MAR038-6 Intercultural Business Competencies Assignment Sample
Introduction
Organisations operating in global markets that are constantly expanding their business operations need to pay close attention to market culture. Market culture varies from one country to another and this predominantly reflects consumer behaviour. Cultural factors affect a company’s operations both internally and externally where internal cultural factors such as maintaining a multicultural workforce, achieving diversity, eliminating cultural conflicts is a major focus for MNCs. In this regard, the following report would explore the various cultural issues that Adidas places and its impact on the organisation’s performance and competitive position. Furthermore, the report would also evaluate the cultural issues existing within Adidas’s internal and external environment and evaluate them to identify the existence of cultural shocks and how it can affect the overall morale and to hear of the human resources. The report also aims to identify the impacts of conflicting values over the organisation’s position, marketing and human resource management and thereby aims to develop solutions that can be incorporated to minimise the impact of identified cultural issues.
Multicultural environment, its significance, and challenges
Multicultural environment refers to the internal and external environment in which an organisation operates where diversity in culture can be noticed. The multicultural environment is a common occurrence for global organisations like Adidas due to which considerations in the market communication strategy as well as product development are greatly determined by taking cultural factors into consideration (Masri, 2019). In a multicultural environment, an organisation is to identify the target customers as well as the predominant culture that determines their consumer behaviour and decision-making process. One of the most challenging issues linked with developing better marketing strategies in a multicultural environment is developing a market communication plan that addresses the majority of the consumers from different cultures (Carr, 2019).
Considering the case of Adidas, it can be seen that the organisation being a multinational organisation faces several challenges due to the presence of a multicultural global environment. The major challenges faced by Adidas, exist both within its internal and external environment, which also affects its competitiveness, especially considering the fact that Adidas is only second to Nike in the sports and fitness goods industry (Smart, 2018). Issues faced by Adidas can significantly minimise its competitiveness against its competitors due to which considering cultural issues plays a major role in developing the majority of its marketing strategies and corporate governance policies. The following section would discuss, identify, and analyse the cultural issues that Adidas at present faces.
Cultural issues faced by Adidas
Some of the major cultural issues that Adidas faces include the cultural issues that exist within the workforce, environmental and sustainability issues, political issues, and influence of different political environments in the global market, use of controversial technologies and animal testing issues.
Cultural issues within the workforce
Based on the case study of Adidas it has been seen that there is an issue linked with the wages that multinational corporations like Adidas are found to be involved in. The supply chain of Adidas is quiet and diverse and the organisation has many raw materials from various suppliers around the world and therefore. Based on a report published by the Clean Clothes Campaign In 2019 it was identified that Adidas holds no evidence where it can reflect that it pays standard wages that can be considered living wages to the workers working for the company and within their supply chain (Refer to appendix). The organisation has also been found to provide a basis that does not match the industry standards and there has been a new step taken by the organisation to fill the gaps that can minimise the wage difference (Reuters, 2018).
On the contrary, it has also been identified that Adidas was paying women of poverty-wage for sewing football shirts. Around 80% of the organisation’s football shirts came from Indonesia and the poverty that the organisation claimed to provide these women did not cover their basic needs, which reflects the organisation’s ignorant attitude towards the workers present within the supply chain (Refer to appendix). It is essential for the organisation to identify these gaps that are concerned with another supply chain. Since a large amount of profit is derived due to the hard work of these individuals, especially women from Indonesia, the organisation needs to take steps to improve its wage policies (Santos and Mayer, 2021). However, in this regard, it can also be stated that the governments of these countries where minimum wages are not provided to the workers working in the lower levels are also responsible to some extent. In developed countries like the UK, the government has established minimum wage policies which are predominantly followed by every organisation operating in the market (McGuinness et al. 2020). Whereas countries like Indonesia, Bangladesh and others who are responsible for satisfying the majority of the clothing and fabric demand in the market do not have such minimum wage policy established in their country’s constitutional framework (Syed, 2020). Therefore, the lack of these regulations also encourages multinational corporations to decide images that suit the profitability of the organisation more than the needs of these daily wage workers (Dowell and Jackson, 2020). Moreover, this can also be identified as an ethical issue of the organisation which can have a major impact on their reputation in the market. Since the organisation has a global reach, these issues are not always highlighted and get a popular opinion. However, if these issues are identified and held in public the organisation can suffer major damage to their adaptation which would have a long-lasting impact on the company’s competitiveness.
