MKTM028 Strategic Marketing MBA
Nowadays, there is an increasing level of the competition that creates the issue for the firms to get the success in the business and to develop a good customer base. So, in order to overcome these issues and to successfully manage the business, there are different ways that are used by the firms. In this, provide the different products and the services as well as different models and the approaches are also used by the firm that assist the firms to get the additional advantages and to increase the market value of the firm (Blank, 2012). Firms also focus on the innovation and the technology improvement that assist the firm to grab the market opportunities and to sustain in the competitive market. Furthermore, there are different firms related to the retail, electronics, automobile, etc that are providing their products and the services for the customers for better management of the business and to get the additional advantage in the business. These firms use the product portfolio management. It assists the firm to have the better resources utilization through manage the business at low cost and the within time (Cottrell, 2015). It also makes easy the firm generate the more revenue and to take the effective investment decisions.
This paper discusses the different importance of the product portfolio management and for this; different real firms are taken for better understating of the portfolio management in the business and in their success. In the meanwhile, different product portfolio management models are also discussed in order to know the use of different stages to manage the products and the services. In addition, some recommendation and the limitation of this paper are presented.
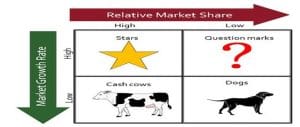
In the research of Da Cruz et al., (2012), the BCG matrix is a portfolio planning model which is been developed by Bruce Henderson of the Boston Consulting Group in the early 1970’s. According to Demirbag et al., (2010), a company’s business units can be classified into four categories i.e., stars, cash cows, dogs, question marks. The BCG model is based on the product life cycle theory and companies should have portfolio of products. It will help the company to be successful. Products with high growth require cash to progress. Products with low growth should produce more cash. Simultaneously, both are required.
Dogs: It has the products which have low growth or market share. Initially, the may show profit, but the profit is needed to invest again to maintain the share.
Question marks: It has the products which have high growth markets with low market share. They need much more amount of cash than they actually produce. If cash is not produced on time they may lag behind and eventually die. For acquiring the market share they need huge amount of cash (Grant, & Jordan, 2015).
Stars: It has the products with high growth market with high market share. They are considered as the market leader, though they also require cash to run the business.
Cash Cows: It has products with low growth markets with high market share. They produce huge amounts of cash in surplus of the reinvestment needed to maintain the market share of the company (Johnson, 2017).
Company which expands its functions with a balanced portfolio can use its power to exploit the hidden growth opportunities. The portfolio has Stars with high market share and growth helps in assuring the future. Cash cows provide cash for that future progress. Question marks to be turned into stars by using the extra cash. Dogs are the sign of failure.
From the research of Eggers (2012), a product portfolio can be defined as the bundle of products and services which a company offers to its consumers. It is the management of the methods, technologies which is been used by the project managers. It helps to analyze the current project. It offers views on company progress prospects, market leadership, types of stock, etc. It is vital for the investors as it supports internal business financial planning. In like manner, Fernhaber, and Patel (2012) stated that It is important component of financial analysis, as it gives context. Comparison can be easily obtained between short term and long term progress opportunities. For effective modelling, the particular drivers of financial performance can be known.
In the research of Gmelin, and Seuring (2014), it also helps in decision-making and helps in the allocation of resources among the various products and services. It balances the product mix to ensure profitability. It is about making strategic choices like which market the company will invest in, what will the products and services as well what will be the technologies. It helps to give suggestions on how to use the scarce resources. It also helps to make choices from the available different alternatives that the company has regarding the projects and new products. It provides a correct balance between the different projects the company have and the resources it has.
Nokia was one of the leading firms in the information technology across the world. This firm found in 1865 and till then firm was continuously performing well due to providing the quality in the products. This firm is found by the Fredrik Idestam, Leo Mechelin and the Eduard Polón (Nokia, 2017). The revenue of the firm was also quite high and it was public limited company listed in the new work and the Helsinki stock exchange. In addition, the total earning of the firm in last year was €23.61 billion that is quite high as compared to the previous year.
