MOD005714 Data Centre & Cloud Infrastructures Assignment
Introduction
A data centre is a physical location where agencies keep their crucial programs and data. It’s critical to consider long term about how to preserve their security and reliability as they expand from centralized on premises facilities to edge deployments to public cloud services. Servers, SANs, and virtual machines make up the infrastructure of Cloud. In order to enable deployments and scalability of Cloud, cloud companies will create infrastructure that is basically comparable. Hardware federation and federating virtual machines are examples of this. A primary data centre and a backup data centre are common in cloud systems. These centers might be named Availability zones inside the same location, or potentially two locations running from a separate Virtual Private Cloud network, under a system like AWS or Google Cloud. Many companies have Virtual Machines, a management platform, an identity authentication system, and backup and recovery systems that span both data centers in both centers and zones. Both physical and virtual servers are depicted in this arrangement, all connected to a shared SAN storage, which is copied across to the secondary data centre in the primary data centre to support disaster recovery and failover should services at the primary data center fail. The presence of a firewall device in the centre denotes a secure network connection between data centers, allowing traffic to be rerouted. If necessary, this also allows for failover of both cloud management nodes and customer Virtual Machines. In the case that the first data center goes down, the secondary data center can take over all cloud services. Crypto file logic (CFL) is a small organization based in different locations throughout the world. This company is very small and possesses only thirty employees. They provide services like PII data for the government using block chain technology. They are using a single server for data centers with very little system for computation, storage devices and network.
Discussion
Data centers are frequently referred to as a single entity, but they are actually made up of several technical components. These can be classified into three groups
Compute: High-end servers supply the memory and processing power needed to operate the applications.
Storage: Many companies’ data is usually stored in a data centre on a variety of media, from tape to solid-state drives, with several backups.
Networking: Routers, switches, application delivery controllers, and other connections between data centre components and the outside world.
Every company begins their journey to data centre optimization at a different point. Each step forward necessitates company preparation for the upcoming technology and developments (Chunling et al 2019). This means that rather than a comprehensive tear and replace, the data centre will be transformed in stages. Each level will have distinct advantages and set the foundation for the next.
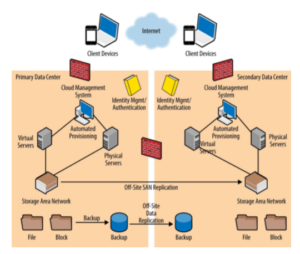
Figure 1: Cloud system of a Data center
(Source: https://crmtrilogix.com/Cloud-Blog)
The stages for optimizing data center in CFL to give services to third parties are
- Operational excellence improvement
The most up-to-date hardware and software capabilities are designed to reduce operating costs, increase efficiency, and ensure security and compliance (Demchenko et al 2020). The purpose of this stage is to replace ageing infrastructure in order to support cloud computing.
- Innovative Service Delivery
Cloud computing enables any company to give on-demand services to their employees, customers, and partners (Hashmi et al 2021). For getting the optimum total cost of ownership (TCO) to a company’s applications, use private, public, or hybrid cloud solutions.
- Taking new opportunity for business
The company may also take advantage of opportunities like big data, Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) programs and social & collaborative computing thanks to the newest infrastructure and cloud computing technologies [Referred to appendix 1].
The initial step to do is poorly performing infrastructure update and upgrade. These can be done through some series of ways. They are
- Compute
With the new faster machines with powerful processors, better CPU capacity, storage capacity and quality improvement, security capability built in and significant small power consumption the server technology is now improved. Companies can do more with replacing less of older servers with fewer new servers (Liang et al 2021). Server innovation also includes capabilities of real in memory computing and supporting real time analysis and reporting. High density, lower cost energy efficient micro server’s structures are perfectly suitable for lightweight workloads such as basic delivery of content, serving web pages and hosting of entries.
Intel offers its Xeon processors for the server workloads to the data center. These processors have more computational cores than traditional Intel processors for better managing server workloads in the data center (Moyeenudin et al 2021). These processors have mostly 32 cores or more for many complicated critical workloads of different tasks. AMD also provides its own branding server processor such as Threadripper and EPYC (Pico et al 2020). These new processors have significantly more cores than the Intel Xeon lineup. So, AMD’s CPU is better suited for server workloads than Intel. However, there are many factors that come in consideration when building a server.
- Network
For growing demands for bandwidth existing 100 megabit per second (Mbps) or 1 gigabit Ethernet (GbE) internet is not very viable. According to Cisco’s 2014 Visual Networking Index, global broadband speeds will grow by 2.7 times by 2018 from 15 Mbps to 42 Mbps. Forward-thinking data centers are replacing slower connections with 10, 40, and 100 GbE connections, which will be required to transmit a threefold increase in Internet traffic by 2018, which is expected to reach 1.6 zettabytes.
So instead of using that, maybe a 10 gigabit connection is better suited for server applications (Pyae 2018). The better quality LAN cable can also increase efficiency and speed of existing data center or virtual machines connections.
- Storage
Intelligent storage solutions with expanded capabilities, for example, have advanced storage technology that makes it more efficient to store and access data. For mixed-use applications, solid-state drives deliver remarkable performance, durability, and consistency (Qayyum et al 2021). Upgrades to storage should be driven by specific business and user needs.
