Managing Business
Executive Summary
The aim of this study is to analyse the importances of managerial skills in order to manage the human resources at different level. Along this, discuss VRIO framework to analyse how organisation contribute value through use their resources.
Moreover, the importance’s of management function is also undertakes for efficiently perform of business operation. In respect to such areas, the findings are that technical, conceptual and interpersonal is important to adopt for different level of management. Other than that, the VRIO tool stated that organisation to achieve the sustainable competitive advantage then there is need to include attributes like rare, hard to imitate, valuable and organised etc.
However, the planning, organising, leading and controlling are the management function on which manager rely to perform the business operation successfully. Thus, these areas contribute towards manage different resources such as human, physical and technical etc.
The purpose of this paper is to manage the business on proper manner in order to gain high competitive advantage. For this, the study critically analyse and discuss the significances of different managerial skills along with discuss the VRIO framework for making better resources and capabilities of organisation (Scarborough, 2016). However, the management functions is also evaluate for bring effectiveness in organisation operation.
Based on these tasks, the organisation can able to control or operate organisation in best possible manner. The reason behind to undertake such activity is to ensure that everything occurs in conformities with standards of organisation.
Additionally, the role of management is quite important to effectively running of business as right management helps to maintain a unity of direction to all its actions.
Thus, it assists to gain organisation goals and requirements effectively and efficiently. This study provides detail understanding about the management of business in the competitive business environment.
Critically analyse different management skills for management levels
There are three levels of management such as Top-level, Middle-level and Lower-level management. Different level consist varied set of actions related to business operations. The level of management identifies the chain of command, amount of authority and status of managerial position (Scheer et al., 2015). These levels of management plays important role to manage different human resources on organisation.
Top-level management: – This level includes the BOD, chief executives and managing director. However, the top management is the ultimate sources of authority and it manages goal or policies for an enterprise (Shrouf & Miragliotta, 2015).
It provides proper guidance’s or directions and they are responsible for the performances of shareholder. Moreover, the top managers require for a strong conceptual skills as this involve knowledge and ability for abstract thinking and formulating ideas. The top manager with this skill can analyse and diagnose the problem and able to find creative solution (Mežinska et al., 2015).
This helps the top manager to design the policies or actions as per the given problem. Thus, the conceptual skills support the manager to eliminate the problems which department and management face in business.
However, the increasing employee turnover rate also can be addressed by manager through use of conceptual skills as this allows gaining understanding about different aspect which leads to provide right solution to organisation.
Middle-level Management: – The middle level includes branch managers and departmental managers which are responsible for functioning of the department by executing plans as per the policies of top managers.
They are responsible for bring coordination in activities within the division or department. In respect to perform the role & responsibility, middle level managers required to posses interpersonal skill (Takey & de Carvalho, 2015).
This is because interpersonal skill present manager ability to interact, work and relate effectively with people. These skills allow the manager to make use of human potential in most appropriate way by motivating the employees for better results.
Moreover, this skill proves to be effective for personnel in regards to feel recognised in workplace and it result in high contribution towards the task by the employees. This skill is also important for middle-level manager as they have to make direct interaction with lower level staff like employee, workers etc.
Lower-level Management: – They are supervisors, foreman, section officer and superintendent etc and responsible for assigning job tasks to various workers along with proper instruction. However, this level of management need for technical skills as manager with this expertise can able to use variety of techniques to achieve their objectives.
The technical skills are not only stick towards handling machines or technology but it also consist of techniques which helps to boost sale, motivate employees, design different types of product and services along with market them. This skill helps supervisor to use different method as per the situation and achieve organisation objective. This skill is important to achieve as lower-level managers have a direct impact on the results and outcomes.
So it is must to select the supervisor and officer with appropriate technical skills (Hopkinson, 2017). Moreover, the technical skills also support towards making positive working environment in the form of boosting confidences among the individuals and influence them to contribute productive results.
In concern to technical skill, there is required to have proper command over communication, time-management, conflict resolution and leadership etc. these areas can help the manager to successfully possess technical skill as with expertise in different languages may help the manager to deal multi-cultured people under one roof.
Use of VRIO framework to determine competitiveness of its resources and capabilities
The VRIO framework helps the organisation to determine use of their resources and capabilities in such a way that result in achievement of competitive advantage. However, the VRIO framework is a strategic tool which is designed to help organisation to protect resources and capabilities to achieve long-term advantage (Chatzoglou et al., 2018).