Product portfolio management in Information technology (Nokia)
In the research of Godey, and Lai (2011), it is stated that in the success of the firm, there was a vital role of the product portfolio management in the success of the firm and to get the additional advantage. The reason in this is that there are different ranges of the products that are provided by the firm for the customers with better quality. Firm also has continuous innovation in the products segments that made it different from other firm and provided the competitive advantage. At the same time, Kraiczy et al., (2014), defined that There are also some other aspects like sensing, wireless connectivity, imaging, power management and materials that firm also has its major focus and due to this, this firm was the fourth-largest telecoms equipment manufacturer across the world. In the same way, firm also considered the need of the customers that assisted the firm to grab the market opportunities and make a strong image of the firm in the market. In the research of Nippa et al., (2011), it is stated that for getting the competitive advantage and to develop the base of the customers in the market, having the different products range is quite essential for the firm and it also help to increase the loyalty of the customers as well. Below is the products life cycle of Nokia that represents the better understanding of the product portfolio management of Nokia (Lowy, and Hood, 2011).
The Role of product life cycle model in Nokia
In this, it can be determined that in the introduction phase, the major focuses of the firm on to develop the understanding about the products among the customers. It is because it is crucial for the firm to successful operate the business. In order to increase the awareness of the customers towards the products and the firm, there are different ways of the promotions such as social media, print media, etc that were used by the firm across the world (Mason, & Evans, 2015). After this, it is analysed that due to having the different products ranges and the continues innovation in the products, firm reached on the growth stage and during this stage, different innovations and the development are done by the firm that made the different and unique position of the firm in the market and provided the competitive advantage.
Additionally, continuous innovation and the best utilization of the products portfolio assisted the firm to reach on the maturity level (Niels et al., 2011). For instance, develop the window phone was the major example of this because Nokia was the only one that produced the window phone and helped to reach on maturity stage. But at the same time, not considering the competitors’ strategies and focus on the change in the technology and the customer needs, firm reached on the declined stage. As well as, the innovation of the windows phone was also not successful invention of Nokia and firm low branding appeal and lack focus on the advertising made the cause of come on the declining stage.
In the success of the firm and to define the success of the firm as per their product portfolio management, there is significant role of the BCG matrix. From the BCG matrix of Nokia, it can be determined that it the cash cows situation, there was the product’s introduction of the firm because there is lack knowledge among the people about the wireless local connectivity, radio implementation, etc. In the dog stage, the new series mobile phone of the firm are covered like Nokia 1100, 2200, 2650, 3350, etc (Picard, 2014). In the star situation, the all cell phone of the N series are considered because the all cell phones of the N series provided the lots of advantage to the firm and increased the market opportunities of the firm as well (Nokia, 2017).
Additionally, the all window phone of the firm are come in the question marks stage. It is because in this innovation of the firm, firm didn’t know about to right way of the investment and firm didn’t know about the future opportunities because the window phone of the firm didn’t provide the success for the firm (Pidun et al., 2011). As a result of this, firm faced so many issues and came under the decline situation of the product life cycle.
In the products mix, firm focuses on to use the competitive pricing and to provide the different verities in the products with better quality. It makes the firm competitive in the market and helps to grab the market opportunities (Nokia, 2017).
It is one of the leading and Japanese multinational automotive manufacturer firms and provides its products across the world. This firm is founded by Kiichiro Toyoda. The firm is quite popular in the international market just because of the quality in the all vehicles with better driving convenience. This firm is found in the 1937 and since 1937, firm is continuously expanding its market and the customer base. In 2016, this firm was the ninth-largest company in the world by revenue as well as it is also world’s second-largest automotive manufacturer that indicates the success of the firm in the market. Due to continue increasing demand of the Toyota products, firm produce approx 10 million vehicles per year and as per the market capitalization, it is the largest firm in Japan (Toyota, 2017).
From the product life cycle analysis, it can be determined that firm is on the maturity stage because of using the product portfolio management and providing the products as per the need and the want of the customers (Prange, 2016).
In this,
| STAR
2.0D 2.0D Saloon
|
CASH COWS
SE Saloon GLi
|
| QUESTION MARK
Xli 1.3
|
DOGS
Sports Cars |
Range in the products and good part on terms of engine, race, balancing, convenience for driver, low maintenance, etc are the major products features of Toyota that makes it different and the most popular brand across the world (Toyota, 2017).