- Facilities
The data center’s physical facility can be improved for space, power management, and cooling, affecting technology performance and extending the life of the data center. If companies follow a set of best practices at every stage of the data centre life cycle. Intel IT has discovered that retrofitting an existing data centre can cost less than new construction [Referred to appendix 2] .
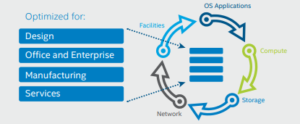
Figure 2: Optimization Cycle of data center
(Source: https://www.connection.com/~/media/pdfs)
Once this is done then some steps can be followed. The next two stages of improving operational efficiency: using unique technical capabilities to supply innovative services and take advantage of new business possibilities. The steps are
- Create a strategy for data center
The company can define the sequence of steps they need to take to get there and the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will evaluate their success by looking at where the data centre is now and where the company needs it to go by looking at where it is now and where the company need it to go.
- Through cloud and virtualization enabling an agile IT industry.
Utilize the natural performance and efficiency of the company’s updated hardware to adopt virtualization for improved resource usage and, ultimately, service quality (QoS). They are laying the groundwork for cloud computing when they start sharing resources like CPU and storage.
- Cloud building and turn IT as service broker
Moving to the cloud entails automating processes for provisioning and managing infrastructure and delivering services to internal and external clients using pooled resources (Zhou et al 2019). IT becomes a trusted advisor or mediator who delivers accessible, integrated, and secure cloud solutions that address business problems rapidly when your firm shifts its focus to cloud service brokerage.
- Success measuring
Measure the progress of the company against the goals and strategy of the data center. Advancing through the plan of three year the ‘KPIs will present the team and business actual results that can be interpreted and used for the next section.
These are some methods that Crypto File Logic (CFL) can follow in order to increase the efficiency of their data center to provide services for consumers and 3rd parties. These models can handle the increasing demands of blockchain services and mitigate any difficulty that might arise from heavy workloads of data centers.
Conclusion
Nowadays IT is serving strategic partnership for innovation of business and at the same time maintaining the business and reducing cost of operation. The main focus point of this is the data center. Organizations’ data centers must improve their infrastructure to provide the efficiency and agility to accelerate growth of business. There are some powerful technologies for providing quick service delivery such as big data, cloud computing, high performance computing. These services provide a huge opportunity for businesses that need this kind of service. The presence of a firewall device in the centre denotes a secure network connection between data centers, allowing traffic for rerouting. If necessary, this also allows for failover of cloud management nodes and customer Virtual Machines. Data centre technology is rapidly evolving, and keeping up is one of the most difficult tasks IT has today. This planning guide examines the problems surrounding data centre optimization, including how to adapt a company’s data centre to suit today’s business needs while building the basis for a next-generation data centre that supports even more business innovation and efficiency.
Reference List
Journals
Chunling, D.U., Xiubin, F.A.N., Jimin, L.I.U. and Huiqi, Z.H.A.O., 2019. CFL Authentication System Solution in Field of Industrial Control Information Security. DEStech Transactions on Computer Science and Engineering, (iccis).
Demchenko, Y. and Cuadrado-Gallego, J.J., 2020. Data Science Professional Profiles. In The Data Science Framework (pp. 109-134). Springer, Cham.
Hashmi, S.A., Ali, C.F. and Zafar, S., 2021. Internet of things and cloud computing‐based energy management system for demand side management in smart grid. International Journal of Energy Research, 45(1), pp.1007-1022.
Liang, Y., Lu, M., Shen, Z.J.M. and Tang, R., 2021. Data Center Network Design for Internet‐Related Services and Cloud Computing. Production and Operations Management.
Moyeenudin, H.M., 2021. Cloud Based Property Management System in Integration with IoT. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education (TURCOMAT), 12(9), pp.206-225.
Pico, P., Valdés, J.P., Pinilla, A., Echeverri, A., Gómez, J.M., Ratkovich, N. and Cifuentes, B., 2020. CFD modelling of the air conditioning system for a Tier 2 Data Centre. Advances in Building Energy Research, pp.1-31.
Pyae, A., 2018. Cloud Computing in Business Intelligence.
Qayyum, A., Ahmad, K., Ahsan, M.A., Al-Fuqaha, A. and Qadir, J., 2021. Collaborative federated learning for healthcare: Multi-modal covid-19 diagnosis at the edge. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.07511.
Zhou, J., Tian, D., Wang, Y., Sheng, Z., Duan, X. and Leung, V.C., 2019. Reliability-optimal cooperative communication and computing in connected vehicle systems. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 19(5), pp.1216-1232.
Appendices
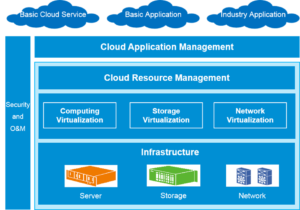
Appendix 1: Data center cloud services
(Source: https://res-www.zte.com.cn/mediares/zte/Global/products/)
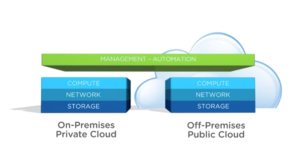
Appendix 2: Different Cloud system
(Source: https://ix-cdn.b2e5.com/images)
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

