MD7001 Evidence Based Medicine Assignment Sample
Title of Literature Review
“Efficacy and widespread use of herbal remedies for treating early Alzheimer’s disease”
Introduction
Herbal products have gained increasing popularity in the first years and 20% of the world population have used this product. Herbal product is the mixture of different organic chemicals which come from processed parts of plants that include flowers, roots, stems and leaves.
Under the current law, it has been found that herbal products have been defined as a dietary supplement as different manufacturers can sell and produce the product without demonstrating efficacy and safety. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) has been characterized by the progressive neurodegenerative disorder which has been considered the main cause of dementia in the elder people.
The main objective of the study is to focus on the clinical trials for reducing the psychological and behavior symptoms of dementia and improve the functional activities status by using herbal medicine. The main scope of the study is to analyze the main concept of the disease and the need of our medicines for the treatment which will provide different chemical responses. Many herbal products have been tested which have been employed for that treatment of the disease and identified effective products.
Main body
Molecular mechanism
The main characteristics of AD are neurofibrillary and AB pathology. For the last 25 years, most of the studies have been conducted for understanding the progression and pathogenesis of the disease for finding effective treatment. In the opinion of Deshpande, Gogia & Singh (2019), due to the failure of clinical trials it has been found that the pathology treatment and the propagation of intracellular abnormal proteins can lead to neurodegenerative disorder.
The extensive analysis of pathological treatment has indicated abnormal protein and structural problems for diagnosis. Therefore, it has been clearly identified that the molecular mechanism and the treatment procedure cannot modify that diagnosis of AD, however it leads to dependent aggregation.
Drug target
The amyloid and tau hypothesis has led to focus on the treatment target however the current therapeutic goal has been used for decreasing amyloid levels by preventing the toxicity and improving phosphorylation. As per the views of Sharma et al. (2019), AD has heterogeneous cause for using a large percentage that has been known for smaller fraction and familiar with the cause of mutation in various types of genes such as beta amyloid precursor protein.
Other different types of genes such as apolipoprotein E have been considered a political factor about the particular disease. In the opinion of Perng, Chang & Tzang (2018), various proteins which include BACE, APP, APOE and the important factors which can improve and play an important role in pathogenesis.
The research has been focused for developing herbal based treatment which can provide for executing new inhibitors for BASE, PS1. There is significant advancement for understanding the brain and the use of cholinesterase inhibitors for enhancing the management process of AD.
As explored by Habtemariam (2019), the mechanism of a new generation of butyryl and acetyl cholinesterase inhibitors have been investigated and studied in the clinical trial of AD. Other different strategies, such as antioxidants, hormone therapy, anti-inflammatory agents and vaccination have also been studied to treat AD.
Herbal treatment
The demonstration of damage to the individual pathway of cholinergic have been forecasted in the brain which need to weight interest for drug development. In the opinion of Phu et al. (2020), acetylcholinesterase inhibitors have been usually prescribed for treating how the drug is helpful for enhancing cognitive function that incorporates thoughts and memory.
The medicines are effective for the patient with mild to moderate AD. In the opinion of Brandt et al. (2019), tacrine is another medicine which has been reportedly used for treating AD. The concept of Tacrine has been investigated for both in neuropsychological test score and trial for randomized placebo controlled trial. However, application of Tacrine has been limited due to its adverse effects that include hepatotoxicity.
As per the opinion of Sharman et al. (2019), the use of antioxidants are effective for treating AD used to reduce individual free radicals which can damage the brain cell. Probiotics have been also reportedly used for enhancing memory and it is used as an antidepressant in AD.
It helps to reduce anxiety like behavior and can lead to psychological stress. Different neurochemicals have been produced by the microbes that can be induced by probiotics due to neurological and immunological effects. As opined by Alexander, Emerson & Kesselheim. (2021), in ayurvedic and Chinese medicine, medicinal plants have been used for treating AD and cognitive disease as well as neurodegenerative changes.
In the views of Cano et al. (2019), various Western medicines have been used for memory loss which are derived from plants. Plant has extracted alkaloids which incorporate anticholinesterase that have been used for treating AD.
In different places of the United Kingdom, galatimine has been derived from the plant that has been used for the treatment of neuro degenerative disorder. More than 5 million Americans have suffered from the disease and by the year 2030, the number will increase by 7.7 million. As argued by Tewari et al. (2018), there are different symptoms of neurodegenerative disorder that mainly appear after the age of 60.