Racial discrimination and internal diversity issues
Apart from the supply chain and daily wage workers who are responsible people living and manufacturing the majority of the products sold by Adidas the organisation also has a diverse workforce where is discrimination exists (Dowell and Jackson, 2020).
It has been seen that the employee diversity in Adidas is not up to the industry standards and only 4.5% of the 1700 employees who work in the headquarters of the company located in Oregon are black (Highsnobiety, 2020). This reflects that discrimination in terms of recruitment exists within the organisation which can be identified from the diversity of our workforce which is quite even and mostly favours the white population. Furthermore, it has also been seen that the black population of the workforce feel marginalised due to the lack of diversity. Even though the organisation has maintained a reputable brand image by working with famous black celebrities like Pharrell Williams, Kayne West and Beyonce discrimination against black workers is a major issue that exists within the organisation (Highsnobiety, 2020).
This has led to a negative stereotype working within the organisation that has not only harmed the behaviour of the employees but has also led to the development of various similar issues in the global context. However, this aspect has been noticed by the organisation’s management and new changes have been initiated where the organisation aims to recruit at least 30% of other weekend positions in the new locations of the country with black employees (Forbes, 2021). The issues linked with ethnicity diversity and gender diversity is a prevalent matter that can affect Adidas and its competitive position in the market considering the fact that the computer and it has worked quite extensively in order to achieve a sustainable and diverse working environment.
Moreover, it has also been seen that the employees working in Adidas are also quite aware of the diversity issues that are present within the workforce (Brooks, 2021). Such issues have been raised by the employees working for the company from time to time however not much has been done by the organisation apart from the recent announcement where they have decided the objective to fail 30% of the workforce with black individuals (Forbes, 2021). This objective has not yet been achieved by Adidas which again reflects that the organisation has only set goals and has not worked upon them therefore the issue remains quite persistent throughout the various ranks of Adidas.
Apart from racial discrimination, it has also been seen that the organisation also has gender discrimination and several female employees of the organisation have reported a male-dominated working culture (Financial Times, 2021). Female employees of the organisation have urged for female equality and in response to this, the organisation has made a commitment to United Nations women empowerment principles to achieve gender equality within the organisation to empower the female employees within the company.
Considering the implication of the cultural issues of the workforce and the cultural behaviour of the employees can be affected and this can lead to the development of organisational culture as in the diversity and ethnic diversity is not respected (Compliance week, 2020). These issues can also lead to the prevalence of favouritism and preference of other management towards a selected few individual belonging to a particular race or gender that can also have an impact on the morale and job satisfaction of the minorities working in Adidas (Shahudin, 2018). It is quite essential for the organisation to take steps before the organisation starts to lose its reputation in the global market which can significantly affect its sales and emails and the overall brand equity that Adidas holds.
Impact of cultural shock
Considering the fact that the organisation operates in a global market there are various currencies where one employee from a particular country is transferred to a foreign nation as an expatriate. In such a situation where the organisation lacks gender and ethnicity diversity employees belonging from other countries might face significant discrimination from the employee is working in the host country (Kostis et al. 2018). This can lead to a significant drop in the performance and job satisfaction of the expatriate. Moreover, it can also lead to the adoption of this culture where if the employee is transferred back to the home country this culture might spread to the other headquarters of Adidas.
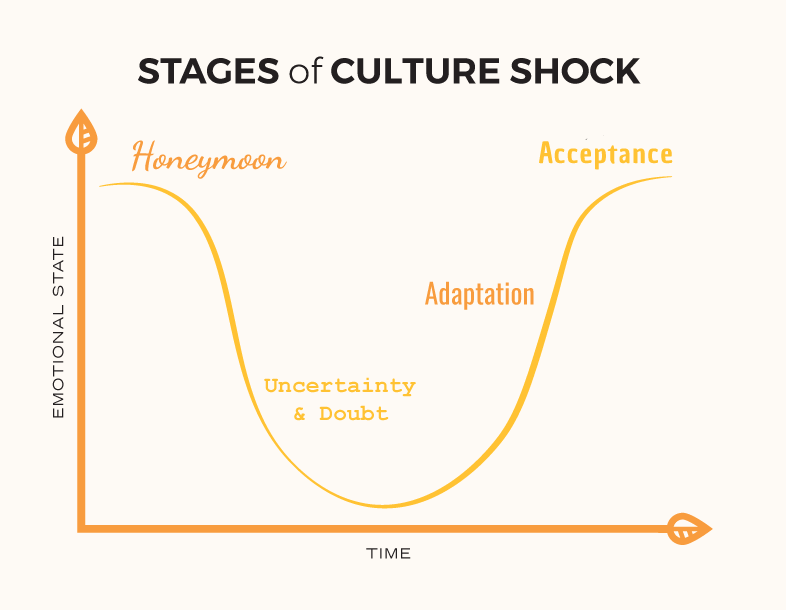
Figure 1: Stages of cultural shock
(Source: Kostis et al. 2018)
Therefore, the culture that discriminates against gender and is also responsible for racial discrimination within the organisation needs to be eliminated with immediate effect. Thus, in simple terms, it can be stated that cultural shock can lead to the spread of misaligned culture from one market to another and this can affect the entire global workforce of the organisation which Adidas needs to avoid at any cost.
Issues linked with the use of technology
In the present generation, technological advancements, and the use of technology in the development and diversification of products have become quite important. However, when it comes to Adidas the organisation has been blamed for using technology that can have potential health issues (Refer to appendix). The organisation has been set to utilise nanotechnology which can not only affect the environment but can have serious health risks. Moreover, there has also been a lack of examination over the materials, especially the nanotechnology that Adidas has incorporated in its products which again raises the question linked with the environment and human safety. Apart from that, when it comes to the clothing material Adidas has been found to avoid GM cotton within its supply chain, which has been pointed out by various ethical consumers. As of 2017 has been identified that 80% of the cotton that is grown are genetically modified and this has led to the preconception that some of the products that are sold by Adidas are made out of genetically modified materials (Refer to appendix). This has led to the loss of reputation when it comes to the use of controversial technology. When it comes to the competitors of Adidas like Nike such issues have not yet been established due to which the organisation has again failed to maintain its competitiveness in terms of using safe and ethical technology to develop and produce its products (Wallace, 2021). This issue can be identified to be an internal cultural issue within the organisation and the prevalence of this, in the long run, can impact the overall production of GM cotton products. As a result, the use of GM cotton products can increase in the clothing and accessories of Adidas, which can be a major ethical approach in the global market (Refer to appendix). This can also become a major issue in the long run for Adidas considering the fact that consumers have become much more aware and ethical about the products that they buy.
Issues linked with animal rights
The organisation has received the worst rating when it comes to animal rights even though the organisation reflects that they do not use animal ingredients or byproducts in the production of their sports gear. It is essential for the organisation to maintain transparency so that independent research can be conducted to identify if the organisation’s products are animal product free (Refer to appendix). Moreover, there is also a lack of evidence when it comes to identifying if the organisation used animals in the testing and development of their products. Competitors of the organisation have transparent policies an internal audit can be done to identify if organisations are using animals in the development of the products however Adidas has no such policies or options that can be explored.
Theoretical underpinnings
Edgar Shein’s cultural model
In order to reflect upon the current culture of Adidas the cultural model of Edgar’s Shein can be taken into consideration where the various cultural issues of the organisation can be evaluated and aligned with the present state of the company.
The cultural model has three distinct divisions that are artefacts creation, values, and basic assumptions (Coghlan, 2021). In these contacts artefacts and creation refers to the existing cultural aspects of the organisation. In this regard, the prevalent issues within the organisation are linked with cultural diversity and lack of gender diversity can be taken into consideration. These issues are persistent within the organisational framework and comprise a major part of the company’s culture. These aspects are linked with the organisation’s culture and determine the value of the organisation which is responsible for developing an overall organisational culture in the various global locations of Adidas (Schein et al. 2021). Apart from multicultural aspects that are prevalent within the organisation, there are other issues that have been identified such as the unethical ways of utilising the daily wage workers within the company’s supply chain. The organisation can be found to be taking advantage of the lack of any regulation established by the Indonesian government regarding minimum wage policy due to which the ways that the organisation provides does not meet the basic needs of the women who work for Adidas. Apart from that, another issue that has been identified where Adidas has been found to be involved in political issues both internally as well as externally. These prevalent cultural issues present within the organisation define other values of the company and compare the values of Adidas with its major computer and it can be stated that it does not meet other industry standards.
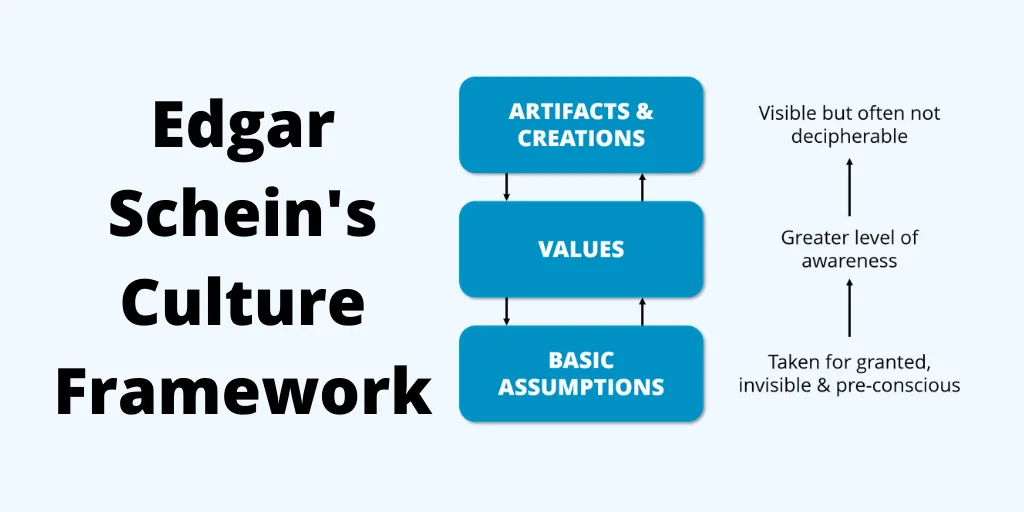
Figure 2: Edgar Schein’s Cultural model
(Figure: Schein, 2019)
Furthermore, the presence of these values within the organisation greatly affects the overall behaviour and cultural attributes of the workforce that can have a major impact on the job satisfaction and employee diversity existing within the company (Schein and Schein, 2019). The lack of female diversity within the organisation has been justified by the organisation considering the sports world is dominated by male athletes. When it comes to endorsement the organisation has often been found to be engaged with male athletes more than female athletes. This is another issue that can be linked with the gender discrimination in which the companies are involved and therefore this leads to the final development of the cultural model that is basic assumptions (Morris et al. 2019).
Basic assumptions include the various aspects that are taken for granted and are pre-consciously developed. In terms of basic assumptions, it can be stated that the presence of a large number of white employees within the organisation is a basic assumption as well as a male-dominated workforce (Sherwood et al. 2018). These assumptions can have a major impact on the company’s reputation, brand image and brand equity (Coghlan, 2018). It is essential for the organisation to rectify these cultural gaps and issues that are prevalent within the organisation’s culture to ensure their competitiveness and ability to minimise the threats imposed by competitors like Nike (Smart, 2018).
Hofstede’s cultural dimensions
Culture plays a major role in diversifying a company and providing capacity for strength at the core of the organization. Thus, analysing culture is essential for achieving the efficiency of the companies and increasing the efficiency of the employees (Yue et al. 2021). In the case of Adidas, it can be seen that the company is encountering various issues in terms of the pay gap, racial discrimination and minimum wage payment to the workers. Furthermore, it has also been witnessed that higher official gets paid more whereas the workers of lower levels get neglected. As per Hofstede’s insight, power distance plays an essential role in forming a division between the higher officials and the lower officials (Hofstede-insights, 2022). Thus, it can be said that in the case of Adidas, power distance can be referred to as high with no equality of payment to work. Furthermore, Masculinity can also be noticed at a high level as women get paid less than men. On the other hand, gender diversity is also low in the company. Adidas can be witnessed to be favouring men over women which evidently proved a high level of masculine culture in the company.
On the other hand, as per the element of uncertainty avoidance, Adidas can be said to be holding a lower position which signifies that the company avoids uncertainty at a decreased rate. The companies which like to avoid uncertainty, do not incline towards the adoption of new technologies (Hofstede-insights, 2022). However, Adidas relies significantly on technologies for benefiting the company with increased profitability and to positively impact the environment. However, in terms of animal rights, the company has violated the laws and has received the worst rating. The company had previously promised that it would not be using any animal products or by-products. Even, several products were witnessed to be sold by the company which contained wool, leather, and others, signifying a breach of commitment. Furthermore, the company has also encountered various environmental issues and has been also rated as “Average Midfield” by the reports. Culture is extensively essential for collaborating all the factors of a company. Without adherence to a strong culture, bringing collaboration towards the operations of the company in terms of profit generation and sustainability and employee performance can be critical (Kumari and Singh, 2018). Due to high power distance, there is a lack of collaborative communication between employees and higher officials and thus the company is unable to meet its obligations efficiently.
Resolving cultural issues/Recommendations
- Even though Adidas had taken steps to ensure that the workforce of the company has a diverse culture there has not been sufficient steps that could make it possible. Therefore, immediate recruitment drives can be started where specifically black individuals can be recruited so that the lack of cultural diversity present within the workforce can be minimised. This would also help the organisation to resolve the state of black minorities in the organisation.
- Additionally, Adidas can also achieve transparency by making their corporate policies public so that independent bodies can prove that the organisation has adopted sustainable business operations and are also maintaining ethical standards of running their business.
- Alongside, Adidas can also change their wage policies, especially ensuring that a living wage is being paid to the women workers and population of Indonesia. This would allow the organisation to achieve a sustainable workforce.
- Adidas can provide training and development programs to their managers and leaders for bringing forth gender diversity efficiently (Ballinger, 2018). With diversified genders, equality can be brought forwards and the mental health of the employees can be enhanced. This can alternatively impact increasing job satisfaction and employee performance.
- Furthermore, in terms of environmental issues, Adidas can formulate a body to whom they can report on an annual basis for keeping check with their activities to positively impact the environment. Additionally, the company can also increase focus on producing products that can be recycled and reused.
Conclusion
Based on the above case study it can be determined that Adidas has been facing several intercultural issues that have impacted the organisation’s brand image position and overall brand equity. Based on the above cultural issues the report has helped in identifying how cultural issues within the workforce can lead to aspects such as cultural shocks as well as how these discriminative cultures can spread to other markets. This has been identified and evaluated with the help of Edgar Shein’s cultural model where aspects such as cultural assumptions based on the organisational culture have been identified and how this can spread from one branch of the company to another. Additionally, Hofstede’s cultural model has also been evaluated to reflect upon cases of issues such as lack of gender diversity and the presence of racial discrimination.
References
Brooks, T.J., 2021. German ncp Releases Final Report under oecd Guidelines on Failure of Adidas to Mitigate Human Rights Effects of Subcontractor Actions in Indonesia. International Labor Rights Case Law, 7(1), pp.24-30.
Carr, D., 2019. The Effectiveness of Collaboration Within Supply Chain Management: A Case Study of Adidas Group.
Coghlan, D., 2018. Edgar Schein at 90: A celebratory and exploratory metalogue. The Journal of Applied Behavioral Science, 54(4), pp.385-398.
Coghlan, D., 2021. Edgar Schein on change: Insights into the creation of a model. The Journal of Applied Behavioral Science, 57(1), pp.11-19.
Compliance week, 2020. Adidas vows more ‘diverse and inclusive’ workplace after key exec departs. [Online]. Available at: <https://www.complianceweek.com/ethics-and-culture/adidas-vows-more-diverse-and-inclusive-workplace-after-key-exec-departs/29157.article> [Accessed on 3 March 2022]
Dowell, E. and Jackson, M., 2020. Woke-washing” your company won’t cut it. Harvard Business Review, 27, pp.1-7.
Forbes, 2021. How adidas Promotes Diversity, Equity, And Inclusion In The Workplace. [Online]. Available at: <https://www.forbes.com/sites/sap/2021/11/10/how-adidas-promotes-diversity-equity-and-inclusion-in-the-workplace/> [Accessed on 3 March 2022]
Financial Time, 2021. Adidas asks employees to share personal data in diversity push. [Online]. Available at: <https://www.ft.com/content/dfa5266e-ecf5-4db0-b186-9ec06d1e6ac8> [Accessed on 3 March 2022]
Highsnobiety, 2020. BLACK EMPLOYEES SAY ADIDAS HAS A DIVERSITY PROBLEM. [Online]. Available at: <https://www.highsnobiety.com/p/adidas-diversity-problem/> [Accessed on 3 March 2022]
Hofstede-insights, 2022. Compare Countries. [Online]. Available at: <https://www.hofstede-insights.com/product/compare-countries/> [Accessed on 3 March 2022]
Khan, S., 2020. Nike and Adidas: A Rivalry Made in Heaven?. SAGE Publications: SAGE Business Cases Originals.
Kostis, P.C., Kafka, K.I. and Petrakis, P.E., 2018. Cultural change and innovation performance. Journal of Business Research, 88, pp.306-313.
Kumari, N. and Singh, D., 2018. Impact of organizational culture on employee performance. Prabandhan: Indian Journal of Management, 11(6), pp.53-63.
Masri, F., 2019. Cross-cultural issues in advertising: implications for brand and global marketing efforts by consumer-oriented companies.
McGuinness, S., Redmond, P. and Delaney, J., 2020. Minimum wage non-compliance. Applied Economics Letters, 27(20), pp.1663-1666.
Morris, E., Vooris, R. and Mahoney, T.Q., 2019. You study like a girl: Experiences of female sport management students. Sport Management Education Journal, 13(2), pp.63-72.
Reuters, 2018. Adidas, Nike urged to ensure fair wages for Asian workers making World Cup kits. [Online]. Available at: <https://www.reuters.com/article/us-asia-workers-worldcup-idUSKBN1J727J> [Accessed on 3 March 2022]
Santos, J.D. and Mayer, S., 2021. Social Networks and Cultural Differences: Adidas’s Case on Twitter and Sina Weibo. In Analyzing Global Social Media Consumption (pp. 121-137). IGI Global.
Schein, E.H. and Schein, P.A., 2019. The corporate culture survival guide. John Wiley & Sons.
Schein, E.H., 2019. A new era for culture, change, and leadership. MIT Sloan Management Review, 60(4), pp.52-58.
Schein, E.H., Turner, R.A., Schein, P.A. and Hayes, T.L., 2021. A long and beautiful conversation with Edgar Schein: His journey through seven decades of social psychology, anthropology, and organizational life.
Shahudin, H.A., 2018. Operational Risk and Its Determinants: Adidas Company and Its Influences on External and Internal Factors. Available at SSRN 3181643.
Sherwood, M., Nicholson, M. and Marjoribanks, T., 2018. Women working in sport media and public relations: no advantage in a male-dominated world. Communication Research and Practice, 4(2), pp.102-116.
Smart, B., 2018. Consuming Olympism: Consumer culture, sport star sponsorship and the commercialisation of the Olympics. Journal of Consumer Culture, 18(2), pp.241-260.
Syed, R.F., 2020. Theoretical debate on minimum wage policy: a review landscape of garment manufacturing industry in Bangladesh. Asian Journal of Business Ethics, 9(2), pp.211-224.
Wallace, B., 2021. Racialized Marketing in the Athletic Apparel Industry: The Convergence of Sneaker Promotion and Black Culture in the United States. The International Journal of the History of Sport, pp.1-15.
Yue, C.A., Men, L.R. and Ferguson, M.A., 2021. Examining the effects of internal communication and emotional culture on employees’ organizational identification. International Journal of Business Communication, 58(2), pp.169-195.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

