete review of external variables that may influence the project’s performance. It investigates the following factors: Social, technological, legal, political, and Environmental.
| Political | The project may have trouble due to government rules and restrictions. Nevertheless, it may profit from government assistance when it comes to money and healthcare industry investment.
|
| Economic | Funding becomes an important part of the undertaking, and the research highlights prospective opportunities for funding, such as NITI Ayog’s medical industry investment initiative, that can aid in financial endurance.
|
| Social | The project intends to solve the issue of missing medicine, a crucial healthcare barrier, and has the potential to significantly improve the welfare of patients and healthcare results. Implementing a medication reminder system is a technical breakthrough that can enhance healthcare efficiency along with patient care.
|
| Technological | On the basis of the health management evaluates the influence of technology breakthroughs and innovations on the healthcare business. This involves assessing how technology affects medical treatments, electronic health records, telemedicine, healthcare infrastructure, data management, and developing digital solutions, as well as how it shapes the future of healthcare delivery and patient outcomes. |
| Legal | On the basis of the maintain patient privacy and prevent legal concerns, the project must adhere to healthcare rules and data protection legislation.
|
| Environmental | Environmental elements are not explicitly addressed in the study, which might render them less significant in the wider context surrounding the healthcare initiative |
Root cause analysis of the problem using a Fishbone Diagram
|
Critical commentary
The objective of the Fishbone study focuses on discovering the fundamental causes of missed medicine concerns in a government-run hospital in Palakkad, Kerala. It thoroughly examines the numerous variables that contribute to the problem, such as communication, learning, and equipment (Tanwar et al., 2020). The investigation is well organized and gives a thorough grasp of possible reasons. It might, however, benefit from further development and validation using data and expertise to confirm the correctness of the identified reasons and their importance in effectively resolving the issue.
SWOT Analysis of the proposed innovation
| Strengths: The project’s goal is to create a robust system for detecting skipped medicine, which will involve a range of disciplines, analysis of stakeholders, and commitment to medical ethical norms. Proper financing and an evaluation of the costs and benefits are taken into account.
|
Weaknesses: There had been problems with scheduling and communication, which brought about last-minute rewrites. The undertaking’s sustainability strategy needs to be refined and future financing sources considered.
|
| Opportunities: The initiative corresponds with investment prospects in the country’s healthcare industry and the prescription reminding system has the potential to improve patient health.
|
Threats: The possibility of not attaining targeted results if effective interaction and preparation are not preserved across the project is one of the major hazards.
|
References:
Alanazi, F.K., Sim, J. and Lapkin, S., (2022). Systematic review: Nurses’ safety attitudes and their impact on patient outcomes in acute‐care hospitals. Nursing open, 9(1), pp.30-43.
Oleribe, O.O., Momoh, J., Uzochukwu, B.S., Mbofana, F., Adebiyi, A., Barbera, T., Williams, R. and Taylor-Robinson, S.D., 2019. Identifying key challenges facing healthcare systems in Africa and potential solutions. International journal of general medicine, pp.395-403.
Ramesh, T.R., Lilhore, U.K., Poongodi, M., Simaiya, S., Kaur, A. and Hamdi, M., 2022. Predictive analysis of heart diseases with machine learning approaches. Malaysian Journal of Computer Science, pp.132-148.
Bryce, C., Grimes, Z., Pujadas, E., Ahuja, S., Beasley, M.B., Albrecht, R., Hernandez, T., Stock, A., Zhao, Z., Rasheed, M.A. and Chen, J., 2020. Pathophysiology of SARS-CoV-2: targeting of endothelial cells renders a complex disease with thrombotic microangiopathy and aberrant immune response. The Mount Sinai COVID-19 autopsy experience. MedRxiv, pp.2020-05.
Tanwar, S., Parekh, K. and Evans, R., 2020. Blockchain-based electronic healthcare record system for healthcare 4.0 applications. Journal of Information Security and Applications, 50, p.102407.
Pérez‐Escamilla, R., Cunningham, K. and Moran, V.H., 2020. COVID‐19 and maternal and child food and nutrition insecurity: a complex syndemic. Maternal & child nutrition, 16(3), p.e13036.
Noyes, J., Booth, A., Moore, G., Flemming, K., Tunçalp, Ö. and Shakibazadeh, E., 2019. Synthesising quantitative and qualitative evidence to inform guidelines on complex interventions: clarifying the purposes, designs and outlining some methods. BMJ global health, 4(Suppl 1), p.e000893.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

