MAN501 Culture and Managerial Implications Assignment Sample
Here’s the best sample of MAN501 Culture and Managerial Implications Assignment, written by the expert.
INTRODUCTION
Become of globalization of economies, there are increased opportunities for multinational organizations to enhance other customer base, financing options, sharing of knowledge through advanced R & D etc (Bian and Forsythe, 2012). Use of technology has reduced the distance among countries but cultural boundaries among nations restrict the management practices in multinational organizations. The knowledge about the cultural diversities helps in predicting the reaction of other belonging to a foreign land while entering in joint venture or negotiating (Chen and Zahedi, 2016). Therefore, for an effective global access, companies are required to understand the diversities in culture prior to finalization of strategies. In this assignment the two biggest economic nations has been analyzed i.e. USA and China.
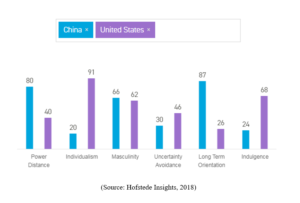
On the basis of Hofstede model, different academic theories will be used for understanding the management style prevailing in each nation. Following study can describe how different culture can affect:
RECRUITMENT SELECTION
One crucial function of HRM is recruitment and selection of employees. The process of recruitment is mostly the same among global employers with slight difference from country to country. In America, recruitment of potential candidate is mostly done on the basis of his/ her performance in the interview (Freshney, 2015). This procedure is mostly followed in majority of companies in America which generally commences with the shortlisting of candidates based on technical and academic expertise with respect to the job requirement. This first phase leads to selection of deserving candidates who are called for second phase in which aptitude and work experience in assessed through the process of interview. After successful clearance of interview candidate is finally selected for the job (Goodrich and Mooij, 2014). Apart from this procedure, majority of companies in China use to consider the test scores of candidates in companies’ own exam. The ability of the candidates is also tested against Chines culture and environment. This kind of judgment of candidates’ adaptability and familiarity of culture is missing in American culture. Hence, there is slight difference in the recruitment and selection process of the two countries.
EMPLOYMENT AND SECURITY
As per Hofstede cultural dimensions (2018), employment ratio is high in USA in comparison to China. With the largest population on the globe Chinese worker always fear of losing their job and open to risk of employment. On the contrary employees in an American firm have high job security and have all opportunities to move ahead in their career by switching their jobs.
NEGOTIATION STYLE
Negotiations involving different nations are based on the interaction between buyers and sellers belonging to two different countries. Negotiation is a vital method for reaching an agreement which is acceptable by all involve during negotiation. This paper will concentrate on cultural factors affecting the negotiation style of China and USA. However, Hartmann et al. (2015) argued that analyzing the national negotiation apart from national culture must also include individual factors like negotiators’ race, age, gender, religious, background, education and like.
GOAL BEHIND NEGOTIATION: RELATIONSHIP OR CONTRACT –
Negotiators belonging to USA prefer to mention the goals on a clear signed contract. The outcome is supported by the short term orientation and low avoidance of uncertainties (refer table). The final aim of the negotiation exercise is to sign contract among the parties involved. This signed agreement provides fixed set of obligations and rights creating binding on the involved parties. As per Helmreich and Merritt (2017), Americans are more inclined towards laws rather than on traditions, culture, religion or relationships. The main focus of Americans is on achieving of goals and objectives and avoids activities like ‘hanging around’. On the other hand, negotiators from China usually like to have good understanding about the parties on the other side. This involves long discussion among negotiators for knowing each other. As mentioned by Helveston et al (2015), Chinese treat signing of contract as commencement of a relationship. This long term orientation results in building of sound relationships which provide support in more negotiations in future and same thing is depicted in the table. As per Khan, Pitts and Williams (2016), the social harmony which is reflected through good manners and well behavior lays the foundation for long term relationship which is far more than just business.
ATTITUDE TOWARDS NEGOTIATION: WIN-LOSE OR WIN-WIN
As per a study performed by Lan et al. (2011), Chinese people show more a win –win attitude for negotiation in comparison to US counterpart. This is because the culture in China believes in social harmony which promotes managing a peaceful environment for negotiation. As per Hofstede cultural dimensions (2018), presence of more individualism in Americans leads to more self-reliant and more independence. This makes them more self-centric and work for gaining benefit from the opposite party during process of negotiation (refer table).
PERSONAL STYLE- FORMAL OR INFORMAL
Americans follow more informal style in comparison to Chinese counterpart. Short term orientation and low power distance is reflected in informal communication among American companies. Americans like informal and small talks for quick flow of information and usually uses first name only for discussing details of the contract. On the contrary, Chinese people are more formal. Chinese people like to address their counterparts with titles and their focus is on business talk rather than personal talk. This denotes the Chinese principle of Confucianism i.e. saving other Mien-tzu (prestige, self- respect, dignity). However, Mu et al (2015) clarified that Chinese people also love to socialize with others but at informal places like nigh club, restaurant for reflecting their hospitality and managing relationship.