The etiology of neurodegenerative disorder has been linked to genetic defects mainly in 10 to 15% of the total cases. In the case of AD, it has been found that there will be loss of neurons in the hippocampus, cortex and subcortical structure. As per the views of Singh et al. (2019), various compounds have been identified with the help of phytochemical studies that include sterols, tannis, polyphenol, lignins for having pharmacological activities that include anti-amyloidogenic and anti-cholinesterase.
Medicinal plants have played a significant role in the management of AD which can lead to memory deposit. In the opinion of Farr & Xiong (2020), the traditional method of therapy mainly includes homeopathy, ayurvedic, siddha and unani systems.
It has been found that the Unani system of medicine mainly offered a scientific health care therapy which provided global interest in the medical profession and primarily focused on medicinal plants. In the views of Broom, Shaw & Rucklidge (2019), apart from this, the traditional system of medicine is protective, preventive, curative and nutritive. Hence, it can be stated that traditional medicines are harmless and set which can treat the patient with fewer side effects.
Concept of herbal medicines have their own origin in the ancient culture that include Indian, Chinese and Egyptian for involvement in herbal methods of treatment. As argued by Craft et al. (2020), it has involved the use of herbal plants for treating AD and encouraging the well-being and general health of patients.
In fact, it has been identified that many pharmaceutical drugs have been based on the synthesized adoption of complex compounds found in the plant. In recent times, it has been projected that the interest in herbal medicine has increased then leads to medicinal use of plants and greater scientific interest for treating disease and improving health without any negative side effects. As per the views of Deshpande, Gogia & Singh (2019), natural medicines and herbal products are the oldest remedies for human beings. It can be stated that medicinal plants have been used by all cultures in the demand of herbal products has grown exponentially globally.
In the human body, the nervous system has been regulated and coordinated with the various involuntary and voluntary activities of the body. As mentioned by Sharma et al. (2019), the autonomic nervous system and the central nervous system are interlinked which provide different drug effects that lead to CNS producing reactions which are associated with the autonomic system.
Different drugs involved within the CNS have depressant send with psycho pharmacological activities and anticonvulsant activities. In the views of Perng et al. (2018), there is a major consequence of AD which is memory deficit and it is a global health problem. Current therapies have numerous and inadequate adverse effects which are needed for the possible treatment of AD and overall memory deficit.
Different types of medicinal plants are being prescribed for enhancing memory and based on the literature the medicinal plants have been applied for the treatment of AD as well as improving memory deficit. As explored by Habtemariam (2019), different types of medicinal plants have been used for the large decades in different cultures for enhancing memory such as Punica granatum, Centella asiatica Linn, Myristica fragrans Bacopa monnieri Linn.
Therefore it can be stated that, the utilization of herbal medicine helped to treat various ailments mainly in the Unani system. However, there is a lack of scientific data for understanding the stability and effectiveness of bioactive chemical constituents in the field of medicinal plants.
Herbal formulation of the mix of herbal ingredients is beneficial with comparing multiple target regulation with single target mainly in the views of Chinese medicine (Brandt et al. 2019). It has been found that there have been few clinical trials which have been examined for understanding the safety and efficacy of herbal formulation mainly in the AD patience.
Mixture of 6 different herbs has been used for reducing the amyloid cytotoxicity that can increase the memory score from the baseline without any difference in aniracetam.
In the phase 3 trial, it has been found that stilbene glycoside is an extract from the Shenwu capsules that has been evaluated on phase one trial for treating AD. On the other hand, GEPT is a combination of five different active components that has been extracted from the Chinese herb and used for the treatment of AD (Sharman et al. 2019).
It has been used for reducing the level of pathogenesis in inhibitors and the promotion of insulin degrading the neprilysin and enzyme. A 24 week preliminary study has been shown that significant improvement in the cognitive function of the patient with mild cognitive impairment can be easily diagnosed [Referred to Appendix 1].
Single herbs or extracts from herbs
Ginkgo Biloba
This herb is an extraction from while leaves complementary therapy and review different 36 trials of ginkgo Biloba. The 9 trials have been found in the six month duration and conducted for a reasonable standard.
Three different studies have found at different doses with a treatment in the effect and the favor of Ginkgo Biloba. That trial sample size was very small which reportedly focused on reducing cognitive decline with mild cognitive impairment (Alexander, Emerson & Kesselheim, 2021). Current evidence of Ginkgo aise clinically predictable significant benefits for the people with cognitive impairment and dementia that negatively affect unreliable and inconsistent means.
Serrate clubmoss
Huperzine is an herb which is extracted from serrate clubmoss herb and has evidence of six trials. The beneficial effect on the improvement of this house is mainly focusing on general cognitive function by providing functional performance and behavior disturbance (Cano et al. 2019). One study has been adequate for understanding the size and quality and focus on the large treatment effect which has been adequate for the best approach.
Ginseng
Panax ginseng is a main active immunity and that can enhance cognitive and psychomotor performance and benefited for improving brain cholinergic function. High dose critically identified for significant improvement on the AD disease. The study has been designed with insufficient description of randomization which can help to find the concurrency in the Western medication.
Salvia officinalis
Salvia Officinalis has been used for treating herbal medicine for the last centuries and extracted from the significantly better outcome for cognitive function. There was no significant difference between placebo and salvia officinalis for understanding the effective treatment and observing the side effect (Tewari et al. 2018). Additionally, it can be stated that salvia officinalis reduce agitation for the patient by providing high quality large scale trials which have been needed for that determination of efficacy of the herbal treatment. The different action mechanism of the herb and the formulation has not been critically identified.
It has been suggested that the chemical composition is the main relationship oil of salvia and Melissa live extract which have been used for the treatment of AD. All of the components have observable effects that may include antioxidative activity for use in muscarinic and nicotinic receptors mainly in the human cerebral cortex (Singh et al. 2019).
The last mechanism has been used for special interest for the modulation of the cholinergic system which plays an important role for enhancing cognitive function. The herbal product has already been targeted for quantifying the systematic review study and focusing on the drag assessment for identifying effective products for that treatment of AD. The use of herbal medication is cost-effective and provides treatment for the reduction of institutionalized care.
Mini herbal products have been employed and tested for the treatment of AD with different chemical responses. Therefore the study has critically identified all the patients including those with AD disease and its significance on herbal treatment for better prognosis (Farr & Xiong, 2020). The studies have critically identified effectiveness of herbal treatment and its substance in the cognitive deterioration of AD.
Conclusion
From the above study, it can be concluded that single herbs or formulations may be able to understand the complement drugs for AD. Current evidence has been focused to underline the different methods and the limitations of using drug treatment for AD patients.
The potential value is to find the analysis development in China for enhancing the mixture that will helpfully show positive results in the coming future. The review of literature has critically defined different management of AD and the use of medicinal plants with the help of potential therapeutic values. The herbal therapy has been anticipated for controlling the AD progression which helps to relieve the symptoms related to the disease.
Therapy can improve the quality of life of patients and memory deficits. Worldwide research has been done for finding effective treatment of the disease and reveals herbal therapy which is an encouraging choice for alternative treatments.
Medicinal plants have been used for different systems and exhibit the powerful mole in the cure of memory disorder. Most of the plants and herbs have been chemically evaluated for finding magnificent and considerable outcomes. Future clinical trials have been involved in dark circle size for investigating the different medicinal plants to underline the mechanism.
Reference list
Alexander, G. C., Emerson, S., & Kesselheim, A. S. (2021). Evaluation of aducanumab for Alzheimer disease: scientific evidence and regulatory review involving efficacy, safety, and futility. Jama, 325(17), 1717-1718. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/2778191
