Assignment Sample on Myocardial Infarction
Introduction
The rise of medical conditions and diseases in present times has been leading to complex funding processes for various classes of people. This is mainly due to the high expenses for treating the clinical conditions that result in difficulty for the patients in getting treatment properly. For this reason, there are various funding procedures followed in different countries that provide support to the patients and help them in arranging funds for their treatment. Many of these funding assistance centres are growing in countries like England, India and the USA to stand beside the patients and help them in getting the required treatment. These centres are mostly supported by Non-Governmental Organisation (NGOs) and Private Governing bodies that have proper licences to carry out the necessary procedures in arranging money for treatment purposes. One of the most common diseases that have been rising and affecting millions of people worldwide is Myocardial Infarction which is Heart Attack.
The clinical condition is being found to affect various classes of people living in England and India both where the income of individuals vary largely. Due to differences in income, individuals often face problems to get the correct treatment for managing clinical conditions like heart attacks. At this time, funding assistance plays an important role as these bodies help the patients arrange the required money for treatment purposes. This particular study is aimed at focusing on the comparative analysis of the funding process of the selected clinical condition in both England and India. Along with this, an evaluation of the maximum spending budget for its treatment has also been discussed for a clear understanding. Furthermore, the benefits and challenges faced by health and services in both India and England have been analysed along with the ethical and ethical framework associated with myocardial infarction.
Overview of Myocardial Infarction in India and England
Myocardial Infarction (MI) or Heart Attack is one of the common clinical conditions that has been affecting millions of people worldwide over the years. However, the number of cases of MI is found to be growing each year and causing the death of approximately 17.9 million people each year (Organization, 2022). MI is mainly caused due to complete or decreased blood flow to a part of the myocardium. This clinical condition is often found to go undetected in most of the patients and can cause serious events like “hemodynamic deterioration and sudden death”. A maximum of the individuals who get affected by the clinical condition, Heart attack are elderly adults and are aged 65 and above. However, cases of other age groups experiencing heart attacks are also observed globally (Wu, He, & Shao, 2020). Some of the common symptoms of MI include “chest pain, shortness of breath, light-headedness, tiredness and feeling nauseous.”
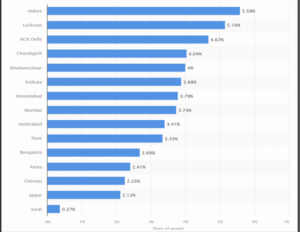
Figure 1: Cities showing rise of cardiovascular diseases in India
(Statista, 2023)
Studies have found that heart diseases like MI are increasing in India and are affecting people of different age groups. Most of the cases are found to be in metropolitan cities like Indore, Lucknow, Delhi and Chandigarh where the stress faced by people is high (Statista, 2023). Contrarily, cities like Jaipur and Surat have lower cardiovascular cases with 2.12% and 0.37% respectively. Similarly, England has been observing a sharp increase in cardiovascular conditions from 2012 to 2020. Around 395000 people have been diagnosed with heart diseases like MI and stroke (Statista, 2022). However, in 2021, the number of cases of coronary heart disease like MI has seen a significant drop and recorded 395000 cases while in 2020, there were 480730 cases.
Treating this health condition often involves a lot of money as it includes taking expensive tests and medicines. Furthermore, (Goo, Park, & Yoo, 2020) asserted that alternative extensive treatment options apart from medicine also need to be sometimes used for treating this clinical condition like surgery. Due to differences in income, many patients struggle to choose the appropriate treatment plan as a result of which death or worsening of the condition occurs. As a measure, some private organisations and NGOs help in arranging funds for the patients so that they are able to get the necessary treatment in time.
Comparative Analysis of the Funding Process of Myocardial Infarction from Patient Perspective
The funding process for myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, is an important aspect of healthcare systems in both India and England. However, there are significant differences in how the funding process for myocardial infarction is managed, particularly from the patient’s perspective. Due to differences in healthcare systems, accessibility and affordability and government support the funding process is different in both the countries. Furthermore, expenses like insurance coverage and out-of-pocket expenses result in a difference in the treatment cost of myocardial infarction in these countries.
India
India has a mixed healthcare system, with both public and private sectors playing a role. Public healthcare facilities are often overburdened and under-resourced which leads to long waiting times and limited access to specialised treatments (Rami, 2023). Since MI is a common disease and has been affecting thousands of people each year, the healthcare system is required to upgrade itself to attend to all the patients efficiently. Patients have also found that accessibility to timely and affordable healthcare is often a challenge in India. This is so because the public healthcare services are “overcrowded” and lack the necessary infrastructure and resources to treat conditions like MI (Dasbiswas, Shelke, Singhal, & Shah, 2020). Although private healthcare is available in India that offers better facilities, they are expensive and are out of reach for many patients. This restricts the patients from getting treated in private institutions for clinical conditions like heart attacks.
Due to high expenses involved in treating MI, health insurance companies pay a major sum of the treatment to the patients as a supporting act. However, depending on the terms and conditions of the policies of various companies, the coverage provided by the companies has different limitations like “waiting periods, exclusions and pre-existing clauses”. Contrarily, (Dubey, Deshpande, Krishna, & Zadey, 2023) mentioned that due to differences in financial background, a major part of the population in India does not have health insurance and cannot face the benefits of it. In addition, patients in India often are required to bear a significant portion of the healthcare expenses out of pocket including expenses related to “hospitalisation, diagnostic tests, medications and other added procedures”. In India, people from different classes and financial backgrounds reside and usually face issues when affected by various clinical conditions (Dubey, Deshpande, Krishna, & Zadey, 2023). The high cost of these out-of-pocket expenses poses a financial threat for individuals and families, especially for those who belong to lower socio-economic backgrounds.
Over the years, various private institutions and NGOs have been taking effective measures to help fundings for patients and provide the necessary support in their treatment. Along with this, the Government of India has also introduced various health schemes and initiatives for the patients (Pandey & Litoriya, 2020). Although the reach and effectiveness of the schemes may vary in different regions and populations, they are aimed at providing the necessary financial support. The support is provided to individuals who need it and help in their treatment process and eventually resulting in lessening the mortality rate of MI in India.
England
The healthcare system of England is more advanced than India and allows its population to get the appropriate help for their medical condition like MI. (Thorlby & Arora, 2020) pointed out that England has a publicly funded National Health Service (NHS), which provides universal healthcare coverage. This governing body, NHS, is aimed to deliver high-quality services and get to learn about any concerning health conditions. NHS is a technology partner to various health and social care systems that uses “digital technology” to transform the social care quality in England. The NHS is financed through general taxation, and patients have access to a range of services, including emergency care (NHSRCINDIA.ORG, 2023). Similarly, in England, patients have access to free emergency care through the NHS. This ensures that individuals experiencing a myocardial infarction can receive prompt medical attention without worrying about immediate financial implications. However, the availability of specialised treatments and procedures may have certain waiting times.
The NHS in England provides comprehensive coverage for myocardial infarction treatments, including hospitalisation, medications, and follow-up care. In this way, the NHS has been providing assistance to the population of England in treating serious clinical conditions like MI. Although the cost of treating heart attacks is high, patients do not need to rely on private insurance to cover the costs. This is due to the associated costs with the immediate treatment and management of a heart attack is often unreliable (Goodair & Reeves, 2022). However, in England, patients covered by the NHS do not have to pay out of pocket for most myocardial infarction treatments. This is so because the NHS covers the costs of hospital stays, tests, and treatments, ensuring that patients are not burdened with significant financial expenses (NHSRCINDIA.ORG, 2023). The NHS in England is primarily funded by the government through general taxation. This ensures that healthcare services, including those related to myocardial infarction, are available to all residents without financial barriers.
The differences in healthcare in both countries, India and England have led to the difference in perspectives of getting treated for MI due to affordability and availability of comprehensive care. Due to easier accessibility and the presence of NHS, England provides better healthcare for MI to its population than India while providing them with the necessary support and care for their treatment.
Comparative Evaluation of Funding Policy on a Country Perspective Including Maximum Spending Budget and Spending Plan for Myocardial Infarction
Funding policy in healthcare refers to the guidelines created by governing bodies to get permission to get the treatment or necessary help in treating a clinical condition. These guidelines are created and passed by the governing bodies of the countries so that the population is able to get fair treatment at optimum cost. India and England have significant differences in their funding policy with respect to treatment due to developmental and medical advancements.
India
During any treatment of diseases including myocardial infarction, India’s funding policy needs to analyse the socio-economic condition. This is so because there is a major difference in the financial conditions of the population of India. Due to this reason, it has been evaluated and found that the average direct cost of hospitalisation for MI in India ranges from ₹1.75 to ₹4.25 lakh depending on the treatment needed (Ryder, et al., 2019). This is almost equivalent to 90% of the annual per capita income of the population. The maximum cost is needed for patients who need open heart surgery and any kind of implantation device to normalise their heart condition. The population who has additional support and health insurance, face lower problems regarding the costs of the treatment than those who do not. As per the studies, only 5-15% of the population of India have health insurance and can enjoy the benefits of it irrespective of the terms and conditions of the health insurance (Sriram & Khan, 2020). The remaining population who does not have these benefits continue to face “catastrophic health spending or distress financing” while getting the needed treatment.
The treatment of MI is a lengthy process and requires the patients to be under treatment and checkups for a long period of time. For this reason, (Sriram & Khan, 2020) narrated the need for extra costs which are usually uncovered by the health insurance companies. This results in demand and expenditure of “out of pocket” funds and leads to situations like borrowing money or selling valuable assets to cover health costs. Many a time, the inability of the patients to arrange funds to buy costly medicines and get treated results in increased mortality rates in India. Although there are some initiatives started by the government and NGOs, the complex procedure of affordability and accessibility creates hurdles for the patients.
England
Unlike India, the economic and medical advancement in England is better. It is mainly due to the presence of the National Health Service (NHS) that provides “universal health coverage and free access to hospital care” for all medical conditions including MI (NHS, 2023). Apart from additional support, the cost of treatment in England is high as in India. The mean treatment cost for MI in England is approximately £848 to £1692, depending on the extensiveness of the clinical condition (Ryder, et al., 2019). However, due to the presence and support from the NHS, the maximum cost for the treatment is covered for the population. As per reports, about £3 billion was spent by the NHS on cardiovascular diseases in 2016-17 (NHS, 2023). This accounted for around 5% of the total expenditure of the NHS to provide the required assistance to its population. Although due to the pandemic, COVID-19, the NHS faced difficulty with the funding and helping its population, it has overcome the challenges efficiently.
After the pandemic, the cost of hospitalisation and other additional costs involved in treating MI have changed. However, the NHS has evaluated the needs and financial conditions of its population and brought minimal changes to its policies (NHS, 2023). This was done so that the population of England does not face severe consequences due to such changes and is able to seek help from the government efficiently in times of need. These effective policies have helped England to maintain its lower mortality rates in MI at 6.9% in 2019 and 7.1% in 2020 (Mehta, Kim, Mathis, Zalmay, & Ghanchi, 2020). Although a slight increase in the mortality rates was observed in 2020, it was due to COVID-19 as a complication to which the mortality number of cases rose. Apart from these, England’s funding and treatment policies allow its population to be influenced by several factors like “risk factors, treatment quality and accessibility”. These factors allow healthcare conditions for the treatment of MI in England to be more efficient than in India.
Benefits and Challenges for Health and Services in UK and India
The National Health Service in the UK is designed to benefit the mass population through free healthcare which is accessible to the permanent citizens. There are also options to take the private healthcare service upon own will and that is known to offer quicker access to specialists. The healthcare service within the UK is founded on the principle of equal access to everyone and improving the health condition across the country (Austin, 2021). A comprehensive healthcare which is free for everyone is facilitated within the UK and it is considered as one of the most crucial benefits. Similarly, the NHS is known to provide “universal coverage” from “routine consultations” to “specialist procedures”. Myocardial Infarction is an emergency situation and is generally regarded as costly in terms of the treatment process. Considering the challenges of UK healthcare service, it has been found that there are longer waiting times, which are not considered as “patient friendly”. Delayed hospital care leads to missed appointments routinely and there is also no freedom to make autonomous healthcare decisions. Patients feel that they have little control over their health under the NHS.
Considering India’s offering in relation with healthcare service, India is considered to be more affordable in emergency and general hospital care compared to the western countries. Besides, in the emergence of the “robust healthcare industry”, India’s goal is to reform its current system to achieve “universal health care” (Bali & M, 2021). Determining the benefits of the healthcare system across India, a high number of “trained medical practitioners” have been witnessed and healthcare is accessible to everyone. However, “provision”, “utilisation” and “attainment” of the healthcare care system is under attained as there is a huge gap among these three factors. Thus, the aim of making healthcare accessible within India is not possible because rural areas in India are severely discriminated against as there is a shortage of medical professionals. Individuals are not served properly, and the health service is not being able to act responsibly for which reputation of the country is hampered significantly.
Legal Framework and Ethical Framework for the Clinical Condition used in UK and India
Health Care condition in the UK is aimed to be improved over the years and ethics for healthcare regulation comprises enhancing compliance. Considering the ethical factors for patient care within UK, it can enhance the overall health outcomes with the help of preventing emergency illness including myocardial Infarction. The supervision of “Care Quality Commission” is necessary in this context. Moreover, while determining the legal framework, “Health and Social Care Act 2008” is prioritised which highlights the aspects of “safe”, “effective”, “compassionate” and “high-quality care”. Besides, within UK, there are six health care regulators that are “Care Quality Commission” (CQC), “Healthwatch England” (HWE), “Professional Standards Authority for Health and Social Care” (PSA). Besides, there are “General Medical Council” (GMC), “Nursing and Midwifery Council” (NMC) and “Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority” (HFEA) (Devaney, 2023). The healthcare regulation within the UK is principles-based and goals-driven that consists of ‘intelligence led”, “expert “,”rigorous inspections” and “ratings of services”. On the other hand, a “Principles-Based Regulation” (PBR) comes under section 8(1)(ca) that facilitates in adopting best practice in internal governance. Thus, the ethical framework comprises “integrity”, “objectivity”, “leadership” and “accountability” so the overall health of the patient can be improved further.
Legal and ethical framework in India is based upon the “Constitution of India”, which highlights the aspect of improving public health as one of the primary duties. The public health act comprises of decentralised model of public health that facilitates wellbeing of individuals despite their financial and educational condition (NHSRCINDIA.ORG, 2023). Myocardial Infarction is one of the leading causes of death among Indians due to their negligence to health and lack of awareness to prevent it is one of the prime considerations as well. Understanding about the legal framework within the India, “Article 47” of the “Constitution of India’s Directive Principles” recognises the “duty of the state”. It enables the factors to raise the “levels of nutrition” and the “standard of living”. The legal framework is associated with the principles of “safety”, “effectiveness”, “timeliness”, “patient-centeredness”, “equity”, and “efficiency”. The ethics of healthcare practice is similar to western countries including UK which prioritise the emergency healthcare such as myocardial infarction with the intention to deliver a “high-quality”, “equitable care”. Especially after the global pandemics, prioritisation on this framework has been witnessed more severely in terms of “community medicine” and “digital health” as the comorbidities has significantly adverse.
Educational and Professional Factors impacting the Management of Healthcare Workforce
Health worker’s educational approach is one of the most significant factors in order to achieve professional advancement in the context of public healthcare. Moreover, it has been observed that after the pandemic, due to lack of professional attitude and lack of professional training, healthcare workers have not been able to achieve patient satisfaction. Considering the professional factors that are associated with quality health care service, “power”, “regulation” and “corporate image” are considered to be crucial in this international healthcare scenario (Fitzgerald, 2020). Strategies to develop professional competencies include medical education where both rural and urban health centres are prioritised simultaneously.
Considering the educational and professional factors from end of healthcare workers in terms of providing better service, the “detailed regulation” of health professional education has been highlighted. It lies within “national responsibility” that leads to considerable variation in “health professional training” across countries. Myocardial infarction is an emergency situation and to treat people in that situation, fundamental expertise are required as “complete cessation of blood flow” to a portion of the myocardium is noticed. Thus, the concept of power is associated with aspects of leaders’ intervention where employees feel valued and powered while making their decision for professional advancement internationally.
Necessary Skills and Knowledge to Manage Finance and the Workforce Resources for the Clinical Condition
The clinical condition of Myocardial Infarction that is commonly known as heart attack needs vast consideration and minute details with the intention to further prevention. Moreover, in order to manage the finance of this critical healthcare condition, healthcare leaders need to have expertise in financial management. A huge resource along with budget are required in terms of making the healthcare organisation ready and occupied to treat this healthcare condition. Besides, in this context the transformational leadership approach can work as the best practice as the leaders can make the budgetary alterations as per the requirements (Drennan & Fiona, 2019). Besides, while determining the skills and knowledge of healthcare leaders, they need to have the ability to educate the target group who are in high risk of this illness. The leaders are responsible for educating the workforce as well so that the employees can contribute their best effort in terms of provisioning satisfaction to patients. The care pathway for the patients’ needs to be well communicated and the communication needs to be easy and comprehensive from the end of leaders. Patients need to be given the authority to make decisions for their own health outcome.
Considering the management for finance and budget, leaders are found to play a pivotal role in managing the economic activities that contributes to the economic success of the healthcare organisation. Managers need to keep an updated record in terms of the organisational financial activities in border to ensure that the healthcare system runs smoothly without any interruption. Running an effective healthcare system requires adequate knowledge in terms of ensuring financial security that reflects in the corporate image necessarily. Keeping the updated patient records ensures that healthcare managers are able to regularly review “patient insurance information”. On the other hand, skill regarding maintaining the treatment protocol and elaborating this protocol to the other employees is important as well (Organization, 2022). Skill regarding mitigating the problem of staff turnover would allow the healthcare organisation to treat patients with better quality with such emergency physiological conditions. Thus, the ability of the healthcare leaders to “double-check” with patients who cannot pay for services is also required.
Recommendation regarding Leadership Skills and Knowledge for Managing Finance and Workforce
Finance and workforce both needs to be managed with a close context so that the corporate image of the organisation can remain satisfied within an international context. Considering the recommendation in order to enhance the leadership skill and ability to manage the finance, the concept of cultural barriers needs to be considered as priority. Similarly, the importance of time management needs to be there from the end of leaders so that they can timely attain the patients with different emergency health conditions. The rate of productivity and quality of patient care would be increased as well with the help of this management skill in terms of managing the employees and finance (Wisittigars & Sununta, 2019). Thus, it is further recommended to differentiate among the priority when it comes to multitasking. Besides, upon facing the condition that requires urgent care for multiple patients, leaders are recommended to know the area of prioritisation and they should be able to delegate tasks to another team member.
Conclusion
From the above discussions, it can be deduced that the number of cases regarding cardiovascular conditions like myocardial infarction is rising each year in present times. It is mainly due to lifestyle changes and increased stress levels of individuals due to rapid globalisation. Apart from underlying health conditions, hypertension due to increased work pressure has been contributing to elevated cases of MI globally. The treatment for MI is costly and also requires the patients to be in constant monitoring and taking medications. This eventually creates hurdles for the patients due to social and economic differences observed in society.
Countries like India and England have been implementing various changes in the funding policies of their healthcare to make it easier for the population to access healthcare and get treated. However, lack of infrastructure and affordability in India has been causing issues for the patients to bear the cost of MI and this in turn is leading to increased mortality rates. Conversely, the presence of NHS in England has been allowing patients to seek help from the government as the maximum part of the cost of MI treatment is covered by NHS. The treatment and funding policies created by both countries have lots of benefits and challenges as it needs to adhere to legal and ethical norms of the society. Furthermore, educational and professional factors also impact the management of healthcare and the treatment of patients too.
References
Bali, A. S., & M, R. (2021). Governing healthcare in India: A policy capacity perspective.” International Review of Administrative Sciences 87. 275-293.
Dasbiswas, A., Shelke, A., Singhal, A., & Shah, B. (2020). Consensus statement: improvement in care and outcomes for patients with ST‐elevation myocardial infarction with timely reperfusion therapy: a pharmaco-invasive approach. International Journal of Advances in Medicine, 1889.
Devaney, S. (2023). ETHICS FOR HEALTHCARE. Retrieved from https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/550543/Dr_Sarah_Devaney_-_Ethics_for_regulators.pdf.
Drennan, M. V., & Fiona, R. (2019). Global nurse shortages: the facts, the impact and action for change. British medical bulletin 130, no. 1 , 25-37.
Dubey, S., Deshpande, S., Krishna, L., & Zadey, S. (2023). Evolution of Government-funded health insurance for universal health coverage in India. he Lancet Regional Health-Southeast Asia,.
Fitzgerald, A. (2020). Professional identity: A concept analysis.” In Nursing forum. 447-472.
Goo, H. W., Park, S. J., & Yoo, S.-J. (2020). Advanced medical use of three-dimensional imaging in congenital heart disease: augmented reality, mixed reality, virtual reality, and three-dimensional printing. Korean journal of radiology, 133-145.
Goodair, B., & Reeves, A. (2022). Outsourcing health-care services to the private sector and treatable mortality rates in England, 2013–20: an observational study of NHS privatisation. The Lancet Public Health,, 638-646.
Mehta, H., Kim, L. N., Mathis, T., Zalmay, P., & Ghanchi, F. (2020). Trends in real-world neovascular AMD treatment outcomes in the UK. . Clinical Ophthalmology.
NHS. (2023). Retrieved from We lead the NHS in England to deliver high quality services for all. : https://www.england.nhs.uk/
NHSRCINDIA.ORG. (2023). 2nd National Consultation on the Draft Public Health . Retrieved from https://nhsrcindia.org/sites/default/files/2021-06/9.2nd%20National%20Consultation%20on%20the%20Draft%20Public%20Health%20Bill%202015.pdf.
Organization, W. H. (2022). owards a global guidance framework for the responsible use of life sciences: summary report of consultations on the principles, gaps and challenges of biorisk management, May 2022. No. WHO/SCI/RFH/2022.01.
Pandey, P., & Litoriya, R. (2020). Implementing healthcare services on a large scale: challenges and remedies based on blockchain technology. Health Policy and Technology, 69-78.
Rami, F. (2023). Health Care During COVID 19: Systems and New Developments. In Covid-19: Health Disparities and Ethical Challenges Across the Globe. Cham: Springer International Publishing., 71-90.
Ryder, S., Fox, K., Rane, P., Armstrong, N., Wei, C.-Y., Deshpande, S., . . . Kleijnen, J. (2019). A systematic review of direct cardiovascular event costs: an international perspective. . Pharmacoeconomics, 895-919.
Sriram, S., & Khan, M. (2020). Effect of health insurance program for the poor on out-of-pocket inpatient care cost in India: evidence from a nationally representative cross-sectional survey. BMC Health Services Research, 20(1), 1-21.
Statista. (2022). Statista. Retrieved from Diagnoses of circulatory system diseases in the UK 2012-2021, by disease type. : https://www.statista.com/statistics/946113/united-kingdom-uk-diagnoses-of-circulatory-diseases-by-disease-type/
Statista. (2023). Retrieved from Share of people with heart problems India 2020, by select city.: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1249091/india-share-of-respondents-with-heart-issues-by-select-city/
Thorlby, R., & Arora, S. (2020). The English health care system. International profiles of health care systems.
WHO. (2023). World Health Organisation. Retrieved from Cardiovascular Diseases: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases#tab=tab_1
Wisittigars, B., & Sununta, S. (2019). Crisis leadership competencies: the facility management sector in Thailand. Facilities, 881-896.
Wu, W., He, J., & Shao, X. (2020). Incidence and mortality trend of congenital heart disease at the global, regional, and national level, 1990–2017. Medicine, 99.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