COMMUNICATION- INDIRECT OR DIRECT
Americans prefer direct communication in comparison to Chinese counterpart. Americans like to receive definite and clear response of their questions and proposals. They prefer to settle things firstly and leave no space for bargaining. They like to receive answer in ‘yes’ or ‘no’ clearly which reflects their cultural value. On the other hand, Chinese tends to have indirect communication. In the view of North and Fiske (2015), people having indirect communication style generally assume the knowledge of others and their communication is mostly affected by circumlocutions, figurative speech forms, gesture, facial expressions and similar body postures.
TIME SENSITIVITY – LOW OR HIGH
US people are more individualistic and short term orientation. As per table, Americans like to complete task quickly for achieving short term goals and later spend the time with family rather than at workplace. They concentrate on completing the work on deadline and try to avoid time in the process of negotiation. On the contrary, Chinese culture follows long term orientation in which they take time for knowing the situation and thereby building a strong relationship with their partners. As noticed by Vogel et al (2015), some Chinese managers belies that more the time spend during negotiation more are the chances of success in business.
EMOTIONS- LOW OR HIGH
The people of China and USA have mostly the same emotion trait. Although, as per a study of Wagner (2016), Chinese people use to suppress their emotions and feeling for having a peaceful environment for business.
AGREEMENT FORM: SPECIFIC OR GENERAL
Americans like to have detailed contract in which all attempts are made to include possible eventualities and circumstances, even when their chances of happening are very less. Americans are of the opinion that ‘deal’ is denoted by contract and contract is required to be referred for handling any new situation which might occur in future. On the other hand, Chinese managers follow general principles in place of detailed rules. As per Chanlat, Davel and Dupuis (2013), Chines managers seek to avoid minute details as far as possible and look for total consideration and generalities, thereby leaving the responsibility for concrete agreement on other party. Chinese believes that the essence of the agreement is the relationship among parties.
AGREEMENT BUILDING – TOP-DOWN OR BOTTOM-UP
The method of agreement building depends on the agreement form that is used i.e. top- down (deductive) or bottom- up (inductive). In the bottom up approach, the agreement commences with particular elements like delivery date, price, and quality of product which ultimately gets converted into a contract. And in to down approach, negotiators commence the agreement with general principles and later moves to specific elements. Americans managers prefer to initiate the contract with specific items while Chinese managers like first to agree on basic principles which would guide towards the specific details in the process of negotiation.
TEAM ORIENTATION: LEADERSHIP STYLE / CONSENSUS VS ONE LEADER
As per a study performed by Ferrell and Fraedrich (2015), both China and USA promote one man leadership; however, Chinese people are more believers than American counterpart. Americans feels pride in making a decision with full authority. Moreover, one man leadership of China reflects the political tradition of the China i.e. though there is collective society there but fixes responsibility of group for performance of individuals. Normally, Chinese managers feel proud in achievement by their teams. In China, individuals use to avoid decision making individually. As per Hofstede cultural dimensions (2018), majority of companies in China follow hierarchical structure, but employees work as team with high trust level for generating social deal during negotiation.
RISK TAKING ATTITUDE- LOW OR HIGH
As per table, Both China and USA are high risk taking nations but China is considered as more risk bearer than USA. The American societies are low uncertainty avoidance in which citizens low the challenges coming in life and have high tolerance for understanding new situations. On the other hand China has high uncertainty avoidance because of which during negotiations they prefer structure and precise direction. Chinese managers search for ways for better trade off during business meetings.
COMMUNICATION STYLE
Communication is used for exchanging information as well as conveying some meanings through using messages, words, body language, formalities, and status and like. Communication can be broadly categories into two heads i.e. nonverbal communication and verbal communication. The style of communication concentrates on the context of message. In the opinion of Thomas and Peterson (2014), understanding the silent language could reveal the inherent culture in an effective way. As per Wiewiora et al (2013), the communication style could also be better understood through process of decision making. For proper understanding of communication, the recipient is required to focus on context, code and meaning in totality. One must learn, the way to behave as well as acquire belief system and elements of value these three areas. As per Ferrell and Fraedrich (2015), the high content message or communication is one in which more information is physical internalized or context; while low context communication is one in which more information is exchanges through codes.
In cultures with low context like one in USA there is direct verbal communication. Americans leaves on doubt for recipients. Their low context communication contains meaning in explicit codes. In US culture nonverbal message contains less information related to the message intended to be send. Hence, the aim of communication is to transfer the message precisely. This communication style is also in line with the short term orientation and individualism culture of America. Americans prefer straight talk and they think of themselves which help them is achieving short term goals. On the other hand the Chinese culture is high context oriented in which indirect verbal communication is preferred for fulfilling Confucian principle i.e. social harmony. Chinese culture avoids direct rejections and use to tell about rejection with reasons through nonverbal message (Hofstede cultural dimensions, 2018). Chinese people seek for social information of others. Words coming from a person’s mouth might contain less meaning then nonverbal communication. Therefore, in China recipient is required to read the body language as well as facial expression of the speaker. Hence, when there is question of real feelings, message in non-verbal communication might lead recipient confused and hides he real intention of speaker which is opposite to the American culture in which real feeling is expressed in verbal message. American culture expresses emotions openly. On the contrary, the Chinese collectivistic culture makes people hide their emotions and compel them to treat politely and showing manners. This attitude is positive with the aim of Chinese in negotiation i.e. relationship building.
PROMOTION
Being an individualistic society, in US the promotion polices of companies are mostly performance oriented in which promotion are provided based on the performance. On the contrary, following the harmony culture in Chinese firms promotions are mostly time bound.
CORRUPTION
Both America and China are suffering from corruption problem, but in China it is one of the worst. In USA, people are aware of their rights and most of the rights are clearly mentioned in digital platforms (Trading Economics, 2018). Also, the power distance is high in China in comparison to America.
GENDER ROLES
According to the Hofstede cultural dimensions (2018), in USA, a high human equality culture prevails because of high individualism and low power distance. Americans share opinions, information and in masculine society people people challenge entities showing equality towards gender. As observed by Thomas and Peterson (2014), even after reduction in gender wage gap in past three years, genders with same experiences at same position has different authorities and different wages (Wagner, 2016). Similarly, in Chinese culture there is tendency to decide work based on gender because of past customs, government policies and communism. In China, Confucianism generated preferences based on gender in which woman are regarded inferior, softness, compromise. Also, the Chinese culture regards male to more deserve the administrative and bureaucratic positions which is also the thought of majority of the population. However, the role of female in the corporate is rising, but it will take some time for woman to occupy important position in the organization. As such, the gender inequality is comparatively much low in America than China.
REWARDS
The system of reward is a motivation factor which largely depends on the culture of the organization. An effective reward system must provide proper balance between performance and effort (Wiewiora, et al, 2013). As per expectancy theory, efforts of employees and rewards are interlinked. Companies are required to access the ability of their employees and assess their personal objective for offering the opportunity to employees to develop themselves. The reward system not just affected by expectancy theory but also impacted by other theories like Maslow Needs theory etc. The needs of an employee are affected by various factors like culture background, education, genders etc. The needs also got changes with the time. In American culture normally people follow non-financial rewards such as holiday leave, promotion for fulfilling their short term achievement and like to spend extra time for their personal life because of involved culture. On the contrary, Chinese mostly have the reward system which offers financial rewards as money is the biggest motivator in Chinese organization.
ETHICS:
Being an individualistic society people put themselves above all in America. On the contrary in China peoples care about others feeling following the harmony based business culture. Ethics are considered important in Chinese business culture in comparison to US culture.
TERMINATION
American organizations follow ‘at will’ termination approach. Majority of employment in USA are ‘at will’ i.e. there is no guarantee of the employer for termination and this requires no notice and severance. It means that, an employee in US culture can be terminated at any time without any cause. On the contrary, in China the approach of termination is ‘termination with cause’. It means that whether it is mentioned in the contract or not but majority of termination in Chinese firms requires payment of severance and with cause. Although there are cases mentioned in the laws in which Chinese employers are not bound to serve notice or pay severance.
ORGANISATION STRUCTURE
In Eastern nations, their organizational structure is hierarchical and the leadership style followed in the organization is mostly autocratic. On eth contrary in western culture, companies believe in flat structure and their leader is mostly democratic. But, organizations in Far East areas such as Korea and China and Middle East follows collectivist culture in which group has more importance over individuals and employees are supposed to work as a member of team. The organizational structure of Chinese companies is more group oriented and has hierarchy system while the organizational structure in US follows more liberty in terms of hierarchy system and mostly follows open door policy at senior level.
PROBLEM SOLVING
Resolving conflicts is a crucial function of human resource management which is easily observable in Western nations in comparison to eastern counterparts. In China, the tendency of holistic and harmony approach is more common in which people resolves their conflicts through compromise and accommodation. While US culture follows ignoring or withdrawing as a usable option for resolving conflict. The harmony and holistic approach in China makes people feel that they have a role to play in the whole system which reduces their chances of disagreement. On the other hand, the US culture problem solving approach encourages exploration and help employees in developing their own ways for resolving conflicts (Helmreich and Merritt, 2017).