Tesco PLC is one of the largest retailers in the world with huge number of stores which are spread across 12 countries. Tesco employs more than 500,000 people and has a huge customer base. It serves the customers online as well as offline. It is a British multinational retailer which is headquartered in UK. If measured by profits it has, it comes on the third number in the world and ninth if calculated by its revenues. It is the market leader in grocery sector. It was founded by Jack Cohen back in 1919, as a category of market stalls. It appeared first in 1924. His business showed progress very fast, and by 1939 he was having 100 Tesco stores across the country. It doesn’t operate only as a grocery store, but it has many other areas like books retailing, clothing, furniture, electronics, toys, internet services, etc (Tesco, 2017). it changed its range of products from being “Tesco Value” items to “Tesco Finest” ones. This change brought huge success for Tesco. Tesco chain showed immense progress, it grew from 500 stores to 2,500 stores fifteen years later. Tesco previous earnings account for around £162 million by the end of February 2017. One of the factors that led to Tesco’s success is its powerful brand. It’s been known for the value it offers to its customers, for the low prices, and for treating the customers effectively. The brand equity of the company has helped it to enlarge its operations into new sectors. It also provides its customers a Club card by which they can earn points whenever they do any shopping with Tesco.
Tesco is one of the largest retailers in the world which has more than 2500 stores globally including India, UK, China, etc. majority of its sales are generated from UK stores. BCG matrix helps to analyze the profitability and future prospects of Tesco.
Cash Cows
In an organization there are few units which are the main source of cash due to high market share. The fresh meat section is the cash cow for Tesco as they have a high demand in the market. The vegetables and the fresh fruits section also serves as an important part of the business unit which gives profit to company along with market share. These components help Tesco to generate revenues. Little investment is needed in the fresh produce market which will help to make it more profitable in the long-run (Tesco, 2017).
Stars
Tesco has some of its products which are identified as stars as they generate enough income for the company. One example of star company in Tesco is the Tesco Bank. Tesco Bank has enlarged its presence by providing its consumers with services like insurance, loan and current account facility (Rudnicki, and Vagner, 2014). As bank sectors have high progress potential, Tesco Bank will gain a higher market share in future. The premium products of Tesco are also stars for the company.
Question Marks
It is not necessary that all the unit of the company will work efficiently. There are some that will create low revenues for the company than expected by them. There is high uncertainty regarding the future of these kinds of products. At the same time, the market development also not has the expected effect on the income generated by these products. There are products in Tesco which are not utilized to their fullest. Tesco Lard is a question mark for the company as the demand for the products is not much (Salazar., and Lunsford, 2014). This is the reason for the declining sales over the years which results in creating pressure on the company.
Dogs
This category includes products which doesn’t perform as per the expectations and are not satisfactory. They have a low return on investment. If the company still wants to manage the operations it should start investing, yet these products are a source of loss for the company. Tesco mobile company is in this category as it has an uncertain future. This sector has a high competition and slow progress. There are two options left for the company either to sell the company or to go for liquidation (Udo-Imeh, et al., 2012).
Tesco provide a wide variety of products to its customers. The range of products includes food, clothing, electronics, internet services, financial services, etc. with its ever large product lines, it also caters to every possible potential customers. In every product line, Tesco sells products from great brands (Tesco, 2017). It also has its own products and brands like Tesco Lard, Tesco lotus, Tesco Value, etc. It has variety of stores and the type of product the customer looks for depends on the type of store. It recently reduced its product lines by 18%.
PLC is product life cycle of any company. Every company has to cross the different stages of PLC in its life of business. The different stages of PLC are introduction, maturity, growth and decline. Every product of the company has to go through these four stages in their lifetime. Tesco has a wide variety of products all over the world. It has a huge customer base. Tesco’s finest grated cheese is in the growth stage as the price is quite low. At the same time, Tesco Lard is in the decline stage because it is not healthy and there are now other better alternatives available.
(Source: Tesco 2017)
The chart depicts that Tesco has a huge customer base which helps it to perform better. The sales is also increased which helped the company to attain high market share. The Business strategy adopted by Tesco is also favourable and helped the company to achieve its objectives. Tesco’s branding is also very effective in providing overall success to the company.
From the above discussion, it is analysed that use of product life cycle, BCG matrix and the product portfolio are not only the ways that can be used by the firm to get the market position of the firm in the market and to get the detail understanding about the product demand in the market. It is because through the BCG matrix, firm can know only the product cycle not the position of the product as well as it also doesn’t provide the ways that can be used by the firm to regarding the product development. So, it can be recommended that there is a need for the firm to use the market research for managing the product portfolio effectively (West et al., 2015). At the same time, it can also be recommended that there is also a need for the firm to follow some other stages like move beyond prioritization, use a variety of methods, build an actionable strategy, present a range of compelling portfolios and build risk into your forecast that will be helpful for the firm to do the best product portfolio in an effective manner.
