MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample
Introduction
Global strategy and sustainability forms are necessary when a company plans to expand its sales in a global market. According to Shabir and AlBishri, (2021), developing a global business strategy is beneficial to generate international sales and not only increases the profit margin but will also increase brand awareness and reputation in local and global markets.
Before developing a global strategy, a business necessarily needs to analyse how its products can function in international markets. At the same time, the company should also identify its global customers, competitors and international standards applicable for global expansion. The following business report will analyse the global strategy scenario in Zara UK.
Task 1:
Internal analysis
1) SWOT analysis
Strengths: Fashionable clothing, global reach and affordable prices of the product have helped Zara gain a competitive edge in the market.
Furthermore, the company has also focused on sustainable manufacturing to increase brand valuation in global markets.
Weaknesses: Zara spends less on advertising and marketing, which eventually have decreased its global reach in past years.
Moreover, inadequate supply chain management has been a major drawback to the company’s growth which needs to be addressed in future (López et. al. 2022).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample
Opportunities: The global market trends are continuously changing; therefore, it builds a greater opportunity for Zara to expand its market by attracting global customers through its products.
Technological advancements have also created online channels where people can purchase a product at their convenience.
Threats: With changing fashion details, Zara faces extreme threats of competition, where people prefer new products with exciting products and price ranges. This can be a major limitation and threat to the company (Kim and Oh, 2020).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample
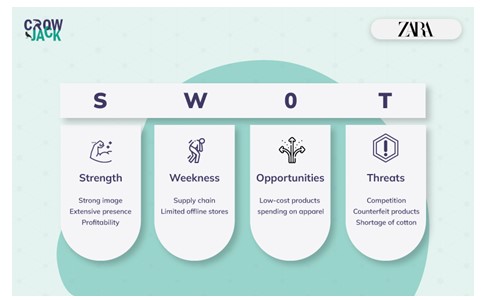
Figure 1: SWOT Analysis of Zara
(Source: A Precise, Pragmatic, and Insightful SWOT Analysis of Zara, 2022)
2) VRIO analysis
Valuable: Through VRIO analysis, it can be stated that the company’s financial resources are extremely valuable as it allows Zara to mitigate external threats by investing in external trade opportunities.
Moreover, by investing in newer products and services, Zara values its competition and ensures that its customers are satisfied.
Rare: Based on the VRIO, the company do not offer extremely rare products that can attract customers in the UK and global markets. Products offered by Zara are easily provided by its competitors, which reduces the company’s competitive advantage over other companies (Cui and Fan, 2021).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample
Imitable: Some products of Zara are easy to imitate, while some are costly to imitate, as noted through the analysis. For example, the food products offered by Zara are not costly; therefore, they can be imitated by its competitors to earn similar profits to Zara.
Organisation: Being a global company, Zara uses its financial resources to invest in the right places by using available trade opportunities.
By doing so, the company is able to maintain its sustainable competitive advantage in the UK and in international markets (Maula, 2022).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample
External analysis
1) PESTEL analysis
Political: Through extensive trade agreements, Zara benefits from operating its business in European nations because it is easy to import raw materials and products within the EU and reduces the cost of production and merchandising in Europe. The free trade policies of the EU provide a massive political benefit to the company.
Economic: Relative affordability and low labour cost are some major advantages Zara experiences when operating in countries like the UK.
The company manufactures a good ratio of products in the UK and other countries like Germany, France and Spain, which eventually minimises the cost of production, thereby improving profits.
Sociocultural: With clever marketing efforts, Zara has been able to create a strong and positive reputation in the market by delivering high-quality products at affordable prices.
Moreover, the company thrives on matching the online shopping trends that exist in the 21st century, where consumers happily prefer Zara products (Mehta, 2021).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample
Technological: Zara is a recognised brand that understands the necessity of technology for global expansion.
The company uses big-data analytics to retrieve necessary information from its customers to understand the touch points that can appeal to customers to buy their products.
Environmental: Many fashion products designed by Zara do not last long, which can be associated with wastefulness. With customers becoming more eco-friendly, the brand must improve its strategies and adopt a more sustainable strategy that can encourage customers to purchase products of the brand (George et. al. 2020).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample
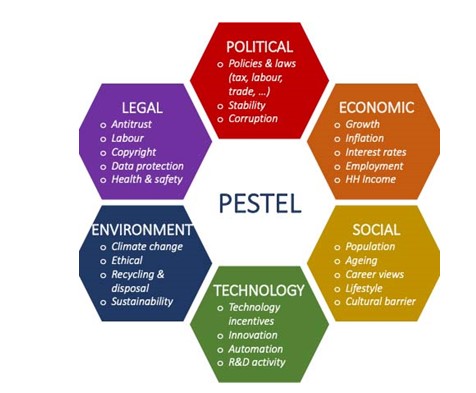
Figure 2: PESTEL Analysis of Zara
(Source: How to conduct an effective PESTEL Analysis?, 2021)
Legal: Like other fashion brands and companies, Zara faces major legal issues related to the copyright law. The company operates to maintain the trending fashion market by increasing the availability of its products at affordable prices.
However, bigger brands often face issues of stealing designs and clothing concepts that can create legal trouble for companies like Zara.
2) Porter 5 forces analysis 250
Competition in the industry: Zara has one of the strongest supply chain responsiveness in European markets, especially in the UK, which provides competitive advantages to the company. However, H&M, Benton and Gap are its biggest competitors that own qualified products such as Zara (Su, 2020).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample
Potential of New Entrants: Despite of changing fashion trends and economic crises in the UK, Zara plans to provide products at a very reasonable price.
However, increasing the value of the euro will eventually increase the product price for customers, where Zara might lose its competitive advantage over other companies. However, the potential of new entrants is extremely low for the company.
Power of suppliers: The bargaining power of suppliers in the fashion industry is extremely high because Zara needs to maintain an established relationship with a single supplier who has knowledge and understanding of the safety and quality of products (Zara et. al. 2021). http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment SampleOn the other hand, Zara is dependent on licensed contractors that provide no room for design variations which is yet another disadvantage for the company.
Power of Customers: Fashion statements released by brands like Zara are not highly effective as the company believes in words that travel mouth to mouth-from one buyer to another.
It should be noted that fashion trends are highly unpredictable; however, the majority of loyal customers still wait for the availability of their brands in the market. Therefore the power of customers is high.
The threat of substitute products: Companies like Gap and H&M can easily compete with Zara by launching products at affordable prices; however, H&M has low supply chain responsiveness to compete with Zara in the UK markets (Das et. al. 2021).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample
Three critical factors
The three critical factors emerging from the analysis are as follows
- Power of Customers
- Political Factors
- Environmental Factors
The competitive advantage of Zara
Zara is a well-established brand in the market that aims to achieve faster growth in the upcoming years. Major competitive advantages of Zara are its pricing strategy, quality of products and its international expansion.
Despite fast growing fashion trends, Zara respects the fact that the majority of its customers belong to middle-class families. Therefore, the brand provides a combination of perfect match and quality at low prices. The company’s global expansion has resulted in the establishment of more than 2200 physical stores and e-commerce websites operating in 48 markets.
Task 2:
Models of Internationalisation:
1) YIP model
The concept of globalisation is based on transformation drivers that build a global competitive structure for multinational fashion industries.
The YIP model explains drivers, opportunities and challenges that help businesses develop strategies for growth, expansion and higher revenues.
Cost drivers: Cost drivers considerably decrease the purchase values and cost of manufacturing when large volumes of products are available in the market. By increasing economies of scale, Zara can enhance volumes of its product which can be considered favourable for the current global market scenario (JANGIR, 2020).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample
Competitive drivers: Many entrepreneurs understand the significance of globalisation as it provides growth opportunities for fashion businesses in the UK and European nations. By adopting the integrated strategy of globalisation and transformation, Zara can increase its competitive advantages to boost its sales and profit.
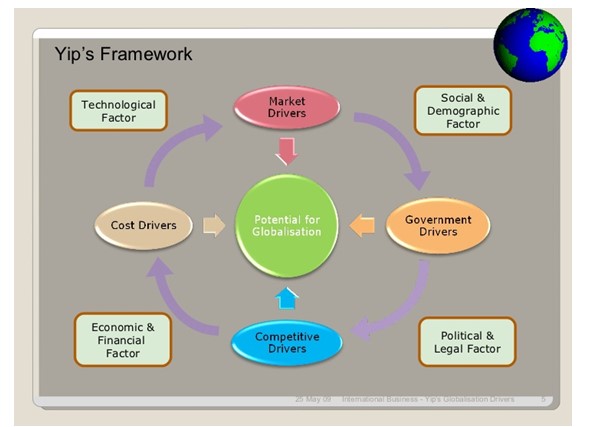
Figure 3: George YIP Internationalisation Model
(Source: George YIP internationalisation model, 2022)
Government drivers: Zara needs to abide by a set of government regulations and economic unions when thinking of a global expansion, which otherwise may create barriers to operation.
Some common barriers can be a tariff, subsidies on products and technological barriers.
Market drivers: Market drivers mean understanding customer needs and tastes, which can successfully drive the global expansion of Zara in different markets. Moreover, it also helps companies increase their revenue by increasing goods availability globally (Nguyen et. al. 2020).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample
2) Uppsala Model
The Uppsala model of internationalisation provides a sequential approach to how companies like Zara can initiate their global expansion process. By assuming that a company does not have efficient knowledge of international processes, the model suggests companies establish themselves in domestic parameters and later on increase their growth and resources to an international level.
Once the company achieves enough knowledge and understanding, it can proceed with a foreign market expansion (Pelikánová et. al. 2021).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample It is usually noticed that businesses initiate the expansion process in fairly nearby markets; however, the model suggests that large scale companies should enter new markets with export agents, which signifies that the company is committed to its customers.
Unlike other models of internationalisation, the Uppsala model focuses on experimental learning, which cannot be obtained from objective knowledge. Therefore, human resource management plays an integral role in enhancing experimental learning. The four successive stages of the model are mentioned below.
- Stage 1: No consistent export activities
- Stage 2: Export with the help of independent representatives
- Stage 3: Developing foreign sales subsidiaries
- Stage 4: Foreign manufacturing and production units
Recommendations of 3 market entry strategies
1) Exporting: Exporting is an effective market entry strategy for Zara as it does not involve a third party in selling different products of the brand. Similarly, exporting will also prove beneficial for the company because they will be able to produce the products in the same countries in which they intend to sell, which will eventually decrease the cost of transportation, manufacturing and warehouse maintenance.
2) Licensing: Zara has numerous products in demand which are preferred by the majority of customers in the UK and outside of the country. In such a situation, the company can transfer the right to sell or use products to another company due to high customer demands (Yip, 2020). http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment SampleThis method is usually known as licensing and is often advantageous when the expansion is at a large level.
3) Franchising: Franchising deals with managing a particular brand by establishing a chain of companies where different buyers can purchase products from the parent company and sell in different parts of the world with a franchised name (Plonka, 2019).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample Franchising was initially popular in American countries; however, the majority of large businesses adopt franchising as a global expansion strategy to enter international markets.
Task 3
Improvement of supply chain management:
Horizontal integrations: Improving supply chain management is crucial for large market-cap companies like Zara. Through Horizontal integration, the company can potentially identify its key competitors, which further can improve its operation in the business.
Apart from that, horizontal integration benefits the supply chain management system by expanding and diversifying the current market, which can also provide a competitive advantage to the brand. In the end, it also enhances revenue, the size of the company and product distribution through horizontal integration (Peters et. al. 2021).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample
Vertical integration: Zara can implement a vertical integration strategy to improve its supply chain management which will enable operations to be conducted with higher efficiencies.
At the same time, it will also reduce the cost of manufacturing and distribution, which is again an additive benefit to the organisation. However, vertical integration often requires heavy capital for expansion which may reduce the company’s return on investment (ROI) and operational flexibility.
Outsourcing: Outsourcing supply chain management is a long adopted strategy by a majority of companies because it is an efficient way of meeting customer demands, thereby minimising the overall cost of the product.
Another advantage of outsourcing is that it helps a company to expand at a higher rate without worrying about political laws and labour demands (Brewer, 2019).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample Lastly, outsourcing is majorly used in improving supply chain management because it reduces the financial risk of transportation and equipment.
Strategic alliances: Strategic alliances are extremely helpful in managing supply chains because when a company accommodates different alliances or partners, each one of them can concentrate on different stages of the supply chain, which can result in higher operational efficiency.
Similarly, they also ensure suitability and protection of resources are maintained when managing supplies and demands in the market (Matalamäki and Joensuu-Salo, 2021).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample Last but not the least, strategic alliances help the company develop low-cost business models; hence a company can enjoy financial benefits too.
Recommendations on Zara’s enhancement of profit scale
Ansoff matrix
Ansoff matrix, also known as the product/market expansion grid, is a significant framework that can be used to enhance the profile scale of Zara.
The grid will not help evaluate growth strategies for the company in future but will also help form effective team management that can conceptualise the process for growth and development.
Market Penetration: Market penetration is the least risky strategy for enhancing a profile scale because, through penetration, Zara can sell its existing products in the market to build relationships and bonds.
Moreover, higher sales and trades will streamline the company’s distribution process, which can help gain a competitive advantage in the international market (Sburlino, 2019).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample
Market development: Market development does not require any research and development and requires less investment because the company does not have to focus on new products; rather, they have to sell existing products in a new customer segment or demographics.
On the other hand, market development will also allow Zara to enter a domestic market which can lead to a regional expansion.
Product development: Product development is yet another strategy to attract new customers by understanding their needs and requirements. Global expansion can also be improved by developing an altogether new product based on public demands and needs (Kang, 2019).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample Hence to expand a market outside the UK, Zara needs to invest a big amount in R&D, which will give them an idea of different new products that can be launched in the market.

Figure 4: The Ansoff Matrix
(Source: Smart Insights, 2021)
Diversification: Diversification is one of the most risky strategies in the market, which is a combination of market development and product development. While it is a challenging strategy, it may offer huge rewards if it is implemented appropriately. It should be noted that diversification can either build new growth opportunities for Zara or it may reduce the firm’s revenue and product value if greater competition exists in the market (Czinkota et. al. 2021). http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample
Task 4
Carroll’s pyramid model
Carroll’s pyramid model is an integrated framework that provides a practical significance of why and how businesses should be socially responsible towards society, the environment and the people living in the society. The framework is explained in four major steps, which are discussed below.
Economic responsibility: Manufacturing goods and services that society needs is a core economic responsibility of Zara, which can benefit the company by generating sales and profits.
According to this model, a company is responsible for making profits as a part of economic responsibility in CSR. Only through this, a business can survive in a market for the long term (Arora, 2020).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample
Legal responsibility: Legal responsibilities in CSR are highly significant as every company operating in different markets needs to comply with government rules and regulations.
Operating in accordance with government laws can initiate smooth functioning, which can benefit service users and providers at the same time (CRISTACHE et. al. 2022).http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment Sample

Figure 5: CARROLL’S PYRAMID OF CSR
(Source: Carroll’s pyramid of CSR, 2021)
Ethical responsibility: Conducting business in an ethical manner is necessary to embrace activities and standards that can benefit the society. An organisation can fulfil its ethical responsibility by meeting society’s expectations and performing operations systematically.
Philanthropic responsibility: Philanthropic responsibility highlights activities where a business wants to give something useful and positive to the community, such as gifts, donations, community development and voluntary support.
Ethical issues faced by Zara
Fast fashion companies like Zara face major ethical concerns because although the company provides high-quality products at less rates, however, the products are not designed to last for a long time which has detrimental environmental and ethical impacts.
- Textile waste is a serious issue with fast fashion because products with inexpensive rates are valued less in the market. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), more than 17 million tons of textile waste were generated in 2019, of which only 7% were recycled and others were dumped.
Verdone al. (2021), states that the recycling rate of clothes is much less than that of other products like paper, plastic and glass. Hence, there is a greater need to adapt cloth recycling techniques to minimise waste in the fashion industry.
- Besides a bulk of textile waste generated every year, fast fashion also impacts the environment and its sustainability through excessive CO2 emissions. According to the Ellen MacArthur Foundation report, fashion industries emit more than 12% of global CO2 emissions each year, which is likely to increase by 25% by the end of 2050. Clothing factories are responsible for emitting a large percentage of carbon which eventually increases with transportation (Palma, 2019). http://MSc Management Global Strategy and Sustainability Assignment SampleThe final time may occur when a customer disposes of a product after prolonged use.
- Sustainability reports indicate that majority of the clothing products in textile industries are made from petrochemical, which has the highest CO2 emission power disrupting the ecological balance and sustainability.
Conclusion
The business report based on global strategy and sustainability provides a detailed internal and external analysis of the business environment which can help Zara gain a competitive advantage over different companies.
Through the analysis, it was confirmed that Zara has potent competitors in the market, such as H&M, Gap and Benton; however, they have yet to be able to compete with Zara because of its higher responsiveness in the market compared to other fashion textile companies.
Similarly, PESTEL analysis and Porter’s five forces helped the company analyse different factors that may impact global expansion today and in future. Last but not the least, the ethical issues of Zara were discussed to encourage sustainability in the market.
References
A Precise, Pragmatic, and Insightful SWOT Analysis of Zara, (2022) [Online]. Accessed through: https://crowjack.com/swot-analysis/zara
Arora, M., (2020). Enhance Business Productivity by Effective Buying and Merchandising. NIFT.
Brewer, M.K., (2019). Slow fashion in a fast fashion world: Promoting sustainability and responsibility. Laws, 8(4), p.24.
Carroll’s pyramid of CSR, (2021). [Online]. Accessed through: https://thecsrjournal.in/understanding-the-four-levels-of-csr/carrols-pyramid-of-csr-2/.
CRISTACHE, N., SUSANU, I.O., BUSILA, A.V., MATIS, C. and PRICOPOAIA, O., (2022). The Impact of Sensory Marketing on the Development of Organisations in the Fashion Industry. Annals of the University Dunarea de Jos of Galati: Fascicle: I, Economics & Applied Informatics, 28(1).
Cui, Y.C. and Fan, BF, (2021). The corporate social responsibility strategy in fast fashion industry: case company Zara.
Czinkota, M.R., Kotabe, M., Vrontis, D. and Shams, S.M., (2021). Product and Service Decisions. In Marketing Management (pp. 341-397). Springer, Cham.
Das, M., Herweyers, L., Moons, I. and Du Bois, E., (2021). Strategic design opportunities to increase sustainable fashion awareness and behaviour. Proceedings of the Design Society, 1, pp.2711-2720.
George YIP internationalisation model, (2022). [Online]. Accessed through: https://hookheavenly.weebly.com/george-yip-internationalisation-drivers.html/
George, M., Ulhaq, I. and Nayak, R., (2020). Sustainable approaches in warehousing and inventory management in the fashion industry. In Supply Chain Management and Logistics in the Global Fashion Sector (pp. 138-158). Routledge.
How to conduct an effective PESTEL Analysis?, (2021). [Online]. Accessed through: https://springworks.ch/en/pestel-analysis/
JANGIR, M., (2020). ZARA’S CASE STUDY (Doctoral dissertation, MANIPAL ACADEMY OF HIGHER EDUCATION).
Kang, S., (2019). Research on green supply chain in textile and apparel industry.
Kim, Y. and Oh, K.W., (2020). Which consumer associations can build a sustainable fashion brand image? Evidence from fast fashion brands. Sustainability, 12(5), p.1703.
López, T., Riedler, T., Köhnen, H. and Fütterer, M., (2022). Digital value chain restructuring and labour process transformations in the fast‐fashion sector: Evidence from the value chains of Zara & H&M. Global Networks, 22(4), pp.684-700.
Matalamäki, M.J. and Joensuu-Salo, S., (2021). Digitalisation and strategic flexibility–a recipe for business growth. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development.
Maula, L., (2022). Achieving an Environmentally Sustainable Fast Fashion Supply Chain by Implementing Lean Processes.
Mehta, M., (2021). Study of Supply Chain Strategies implemented by various companies in Fast Fashion Industry (Doctoral dissertation, School of Petroleum Management).
Nguyen, H.T., Le, D.M.D., Ho, T.T.M. and Nguyen, P.M., (2020). Enhancing sustainability in the contemporary model of CSR: A case of fast fashion industry in developing countries. Social Responsibility Journal.
Palma, E.D., (2019). Family ownership as a source of growth in Italian luxury fashion companies: the Max Mara case (Doctoral dissertation).
Pelikánová, R.M., Němečková, T. and MacGregor, R.K., (2021). CSR statements in international and Czech luxury fashion industry at the onset and during the COVID-19 pandemic—slowing down the fast fashion business? Sustainability, 13(7), p.3715.
Peters, G., Li, M. and Lenzen, M., (2021). The need to decelerate fast fashion in a hot climate-A global sustainability perspective on the garment industry. Journal of cleaner production, 295, p.126390.
Plonka, M.B., (2019). Implementing CSR in the fashion industry: measuring the designers´ perceptions and commitment.
Sburlino, M., (2019). Fashion as a matter of values. On how a transformative educating process can initiate a positive change. In Sustainable Fashion: Consumer Awareness and Education (pp. 53-75). Springer, Singapore.
Shabir, S. and AlBishri, N.A., (2021). Sustainable Retailing Performance of Zara during COVID-19 Pandemic. Open Journal of Business and Management, 9(03), p.1013.
Smart Insights, (2021). The Ansoff Model is a matrix that helps marketing leaders identify business growth opportunities for their marketing strategies in a challenging market. [Online]. Accessed through: https://www.smartinsights.com/marketing-planning/create-a-marketing-plan/ansoff-model/.
Su, Y.Z., (2020). The Internationalisation Strategies of Fast Fashion Clothing Retailer Brands: A Cases Study of ZARA, H&M, UNIQLO, and Gap.
Verdone, F., Cantarero, S. and Puig, F., (2021). Capturing the Resilience of the Textile Companies as a Specific Response of the Fashion industry. In Firms in the Fashion Industry (pp. 141-161). Palgrave Macmillan, Cham.
Yip, D.K.M., (2020). Creative Base Design: A New Form of Self-Expression in Competitive Games. In New Media Spectacles and Multimodal Creativity in a Globalised Asia (pp. 171-189). Springer, Singapore.
Zara, C., Iannuzzi, M. and Ramkumar, S., (2021), October. The Impact of Circular Economy on Public Equity in Europe. Understanding De-Risking Effect and Risk-Adjusted Performance. In Understanding De-Risking Effect and Risk-Adjusted Performance (October 8, 2021). The following version was submitted to (Dec 2021) and accepted by (July 2022) Bancaria, Forum section-double blind review.