This tool proves to be effective for firm as they able to develop that strategy which provides value to customer. It helps to achieve sustainability in business.
There are four component are used to take decision in VRIO tool. It includes Valuable, Rare, Inimitable and Organised etc.
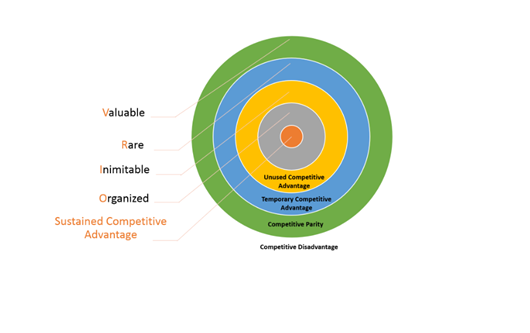
(Sources: Lin & Tsai, 2016)
Valuable: – When resources are valuable then it provides benefit to organisation. However, resources are valuable but it doesn’t fit into any other dimension of framework then it not contributes competitive advantage. Thus, organisation can achieve competitive parity with resources that are valuable and neither rare nor hard to imitate.
Rare: – These are those resources which are uncommon and not possessed by most organisations. It is found that when resources are valuable and rare in market then that gives more competitive advantage. This occurs usually with the involvement into the innovation practice which helps the firm to bring uniqueness all time (Grover et al., 2018).
Thus, the firm which have a capability to bring rare resources then it will give the value. In current scenario, the increasing competition put pressure on firm to imitate the resource without too much trouble. For example, there are various forged product present in market which occupy large consumer market. So it is a challenging task to bring rare in product and service.
Hard to imitate: – Resources are valuable if it is hard to imitable and rare in nature. There can be several reasons why resources are hard to imitate such as resources tend to expensive or protected by legal means such as patent and trademark. Thus, resources with valuable, rare and hard to imitate provided the competitive advantage.
Organised to capture value:- Organisation needs to organise resources in form of incorporate right processes, structure and culture etc. It results in capture of value. The resources that are valuable, rare, hard to imitate and organised to capture value tend to offer high competitive advantage (Wilkins, 2016).
The resources can’t be providing high value to firm until unless does not organised well. However, the firm which is capable enough to achieve rare, valuable and imitable resources can able to achieve sustained competitive advantage.
Therefore, these are the aspects in VRIO framework which contribute towards achieving of competitive advantage. In practical manner, organisation can better manipulate and stretch their resources and capabilities in the form of apply this tool into the business internal operations.
Step 1: Identify valuable, rare, costly and imitate resources:-
There are two kind of resources such as tangible (land, building and machinery) and intangible (brand reputation, trademarks, intellectual property).
The tangible resources are easily available so they provide competitive advantage but intangible resources can’t be acquired easily and offer the benefit of sustained competitive advantage. That’s why intangible resources are found rare, costly, valuable and hard to imitate.
Step 2: To find out firm is organised to exploit these resources:-
In regards to this, organisation need to focus on the firm structure, policy and control system as these areas helps the firm to exploit their resources.
Step 3: Protect the resources:-
This step stated that when organisation found resources or capability that has all 4 VRIO attributes then there is need to protect it (Indartono & Wibowo, 2017). This could help the firm to achieve the sustained competitive advantage.
In regards to this resource, the manager need to make top management aware it and suggest how it can be used to lower the costs or make differentiate the products and services. After that, there is need to figure out is it costly to imitate the resources.
Step 4: Constantly review VRIO resources and capabilities
There is need to monitor the value of resources as they changes as per the time. The competitors also focus on making imitate of resources in order to achieve competitive advantage. So in that case, there is need to bring new resources for attaining the sustained competitive advantage.
This way, firm can control better resources and capabilities over the longer duration.
Significances of four functions of management for the operation of organisation
There are four function of management without which it becomes impossible to run successful business. These are planning, organising, leading and controlling etc.
Planning: – It involves the activities related to deciding where to take company and select the steps to get it there. For this, it requires to analyse the current position of firm like challenges and problem. As per that, manager can forecast future business and economic condition then they formulate objective to reach by certain deadlines (Mijumbi et al., 2016).
Thus, this function contribute benefits for business in term to reduce the chances of waste as with the planning, manager estimate the activities which they need to perform within standard resources. Moreover, the planning function also proves to be effective when external factors will affect the firm both positively and negatively.
Thus, the finding which is collected within the strategic planning will contribute benefit for the business in future scenario in regards to achieve positive result. However, planning assist the management to get an idea about their role and expectation which manager want from them.
Organising:- Manager implement the planning through bring physical, human and physical resources together for achieve the objectives. In this, they identify the activities, classify the activities, and assign it to individuals into groups and individuals by provide them responsibility with authority (Peaucelle, 2015). The function of organising is important for business in term to perform the activities which are ready planned.
However, the hiring of right people with relevant skills helps the organisation to perform the task with expertise. This leads to development positive work results which support achievement of goals and objective. Thus, organising function is quite important to implement the plan into practical manner.
Leading: – Leading is the important function in order to get the work done. In this, leading style plays an important role to influences the personnel as right guidance’s result in performances of work on time with efficiency. This step is also considered as important for business in regards to motivate the personnel to work harder and contribute the productive results. However, effective leader helps to bring right communication, human attitude towards work (Williams, 2015). These benefit support the positive work environment.
Controlling:- This function involves the measuring of achievement against the established objectives and goals. In this, any deviation occur then manager find to possible solution (Nhema, 2015). This step helps the business to identify the area of improvement and accordingly business able to perform the business operation in effective and efficient manner.
On the basis of above study, there are some recommendations that help to achieve business management:-
- Reward and recognition method helps to encourage employees and make them feel recognised.
- Implement the right communication strategy through incorporate digital platform like E-mail, social-site.
- Hold meeting regular for making tactical and strategic business planning
From the above discussion, it is concluded that managing business is important to achieve for procuring the success towards long duration. However, right managerial skills, VRIO framework and four management functions play a significant role to manage the resources and achieve the goals and objectives.
Chatzoglou, P., Chatzoudes, D., Sarigiannidis, L., & Theriou, G. (2018). The role of firm-specific factors in the strategy-performance relationship: Revisiting the resource-based view of the firm and the VRIO framework. Management Research Review, 41(1), 46-73.
Grover, V., Chiang, R. H., Liang, T. P., & Zhang, D. (2018). Creating strategic business value from big data analytics: A research framework. Journal of Management Information Systems, 35(2), 388-423.
Hopkinson, M. (2017). The project risk maturity model: Measuring and improving risk management capability. UK: Routledge.
Indartono, S., & Wibowo, F. W. (2017). VRIO and THES based development of university competitive advantage model in formulating university strategic plan. International Information Institute (Tokyo). Information, 20(10A), 7275-7283.
Lin, C., & Tsai, H. L. (2016). Achieving a firm’s competitive advantage through dynamic capability. Baltic Journal of Management, 11(3), 260-285.
Mežinska, I., Lapiņa, I., & Mazais, J. (2015). Integrated management systems towards sustainable and socially responsible organisation. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 26(5-6), 469-481.
Mijumbi, R., Serrat, J., Gorricho, J. L., Latré, S., Charalambides, M., & Lopez, D. (2016). Management and orchestration challenges in network functions virtualization. IEEE Communications Magazine, 54(1), 98-105.
Nhema, A. G. (2015). Relevance of classical management theories to modern public administration: A review. Journal of Public Administration and Governance, 5(3), 165-179.
Peaucelle, J. L. (2015). Henri Fayol, the manager. UK: Routledge.
Scarborough, N. M. (2016). Essentials of entrepreneurship and small business management. UK: Pearson.
Scheer, J. K., Bakhsheshian, J., Fakurnejad, S., Oh, T., Dahdaleh, N. S., & Smith, Z. A. (2015). Evidence-based medicine of traumatic thoracolumbar burst fractures: a systematic review of operative management across 20 years. Global spine journal, 5(01), 073-082.
Shrouf, F., & Miragliotta, G. (2015). Energy management based on Internet of Things: practices and framework for adoption in production management. Journal of Cleaner Production, 100, 235-246.
Takey, S. M., & de Carvalho, M. M. (2015). Competency mapping in project management: An action research study in an engineering company. International Journal of Project Management, 33(4), 784-796.
Wilkins, S. (2016). Establishing international branch campuses: a framework for assessing opportunities and risks. Journal of Higher Education Policy and Management, 38(2), 167-182.
Williams, C. (2015). Effective management. USA: Cengage Learning.