From the above discussion, it can be determined that there is a vital role of the BCG matrix and the product life cycle in the success of the firm as well as in the successful management of the product portfolio. BCG matrix helps the firm to get the idea about the value of the products and to take the decisions accordingly. In like manner, it can also be stated that firms like Tesco, Toyota and the Nokia had the good use of the PLC, BCG matrix and the portfolio bubble chart that provided the advantage for the firm to get the success in the market.
Blank, S. (2012) The startup owner’s manual: The step-by-step guide for building a great company. USA: BookBaby.
Cottrell, S. (2015) Skills for success: Personal development and employability. UK: Palgrave Macmillan.
Da Cruz, M. R. P., Ferreira, J. J., and Azevedo, S. G. (2012) A static and dynamic strategic portfolio analysis: the positioning of Iberian seaports. South African Journal of Business Management, 43(1), pp. 33-43.
Demirbag, M., Sahadev, S., and Mellahi, K. (2010) Country image and consumer preference for emerging economy products: the moderating role of consumer materialism. International Marketing Review, 27(2), pp. 141-163.
Eggers, J. P. (2012) All experience is not created equal: learning, adapting, and focusing in product portfolio management. Strategic Management Journal, 33(3), pp. 315-335.
Fernhaber, S. A. and Patel, P. C. (2012) How do young firms manage product portfolio complexity? The role of absorptive capacity and ambidexterity. Strategic Management Journal, 33(13), pp. 1516-1539.
Gmelin, H. and Seuring, S. (2014) Achieving sustainable new product development by integrating product life-cycle management capabilities. International Journal of Production Economics, 154, pp. 166-177.
Godey, B., and Lai, C. (2011) Construction of international brand portfolios: impact on local brands. Journal of Product & Brand Management, 20(5), pp. 402-407.
Grant, R. M., & Jordan, J. J. (2015) Foundations of strategy. USA: John Wiley & Sons.
Johnson, G. (2017) Exploring strategy: text and cases. USA: Pearson.
Kraiczy, N. D., Hack, A., and Kellermanns, F. W. (2014) New product portfolio performance in family firms. Journal of Business Research, 67(6), pp. 1065-1073.
Lowy, A. and Hood, P. (2011) The power of the 2 x 2 matrix: Using 2 x 2 thinking to solve business problems and make better decisions. USA: John Wiley & Sons.
Mason, R., & Evans, B. (2015) The Lean Supply Chain: Managing the Challenge at Tesco. UK: Kogan Page Publishers.
Niels, G., Jenkins, H., & Kavanagh, J. (2011) Economics for competition lawyers. UK: Oxford University Press.
Nippa, M., Pidun, U., and Rubner, H. (2011) Corporate portfolio management: Appraising four decades of academic research. The Academy of Management Perspectives, 25(4), pp. 50-66.
Nokia. (2017) [Online] Available at: https://www.nokia.com/en_int/phones/all-phones (Accessed: 01 August 2017).
Picard, R. G. (2014) Media product portfolios: Issues in management of multiple products and services. UK: Routledge.
Pidun, U., Rubner, H., Krühler, M., Untiedt, R. and Nippa, M. (2011) Corporate portfolio management: Theory and practice. Journal of Applied Corporate Finance, 23(1), pp. 63-76.
Prange, C. (Ed.). (2016) Market Entry in China: Case Studies on Strategy, Marketing, and Branding. USA: Springer.
Rudnicki, W., and Vagner, I. (2014) Methods of strategic analysis and proposal method of measuring productivity of a company. Zeszyty Naukowe Małopolskiej Wyższej Szkoły Ekonomicznej w Tarnowie, 2 (25), pp. 175-184.
Salazar, F. J., and Lunsford, R. (2014) Onshoring: An i-Opener for Apple, Inc. International Journal of Trends in Economics Management & Technology (IJTEMT), 3(2).
Tesco. (2017) [Online] Available at: https://www.tesco.com/ (Accessed: 01 August 2017).
Toyota. (2017) [Online] Available at: http://www.toyotabharat.com/ (Accessed: 01 August 2017).
Udo-Imeh, P. T., Edet, W. E. and Anani, R. B. (2012) Portfolio analysis models: a review. European Journal of Business and Management, 4(18), pp. 101-117
West, D. C., Ford, J., & Ibrahim, E. (2015) Strategic marketing: creating competitive advantage. USA: Oxford University Press.



Por favor, más de este feedback. Me alegra esta observación. Me hace querer esta idea.
https://maps.app.goo.gl/TPhBVJXniTB8QdM2A