ORGANISATION NORMS
Both USA and China have strict and clear organization norms. Companies have clear policies and practices which are to be followed strictly. The norms of the organization clearly laid down do and don’t at workplace.
NEPOTISM
Nepotism is common in both Chinese and US culture. One can easily find cases in both US and Chinese firms in which a candidate gets the job because of some kind of favourism such as father working in the organization etc.
CONCLUSION:
On the basis of Hofstede cultural dimensions (2018), it can be concluded that culture of a nation plays a crucial role in behavior and attitude of people of the nation. With the globalization of business, managers are required to deal with the force belonging to diverse culture. The impact of culture on USA people has made them more individualistic as compared to Chinese counterpart who has a culture of communalism, and harmony. The culture of the nation also impact the organizational culture of the organization which affects an organizations’ negotiation methods, structure, promotion policy, termination policy, recruitment policy, communication flow, norms, problem solving , ethics, reward system etc. An understanding of culture of different nations would a manager to manage global workforce more efficiently.
REFERENCES:
- Bian, Q. and Forsythe, S., 2012. Purchase intention for luxury brands: A cross cultural comparison. Journal of Business Research, 65(10), pp.1443-1451.
- Chanlat, J.F., Davel, E. and Dupuis, J.P., 2013. Cross-cultural management: culture and management across the world. Routledge.
- Chen, Y. and Zahedi, F.M., 2016. Individuals’ Internet Security Perceptions and Behaviors: Polycontextual Contrasts Between the United States and China. Mis Quarterly, 40(1), pp.205-222.
- Ferrell, O.C. and Fraedrich, J., 2015. Business ethics: Ethical decision making & cases. Nelson Education.
- Freshney, R.I., 2015. Culture of animal cells: a manual of basic technique and specialized applications. USA: John Wiley & Sons.
- Goodrich, K. and De Mooij, M., 2014. How ‘social’are social media? A cross-cultural comparison of online and offline purchase decision influences. Journal of Marketing Communications, 20(1-2), pp.103-116.
- Hartmann, C., Shi, J., Giusto, A. and Siegrist, M., 2015. The psychology of eating insects: A cross-cultural comparison between Germany and China. Food quality and preference, 44, pp.148-156.
- Helmreich, R.L. and Merritt, A.C., 2017. Culture at work in aviation and medicine: National, organizational and professional influences. UK: Routledge.
- Helveston, J.P., Liu, Y., Feit, E.M., Fuchs, E., Klampfl, E. and Michalek, J.J., 2015. Will subsidies drive electric vehicle adoption? Measuring consumer preferences in the US and China. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 73, pp.96-112.
- Hofstede Insights. 2018. County Comparison [Online] Available at: https://www.hofstede-insights.com/country-comparison/china,the-usa/ (Accessed: 22 Sep, 2018).
- Khan, T., Pitts, M. and Williams, M.A., 2016. Cross-cultural differences in automotive hmi design: a comparative study between uk and indian users’ design preferences. Journal of Usability Studies, 11(2), pp.45-65.
- Lan, X., Legare, C.H., Ponitz, C.C., Li, S. and Morrison, F.J., 2011. Investigating the links between the subcomponents of executive function and academic achievement: A cross-cultural analysis of Chinese and American preschoolers. Journal of experimental child psychology, 108(3), pp.677-692.
- Mu, Y., Kitayama, S., Han, S. and Gelfand, M.J., 2015. How culture gets embrained: Cultural differences in event-related potentials of social norm violations. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(50), pp.15348-15353.
- North, M.S. and Fiske, S.T., 2015. Modern attitudes toward older adults in the aging world: A cross-cultural meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 141(5), p.993.
- Thomas, D.C. and Peterson, M.F., 2014. Cross-cultural management: Essential concepts. Sage Publications.
- Trading Economics. 2018. China GDP Annual Growth Rate. [Online] Available at: https://tradingeconomics.com/china/gdp-growth-annual (Accessed: 3rd August, 2018).
- Trading Economics. 2018. United States GDP Annual Growth Rate. [Online] Available at: https://tradingeconomics.com/united-states/gdp-growth (Accessed: 3rd August, 2018).
- Vogel, R.M., Mitchell, M.S., Tepper, B.J., Restubog, S.L., Hu, C., Hua, W. and Huang, J.C., 2015. A cross‐cultural examination of subordinates’ perceptions of and reactions to abusive supervision. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 36(5), pp.720-745.
- Wagner, R. 2016. The invention of culture. USA: University of Chicago Press.
- Wiewiora, A., Trigunarsyah, B., Murphy, G. and Coffey, V., 2013. Organizational culture and willingness to share knowledge: A competing values perspective in Australian context. International Journal of Project Management, 31(8), pp.1163-1174.
________________________________________________________________________________
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