Brandt, J., Buchholz, A., Henry-Barron, B., Vizthum, D., Avramopoulos, D., & Cervenka, M. C. (2019). Preliminary report on the feasibility and efficacy of the modified Atkins diet for treatment of mild cognitive impairment and early Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 68(3), 969-981. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2020.00422/full
Broom, G. M., Shaw, I. C., & Rucklidge, J. J. (2019). The ketogenic diet as a potential treatment and prevention strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. Nutrition, 60, 118-121. https://www.mdpi.com/708436
Cano, A., Ettcheto, M., Chang, J. H., Barroso, E., Espina, M., Kühne, B. A., … & García, M. L. (2019). Dual-drug loaded nanoparticles of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG)/Ascorbic acid enhance therapeutic efficacy of EGCG in a APPswe/PS1dE9 Alzheimer’s disease mice model. Journal of Controlled Release, 301, 62-75. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168365919301579
Craft, S., Raman, R., Chow, T. W., Rafii, M. S., Sun, C. K., Rissman, R. A., … & Aisen, P. S. (2020). Safety, efficacy, and feasibility of intranasal insulin for the treatment of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease dementia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA neurology, 77(9), 1099-1109. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2018.00548/full
Deshpande, P., Gogia, N., & Singh, A. (2019). Exploring the efficacy of natural products in alleviating Alzheimer’s disease. Neural regeneration research, 14(8), 1321. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc6524497/
Farr, A. C., & Xiong, M. P. (2020). Challenges and opportunities of deferoxamine delivery for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and intracerebral hemorrhage. Molecular pharmaceutics, 18(2), 593-609. https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=AGmQDwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA1&dq=Efficacy+and+widespread+use+of+herbal+remedies+for+treating+early+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&ots=mWOEotTeDR&sig=DSHZP1tOtgk6Vfx5arkcICf49jY
Habtemariam, S. (2019). Natural products in Alzheimer’s disease therapy: would old therapeutic approaches fix the broken promise of modern medicines?. Molecules, 24(8), 1519. https://www.mdpi.com/447602
Perng, C. H., Chang, Y. C., & Tzang, R. F. (2018). The treatment of cognitive dysfunction in dementia: a multiple treatments meta-analysis. Psychopharmacology, 235(5), 1571-1580. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00213-018-4867-y
Phu, H. T., Thuan, D. T., Nguyen, T. H., Posadino, A. M., Eid, A. H., & Pintus, G. (2020). Herbal medicine for slowing aging and aging-associated conditions: efficacy, mechanisms and safety. Current Vascular Pharmacology, 18(4), 369-393. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352873718300799
Sharma, R., Kuca, K., Nepovimova, E., Kabra, A., Rao, M. M., & Prajapati, P. K. (2019). Traditional Ayurvedic and herbal remedies for Alzheimer’s disease: from bench to bedside. Expert review of Neurotherapeutics, 19(5), 359-374. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/14737175.2019.1596803
Sharman, M. J., Verdile, G., Kirubakaran, S., Parenti, C., Singh, A., Watt, G., … & Münch, G. (2019). Targeting inflammatory pathways in Alzheimer’s disease: a focus on natural products and phytomedicines. CNS drugs, 33(5), 457-480. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40263-019-00619-1
Singh, S. K., Srivastav, S., Castellani, R. J., Plascencia-Villa, G., & Perry, G. (2019). Neuroprotective and antioxidant effect of Ginkgo biloba extract against AD and other neurological disorders. Neurotherapeutics, 16(3), 666-674. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13311-019-00767-8
Tewari, D., Stankiewicz, A. M., Mocan, A., Sah, A. N., Tzvetkov, N. T., Huminiecki, L., … & Atanasov, A. G. (2018). Ethnopharmacological approaches for dementia therapy and significance of natural products and herbal drugs. Frontiers in aging neuroscience, 10, 3. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00003/full
Appendix 1: Cognitive function in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment
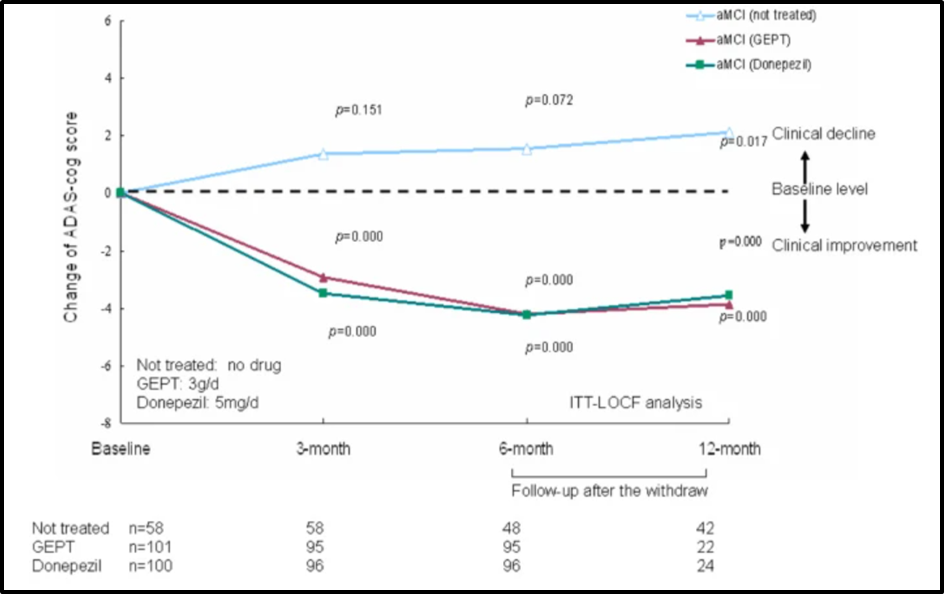
(Source: Tewari et al. 2018)
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services: