PGSSC 01 Critical Analysis of the Northern Rock case Scenario Assignment
Get the best sample on Critical Analysis of the Northern Rock case Scenario Assignment.
Introduction
The core reason that induced the Northern Rock was the submerged crisis that incurred the selling of the mortgages in order to manage the concurrent demand of mortgage-backed securities. The timeline of the initial outcome induced from February 2003 reflected the danger of derivatives and mortgages backed securities. The danger was followed by the June 2004-06 increased rates of interest leading to housing prices skyrocketing due to Fed raises that increased interest rates by six times. At the time of August 2005, the economists predicted the chances of danger for the Central banks due to the increased number of holding derivatives to boost the operating bank profit margin. This event was followed by the December 2005 yield curve related inverts downwards with the trend of investors buying more Treasury’s leading to faster failing than on short-term notes. Initially, the home price fell drastically a reported first time within 11 years that led to the 2007 subprime crisis inducing the banking crisis concerning the era.
The paper presents a critical analysis of the Northern Rock case scenario in detail. The present study will analyse the core issues that led to the outbreak of the Northern Rock initial selling out to the public companies in detail.
Critical evaluation of the UK government decision to take over NR and its implication for UK taxpayers
The subprime crisis has induced the financial turmoil that led to the NR losing its ability. However, the subprime crisis must not be criticized entirely for the NR crisis (Subprime Mortgage Crisis and Its Aftermath, 2020). The NOR operation for gaining the profit margin was determined as the main issue that led to the initial outcomes of NR being selling out to Virgin money.
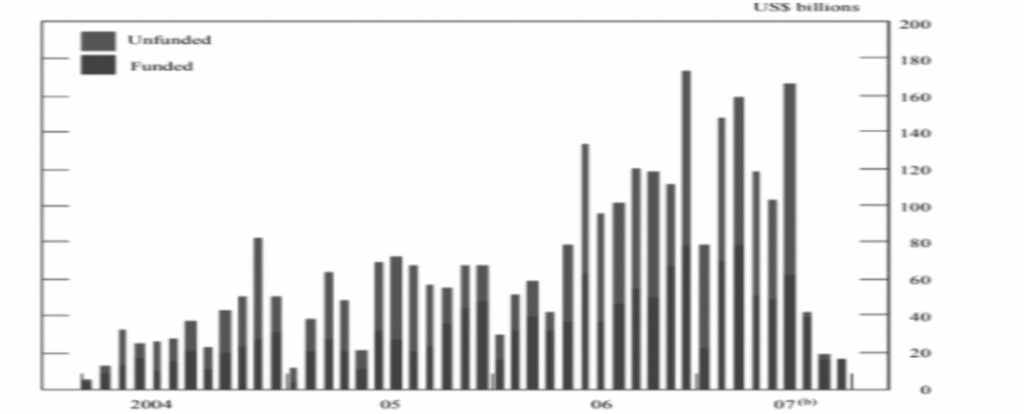
Figure 1: Global collateralized debt obligation issuance
Source: (Llewellyn, 2009)
The above figure reflects the volume related to global CDO assimilated issues prevailing due to the financial turmoil. Thi induced an Arthur sharp increment within the year 2006 and the first initial phase of the year 2007. It was initially followed by the series of total collapse in the month of summer of the year triggering due to the development in SPM markets. The increment in the mortgage loan was being rather securitized that was contributing to the CDO issues leading to the high number of risks of maintaining derivations and mortgages security (UK government’s £37 billion bailout of Northern Rock in 2007 pays off, 2020). The issue within NR that led to this condition was reported to be an ineffective business model that makes the business prone to a hazardous situation, lack of proper deposit protection within the British DPS induced the situation and moral hazard. Apart from these persisting issues, the NR lacking corporate governance is also in question (Northern Rock: How the crisis improved savers’ protection, 2020). A rather multi-dimensional problem was evident due to the lack of responsibility within the Bank of England, British DPS, and board.
This raises the question of the practical bailey of the bank and management practices. However, critical analysis has reflected that government intervention does help NR in gaining support and power back (Llewellyn, 2009). Contrary the issues would have not taken place in the first place by effective risk monitoring activities and changes within the supervision and regulation actions (Northern Rock’s Bank of England bailout ‘should have been secret’, 2020). The NR case has highlighted the extensive need for the banks in taking a considerable amount of interest within attaining financial stability and valuing actions for the protection of the depositors is highly important.
Critical analysis of publication
Llewellyn, (2009) has indicated the positive outcome that was induced to the NR initial affair. The fir aspect highlighted by the article is the significance of supervisors of the banks considering the risk characteristics involved in the business models and initiating the robust stress test. The even determined the vulnerability they’re prone to due to their operating style making them prone to LPHI risk mainly. However, secondly, it was determined that the reform in relation to the government intervention was highly needed due to the increasing inconsistency in performing leading to higher financial risks and inducing a crisis (Tooze, 2018). The public was conscious due to the particular event regarding the bank operations and outcomes that further forced the requirement of meaning the operations and transparency demanded by the public and investors depositing their money (Crooks and Kuipers, 2018). The need related to the depositor protection demand determined that initially forced the Bank of England and FSA to make necessary changes and review of the operation undertaken as a result. Apart from these, the Bank of England’s potential was determined in preparing the Banks in the market from dissolving and incurring higher risk and uncertainty by the right intervention. However, it was identified the banks are required to determine the area the change is required.
It is highly necessary to revisit the ways the operating banks within the UK economy are conducting their operations and actions as it is leading to higher danger for the economy in terms of financial condition (Goodhart, 2016). Lastly, the author has highlighted the higher requirement for straining on the effective governance assimilated practice and arrangements within the financial services offered companies. The emphasis on financial supervision is highlighted within the paper as the banks that are operating with a higher likelihood of risks require necessary improvements. On the other hand, the issue has highlighted two main central areas of issues to the attention of the UK public. Further, the pivotal role of the government is possibly rather underwriting of risk mainly by the tax players and secondly, the question related to moral hazard is prevailing.
Conclusion
The critical analysis of the Northern bank and subprime crisis has provided a better understanding of assimilation to the need for the UK crisis management arrangements within the bank that need to be refined. The lack of transparency that was practiced by Northern Rock to increase the profit margin made the business exposed to a higher degree of risks. It is important to make certain changes related to deposit protection-related arrangements in the UK performing banks. The effective revision of the division of the made probabilities among the Bank of England and FSA in terms of the treasury is important. However, the UK government support has saved the Northern Rock and savers in retaining their deposits. It is believed that the government must have to keep it a secret as such action affects the depositors’ confidence in the banks’ capabilities. It can reduce the chance of investors and savers keeping their money in banks that can affect the economy as a result.
Reference List
BBC News. 2020. Northern Rock: How The Crisis Improved Savers’ Protection. [online] Available at: <https://www.bbc.com/news/business-41226937> [Accessed 25 December 2020].
BBC News. 2020. Northern Rock’s Bank Of England Bailout ‘Should Have Been Secret’. [online] Available at: <https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-england-tyne-41172945> [Accessed 25 December 2020].
Crooks, A. and Kuipers, S.R.S., 2018. Northern Rock and Anglo Irish: Crisis Decision Making in the Global Financial Crisis.
Goodhart, C.A., 2016. Run on Northern Rock, the. In Banking Crises (pp. 271-281). Palgrave Macmillan, London.
Llewellyn, D.T., 2009. The Northern Rock Crisis: A Multidimensional Problem Waiting to Happen. In Financial Institutions and Markets (pp. 101-128). Palgrave Macmillan, New York.
The Balance. 2020. Subprime Mortgage Crisis And Its Aftermath. [online] Available at: <https://www.thebalance.com/subprime-mortgage-crisis-effect-and-timeline-3305745> [Accessed 25 December 2020].
The National. 2020. UK Government’s £37 Billion Bailout Of Northern Rock In 2007 Pays Off. [online] Available at: <https://www.thenationalnews.com/business/uk-government-s-37-billion-bailout-of-northern-rock-in-2007-pays-off-1.625760> [Accessed 25 December 2020].
Tooze, A., 2018. The Forgotten History of the Financial Crisis: What the World Should Have Learned in 2008. Foreign Aff., 97, p.199.
Know more about UniqueSubmission’s other writing services:

